



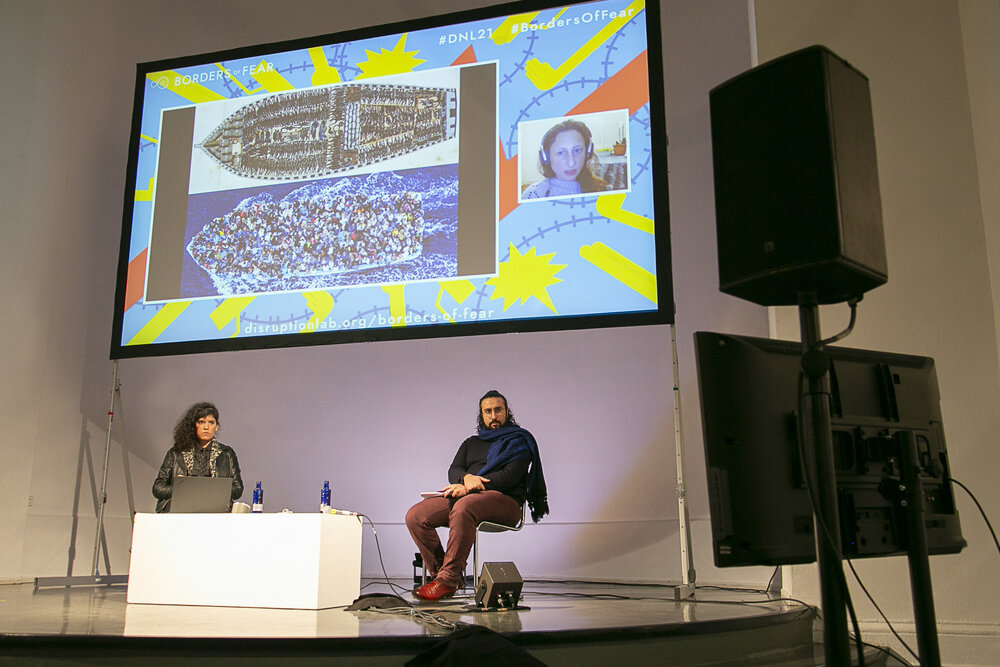
The 21st conference of the Disruption Network Lab “Borders of Fear” was held on the 27th, 28th, and 29th November 2020 in Berlin’s Kunstquartier Bethanien. Journalists, activists, advocates, and researchers shed light on abuses and human rights violations in the context of migration management policies. Keynote speeches, panel discussions and several workshops were held involving a total number of 18 speakers and bringing together hundreds of online viewers.
Drawing on insights from humanities, science and technology studies, participants analysed from different perspectives the spread of new forms of persecution and border control targeting people on the move and those seeking refuge. They reflected collectively on forms of social justice and discussed the politics of fear that crystalize the stigmatisation of migrants. By concretely addressing these issues the conference also investigated the deployment of technology and the role of media to consolidate a well-defined structure of power, and outlined the reasons behind the rise of borders and walls, factors that lead to cultural and physical violence, persecution, and human rights violations.
In her introductory statement Dr. Tatiana Bazzichelli, founder and director of the Distruption Network Lab, presented the programme of the conference meant to address the discourse of borders both in their material function, and in their defining role within a strategy of dehumanization and racialisations of individuals. Across the globe, an unprecedented number of people are on the move due to war, economic and environmental factors. Bazzichelli recalled the urgent need to discuss human-right-related topics such as segregation and pushbacks, refugee camps and militarization of frontiers, considering the new technological artilleries available for states, investigating at the same time how border policing and datafication of society are affecting the narrative around migrants and refugees in Europe and the in the West.
The four immediate key content takeaways of the first day were the will to prevent people from reaching countries where they can apply for refugee status or visa; the externalisation polices of border control; the illegal practice of pushbacks; and systematic human rights violations by authorities, extensively documented but difficult to prove in court.

The conference opened with the short film by Josh Begley “Best of Luck with the Wall” – a voyage across the US-Mexico border – stitched together from 200,000 satellite images, and a talk by lawyer Renata Avila, who gave an overview of the physical and socio-economic barriers, which people migrating encounter whilst crossing South and Central America.
Avila took step from the current crises in South and Central America, to describe the dramatic migration through perilous regions, a result of an accumulation of factors like inequality, corruption, mafia, and violence. Avila pointed out that oligarchic systems from different countries appear to be interconnected in complicated architectures of international tax evasion, ruthless exploitation of resources, oppression, and the use of force. In those same places, people experience the most brutal inequality, poverty and social exclusion.
Since the ‘90s the regional free trade agreement meant open borders for products but not for people. In fact, it was an international policy with devastating effects on local economies and agriculture. People on the move in search for a better future somewhere else found closed borders and security forces attempting to block them from heading north towards Mexico and the U.S. border. In these years, the police forceful response to the migrants crossing borders have been widely praised by the governments in the region.
The fact of travelling alone is a red flag, especially for women, and the first wall people meet is in their own country. People on their way to the north experience every kind of injustice. Latin America has often been regarded as a region with deep ethnic and class conflicts. Abandoning possible stereotypical representations, we see that the bodies of the people on the move are at large sexualised and racialized for political reasons. Race, therefore, is another factor to consider, especially when we look at the journey of individuals on the move. Aside, languages in South America could also represent a barrier for those who travel without translators in a continent with dozens of indigenous languages.
Avila concluded her intervention mentioning the issue of digital colonialism and the relevance of geospatial data. Digital is no longer a separated space, she warned, but a hybrid one relevant for all individuals and whose rules are dictated by a small minority. People and places can be erased by those very few companies that can collect data, and –for example– draw and delete borders.
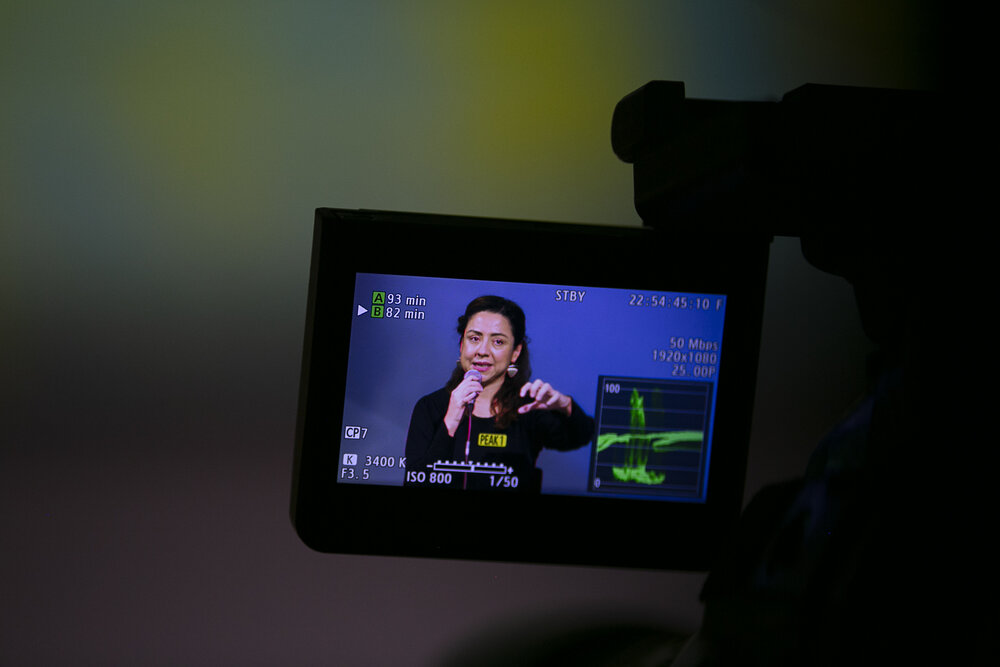

The panel on the first day titled “Migration, Failing Policies & Human Rights Violations,” was moderated by Roberto Perez-Rocha, director for the international anti-corruption conference series at Transparency International, and delivered by Philipp Schönberger and Franziska Schmidt, coordinators of the Refugee Law Clinic Berlin, together with investigative journalist and photographer Sally Hayden. The panellists referred to their direct experience and work, and reflected on how the EU migration policy is factually enforcing practices that cause violation of human rights, suffering, and desperation.
The Refugee Law Clinic Berlin e. V. is a student association at the Humboldt University of Berlin, providing free of charge and independent legal help for refugees and people on the move in Berlin and on the Greek island of Samos. The organisation also offers training on asylum and residence law in Berlin and runs the website ihaverights.eu, designed to allow access to justice to those in marginalised communities.
Through a legal counselling project on the Greek island of Samos, the collective helps people suffering from European illegal practices at the Union’s borders, providing the urgent need of effective ways to guarantee them access to justice and protection. As Schönberger and Schmidt recalled, refugees, and people on the move within the EU find several obstacles when it comes to the enforcement of their rights. For such a reason, they shall be guaranteed procedural counselling by the law to secure, among other services, a fair asylum procedure. However, the Clinic confirmed that such guarantees are not being completely fulfilled in Germany, nor at Europe’s borders, in Samos, Lesvos, Leros, Kos, or Kios.
The panellists explained how their presence on the island gives a chance to document that these camps of human suffering are actually a structural part of an EU migration policy aimed at deterring people from entering the Union, result of deliberate political decisions taken in Brussels and Berlin. Human rights violations occur before arriving on the island, as people are intercepted by the Greek coastguard or by the European Border and Coast Guard Agency (Frontex), and then pushed back to the Turkish border.
The camp in Samos, with a capacity of a maximum 648 people, is instead the home to 4,300 residents, with no water, no sanitary services, poisonous food, and no medical services. Even very serious cases documented to local health authorities remain unattended. The list of violations is endless and the complete lack of adequate protection for unaccompanied minors represents another big issue in this like in all others Greek hotspots, together with the precarity of vulnerable groups, whose risks increase with race, gender, and sexual identity.
The legal team from Berlin prepares applications to the EUCHR court and in these years has filed also 60 requests for urgent procedure due to the risk of irreparable harm, which were granted, ordering adequate accommodation and medical treatment for people in extreme danger.

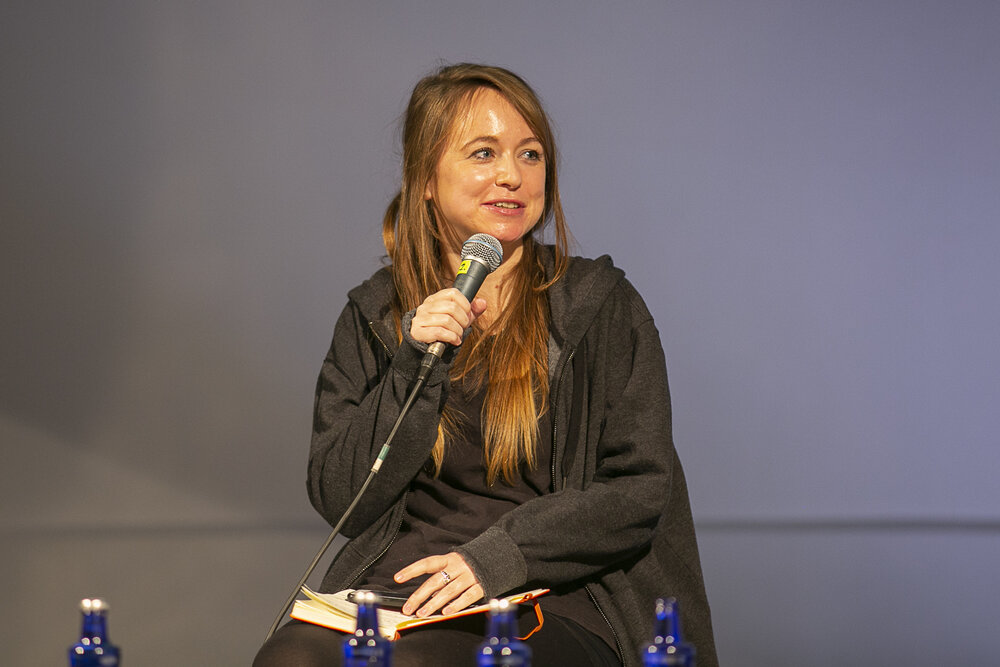
Many observers criticise that the sufferings in the Aegean and on the Greek islands is the result of precise political decisions. Agreed in March 2016, the EU-Turkey deal is a statement of cooperation that seeks to control the crossing of people from Turkey to the Greek islands. According to the deal, every person arriving without documents by boat or without official permission or passage to the Greek islands would be returned to Turkey. In exchange, EU Member States would take Syrian refugees from Turkey. NGOs and international human rights agencies denounce that Turkey, Greece, and the EU have completely failed on humanitarian grounds and dispute the wrong premise that Turkey is a safe country for refugees and asylum-seekers.
Journalist and photographer Sally Hayden looked at the EU-Turkey deal, defining it as a prototype for what would then happen in the central Mediterranean. Libya, a country at war with multiple governments, is the destination of people on move and refugees from all over Africa, willing to cross the Mediterranean Sea. As it is illegal to stop and push people back, for years now the EU has been financing the Libyan coastguard to intercept and pull them back. What follows is a period of arbitrary and endless detention.
Hayden writes about facts; she is not an activist. When she talks about Libya, she refers to objective events she can fact check, and individual stories she has personally collected. Her reports represent a country at war, unsafe not just for refugees and people on the move but for Libyans too. With her work, the journalist has extensively documented how refugees and migrants smuggled into Libya are subject to human trafficking, forced labour, sexual exploitation and tortures, trapped in an infernal circle of violence and death. She recalled her experience with the detainees in Abu Salim, where 500 hundred people suffer from illegal and brutal incarceration inside a centre affiliated with the government in Tripoli. In July 2020, during the conflict, one of these many prisons not far from the city was bombed. At least 53 illegally detained people were killed.
Hayden’s work provides a picture of the results of Europe’s management of the migration crises in the Mediterranean and Northern Africa. EU funds are employed for militarization of borders and externalisation of frontiers control. The political context, in which this occurs, is the cause of years and sometimes decades of lack of investment in reception and asylum systems in line with EU-State’s generic obligations to respect, protect and fulfil human rights.
All panellists called for the immediate intervention to evacuate camps and prisons that were the result of the EU migration policies, to allow migrant victims of abuses and refugees to seek justice and safety elsewhere.

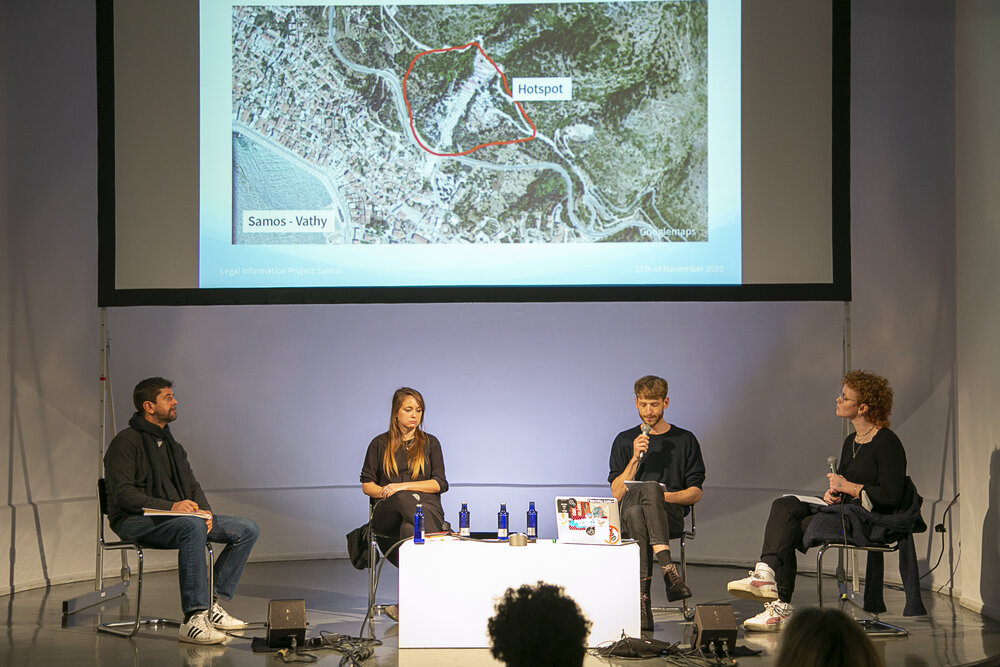
The evening closed with the panel discussion titled “Illegal Pushbacks and Border Violence” and moderated by Likhita Banerji, a human rights and technology researcher at Amnesty International. Banerji reminded the audience that in the first nine months of 2020 there had already been 40 pushbacks, illegal rejections of entry, and expulsions without individual assessment of protection needs, had been documented within Europe or at its external borders. Since these illegitimate practices are widespread, and in some countries systematic, these pushbacks cannot be defined as incidental actions. They appear, instead, to be institutionalised violations, well defined within national policies.
People who shall receive asylum or be rescued, are instead pushed back by police forces, who make sure that the material crossing of the borders remains undocumented. EU member States want to keep undocumented migrants, asylum seekers and refugees outside of their jurisdiction to avoid moral responsibilities and legal obligations. During the second panel of the day, Hanaa Hakiki, legal advisor at the ECCHR Migration Program, filmmaker and reporter Nicole Vögele, and Dimitra Andritsou, researcher at Forensic Architecture, had the chance to go in-depth and to consider the different aspects of these violations.
Hanaa Hakiki, in her intervention “Bringing pushbacks to justice” presented the difficulties that litigators experience in court to materially document pushbacks, which are indeed not meant to be proven. She defined pushbacks as a set of state measures, by which refugees and migrants are forced back over the border – generally shortly after having crossed it – without consideration of their individual circumstances and without any possibility for them to apply for asylum or to put forward arguments against the measures taken.
There are national and international laws that need to be considered in these cases, constituting binding legal obligations for all EU Member States. As a general principle, governments cannot enact disproportionate force, humiliating and degrading treatment or torture, and must facilitate the access to asylum, guarantee protection to people, and provide them access to individualised procedures in this sense.
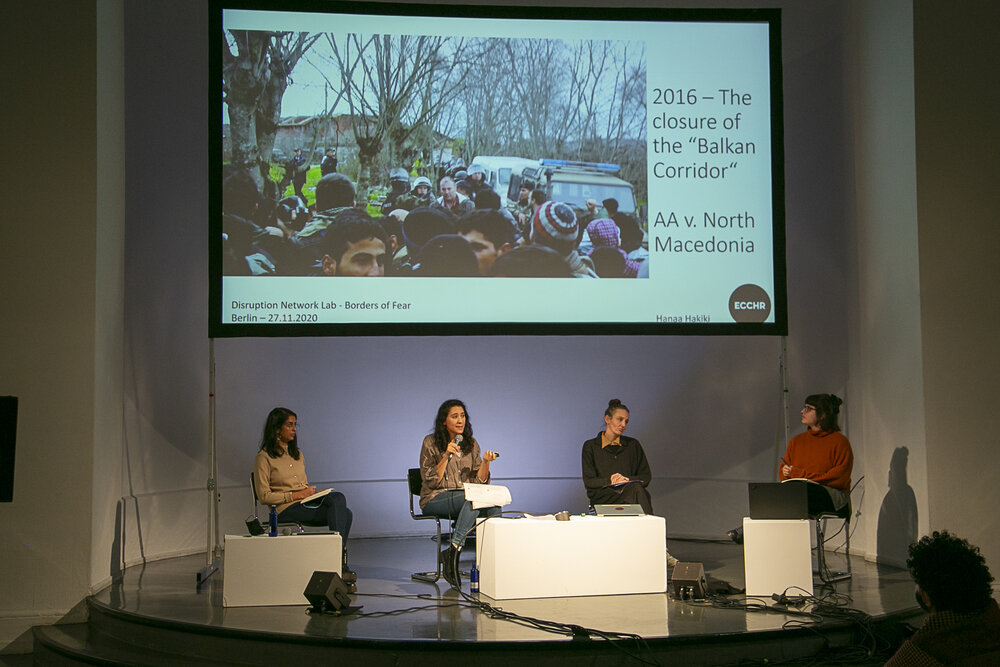
Member States know that pushbacks have been illegal since a 2012 ECtHR judgment, known as the “Hirsi Jamaa Case,” which found that Italy had violated the law in forcing people back to Libya. However, the effective ban on direct returns led European countries to find other ways to avoid responsibility for those at sea or crossing their borders without documents, and concluded agreements with neighbouring countries, which are requested to prevent migrants from leaving their territories and paid to do so, by any means and without any human rights safeguards in place. By outsourcing rescue to the Libyan authorities, for example, pushbacks by EU countries turned into pullbacks by Libyan coastguard.
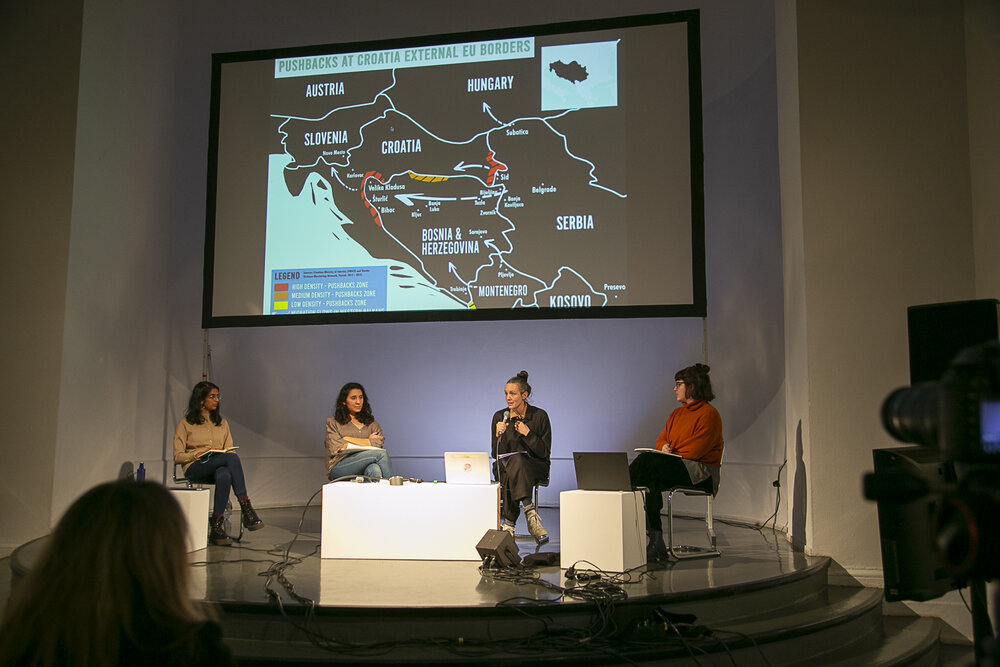
Land-pushbacks are still common practice. Hakiki explained that the European Centre for Constitutional and Human Rights (ECCHR) has worked with communities of undocumented migrants since 2014, considering potential legal interventions against the practice of pushbacks at EU borders, and assisting affected persons with individual legal proceedings. She presented three cases the ECCHR litigated in Court (N.D. and N.T. v. Spain; AA vs North Macedonia; SB vs. Croatia) proving that European countries illegally push people back, in violation of human rights laws. Despite the fact that this is still a common practice, it is very difficult to document these violations and have the authorities condemned.

During the beginning of the Syrian conflict, in 2015, refugees were able to travel via Serbia and Hungary into Central and Northern Europe. A couple of years later the EU decided to close down again this so-called Balkan Route, with the result that more and more people found themselves stuck in Bosnia-Herzegovina, prevented from continuing onward to Europe’s territories. From there a person can try to enter the European Union dozens of times, and each time is stopped by Croatian security forces, beaten, and then dragged back across the border to Bosnia-Herzegovina.
After having seen the effects of these illegal practices and met victims of dozens of violent pushbacks in Sarajevo, in 2019 the reporter Nicole Vögele and her crew succeeded in filming a series of these cross-border expulsions from Croatia to Bosnia Herzegovina near the village of Gradina, in the municipality of Velika Kladuša. The reporter, one of the few who succeeded in documenting this practice, also interviewed those who had just been pushed back by the Interventna Policija officers. The response of the Bosnian authorities to her reportage was a complete denial of all accusations.
Vögele then presented footage taken at the EU external border in Croatia, in March 2020, showing masked men beat up refugees and illegally pushing them back to Bosnia. The journalist and her team found the original video, analysed its metadata, and interviewed the man captured on it. Once again, their work could prove that these practices are not isolated incidents.
The panel closed with the investigation by Forensic Architecture part of a broader project on cases of pushbacks across the Evros/Meriç river. Team member Dimitra Andritsou presented the organisation founded to investigate human rights violations using a range of techniques, flanking classical investigation methods including open-source investigation video analysis, spatial and architectural practice, and digital modelling.
Forensic Architecture works with and on behalf of communities affected by state and military violence, producing evidence for legal forums, human rights organisations, investigative reporters and media. A multidisciplinary research group – of architects, scholars, artists, software developers, investigative journalists, archaeologists, lawyers, and scientists – based at the University of London, works in partnership with international prosecutors, human rights organisations, political and environmental justice groups, and develops new evidentiary techniques to investigate violations of human rights around the world, armed conflicts, and environmental destruction.
The Evros/Meriç River is the only border between Greece and Turkey that is not sea. For years migrants and refugees trying to cross it to enter Europe have been reporting that unidentified and generally masked men catch, detain, beat, and push people back to Turkey. Mobile phones, documents, and the few personal things they travel with are confiscated or thrown into the river, not to leave any evidence of these violations behind. As Andridsou described, both Greek and EU authorities systematically deny any wrongdoing, refusing to investigate these reports. The river is part of a wider ecosystem of border defence and has been weaponised to deter and let die those who attempt to cross it.

In December 2019, the German magazine Der Spiegel obtained rare videos filmed on a Turkish Border Guard’s mobile phone and on a surveillance, camera installed on the Turkish banks of the river, which apparently documented one of these many pushback operations. Forensic Architecture was commissioned to analyse the footages. A team of experts was then able to geolocate and timestamp the material and could confirm that the images were actually taken few hundred metres away from a Greek military watchtower in Greece.
Andritsou then presented the case of a group of three Turkish political asylum seekers, who entered Greek territory on 4 May 2019, always crossing the Evros/Meriç river. In this case a team of Forensic Architecture could cross-reference different evidence sources, such as new media, remote sensing, material analysis, and witness testimony and verify the group’s entry and their illegal detention in Greece. A pushback to Turkey on the 5 May 2019 led to their arrest and imprisonment by the Turkish authorities.
Ayşe Erdoğan, Kamil Yildirim, and Talip Niksar had been persecuted by the Turkish government on allegations of involvement in Fettulah Gulen’s movement. The group on the run had shared a video appealing for international protection against a possible forced return to Turkey and digitally recorded the journey via WhatsApp. All their text messages with location pins, photographs, videos and metadata prove their presence on Greek soil, prior to their arrest by the Turkish authorities. The investigation could verify that the three were in a Greek police station too, a fact that matches their statement about having repeatedly attempted to apply for asylum there. Their imprisonment is a direct result of the Greek authorities contravening the principle of non-refoulement.
Some keywords resonated throughout the first day of the conference, as a fil rouge connecting the speakers and debates held during the panels and commentaries by the public. Violence, arbitrariness and lawlessness are wilfully ignored –if not backed– by EU Member States, with authorities constantly trying to hide the truth. Thousands of people live under segregation, with no account or trace of being in custody of authorities free to do with them whatever they want.

Technology has always been a part of border and immigration enforcement. However, over the last few years, as a response to increased migration into the European Union, governments and international organisations involved in migration management have been deploying new controversial tools, based on artificial intelligence and algorithms, conducting de facto technological experiments and research involving human subjects, refugees and people on the move. The second day of the conference opened with the video contribution by Petra Molnar, lawyer and researcher at the European Digital Rights, author of the recent report “Technological Testing Grounds” (2020) based on over 40 conversations with refugees and people on the move.
When considering AI, questions, answers, and predictions in its technological development reflect the political and socioeconomic point of view, consciously or unconsciously, of its creators. As discussed in the Disruption Network Lab conference “AI traps: automating discrimination” (2019)— risk analyses and predictive policing data are often corrupted by racist prejudice, leading to biased data collection which reinforces privileges of the groups that are politically more guaranteed. As a result, new technologies are merely replicating old divisions and conflicts. By instituting policies like facial recognition, for instance, we replicate deeply ingrained behaviours based on race and gender stereotypes, mediated by algorithms. Bias in AI is a systematic issue when it comes to tech, devices with obscure inner workings and the black box of deep learning algorithms.
There is a long list of harmful tech employed at the EU borders is long, ranging from Big Data predictions about population movements and self-phone tracking, to automated decision-making in immigration applications, AI lie detectors and risk-scoring at European borders, and now bio-surveillance and thermal cameras to contain the spread of the COVID-19. Molnar focused on the risks and the violations stemming from such experimentations on fragile individuals with no legal guarantees and protection. She criticised how no adequate governance mechanisms have been put in place, with no account for the very real impacts on people’s rights and lives. The researcher highlighted the need to recognise how uses of migration management technology perpetuate harms, exacerbate systemic discrimination, and render certain communities as technological testing grounds.
Once again, human bodies are commodified to extract data; thousands of individuals are part of tech-experiments without consideration of the complexity of human rights ramifications, and banalizing their material impact on human lives. This use of technology to manage and control migration is subject to almost no public scrutiny, since experimentations occur in spaces that are militarized and so impossible to access, with weak oversight, often driven by the private sector. Secrecy is often justified by emergency legislation, but the lack of a clear and transparent regulation of the technologies deployed in migration management appears to be deliberate, to allow for the creation of opaque zones of tech-experimentation.
Molnar underlined how such a high level of uncertainty concerning fundamental rights and constitutional guarantees would be unacceptable for EU citizens, who would have ways to oppose these liberticidal measures. However, migrants and refugees have notoriously no access to mechanisms of redress and oversight, particularly during the course of their migration journeys. It could seem secondary, but emergency legislation justifies the disapplication of laws protecting privacy and data too, like the GDPR.

The following part of the conference focused on the journey through Sub-Saharan and Northern Africa, on the difficulties and the risks that migrants face whilst trying to reach Europe. In the conversation “The Journey of Refugees from Africa to Europe,” Yoseph Zemichael Afeworki, Eritrean student based in Luxemburg, talked of his experience with Ambre Schulz, Project Manager at Passerell, and reporter Sally Hayden. Afeworki recalled his dramatic journey and explained what happens to those like him, who cross militarized borders and the desert. The student described that migrants represent a very lucrative business, not just because they pay to cross the desert and the sea, but also because they are used as cheap labour, when not directly captured for ransom.
Once on the Libyan coast, people willing to reach Europe find themselves trapped in a cycle of waiting, attempts to cross the Mediterranean, pullbacks and consequent detention. Libya is a country at war, with two governments. The lack of official records and the instability make it difficult to establish the number of people on the move and refugees detained without trial for an indefinite period. Libyan law punishes illegal migration to and from its territory with prison; this without any account for individual’s potential protection needs. Once imprisoned in a Libyan detention centre for undocumented migrants, even common diseases can lead fast to death. Detainees are employed as forced labour for rich families, tortured, and sexually exploited. Tapes recording inhuman violence are sent to the families of the victims, who are asked to pay a ransom.
As Hayden and Afeworki described, the conditions in the buildings where migrants are held are atrocious. In some, hundreds of people live in darkness, unable to move or eat properly for several months. It is impossible to estimate how many individuals do not survive and die there. An estimated 3,000 people are currently detained there. The only hope for them is their immediate evacuation and the guarantee of humanitarian corridors from Libya –whose authorities are responsible for illegal and arbitrary detention, torture and other crimes– to Europe.

The second day closed with the panel “Politics & Technologies of Fear” moderated by Walid El-Houri, researcher, journalist and filmmaker. Gaia Giuliani from the University of Coimbra, Claudia Aradau, professor of International Politics at King’s College in London, and Joana Varon founder at Coding Rights, Tech and Human Rights Fellow at Harvard Carr Center.
Gaia Giuliani is a scholar, an anti-racist, and a feminist, whose intersectional work articulates the deconstruction of public discourses on the iconographies of whiteness and race, questioning in particular the white narrative imaginary behind security and borders militarization. In her last editorial effort, “Monsters, Catastrophes and the Anthropocene: A Postcolonial Critique” (2020), Giuliani investigated Western visual culture and imaginaries, deconstructing the concept of “risk” and “otherness” within the hegemonic mediascape.
Giuliani began her analyses focusing on the Mediterranean as a border turned into a biopolitical dispositive that defines people’s mobility –and particularly people’s mobility towards Europe– as a risky activity, a definition that draws from the panoply of images of gendered monstrosity that are proper of the European racist imaginary, to reinforce the European and Western “we”. A form of othering, the “we” produces fears through mediatized chronicles of monstrosity and catastrophe.
Giuliani sees the distorted narrative of racialized and gendered bodies on the move to Europe as essential to reinforce the identification of nowadays migrations with the image of a catastrophic horde of monsters, which is coming to depredate the wealthy and peaceful North. It´s a mechanism of “othering” through the use of language and images, which dehumanizes migrants and refugees in a process of mystification and monstrification, to sustain the picture of Europe as an innocent community at siege. Countries of origins are described as the place of barbarians, still now in post-colonial times, and people on the move are portrayed as having the ability to enact chaos in Europe, as if Europe were an imaginary self-reflexive space of whiteness, as it was conceived in colonial time: the bastion of rightfulness and progress.
As Giuliani explained, in this imaginary threat, migrants and refugees are represented as an ultimate threat of monsters and apocalypse, meant to undermine the identity of a whole continent. Millions of lives from the South become an indistinct mass of people. Figures of race that have been sedimented across centuries, stemming from colonial cultural archives, motivate the need to preserve a position of superiority and defend political, social, economic, and cultural privileges of the white bodies, whilst inflicting ferocity on all others.
This mediatized narrative of monsters and apocalypse generates white anxiety, because that mass of racialized people is reclaiming the right to escape, to search for a better life and make autonomous choices to flee the objective causes of unhappiness, suffering, and despair; because that mass of individuals strives to become part of the “we”. All mainstream media consider illegitimate their right to escape and the free initiative people take to cross borders, not just material ones but also the semiotic border that segregate them in the dimension of “the barbarians.” An unacceptable unchained and autonomous initiative that erases the barrier between the colonial then and the postcolonial now, unveiling the coloniality of our present, which represents migration flows as a crisis, although the only crisis undergoing is that of Europe.
On the other side, this same narrative often reduces people on the move and refugees to vulnerable, fragile individuals living in misery, preparing the terrain for their further exploitation as labour force, and to reproduce once again racialized power relations. Here the process of “othering” revivals the colonial picture of the poor dead child, functional to engender an idea of pity, which has nothing to do with the individual dignity. Either you exist as a poor individual in the misery –which the white society mercifully rescues– or as a part of the mass of criminals and rapists. However, these distinct visual representations belong to the same distorted narration, as epitomized in the cartoons published by Charlie Hebdo after the sexual assaults against women in Cologne on New Year’s Eve 2015.

Borders have been rendered as testing ground right for high-risk experimental technologies, while refugees themselves have become testing subjects for these experiments. Governments and non-state actors are developing and deploying emerging digital technologies in ways that are uniquely experimental, dangerous and discriminatory in the border and immigration enforcement context. Taking step from the history of scientific experiments on racialized and gendered bodies, Claudia Aradau invited the audience to reconsider the metaphorical language of experiments that orients us to picture high-tech and high-risk technological developments. She includes instead also tech in terms of obsolete tools deployed to penalise individuals and recreate the asymmetries of the digital divide mirroring the injustice of the neoliberal system.
Aradau studies technologies and the power asymmetries in their deployment and development. She explained that borders have been used as very profitable laboratories for the surveillance industry and for techniques that would then be deployed widely in the Global North. From borders and prison systems –in which they initially appeared– these technologies are indeed becoming common in urban spaces modelled around the traps of the surveillance capitalism. The fact that they slowly enter our vocabularies and daily lives makes it difficult to define the impact they have. When we consider for example that inmates’ and migrants’ DNA is collected by a government, we soon realise that we are entering a more complex level of surveillance around our bodies, showing tangibly how privacy is a collective matter, as a DNA sequence can be used to track a multitude of individuals from the same genealogic group.
Whilst we see hyper-advanced tech on one side, on the other people on the move walk with nothing to cross a border, sometimes not even shoes, with their personal belongings inside plastic bags, and just a smartphone to orientate themselves, and communicate and ask for help. An asymmetry, which is –once again– being deployed to maintain what Aradau defined as matrix of domination: no surveillance on CO2 emissions and environmental issues due to industrial activities, no surveillance on exploitations of resources and human lives; no surveillance on the production of weapons, but massive deployment of hi-tech to target people on the move, crossing borders to reach and enter a fortress, which is not meant for them.
Aradau recalled that in theory, protocols ethics and demands for objectivity are necessary when it comes to scientific experiments. However, the introduction in official procedures of digital tech devices and software such as Skype, WhatsApp or MasterCard or a set of apps developed by either non-state or state actors, required neither laboratories nor the randomized custom trials that we usually associate with scientific experimentation. These heterogeneous techniques specifically intended to work everywhere and enforced without protocols, need to be understood under neoliberalism: they rely on pilot projects trials and cycles of funds and donors, whose goal is every time to move to a next step, to finance more experiments. Human-rights-centred tech is far away.
Thus, we see always more experiments carried out without protocols, from floating walls tech to stop migrants reaching the Greek shores, to debit cards used as surveillance devices. Creative experiments come also with the so-called refugees’ integration, conceived by small-scale injections of devices into their reality for limited periods, with the purpose of speculatively recompose rotten asymmetries of power and injustice. In Greece, as Aradau mentioned, the introduction of Skype in the process of the asylum application became an obstacle, with applicants continually experiencing debilitation through obsolete technology that doesn’t work or devices with limited access, disorientation through contradictory and outdated information.
There is also a factual aspect: old and slow computers, documents that have not been updated or have been updated at different times, and lack of personnel are justified by saying that resources are limited. A complete lack or shortage of funds, which is one other typical condition of neoliberalism, as we can see in Greece. In this, tech recomposes relations of precarity in a different guise.
Aradau concluded her contribution focusing on the technologies that are deployed by NGOs, completely or partially produced elsewhere, often by corporate actors who remain entangled in the experiments through their expertise and ownership. Digital platforms such as Facebook, Microsoft, Amazon, or Google not only shape relations between online users, she warned, but concerning people on the move and refugees too. Google and Facebook –for example– dominate the relations that underpin the production of refugee apps by humanitarian actors.
Google is at the centre of a sort of digital humanitarian ecosystem, not only because it can host searches or provide maps for the apps, but also because it simultaneously intercepts data flows so that it acts as a surplus data extractor. In addition, social networks reshape digital humanitarianism through data extractive relations and provide big part of the infrastructure for digital humanitarianism. Online humanitarianism becomes thus a particularly vulnerable site of data gathering and characterised by an overall lack of resources –similarly to the Greek state. As a result, humanitarian actors cannot tackle the depreciation messiness and obsolescence of their tech and apps.

The last day of the conference concentrated on the urgent need to creating safe passages for migration, and pictured the efforts of those who try to ensure safer migration options and rescue migrants in distress during their journey. Lieke Ploeger, community director of the Disruption Network Lab, presented the panel discussion “Creating Safe Passages”, moderated by Michael Ruf, writer and director of documentary and theatre plays. Ruf´s productions include the “Asylum Dialogues” (2011) and the “Mediterranean Migration Monologues” (2019), which have been performed in numerous countries more than 800 times by a network of several hundred actors and musicians. This final session brought together speakers from the Migrant Media Network (MMN), the Migrant Offshore Aid Station (MOAS), and SeaWatch e.V. to discuss their efforts to ensure safer migration options, as well as share reliable information and create awareness around migration issues.
The talk was opened by Thomas Kalunge, Project Director of the Migrant Media Network, one of r0g_agency’s projects, together with #defyhatenow. Since 2017 the organisation has been working on information campaigns addressed to people in rural areas of Africa, to explain that there are possible alternatives for safer and informed decisions, when they choose to reach other countries, and what they may come across if they decide to migrate.
The MMN team organises roundtable discussions and talks on various topics affecting the communities they meet. They build a space in which young people take time to understand what migration is nowadays and to listen to those, who already personally experienced the worst and often less discussed consequences of the journey. To approach possible migrants the MMN worked on an information campaign on the ethical use of social media, which also helps people to learn how to evaluate and consume information shared online and recognise reliable sources.
The MMN works for open culture and critical social transformation, and provides young Africans with reliable information and training on migration issues, included digital rights. The organisation also promotes youth entrepreneurship “at home” as a way to build economic and social resilience, encouraging youth to create their own opportunities and work within their communities of origin. They engage on conversations on the dangers of irregular migration, discussing together rumours and lies, so that individuals can make informed choices. One very relevant thing people tend to underestimate, is that sometimes misinformation is spread directly by human smugglers, warned Kalunge.
The MMN also provides people from remote regions with offline tools that are available without an internet connection, and training advisors and facilitators who are then connected in a network. The HyracBox for example is a mobile, portable, RaspberryPi powered offline mini-server for these facilitators to use in remote or offline environments, where access to both power and Internet is challenging. With it, multiple users can access key MMN info materials.
An important aspect to mention is that the MMN does not try to tell people not to migrate. European government have outsourced borders and migration management, supporting measures to limit people mobility in North and Sub-Saharan Africa, and it is important to let people know that there are real dangers, visible and invisible barriers they will meet on their way.
Visa application processes –even for legitimate reasons of travel– are very strict for some countries, often without any information being shared, even with people who are legitimately moving for education, to work or get medical treatment. The ruling class that makes up the administrative bureaucracy and outlines its structures, knows that who controls time has power. Who can steal time from others, who can oblige others to waste time on legal quibbles and protocol matters, can suffocate the others’ existence in a mountain of paperwork.
Human smugglers then become the final resort. Kaluge explained also that, at the moment, the increased outsourcing of the European border security services to the Sahel and other northern Africa countries is leading to diversion of routes, increased dangerousness of the road, people trafficking, and human rights violations.

Closing the conference, Regina Catrambone presented the work that MOAS does around the world and the campaign for safe and legal routes that is urging governments and international organisations to implement regular pathways of migration that already exist. Mattea Weihe presented instead the work of SeaWatch e. V., an organisation which is also advocating for civil sea rescue, legal escape routes and a safe passage, and which is at sea to rescue migrants in distress.
The two panellists described the situation in the Central Mediterranean. Since the beginning of the year, over 500 migrants have drowned in the Mediterranean Sea (November 2020). While European countries continue to delegate their migration policy to the Libyan Coast Guard, rescue vessels from several civilian organisations have been blocked for weeks, witnessing the continuous massacre taking place just a few miles from European shores. With no common European rescue intervention at sea, the presence of NGO vessels is essential to save humans and rescue hundreds of people who undertake this dangerous journey to flee from war and poverty.
However, several EU governments and conservative and far right political parties criminalise search and rescues activities, stating that helping migrants at sea equals encouraging illegal immigration. A distorted representation legitimised, fuelled and weaponised in politics and across European society that has led to a terrible humanitarian crisis on Europe’s shores. Thus, organisations dedicated to rescuing vessels used by people on the move in the Mediterranean Sea see all safe havens systematically shut off to them. Despite having hundreds of rescued individuals on board, rescue ships wait days and weeks to be assigned a harbour. Uncertainty and fear of being taken back to Libya torment many of the people on board even after having been rescued. After they enter the port, the vessels are confiscated and cannot get back out to sea.
By doing so, Europe and EU Member States violate human rights, maritime laws, and their national democratic constitutions. The panel opened again the crucial question of humanitarian corridors, human-rights-based policy, and relocations. In the last years the transfer of border controls to foreign countries, has become the main instrument through which the EU seeks to stop migratory flows to Europe. This externalisation deploys modern tech, money and training of police authorities in third countries moving the EU-border far beyond the Union’ shores. This despite the abuses, suffering and human-rights violations; willingly ignoring that the majority of the 35 countries that the EU prioritises for border externalisation efforts are authoritarian, known for human rights abuses and with poor human development indicators (Expanding Fortress, 2018).
It cannot be the task of private organizations and volunteers to make up for the delay of the state. But without them no one would do it.
States are seeking to leave people on the move, refugees, and undocumented migrants beyond the duties and responsibilities enshrined in law. Most of the violations, and the harmful technological experimentation described throughout the conference targeting migrants and refugees, occurs outside of their sovereign responsibility. Considering that much of technological development occurs in fact in the so-called “black boxes,” by acting so these state-actors exclude the public from fully understanding how the technology operates.
The fact that the people on the move on the Greek islands, on the Balkan Route, in Libya, and those rescued in the Mediterranean have been sorely tested by their journeys, living conditions, and, in many cases, imprisoned, seems to be irrelevant. The EU deploys politics that make people who have already suffered violence, abuse, and incredibly long journeys in search of a better life, wait a long time for a safe port, for a visa, for a medical treatment.

All participants who joined the conference expressed the urgent need for action: Europe cannot continue to turn its gaze away from a humanitarian emergency that never ends and that needs formalised rescue operations at sea, open corridors, and designated authorities enacting an approach based on defending human rights. Sea rescue organisations and civil society collectives work to save lives, raise awareness and demand a new human rights-based migration and refugee policy; they shall not be impeded but supported.
The conference “Borders of Fear” presented experts, investigative journalists, scholars, and activists, who met to discuss wrongdoings in the context of migration and share effective strategies and community-based approaches to increase awareness on the issues related to the human-rights violations by governments. Here bottom-up approaches and methods that include local communities in the development of solutions appear to be fundamental. Projects that capacitate migrants, collectives, and groups marginalized by asymmetries of power to share knowledge, develop and exploit tools to combat systematic inequalities, injustices, and exploitation are to be enhanced. It is imperative to defeat the distorted narrative, which criminalises people on the move, international solidarity and sea rescue operations.
Racism, bigotry and panic are reflected in media coverage of undocumented migrants and refugees all over the world, and play an important role in the success of contemporary far-right parties in a number of countries. Therefore, it is necessary to enhance effective and alternative counter-narratives based on facts. For example, the “Africa Migration Report” (2020) shows that 94 per cent of African migration takes a regular form and that just 6 per cent of Africans on the move opt for unsafe and dangerous journeys. These people, like those from other troubled regions, leave their homes in search of a safer, better life in a different country, flee from armed conflicts and poverty. It is their right to do so. Instead of criminalising migration, it is necessary to search for the real causes of this suffering, war and social injustice, and wipe out the systems of power behind them.
Videos of the conference are also available on YouTube via:
For details of speakers and topics, please visit the event page here: https://www.disruptionlab.org/borders-of-fear
Upcoming programme:
The 23rd conference of the Disruption Network Lab curated by Tatiana Bazzichelli is titled “Behind the Mask: Whistleblowing During the Pandemic.“ It will take place on March 18-20, 2021. More info: https://www.disruptionlab.org/behind-the-mask
To follow the Disruption Network Lab sign up for the newsletter and get informed about its conferences, meetups, ongoing researches and projects.
The Disruption Network Lab is also on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
Our times are characterized by the accelerating collapse and redrawing of multiple borders: between nation states, personal identities, and the responsibilities we have for each other. Also between the old distinctions, work and pleasure.
Some leaders as part of the new world order, tell us through their political actions and their fashion accessories, that they “Just Don’t Care”. This “political art-form”1 of not caring permits an insidious spread of hatred online and on the ground. In recent times, the digital condition has lent it’s networks and platforms to this poisonous, rhetorical hyperbole, turning against immigrants, and others who do not fit into the framework of a western world, oligarch orientated vision. Mass extraction and manipulation of social data has facilitated the circulation of fake news and the production of fear, anxiety and uncertainty. Together these fuel the machine of structural violence adding to the already challenging conditions created by Austerity policies, growing debt and poverty.
In the face of these outlandish difficulties our digital tools and networks – taken up with a spirit of cultural comradeship. More inspiring narratives are emerging from across disciplines and backgrounds, to experiment with new solidarity-generating approaches that critique and build platforms, infrastructures and networks, offering new possibilities for reassessing and re-forming citizenship and rights.
The exhibition and labs for Playbour – Work, Pleasure, Survival, have created new contexts for collaboration. Artists (from the local area and internationally), game designers and architects, come together with researchers from psychology and neuroscience addressing the data driven gamification of life and everything.

In her interview, the curator Dani Admiss discusses how they reassess the power relationships of the gallery, park users and the local authorities, asking who owns the cultural infrastructure and public amenities – and so create a polemic to open up questions of public value. The exhibition is open every weekend through 14 July to 19 August 2018.
The artists featured in Transnationalisms exhibition curated by James Bridle address the effect on our bodies, our environment, and our political practices of unstable borders.
“They register shifts in geography as disturbances in the blood and the electromagnetic spectrum. They draw new maps and propose new hybrid forms of expression and identity.”2

“Thiru Seelan, a Tamil refugee who arrived in the UK in 2010 following detention in Sri Lanka during which he was tortured for his political affiliations, dances on an East London rooftop. His movements are recorded by a heat sensitive camera more conventionally often used to monitor borders and crossing points, where bodies are identified through their thermal signature.”3
The show opens at Furtherfield from September 14th to October 26th 2018, touring as part of State Machines the EU cooperation which investigates the new relationships between states, citizens and the stateless made possible by emerging technologies.
We have another interview with artist and activist Cassie Thornton, where we discuss her current project Hologram, which examines health in the age of financialization, and works to reveal the connection between the body and capitalism. Her interview focuses on a series of experiments that actively counter the effects of indebtedness through somatic – or body – work including her focus on the way in which institutions produce or take away from the health of the artists and workers they “support”.
“In my work for the past decade, I have been developing practices that attempt to collectively discover what debt is and how it affects the imagination of all of us: the wealthy, the poor, the indebted, financial workers, babies, and anyone in-between.” Thornton

Finally I interview Tatiana Bazzichelli, artistic director and curator of the Disruption Network Lab, in Berlin, questions about art as Investigation of political misconducts and Wrongdoing. Since 2015, the Disruption Network Lab has cultivated a stage and a sanctuary for otherwise unheard and stigmatised voices to delve into and explore the urgent political realities of their existence at a time when the media establishment has no investment in truth telling for public interest.
“When the speakers are with us and open their minds to our topics, I feel that we are receiving a gift from them. I come from a tradition in which communities, networks and the sharing of experience were the most important values, the artwork by themselves.” Bazzichelli.
The programme creates a conceptual and practical space in which whistleblowers, human right advocates, artists, hackers, journalists, lawyers and activists are able to present their experience, their research and their actions – with the objective of strengthening human rights and freedom of speech, as well as exposing the misconduct and wrongdoing of the powerful.
To conclude, all one needs to say is…
“Whether in the variety of human, backgrounds and perspectives, biodiversity or diversity of technologies, coding languages, devices, or technological cultures. Diversity is Proof of Life.” Ruth Catlow, 2018.
Featured image: XRay by Claude Chuzel
“One of the most consequential outcomes of this ubiquitous mode of organization of social life is that we have become so accustomed to relating to space in “either/or” and “here/there” terms that we have become mentally trapped inside this binary border-based model, making it difficult to imagine alternative ways of territorial organization.” Popescu [1a]
Maps inform us where things are situated. The borders depicted in each map propose a different view on the social conditions, attitudes, and interactions with others in the world. The AntiAtlas of borders project shows us different approaches for understanding “the mutations of control systems along land, sea, air and virtual states” and their borders. It has done this through the combined contributions of social and ‘hard’ science researchers and artists, all engaged in creative practices including Internet art, tactical geography, filmmakers, performers and hackers. The project also includes other relevant actors such as people working as professionals for customs agencies, surveillance industries and the military.
This is the first of two interviews with Isabelle Arvers who has collaborated with the IMERA team (the Mediterranean Institute for Advanced Research of Aix-Marseille University), to curate this expansive and dynamic project. The first interview discusses the operational side of the project and the next interview examines selected writings, artworks, projects and ideas featured as part of the project.

Marc Garrett: Before we begin the interview it would great if you could tell us when and where the exhibitions, events, publications and other parts of the project begin?
Isabelle Arvers: The AntiAtlas programme will run from 30 September 2013 to 1 March 2014 and will be composed of five initiatives: an inaugural international symposium, two exhibitions, a website and the publication of a book. The International Conference will be held from 30 September – 2 October 2013 at the New Conservatory of Aix en Provence. The main aim of this conference is to present the results of the interdisciplinary workshops that took place in the last two years at IMéRA et at the Higher School of Art of Aix-en-Provence.
The AntiAtlas of borders will present two interlinked exhibitions. The first will take place in Aix-en-Provence at the Musée des Tapisseries from 1 October to 3 November 2013. The second will take place in Marseille at La Compagnie creative arts centre from 13 December 2013 to 1 March 2014. The two exhibitions will present works developed in collaboration with social scientists, researchers in the hard sciences and artists. They will offer several levels of reading and forms of participation. Visitors will discover new works, engage with transmedia documentation and participate in experiments. They will interact directly with robots, drones, video games, walls and systems. The aim is to encourage everyone to reflect on how we are directly and personally affected by the transformations of borders in the 21st century.
The final version of the website www.antiatlas.net/eng is an online extension of the exhibitions. Most importantly, the website provides access to works of net.art and artistic interventions in the form of an online gallery of works. This website and its documentation will extend the progress and reach achieved by the project. It will act as an archive and documentation site for the general public, artists, researchers and institutions.
In 2014, an AntiAtlas of border publication will be produced, gathering publications of researchers and artists on different and selected themes of the international conference and the two exhibitions.


MG: What has been your involvement with AntiAtlas?
IA: When I met the IMERA team (the Mediterranean Institute for Advanced Research of Aix-Marseille University), they were looking for a curator in order to disseminate the outcomes of the past three years of seminars they conducted on borders. I saw this project as a great opportunity as there was a political dimension within it that attracted me. Also, I am deeply interested in tactical media and tactical geography and by new forms of visualisation and new aesthetics related to systems of control like drones, robots, satellites or surveillance cameras.
I wanted to create a participatory event that would allow people to follow our work online and offline. I also wanted to mix different kinds of works from research in the hard and social sciences to artistic installations, websites, games and videos. To do so, we decided to create a website www.antiatlas.net that would gather artworks, research articles and interviews, an online gallery and also all the presentations given during the different seminars conducted by IMERA on borders during the last three years. Thanks to the website, we were able to launch a call for proposals as I wanted to get the testimonies and the voice of migrants about their vision on borders.

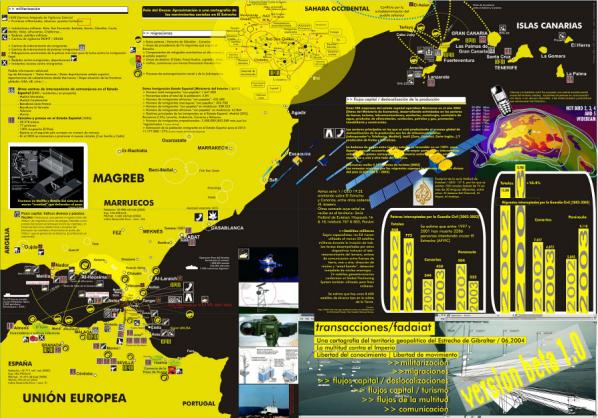
Very quickly we understood that we needed to get more funding and partners, so I offered to seek media, private and institutional partnerships as well as to manage the communication of the entire event. This fundraising was needed to promote a global vision of the antiAtlas of borders and to link all the parts of the event: from the website, to the call for proposal, till the international seminar and the two exhibitions. Because of my multiple engagements in the project, I became one of the 5 co-producers of the programme.
MG: This is a complex project. It is noticeable that there is a diverse and dynamic, cross section of different practices being bridged to make it all happen. Has it been difficult to combine all of these practices so they can relate to each other coherently?
IS: Combining all these different practices was a wonderful and exciting adventure. During one year and a half, we worked very closely with the scientific and artistic committee and tried to exchange as much as possible between different visions and ways of working. I learned a lot from researchers and was amazed by the deep understanding and knowledge they have on the subject of borders. Thanks to their research and to their approaches to this issue, I was able to get a very diverse understanding of this complex subject. From me, they discovered the online communication and the power of the web and social networks to diffuse and share the information. They also got a better understanding of the tactical media field and we learned so much from each other that this experience is already a beautiful success in sharing and learning from passionate human beings. I come from media art world and I tried to respond to a scenario that the committee conceived with artists’ works, which is a very different way for me to work. This time I had a script to follow; the way I did it was to try to find some ludic interactive installations, as well as documentary projects or games, in order to allow the experimentation of the subject by the audience. They trusted me even if it wasn’t a field they knew well.

MG: Do you feel that it has de-compartmentalised these varied fields of knowledge successfully?
IS: What was particularly positive in the last seminars on borders we organised was that they allowed plenty of time to discuss and facilitate the exchange between the different perspectives. A specific example is a game project resulting from the collaboration between an anthropologist – Cédric Parizot – and a interactive laboratory from the Superior art School of Aix-en-Provence, which is led by the artist and game designer Douglas Edric Stanley. The idea is to create a “crossing industry game” drawing on the data collected by Cédric Parizot on trafficking. The collaboration addressed the visualisation, contextualisation and re-appropriation of a field of knowledge through game mechanics. I think that this experience really enriched all the team. The anthropologist was able to analyse his data in a different way, while the interactive students got closer to the reality of trafficking as they were experiencing through a game.
There are many other cross-disciplinary projects made in the framework of the AntiAtlas. I would say that what we want is to multiply different experiences and forms of knowledge on borders across and between the separate but intersecting fields of art and science. The exhibition is conceived to mix everything: research through the documentation space, researchers’ interviews, counter cartographies, interactive installations on biometrics and surveillance technologies, applications to divert control systems and documentaries providing a wider point of view on multiple dimensions of borders and their representations. Artists and researchers meet three times per year, some of them collaborate on trans-disciplinary projects, so that the conditions to meet and de-compartmentalise these fields are created. This is only the beginning. The process still needs to be pushed and facilitated as the antiAtlas is an attempt to create a new kind of cross-disciplinary encounter, let’s see how it will evolve!
This first interview with Arvers attended to organisational and operational aspects of the inter-disciplinary border-crossing within AntiAtlas project. The complex task of collating, sharing and collaborating to make it all happen at all could use its own map. The processes and engagements that evolved as the project took shape involved a collaboration of many different fields and practices, individuals, groups, organisations and cross cultural relations. This transdisciplinary approach helps us to unpack the deep levels of the meanings and value of crossing borders, in an organisational sense. Their dedication to transcend the seemingly ‘scripted’ blockages and restraints echoes a strong feeling that we need to re-assess the maps given to us, and what this means.
“What is needed to escape the modern mental “territorial trap” are ways of seeing and drawing that reveal what the geographical abstraction of the borderline obscures. It is only in this way, then, that we will acquire the necessary tools to think through a technologically enabled world of border flows and portals” Popescu.[1b]
Isabelle Arvers is an independent author, critic and exhibition curator. She specializes in the immaterial, bringing together art, video games, Internet and new forms of images by using networks and digital imagery. She has organized a large number of exhibitions in France and overseas (Australia, Canada, Brazil, Norway, Italy, Germany) and collaborates regularly with the Centre Pompidou and French and international festivals. http://www.isabellearvers.com/
“It is not accidental that at a point in history when hierarchical power and manipulation have reached their most threatening proportions, the very concepts of hierarchy, power and manipulation come into question. The challenge to these concepts comes from a redsicovery of the importance of spontaneity – a rediscovery nourished by ecology, by a heightened conception of self-development, and by a new understanding of the revolutionary process in society.” Murray Bookchin. Post-scarcity and Anarchism (1968).
The rise of neo-liberalism as a hegemonic mode of discourse, infiltrates every aspect of our social lives. Its exponential growth has been helped by gate-keepers of top-down orientated alliances; holding key positions of power and considerable wealth and influence. Educational, collective and social institutions have been dismantled, especially community groups and organisations sharing values associated with social needs in the public realm. [1] Bourdieu.
In this networked society, there are controversies and battles taking place all of the time. Battles between corporations, nation states and those who wish to preserve and expand their individual and collective freedoms. Hacktivist Artists work with technology to explore how to develop their critical and imaginative practice in ways that exist beyond traditional frameworks of art establishment and its traditions. This article highlights a small selection of artists and collaborative groups, whose work is linked by an imaginative use of technology in order to critique and intervene into the opressive effects of political and social borders.
In June 2000, Richard Stallman [2] when visiting Korea, illustrated the meaning of the word ‘Hacker’ in a fun way. When at lunch with some GNU [3] fans a waitress placed 6 chopsticks in front of him. Of course he knew they were meant for three people but he found it amusing to find another way to use them. Stallman managed to use three in his right hand and then successfully pick up a piece of food placing it into in his mouth.
“It didn’t become easy—for practical purposes, using two chopsticks is completely superior. But precisely because using three in one hand is hard and ordinarily never thought of, it has “hack value”, as my lunch companions immediately recognized. Playfully doing something difficult, whether useful or not, that is hacking.” [4] Stallman
The word ‘hacker’ has been loosely appropriated and compressed for the sound-bite language of film, tv and newspapers. These commercial outlets hungry for sensational stories have misrepresented hacker culture creating mythic heroes and anti-heroes in order to amaze and shock an unaware, mediated public. Yet, at the same time hackers or ‘crackers’ have exploited this mythology to get their own agendas across. Before these more confusing times, hacking was considered a less dramatic activity. In the 60s and 70s the hacker realm was dominated by computer nerds, professional programmers and hobbyists.
In contrast to what was considered as negative stereotypes of hackers in the media. Steven Levy [5], in 1984 published Hackers: Heroes of the Computer Revolution [6]. In three parts, he writes about the canonical AI hackers of MIT, the hardware hackers who invented the personal computer industry in Silicon Valley, and the third-generation game hackers in the early 1980s. Yet, in this publication, what has had the most impact on hacker culture and is still used widely as a guideline by many is the ‘hacker ethic’. He identified this Hacker Ethic to be a code of practice consisting of key points such as that “all information is free”, and that this information should be used to “change life for the better”.
1. Access to computers—and anything which might teach you something about the way the world works—should be unlimited and total. Always yield to the Hands-on Imperative!
2. All information should be free.
3. Mistrust authority—promote decentralization.
4. Hackers should be judged by their hacking, not bogus criteria such as degrees, age, race or position.
5. You can create art and beauty on a computer.
6. Computers can change your life for the better.
Levy’s hacker ethic promotes the idea of performing a duty for the common good, an analogy to a modern day ‘Robin Hood'[ibid]. Proposing the concept that hackers are self-reliant whilst embracing a ‘healthy’ anti-authoritarian stance, combined with free and critical thinking. Proposing that hackers should be judged by their ability to hack, and presenting hacking as an art-form. Levy also says that the Free and open source software (FOSS) movement is the descendant of the hacker ethic. However, Levy’s hacker ethic has often been quoted out of context and misunderstood as to refer to hacking as ‘breaking’ into computers. This specifically prescribed role, denies the wider and creative context of what hacking is and could be. It does not have to be just about computer security.
This leads us to ‘crackers’. All crackers hack and all hackers hack. But, crackers are seen as second rate wannabe hackers by the older generation of hackers. The Black Hat Hacker or cracker designs and releases malicious code, gathers dangerous information and brings down sensative systems. The White Hat Hacker hunts down and destroys malicious code, and the casual hacker who hacks in order to learn information for his or her own curiosity; both generally dislike ‘Black Hats’ and ‘Crackers’, and tend to view them as computer criminals and dysfunctional juveniles. Lately, crackers have also been labeled as ‘script kiddies’. As a kind of snobbish insult, it refers to those who are not capable of building or programming their own tools, but tend to use scripts and programs written by others to perform their intrusions. To add to the confusion we also have the term ‘Grey hat’. Which refers to a hacker acting between black hat and white hat. Indeed, this could demonstrate where art hacktivists reside, challenging the trappings of the traditional concept of goody and baddy.
“There is another group of people who loudly call themselves hackers, but aren’t. These are people (mainly adolescent males) who get a kick out of breaking into computers and phreaking the phone system. Real hackers call these people ‘crackers’ and want nothing to do with them.” [7] Raymond.
“The basic difference is this: hackers build things, crackers break them.” [ibid] Raymond.
But before we judge,
let’s view a snippet of the \/\The Conscience of a Hacker/\/ by +++The Mentor+++
Written on January 8, 1986.[8]
“This is our world now… the world of the electron and the switch, the
beauty of the baud. We make use of a service already existing without paying
for what could be dirt-cheap if it wasn’t run by profiteering gluttons, and
you call us criminals. We explore… and you call us criminals. We seek
after knowledge… and you call us criminals. We exist without skin color,
without nationality, without religious bias… and you call us criminals.
You build atomic bombs, you wage wars, you murder, cheat, and lie to us
and try to make us believe it’s for our own good, yet we’re the criminals.”
The term ‘Hacktivism’ was officially coined by techno-culture writer Jason Sack in a piece about media artist Shu Lea Cheang published in InfoNation in 1995. Yet, the Cult of the Dead Cow [9] are also acknowledged as defining the term. The Cult of the Dead Cow are a group of hackers and artists. They say the Hacktivism phrase was originally intended to refer to the development and use of technology to foster human rights and the open exchange of information.
Hacktivism techniques include DoS attacks, website defacement, information theft, and virtual sabotage. Famous examples of hacktivism include the recent knocking out of the PlayStation Network, various assistances to countries participating in the Arab Spring, such as attacks on Tunisian and Egyptian government websites, and attacks on Mastercard and Visa after they ceased to process payments to WikiLeaks.
Hacktivism: a policy of hacking, phreaking or creating technology to achieve a political or social goal.
“Hacktivism is a continually evolving and open process; its tactics and methodology are not static. In this sense no one owns hacktivism – it has no prophet, no gospel and no canonized literature. Hacktivism is a rhizomic, open-source phenomenon.” [10] metac0m.
The practice or behaviour of Hacktivism is at least as old as Oct 89 when DOE, HEPNET and SPAN (NASA) connected to (virtual) networked machines world wide. They were penetrated by the anti-nuclear group WANK worm.
WANK penetrated these machines and had their login screens altered to…
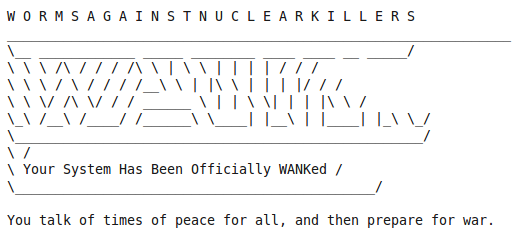
HACKING BORDERS: Examples of Art Hacktivism & Cultural Hacking…

“Radical groups are discovering what hackers have always known: Traditional social institutions are more vulnerable in cyberspace than they are in the physical world. And some members of the famously sophomoric hacker underground are becoming motivated by causes other than ego gratification.” [11] Harmon.
Hacktivism, exploits technology and the Internet, experimenting with the immediacy of distributable networks as a playful medium for independent, creative and free expression. There has been a gradual and natural shift from net art (and net.art) into Hacktivism. Net Art in spirit, has never really been just about art being viewed on a web browser alone. Some of the very same artists whose artwork involved being shown in browsers and making code behind the browser as part of the art, have also expanded their practice outside of the browser. One such artist is Danja Vasiliev, “Fifteen years ago WWW was something very new in Russia and besides the new dial-up aesthetics and world-wide means it brought a complete new layer of existence – “netosphere”, which made my youth.” Vasiliev very soon moved on from playing with browsers into a whole new territory. [12]
Danja co-founded media-lab moddr_ in 2007, a joint project at Piet Zwart Institute alumni and WORM Foundation. Based in Rotterdam moddr_ is a place for artists and hackers, engaging with critical forms of media-art practice. He collaborated with Gordan Savicic and Walter Langelaar from the moddr.net lab on the project Web 2.0 Suicide Machine, which lets you delete your social networking profiles and kill your virtual friends, and it also deletes your own profile leaving your profile image replaced by a noose.”The idea of the “Web 2.0 Suicide Machine” is to abandon your virtual life — so you can get your actual life back, Gordan Savicic tells NPR’s Mary Louise Kelly. Savicic is the CEO — which he says stands for “chief euthanasia officer” — of SuicideMachine.org.” [13]

Just like another project called ‘Face to facebook’ that stole 1 million facebook profiles and re-contextualized them on a custom made dating website (lovely-faces.com), set up by Italian artists Paolo Cirio and Alessandro Ludovico, whom also just so happens to be editor in chief of Neural magazine. Web 2.0 Suicide Machine, had to close its connections down regarding its Facebook activities after receiving a cease and decease letter from Facebook. [14]
Julian Oliver and Danja Vasiliev teamed up and formed the mysterious group Men in Grey. The Men In Grey explore our online vulnerabilities by tapping into, intervening into wireless network traffic. Observing, tracing and copying what we do. This hack then redisplays our activities back to us, showing the data of our online interactions.
At first no one (except myself & a few others) knew who they were. When they first arrived on the scene I started an interview with them and then suddenly, I was asked to hold back due to their antics on the Internet and interventions in public environments receiving much coverage. They were not sure how it would pan out for them. Partly due to the anonymous nature of their project, and also because of the sudden impact of the larger hacktivist group Anonymous getting much press in commercial media themselves.
“Men In Grey emerge as a manifestation of Network Anxiety, a fearful apparition in a time of government wiretaps, Facebook spies, Google caches, Internet filters and mandatory ISP logging.” M.I.G
“Spooks are listening into calls, just like they always have,” said Eric King of London’s Privacy International, in an e-mail. “With A5/1 being broken—you can decrypt and listen into 60 calls at once with a box smaller than a laptop.” [15]
Later they won the Golden Nica (1st prize) Interactive Arts category, Prix Ars Electronica in 2011. In a show called Project Space — M.I.G. — Display of unknown, quarantined equipment hosted at the Aksioma Project Space Komenskega, Ljubljana 2011. The statement read:
“The particularly threatening quality of the Men In Grey equipment is its apparently invasive nature; it seems able to penetrate – and even hack into – virtually any electronic device in its reach. While we are all aware of the wire-tapping and data retention done by the government (along with the spying carried out by corporations like Facebook and Google), Men In Grey seem to operate with a range of tools and techniques well beyond those that are currently known to be in use.”

Hacktivism involves many different levels of social intervention and engagement. Whether it is to do with direct action, self-referential geekiness, obscure networked antics, crtical gaming, or peer 2 peer and collective change. Hacktivists challenge defaults put in place by other people, usually the systems imposed upon them and the rest of us by authority. Even though the subjects themselves may be concerning serious matters, humour and playfulness are both essential ingredients.
“A promising tactic for the early Situationists was the unpredictable yet forceful potential of play — what anthropologist Victor Turner termed the “liminoid,” or the freeing and transformational, moments of play when the normal roles and rules of a community or society are relaxed.” [16] Dovey & Kennedy.
One group crossing over from the digital into physical and social realms, is Tiltfactor. [17] Their form of intervention is not necessarily about causing political controversy, but is engaged in reaching people through games of play. Experimenting with social everyday contexts, making games that tackle less traditional topics, such as public health, layoffs, GMO crops. One of the many games creating awareness on these subjects, is POX “Our game actually helps a player understand how a disease can spread from one place to another and how an outbreak might happen” says Mary Flanagan. [18]
A local public health group called Mascoma Valley Health in the New Hampshire region of the US approached Tiltfactor with the problem of the lack of immunization. “At first, a game about getting people immunized seemed like one of the most “un-fun” concepts imaginable. But that sinking feeling of impossibility almost always leads to good ideas later.” [19] Flanagan.

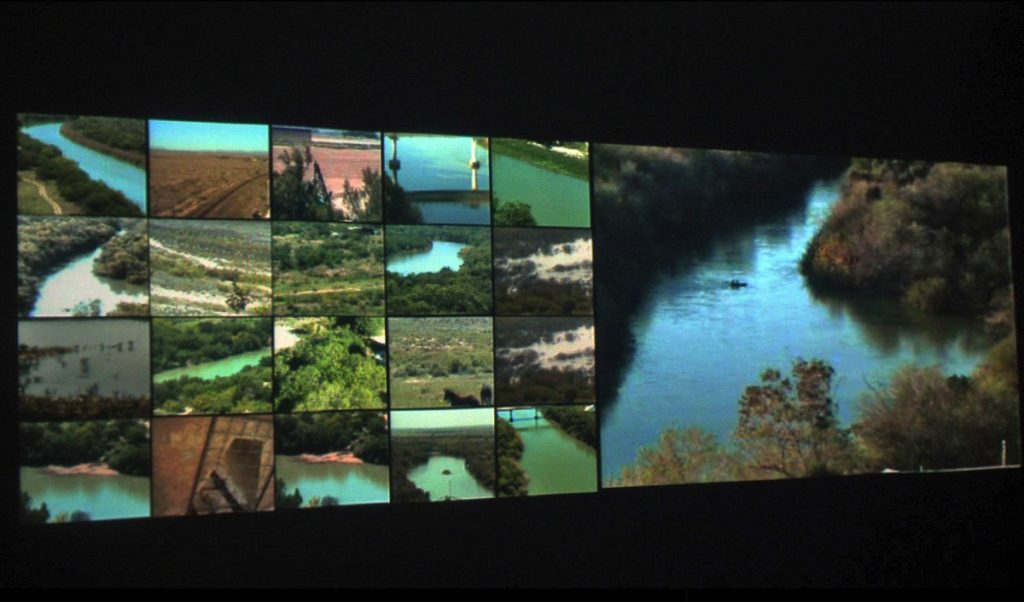
“Geopolitical space has always been a conflicted and fragile topic. Borders and frontiers are changing so fast, that sometimes it seems that our sociopolitical status can change from “citizen” to “immigrant” from one moment to another, or simply live under the “immigrant” status all your life. We’re getting used to words like refugees, enclaves, war, borders, limits –and the list has no end.” Ethel Baraona Pohl & César Reyes

Ricardo Dominguez collaborated with Brett Stalbaum, Micha Cardenas, Amy Sara Carroll & Elle Mehrmand, on (TBT) (and others), on a hand-held mobile phone device that aids crossers of the Mexico-US border. An inexpensive tool to support the finding of water caches left in the Southern California desert by NGO’s for those crossing the border.
“The entire group of artists who are part of Electronic Disturbance Theater 2.0/b.a.n.g. lab working on the Transborder Immigrant Tool (TBT) was being investigated by UCSD and 3 Republican Congressmen starting on January 11, 2010. Then I came under investigation for the virtual sit-in performance (which joined communities statewide against the rising students fees in the UC system and the dismantling of educational support for K–12 across California) against the UC Office of the President (UCOP) on March 4, 2010. This was then followed by an investigation by the FBI Office of Cybercrimes.” [20] Ricardo Dominguez.

In an interview with Lawrence Bird Dominguez discusses that the TBT is still developing as a gps tool, but infers that it is not just a tool but also ‘border disturbance art’, consisting of different nuances existing as part of a whole with other factors at play. Such as a hybrid mix of things, objects and expressions “artivism, tactical poetries, hacktivism(s), new media theater, border disturbance art/technologies, augmented realities, speculative cartographies, queer technologies, transnational feminisms and code, digital Zapatismo, dislocative gps, intergalactic performances, [add your own______].” [ibid]
“Borders are there to be crossed. Their significance becomes obvious only when they are violated – and it says quite a lot about a society’s political and social climate when one sees what kind of border crossing a government tries to prevent.” [21] Florian Schneider

National borders are front-lines of political and social friction. The exerience of asylum-seekers and political migrants reflect some of the most significant issues of our time. Immigration is a toxic issue and unpopular with voters. Bunting’s BorderXing Guide, plays on the fear of invisible alien hordes of people crossing our borders illegally.
The context of this work fits well with issues about borders, whether it is about creating borders online or physical environments. Only those needing to cross a border are allowed access to the site, it is limited to ‘social clients’ who have a static IP (Internet Protocol) address and who, most notably, have gained the artist’s confidence. Such as peer activists and immigrants using libraries, colleges, cultural centres. The site allows those who would other wise end up crossing borders in harmful ways, such as in containers, on the backs of (and underneath) lorries and planes.
Heath Bunting’s BorderXing Guide website primarily consists of documentation of walks that traverse national boundaries, without interruption from customs, immigration, or border police. The work comments on the way in which movement between borders is restricted by governments and associated bureaucracies. It is a manual written not at distance like a google map, but by foot. A physical investigation, involving actually going to these places; trying these discovered routes out and then sharing them with others. A carefully calculated politics of public relations.
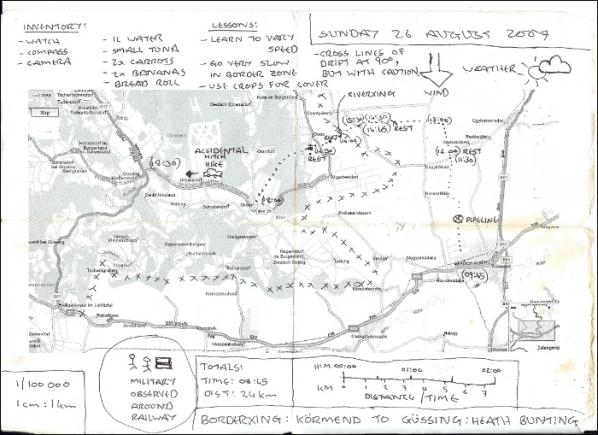
“The Feral Trade Café is more than just an art space that’s a working café, it’s about provoking people to question the way big food corporations operate by looking at the journey of the food we end up scraping into our pampered bins.” [22] Gastrogeek
Feral Trade uses social and cultural hand baggage to transport food based items between cities, often using other artists and curators as mules. Feral Trade products (2003-present), alongside ingredient route maps, bespoke food packaging, video and other artefacts from the Feral Trade network. The goods rangefrom coffee from El Salvador, hot chocolate from Mexico and sweets from Montenegro, as well as locally sourced bread, vegetables and herbs.
Kate Rich uses the word ‘feral’ as a process refering to being deliberately wild, as in pigeon, as opposed to romantic nature wild as the wolf. It is an unruly wild, shitting everywhere, disruption and annoyance in contrast to ‘official’ human structures and connected infrastructures. Feral Trade freight operates largely outside commercial channels, using the surplus potential of social, cultural and data networks for the distribution of goods. Working with co-operatives, small growers and food producers.
The Feral Trade Courier is a live shipping database for a freight network running outside commercial systems. The database offers dedicated tracking of feral trade products in circulation, archives every shipment and generates freight documents on the fly.

Every shipment is different and has its own story of how and where it was delivered from. Also included is information on who the carriers are with details about producers and their local culture as contextual information. The product packaging itself is also a carrier of information about social, political context and discussions with producers and carriers.
![Feral Trade at Furtherfield's Gallery (2009) [23] Link to exhibition](http://www.furtherfield.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/3657297700_42b1c26014_b.jpg)
Since the rise of the Internet individual and collective actions are symbiotically connected to the every day. In a world transformed, common people have access to tools that can change ‘our’ cultures independently; sharing information, motivating actions and changing situations. We know of the Arab Spring, the Occupy movement, Anonymous and Wikileaks and how successful they have been in exploiting technology and social networks. Technology just like any other medium is a flexible material. By tweaking, breaking and remaking ‘something’ you can re-root it’s function, change its purpose.
The links between these mass social movements and the artists here are not just relating to technology’s use but, a shared critique at the same enemy, neo-liberalism.
“”Neo-liberalism” is a set of economic policies that have become widespread during the last 25 years or so. Although the word is rarely heard in the United States, you can clearly see the effects of neo-liberalism here as the rich grow richer and the poor grow poorer.” [24] Martinez & Garcia.
At the same time as highlighting the continual privatization of human society. This form of art practice shows us the cracks of where a social divide of gate-keeping has maintained power within the Western World’s, traditional art structures. We now realize that the art canons we have been taught to rely on as reference are more based around privelage, centralization and market dominance rather than democratic representation or even just pure talent. Hacktivist artists adapt and recontextualize with a critical approach, towards a larger and more inclusive context beyond their own immediate selves. Demonstrating a respect and use of autonomy, and an awareness of social contexts and political nuances, freeing up dialogue for new discussions which include a recognition of social contexts, as a vital ingredient and valued resource in art. Re-aligning, reconfiguring the defaults of what art is today.