



Post Digital Print
The Mutation of Publishing Since 1894
Alessandro Ludovico, 2012
Onamatopee 77
The sticky fingerprints on the black-and-pink 1970s photomechanical typography-style lettered cover of “Post Digital Print” speak volumes about the nature of physical print after the event of digital typography. It is this sense, of print in a state of technical and historical play after the full event of the digital rather than its end or irrelevance, that Alessandro Ludovico is considering history of print publishing here. But why 1894?
Ludovico dates the first announcement of “the death of print” to that year. More than a century later independent bookshops, large bookshop chains, newspapers and magazines are having to compete with Internet-based publishing or be wiped out. It’s not clear whether physical print publishing believes it can survive this encounter with the digital. Ludovico explains how it can and why it is important that it should.
There are three main threads to “Post Digital Print”. The first is a wide-ranging technical history of print, including technologies that were imagined or proposed but never became widespread. The second is a history of radical political and avant-garde historical use, misuse and critique of those technologies. And the third is an analysis of the social and technological networks that distributed the products of the first two. These threads tie together finally in a consideration of the current situation and future prospects of physical print publishing.
The mainstream history of printing goes from movable type through hot metal to photomechanical and finally PostScript-based publishing. This is how books and newspapers have reached millions of people. But not every print production technology has lasted or gained mass adoption. I was surprised to read that Ezra Pound once wrote a poem specifically for Bob Brown’s “Readies” (an imagined 1930s motorized-paper-strip book replacement), and in the first half of the twentieth century newspapers were transmitted by telegraph, telephone and radio ready to be listened to or remotely printed.
The technical failings of dead media become aesthetic affordances in their afterlives. Letterpress embosses the paper it is printed on, lithography suffers misregistration and other artifacts, and newsprint smears and creases. These are now the very qualities people seek from those media. This is different from mere nostalgia, in that it is used to create a contemporary aesthetic, but what of the “Readies” and other book replacements that never were? They are the subconscious or the dreams of print technology, forgotten futures that help to understand the paths that were taken.

Not every print technology was designed to print millions of copies. Spirit duplicators, photocopiers and print-on-demand publishing all allowed democratic access to print for smaller print runs of projects with less mass appeal. Ludovico tracks this thread of print history from mid-twentieth-century science fiction fanzines through the alternative press to the contemporary fanzine scene.
Artists and political groups pushed the technology and aesthetics of each new print technology with pamphlets, unlicensed newspapers, the alternative press, fanzines, and books and journals. Ludovico uses avant-garde and culture jamming artistic publications, from the Dadaists and Futurists to the Yes Men and Decapitator to demonstrate how artists have pushed the form and content of print publications.
Once you have printed a publication you must distribute it. For publications outside of mainstream or official culture, this is a task that has varied in difficulty from inconvenient to deadly. British newspapers had to be licensed (and thereby censored) by the state in the early nineteenth century. Alternative political views were printed in unlicensed newspapers printed by sympathetic printers. These newspapers outsold the official press, and were subject to repression by the state, leading to funds being set up to support the families of arrested printers.
In the Soviet union, Samizdat copies of books were produced with stolen or smuggled paper and borrowed presses. Less dramatically but still outside the mainstream or official culture, the alternative press and fanzine scenes have survived through mail-order print and online catalogues and through conventions. And the Fluxus scene distributed its print products through an international network of distributors.
The “gesture” of publishing, as Ludovico calls it, is an editorial one and without this editorial control the Internet of blogs and social media presents a problem of filtering rather than access. Writing from the web can be taken into print cheaply through print-on-demand, led by the example of James Bridle’s “My Life In Tweets”, 2009. Where an artist led, business followed and there are now many services that will print your social media as books for you.
(What of eBooks? Ludovico considers their technology and its history in depth, but is not hopeful for them. They simulate print ever more closely, confirming Ludovico’s argument that print is the better interface. They have an environmental impact that makes books look more appealing, and suffer all the problems of censorship and technological obsolescence that print now does not.)

In the final chapter (“The Network”) the author enters the story that he is telling. Since the early 1990s Ludovico has produced the magazine “Neural” (I’m a subscriber and I cannot recommend it highly enough), and has been involved in other art projects, events and interventions that have placed him in the thick of the action of the changes in publishing and textual media that have occurred over this period. Rather than affect a false objectivity, Ludovico lets you know where he is coming from and shares the particularities of his broad experience. This lends his conclusions a context and authority that mere theory might lack.
The history and experience that Ludovico lays out leads to the present crisis of print and answers it with the terms that he has established. How can we continue to print physical books? With the kinds of networks that have always propagated and paid for art and for the alternative press. Why should we continue to make them? Because they are better interfaces, archives, and art objects than purely digital objects.
Post-digital print is print with its production and in some ways its very meaning transformed. Print must adopt digital-inspired models of production and distribution to survive. As Ludovico argues it must adopt the digital strategy of the network, in a free and open way. If it does not, we lose a vital part of our collective cultural voice and memory.
“Paper is flesh, screen is metal. … Flesh and metal will thus merge as in a cyberpunk film, hopefully spawning useful new models for carrying and spreading unprecedented amounts of information and culture.” (Post-Digital Print, p117)
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
(Thank you to Freek Lomme of Onomatopee for providing the book interior images.)
“a symbol of indeterminate meaning, floating/rotating into the empty white WAG room with no viewers” Bill Miller
Widget Art Gallery. July 17th – August 17th 2013.
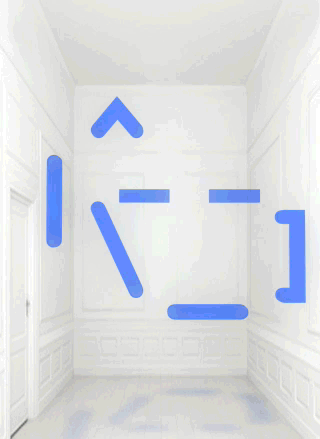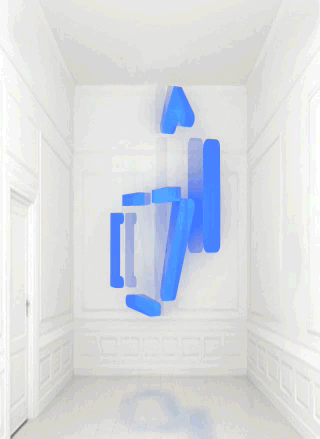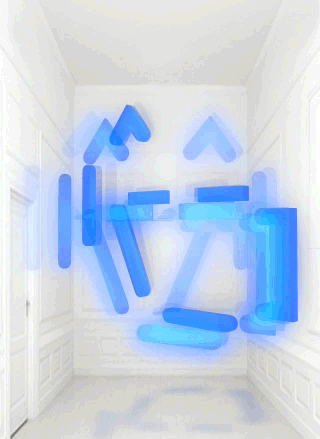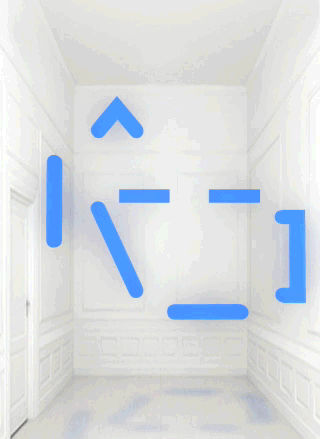
Chiara Passa’s Widget Art Gallery (WAG) has been serving art online since 2009. Named for the ability to install the contents of its web pages as a Mac OS X “dashboard widget” or iOS icon, it presents virtual art objects against a standard backdrop or in a standard virtual environment that looks like a white-painted townhouse room repurposed as a small gallery space in an exclusive part of town.
The instructions for using the WAG are Apple hardware-centric, and as I don’t have an Apple device I had to cheat and view it on my GNU/Linux desktop. Digital art’s medium specificity consists in part of its reliance on the facilities of particular hardware and operating systems. This can be exclusive, not everyone owns Apple hardware, but it can also be realistic, Apple’s hardware currently defines computing in the popular imagination.
The image of the gallery in the widget, like the image of a leather desk organizer or a wire mesh microphone in an mobile app, or the very idea of “the desktop” in a desktop GUI, it is a skeuomorph. It is a non-functioning symbolic form that cues the viewer in to the affordances that the experience of the software offers. Like the white cube of a real art gallery, it frames the experience of looking at the artwork and emphasises its seriousness, value, and singularity.
From July to August 2013 the work inhabiting this virtual space is Bill Miller’s “A Symbol“. The titular icon is a composition of soft light blue graphic elements that look like ASCII art that are not aligned to a teletype grid. Or like a misaligned LED matrix. It evokes the art of early military computer games, or the more complex emoticons, or maybe a lamp or a teapot. It rotates, blurs, flickers and stops, glitching and returning.
Widget Art Gallery installations are presented as animated GIFs, but they are different from the usual hilarious recuperations of Compuserve’s low-bandwidth image format in their lack of all-overness and of mass media appropriation. Animated GIFs are often glitched, but with “A Symbol” it is the object depicted in the animated image that is glitching, not the image itself.
The rotating symbol used to be a staple of broadcast television identities. The flickering or glitching symbol signifies signal hacking, technical difficulties, or coming into or out of being by teleportation or rezzing. Popular culture reactions to technology emphasize its flaws and failures to make its smooth surfaces tractable to the imagination. But this symbol remains opaque and self-assured, always returning to its original state.

The symbol’s reflection on the floor pushes it into and anchors it in the imaginary space of the gallery. Like drop shadows in graphic design or the handling of shadows and highlights in paintings it is a visual spatial strategy to make its subject seem more real and in the same space as the viewer. The rhythm and pauses in its rotation, especially the pauses, make it seem intentional and sculptural, they give it a solidity in time as well as space.
The accessibility and framing of the Widget Art Gallery mean that “A Symbol” can travel with and be accessed by its audience over time in a variety of settings, making it even more a reflection of their lives. “A Symbol” is retro digital but with a contemporary electroluminescent aesthetic glow like a Tron Legacy costume or an Android startup screen, militaristic but emotive, hard-edged but glitching, opaque yet evocative. It is a sign of the times.
Richard Stallman[1] the outspoken promoter for the Free Software movement, hates Facebook with a passion. He proposes that we should all leave Facebook and either find or build our own alternatives. The evidence offered by Stallman’s and the Electronic Frontier Foundation’s (EFF), who have been fighting for Internet freedoms since the 90s [2] shows how necessary it is that we understand and are more pro-active in managing the personal data that we give away through our online activities.
When we subscribe to Web 2.0 platforms such as Facebook we are at the mercy of the data brokers. These companies trade in people’s personal data; information which is aggregated by monitoring user actions and interactions across social media. This information can include “names, addresses, phone numbers, details of shopping habits, and personal data such as whether someone owns cats or is divorced.”[3] Fast moving developments in social media, make it difficult to keep up with the effects and consequences of these platforms. This is why the work of groups such as Commodify Inc. is so valuable. They bring imaginative and critical attention to the situation, sharing their knowledge of these daily networked complexities and correcting what they see as its negative effects.
Commodify Inc. is an artist-run Internet startup producing projects to help individuals capitalize on their online monetary potential. Their intention is to correct the imbalance of power in markets where users have no control over the transactions made with their personal data. They have completed various artistic projects and interventions on social media like, Fame Game, Give Me My Data, and Web 2.0 Suicide Machine. The co-founders are Birgit Bachler, Walter Langelaar, Owen Mundy, Tim Schwartz, with additional contributors Joelle Dietrick and Steven Alvarado.
Their new project Commodify.Us, was initiated when Owen Mundy and Tim Schwartz were invited by moddr_ to a residency in their lab in the summer of 2012 – when they were still a part of the WORM collective in Rotterdam. They worked on an initial idea that would succeed previous experiences of their already well-known and respected projects.
Commodify.Us is currently in beta phase. It promises to provide a platform for people to regain control over the commercial exploitation of their own personal data.

Intrigued by this project I contacted one of the co-founders, Walter Langelaar via email and asked him a few questions about this new platform.
Marc Garrett: Commodify.Us is for people to have greater control over their data. And it works when users export their data from social media websites and upload it to your platform. How will these users gain more control over their data and why is this important?
Walter Langelaar: Commodify.Us provides a platform for you to regain control over the commercial exploitation of your personal data. After exporting your profile data from social media websites and uploading the data to Commodify.Us, you can directly get in contact with interested buyers. On the importance for users I would say that it’s part raising awareness surrounding the monetization of profile data, and part creating a platform where people might work out and discuss how to do this themselves.
MG: It proposes to re-imagine the potential of relational data, creating a casting agency for virtual personas. I’m wondering what this may look like?
WL: We were too. In an early stage of the project we played with the idea that peoples’ various profiles could function like that within an agency; a client would ask for a specific set of qualities and/or characteristics within a set of profiles, and we could provide for this based on the uploads and their licensing options as set by the user. In the end we abandoned this idea for clarity.
MG: Commodify.Us offers people the opportunity to be part of an economy where interested buyers will pay to use the data supplied, unlike existing social media websites. How does this work?
WL: We are gearing up for a launch where the main goal will be to get a critical mass of around, a 1000 profiles. We anticipate that only with this kind of mass or volume will our initiative take hold with the potential buyers we have in mind, and the same goes for the more creative projects that could use the (open) data. Regarding the open profile data and otherwise licensed profiles that allow for reuse, we are researching the idea of ‘Fair Data’ (as in Fair Trade) and how to implement this as a profitable protocol for the end-user.

“Net activists construct tools whose intervention potential can be initiated by users under net conditions. These tools enable activists to develop new strategies in the data space of the Internet because they offer new means: New means afford new ends.”[4] (Dreher)
In his publication Networks Without a Cause: A Critique of Social Media, Geert Lovink lays down the gauntlet and asks us to “collectively unleash our critical capacities to influence technology design and workspaces, otherwise we will disappear into the cloud.” Anna Munster opens her excellent survey, Data Undermining: The Work of Networked Art in an Age of Imperceptibility, by saying “The more data multiplies both quantitatively and qualitatively, the more it requires something more than just visualisation. It also needs to be managed, regulated and interpreted into patterns that are comprehensible to humans.”[5] Commodify.Us goes one step further by allowing users to manage, regulate, repattern and reappropriate their own data using tools that share an essential functionality (if not purpose) with the power tools of Web 2.0.
Those previously seen as rebellious hacktivists are moving into new territories that deal with concepts of service. There has been a significant rise of artists exploring technology to influence mass Internet activity, against the domination of corporations who are data mining and tracking our on-line activities. Another example is TrackMeNot developed by Daniel Howe and Helen Nissenbaum. This is an extension created for the Firefox browser. “It hides users’ actual search trails in a cloud of ‘ghost’ queries, significantly increasing the difficulty of aggregating such data into accurate or identifying user profiles.”[6]
Howe and Nissenbaum mention they are aware their venture is not an immediate solution. However, the more we hear of and join these imaginative strategies “whereby individuals resist surveillance by taking advantage of blind spots inherent in large-scale systems” [7], and the more we adapt our behaviours to adopt these new ‘activist’ services, the more we demonstrate the demand for these new alternatives. And by so doing, we argue for the value of services that we can trust not to steal or manipulate our social contexts for financial and political gain.

A significant value offered by the Commodify.Us platform is the power to manage our own data. The simple act of downloading our own data from Facebook, and then uploading it to Commodify.Us supports us to rethink what all this information is. What once was just abstract data suddenly becomes material that we can manipulate. Alongside this realization arrives the understanding that this material was made by our interactions with all these platforms, and that other people are spying on us and making money out of it all. Once this data material is uploaded onto the Commodify.Us platform, it asks if we want this stuff to be a product under our own terms, or if we wish to make art out of it using their tools.
This is a cultural shift that demonstrates how contemporary Hacktivists are developing software that promises to offer realistic service infrastrucutures. When I interviewed Charlie Gere in 2012[8] he said that these artists “are not part of the restricted economy of exchange, profit, and return that is at the heart of capitalism, and to which everything else ends up being subordinated and subsumed. Thus they find an enclave away from total subsumption not outside of the market, but at its technical core.” For me, this kind of work is of central importance to the contemporary era, and it only occurs where artists cross over into territories where their knowledge of networks directly contributes to the building of alternative structures of social independence.
#Carnivast (Windows and Android apps, 2012) Mez Breeze and Andy Campbell.
Behind the rollercoaster hype cycle of Virtual Reality (VR) over the last quarter of a century, artists have kept working with VR as an increasingly mature medium. Realtime interactive 3D computer graphics is the most visually immersive medium for illusion in art, and text is the most imaginatively immersive. Both have been used to create virtual reality, with 3D virtual worlds in the case of the former and text-based worlds such as MUDs, MUCKs and MOOs in the case of the latter. They might appear to clash but there is a long history of 3D VR that incorporates text into or as its spatial environment.

I reviewed Mez Breeze’s book “Human Readable Messages”, which collects Mez’s “Mezangelle” micro net.text artworks, for Furtherfield here and wrote:
Mezangelle surfaces and integrates the hidden aesthetics of computer mediated human activity, setting computing and human language in tension and synthesizing them. It expands the expressive possibilities of text and is a form of realism about the conditions in which human reading is currently flourishing. “Human Readable Messages” provides an ideal opportunity to familiarize ourselves with Mezangelle in the depth that it deserves and rewards.
Collected in book form, the ephemerally distributed but thoughtfully crafted code-like text of Mezangelle becomes a book of days. Placing the avowedly low-bandwidth textuality of Mezangelle into virtual space might seem perverse, but that is what the App “#Carnivast”, produced with Andy Campbell, does very successfully.
Launching #Carnivast displays a virtual world looking like the insides of a nebula rendered in cheesecloth, accompanied by a glitchy, breathy, echoey, wavey, phaser-y, stringy soundscape. Superimposed over this in white formal capital san-serif type is the hashtag title “#CARNIVAST”. To the top left of the screen are some small button controls. Warm autumnal evening motes of colour flicker slowly across the view as the virtual world rotates slowly giving a combined impression of immensity, solidity, weight, and atmosphere. The textures on the surfaces of the world (or that are the surfaces of the world) slide slowly over each other creating interference patterns.

It’s a sensuous world, although not entirely a comfortable one, and one that invites exploration of its depths, or at least a closer look at its surfaces. The motes and the breathing are reminiscent of Char Davis’ ambitious “Osmose” (1995), the aqualung-controlled immersive virtual forest environment.
Selecting a world from the buttons and exploring it by swiping and pinching shows that the texture of the surfaces of the virtual world is Mezangelle, undulating over and through the world in a way reminiscent of some of the scenes from Laurie Anderson’s interactive CD-ROM “Puppet Motel” (also 1995) or of Michael Takeo Magruder’s VRML visualizations. The finesse of the text and the undulating environment contrast with Jeffrey Shaw’s “Legible City” (1989), a virtual environment of larger-scale text, Barbara Kruger’s Futura gallery installations, or the jagged phosphor green glow of Neo’s view of the underlying code of reality in the Matrix.
#Carnivast is very much its own experience, a series of distinctive spaces to float in. The first and third world are curvilinear and warmly coloured, the first feels like the interior of a nebula or a tokamak, the third feels like the inside of a cell or an atom. The second world is rectilinear and more acidicly coloured, closest to traditional imaginings of cyberspace. They are all meditative spaces, somewhere to spend time outside of the everyday world and to reflect. Mezangelle is an unlikely construction material for such a space, it demands too much attention to be decorative and contains rough ASCII symbols that contrast with the smooth curves or rectilinear forms of each space. It exists in tension with the surfaces of the virtual worlds, and it is this that gives #Carnivast its conceptual energy.
If you’re unfamiliar with Mezangelle, the [] button switches the screen to a rotating carousel of panels of coloured Mezangelle text that you can swipe through. Mezangelle is personal expression in an impersonal style with a social context. The geometry of the virtual spaces of #Carnivast is a substitute for the latter, and it creates an unlikely but compelling allegorical visualization of the flow of Mezangelle through mailing lists and blogs. It is a model of the social and conversational Internet rather than its technological infrastructure.
#Carnivast is finely tuned to make a space that you can lose all sense of time and self in as you explore it. As well as running on Windows PCs it works well on different sizes of portable device (I tried it on a phone, on a small tablet and a 9 inch tablet), and would work well large-scale in a gallery. How I would love to see it is modified to work with the Oculus Rift, the new consumer stereo vision head-mounted display (HMD). A Rift-enabled #Carnivast would afford a less constant opportunity of escape than the mobile version, but would be even more immersive. It’s a shame that the software is proprietary (closed source), as otherwise the community could add that feature.
#Carnivast is a mature VR artwork that represents an immersive extension of the strategies of Mezangelle into an exploration of virtual and network space. Explore it in evenings at the desktop, or keep it on your phone and get away from commuter noise and crush whenever you need to. It is a meditative experience deepened through restraint in its choices of navigation and materials and through fine tuning of its aesthetics and experience.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
Featured image: Thomson and Craighead, Here (2013)
Visiting Jon Thomson and Alison Craighead’s survey exhibition, Never Odd Or Even, currently on show at Carroll / Fletcher Gallery, I found myself confronted with an enigma. How to assemble a single vision of a body of work, impelled only by the dislocated narratives it offers me? ‘Archaeology’ is derived from the Greek word, arche, meaning ‘beginning’ or ‘origin’. The principle that makes a thing possible, but which in itself may remain elusive, unquantifiable, or utterly impervious to analysis. And so it is we search art for an origin, for an arising revelation, knowing full well that meaning is not something we can pin down. Believing, that the arche of a great work is always just about to take place.

In an essay written especially for the exhibition, David Auerbach foregrounds Thomson and Craighead’s work in the overlap between “the quotidian and the global” characteristic of our hyperconnected contemporary culture. Hinged on “the tantalising impossibility of seeing the entire world at once clearly and distinctly” [1] Never Odd Or Even is an exhibition whose origins are explicitly here and everywhere, both now and anywhen. The Time Machine in Alphabetical Order (2010), a video work projected at the heart of the show, offers a compelling example of this. Transposing the 1960 film (directed by George Pal) into the alphabetical order of each word spoken, narrative time is circumvented, allowing the viewer to revel instead in the logic of the database. The dramatic arcs of individual scenes are replaced by alphabetic frames. Short staccato repetitions of the word ‘a’ or ‘you’ drive the film onwards, and with each new word comes a chance for the database to rewind. Words with greater significance such as ‘laws’, ‘life’, ‘man’ or ‘Morlocks’ cause new clusters of meaning to blossom. Scenes taut with tension and activity under a ‘normal’ viewing feel quiet, slow and tedious next to the repetitive progressions of single words propelled through alphabetic time. In the alphabetic version of the film it is scenes with a heavier focus on dialogue that stand out as pure activity, recurring again and again as the 96 minute 55 second long algorithm has its way with the audience. Regular sites of meaning become backdrop structures, thrusting forward a logic inherent in language which has no apparent bearing on narrative content. The work is reminiscent of Christian Marclay’s The Clock, also produced in 2010. A 24 hour long collage of scenes from cinema in which ‘real time’ is represented or alluded to simultaneously on screen. But whereas The Clock’s emphasis on cinema as a formal history grounds the work in narrative sequence, Thomson and Craighead’s work insists that the ground is infinitely malleable and should be called into question.

Another work, Belief (2012), depicts the human race as a vast interlinked, self-reflexive system. Its out-stretched nodes ending at webcams pointing to religious mediators, spiritual soliloquists and adamant materialists, all of them searching to define what it means to be in existence. Projected on the floor of the gallery alongside the video a compass points to the location each monologue and interview was filmed, spiralling wildly each time the footage dissolves. Each clip zooms out of a specific house, a town, a city and a continent to a blue Google Earth™ marble haloed by an opaque interface. Far from suggesting a utopian collectivity spawned by the Google machine, Belief once again highlights the mutable structures each of us formalise ourselves through. As David Auerbach suggests, the work intimates the possibility of seeing all human kind at once; a world where all beliefs are represented by the increasingly clever patterns wrought through information technology. Instead, culture, language and information technology are exposed as negligible variables in the human algorithm: the thing we share is that we all believe in something.

Never Odd Or Even features a series of works that play more explicitly with the internet, including London Wall W1W (2013), a regularly updated wall of tweets sent from within a mile of the gallery. This vision of the “quotidian” out of the “global” suffers once you realise that twitter monikers have been replaced with each tweeter’s real name. Far from rooting the ethereal tweets to ‘real’ people and their geographic vicinity the work paradoxically distances Thomson and Craighead from the very thing twitter already has in abundance: personality. In a most appropriate coincidence I found myself confronted with my own tweet, sent some weeks earlier from a nearby library. My moment of procrastination was now a heavily stylised, neutralised interjection into Carroll / Fletcher gallery. Set against a sea of thoughts about the death of Margaret Thatcher, how brilliant cannabis is, or what someone deserved for lunch I felt the opposite of integration in a work. In past instances of London Wall, including one at Furtherfield gallery, tweeters have been contacted directly, allowing them to visit their tweet in its new context. A gesture which as well as bringing to light the personal reality of twitter and tweeters no doubt created a further flux of geotagged internet traffic. Another work, shown in tandem with London Wall W1W, is More Songs of Innocence and of Experience (2012). Here the kitsch backdrop of karaoke is offered as a way to poetically engage with SPAM emails. But rather than invite me in the work felt sculptural, cold and imposing. Blowing carefully on the attached microphone evoked no response.
The perception and technical malleability of time is a central theme of the show. Both, Flipped Clock (2009), a digital wall clock reprogrammed to display alternate configurations of a liquid crystal display, and Trooper (1998), a single channel news report of a violent arrest, looped with increasing rapidity, uproot the viewer from a state of temporal nonchalance. A switch between time and synchronicity, between actual meaning and the human impetus for meaning, plays out in a multi-channel video work Several Interruptions (2009). A series of disparate videos, no doubt gleaned from YouTube, show people holding their breath underwater. Facial expressions blossom from calm to palpable terror as each series of underwater portraits are held in synchrony. As the divers all finally pull up for breath the sequence switches.

According to David Auerbach, and with echoes from Thomson and Craighead themselves, Never Odd Or Even offers a series of Oulipo inspired experiments, realised with constrained technical, rather than literary, techniques. For my own reading I was drawn to the figure of The Time Traveller, caused so splendidly to judder through time over and over again, whilst never having to repeat the self-same word twice. Mid-way through H.G.Wells’ original novel the protagonist stumbles into a crumbling museum. Sweeping the dust off abandoned relics he ponders his machine’s ability to hasten their decay. It is at this point that the Time Traveller has a revelation. The museum entombs the history of his own future: an ocean of artefacts whose potential to speak died with the civilisation that created them. [2] In Thomson and Craighead’s work the present moment we take for granted becomes malleable in the networks their artworks play with. That moment of arising, that archaeological instant is called into question, because like the Time Traveller, the narratives we tell ourselves are worth nothing if the past and the present arising from it are capable of swapping places. Thomson and Craighead’s work, like the digital present it converses with, begins now, and then again now, and then again now. The arche of our networked society erupting as the simulation of a present that has always already slipped into the past. Of course, as my meditation on The Time Traveller and archaeology suggests, this state of constant renewal is something that art as a form of communication has always been intimately intertwined with. What I was fascinated to read in the works of Never Odd Or Even was a suggestion that the kind of world we are invested in right now is one which, perhaps for the first time, begs us to simulate it anew.
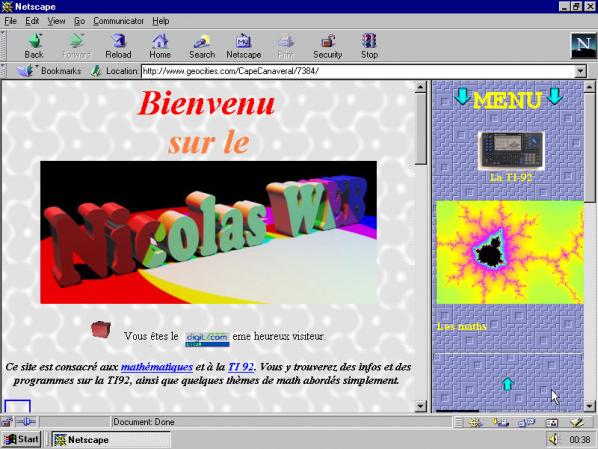
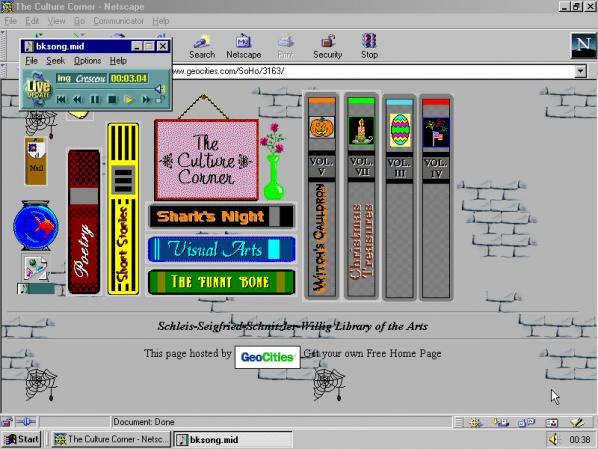
Featured image: A random Geocities homepage, last updated sometime around 1997
Daniel Rourke visits the Photographers’ Gallery in central London and reviews their latest exhibit One Terabyte of Kilobyte Age by artists Olia Lialina and Dragan Espenschied, on THE WALL. Over an eight week period (18 April – 17 June 2013) they feature a non-stop stream of video captures of what they term as the lost city and its archival ruins. A documentation of a past visual culture of the web and the creativity of its users with new pages changing every 5 minutes. The project provides a glimpse into web publishing when users were in charge of design and narration in contrast to the automated templates of Facebook, YouTube and Flickr.
Sifting through a dormant internet message board, or stumbling, awestruck, on a kippleised [1] html homepage, its GIF constellations still twinkling many years after the owner has abandoned them, is an encounter with the living, breathing World Wide Web. At such moments we are led, so argues Marisa Olson, ‘to consider the relationship between taxonomy à la the stuffed-pet metaphor and taxonomy à la the digital archive.’ [2] How such descript images, contrived jumbles of memory and experience, could once have felt so essential to the person who collated them, yet now seem so indecipherable, stagnant, even – dare we admit it – insane to anyone but the most hardened retro-web enthusiast.
On show at London’s Photographers gallery until June 17th is an extensive archival exhibit designed to manage, reveal and keep these experiences alive. One Terabyte Of Kilobyte Age (1tb) is the fifth work to be commissioned for the Photographer Gallery’s ‘The Wall’, curated by two artists long associated with the era of the web the exhibition reveres: Olia Lialina and Dragan Espenschied. Perhaps best known for their book Digital Folklore (2009) the artists and retro-web evangelists have, with the 1tb project, strengthened their status as archivists, an impulse Hal Foster famously argued ‘concerned less with absolute origins than with obscure traces’ [3]. In the same year that Dragan and Olia launched their guide to the folk web, Yahoo! announced they were to close one of its greatest sources of inspiration: Geocities. A vast expanse of personal webpages, many of which had long since slid into html decrepitude, represented for Yahoo! little but financial embarrassment. So ancient and outmoded was Geocities that many contemporary browsers were incapable of capturing its essence, fragmenting images and link rolls randomly across modern laptop screens in an attempt to render their 800×600 pixel aura. Scraping and downloading the terabyte or so of data that made up the Geocities universe was thought important enough by some that a taskforce was put together, made up of technical wizards and wizardesses driven by the profound notion that all existent culture is worth saving. From Olia and Dragan’s webpage:
In between the announcement and the official date of death a group of people calling themselves Archive Team — managed to rescue almost a terabyte of Geocities pages. On the 26th of October 2010, the first anniversary of this Digital Holocaust, the Archive Team started to seed geocities.archiveteam.torrent.
Olia and Dragan’s gesture, to feed the wealth of culture contained in that torrent back to the masses in a palatable form, is a project whose fruition at the Photographer’s Gallery is but a minor part. After downloading, storing and sorting the 16,000 archived Geocities sites the task of exactly how to display them is a problem. Since most browsers would mangle the look and feel of the Geocities pages Olia and Dragan have turned to two main methods of re-representation. The first, let loose on an automated Tumblr blog that updates over 70 times a day, is an ever growing series of front-page screen captures. In this form 1tb bends to the will of a contemporary web user who concerns themselves with likes, reposts and uplinks.
Reflecting on the Tumblr-archive of the torrent-archive of the Geocities-archive, Olia and Dragan’s site contemporary-home-computing highlights particular screen captures that have garnered the most reposts and likes from their Tumblr followers. The results say much for the humour that still drives online culture, but perhaps little about the original contexts from whence those screen captures came. For instance, the screen captures that garner most attention are usually the ones that have failed a part of the retrieval/display/capture process. These ‘obscure traces’ may be GIF heavy sites, half loaded to interesting aesthetic affect, or, perhaps the most telling, captures that show nothing but the empty shell of a Netscape Navigator browser, caught forever like a millennium bug in digital amber.
The second mode of capture and re-display takes place at the Photographer’s Gallery itself. Depicted on nine large intersecting HD video screens set into ‘The Wall’ of the entrance-cum-café, one’s first experience of the exhibit is ponderous. The display cycles through the vast array of Geocities homepages at five minute intervals, giving viewers a more than generous dose of 800×600 px nostalgia. Whether the websites that fade into view are a barrage of animated GIFs,insightful commentary on life in the late 1990s, or a series of barren ‘Under Construction’ assemblages, is up to chance.
As a reviewer, sent to derive something from the gallery experience, the wall leered at me with gestures that sent my inner taxonomist into a frenzy. Confronted with such tiny slithers of the archive, in such massive doses, it quickly becomes obvious that the real potential of the project has not been quite realised. Rather than static screen captures The Wall shows cleverly rendered quicktime videos, allowing the GIF whiskers of a Hello Kitty mascot to quiver once more. If you are lucky, or have the patience to watch a long series of the sites fade into view, you’ll be greeted by flickering ‘Welcome’ banners, by cartoon workmen tirelessly drilling, by unicorns cantering and sitemeter bars flashing. But The Wall also feels wholly at odds with its content, caught up in a whirl of web nostalgia that minimises the lives, experiences and aesthetic choices of a defining generation to static flashes that you can’t click on, no matter how much you want to. Archives are living, breathing entities wont to be probed for new meanings and interpretations. Whether depicted as static or faux animated, One Terabyte Of Kilobyte Age is a project with an endless surface, with little way for its viewers to delve deeper.
Trawling through the 1tb Tumblr is a much more visceral experience than the one that greets you at the Photographer’s Gallery, but the sense of a journey waiting to be embarked on is lost somewhat in the move to the Tumblr kingdom. Every five minutes offers a new chance to spot similarities on The Wall, to ponder on the origins of a site or, more profoundly, wonder where the people that toiled to make them are now. Before the days of user driven content, of Facebook timelines, and even before RSS feed aggregators, the whole web felt something like this. Today’s web is unarguably more dynamic, with a clean aesthetic that barely shifts behind the waves of content that wash over its surface. But the user has been relegated to shuffler of material.
The Geocities homepage was designed, and kept updated by an army of amateur enthusiasts, organising bandwidth light GIFs in ever more meaningful arrays, in the unlikely event that another living soul would stumble upon them. There is much to love about One Terabyte Of Kilobyte Age, and much to be learned from it given the time. But part of me wishes that the Photographer’s Gallery had given over their trendy café to a row of beige Intel 486 computer stacks, their unwieldy tube monitors better capturing the spirit of the web alá 1996. The clash between the 90s amateur enthusiast and the avid content shuffler of the 2010s is inherent in the modes of display Olia and Dragan chose for their project. Beginning from a desire to save and reflect on our shared heritage, 1tb now represents itself as pure content. An impulse to probe the archive replaced by an impulse to scroll endlessly through Tumblr streams, clicking like buttons on screen captures we hope will distract/impress/outrage our friends until the next cat video refreshes into view.
Go, go to the Photographer’s Gallery tomorrow, grab yourself a coffee and let the Geocities archive wash over you. If you can do it without Instagramming a snap to your friends, without updating your Facebook page with tales of your nostalgic reverie, if you can let the flickering screen captures do their own talking , only then can you claim you truly re-entered the kilobyte age.
Cyposium
an online symposium on cyberformance
Friday 12th October 2012
http://www.cyposium.net/
We all perform on the Internet. The social media profiles that we are contractually obliged to give our real names to are just as much performances as our World Of Warcraft or Minecraft avatars. Yet these impromptu performances of our socialised and fantasy selves lack the literary quality of drama. Not drama in the sense of a Usenet or Tumblr flamewar, but in the sense of theatre.
The 1993 New Yorker cartoon captioned “On the Internet, nobody knows you’re a dog” identifies two important features of the early public Internet. Firstly it’s a place, somewhere you can get onto. Secondly that place has limited bandwidth for establishing identity and communicating affect. This meant that the Cyberspace of the net became a site for identity play and imagined realities.
As the text-based virtual reality of MOOs gave way to the image-based Palace Chat and then three dimensional AlphaWorld the available bandwidth increased and with it the available ambiguity decreased. Describing a character or a scene or an action with a few words leaves the members of the audience much freer to exercise their own imaginations than seeing it in full motion animation with a high polygon count.
The visual, social and even economic order of virtual worlds and social media have become a more fixed and uncritical embodiment of mass media and the established social order. This has reduced their potential for alterity but it has made them useful representations both of shared reality and shared fantasy that can be used as a stage on which to perform critically, reintroducing the literay against the grain of their unreflective consumption of identity and spectacle.
Throughout this history, from the early 1990s to today, the Internet’s affordances have been used to produce dramatic performance in Cyberspace, “cyberformance”. The problem is we don’t remember this, at least not as clearly as we should. Individually, institutionally, and technologically we have lost our memories of artistically groundbreaking and important performances.
This problem is not unique to cyberformance. All digital art suffers from the decay of digital media and the creeping obsolescence of the hardware that it runs on. Internet art suffers from bitrot, software obsolescence, linkrot, the loss of web pages and sites elsewhere on the net that are connected to the work, and netrot, changes in the protocols used to distribute it.
Above and beyond those problems, cyberformance involves live perfomance. Unique events produced by historical communities at a particular moment using media that will rapidly become obsolete need to be recorded in order to be remembered or at least to be critically re-evaluated later. This creates a second layer of conservation and archiving problems.
Take the example (outside of Cyposium) of Judy Malloy’s “Brown House Kitchen”, a narrative environment created in the LambdaMOO text-based virtual reality. Despite being mentioned in surveys of virtual art in the 1990s, despite being produced with institutional support, and despite being stored on one of the longest-running textual virtual world servers the software objects that made up the work were recycled as part of the normal running of LambdaMOO and are now lost. Many other text-based virtual realities, some specifically designed for dramatic works, are not even online any more. And the protocols used to access them are old, with software to connect to them increasingly not installed by default on newer operating systems. Even those created after the Internet Archive started will not appear in it, as they are not web-based.
I mention LambdaMOO as by chance I was researching text based virtual worlds and performance in the months before Cyposium was announced. One work that was described in the literature but untraceable online was Stephen A. Schrum’s “NetSeduction”. Which Schrum presented and discussed at Cyposium. And the script of the original performance was made available through the Cyposium website. Without Cyposium, these resources would not have been made available.
These contrasting examples drive home just how badly needed Cyposium was. The Internet does enable us to digitise and experience more culture than ever before, but it also erases our memories of the culture that is native to it. And the often highly experimental nature of cyberformance makes it harder to record and remember than almost any other kind of technologically enabled art.
As well as addressing a specific need to recover the history of net performance, Cyposium is an exemplary model for a new kind of online event in the era of Massively Online Open College courses. It performs the function of a symposium or convention online, reducing barriers to access and increasing reach for institutions, speakers and audience members. The Waterwheel Tap software used for most of Cyposium allows side-channels of audience communication, which help to build a sense of place and community and allow the audience to ask (and answer) questions and share knowledge among themselves and with the speakers.
The panel discussions that Waterwheel enabled meant that old and new net performers could discuss each others work in the light of new developments or freshly reconsidered history. And we, the audience, wheoever we were and wherever we were, could watch and learn from this discussion and join in. I am often wary of the word “open”, but there was an intellectual and social generosity and inclusiveness to Cyposium that made it feel like a very open event.
A ripple of excitement went through the mailing lists I subscribe to when Cyposium was announced. Its organizers and line up promised something special, and the event itself didn’t disappoint. To be part of the audience, chatting in text alongside the live streaming video presentations, was to be part of both a welcoming ad hoc conversational community of interest and participating in a key moment in a larger historical conversation.
Cyposium went beyond recovering and presenting the history of online performance. It brought together net performers old and new in productive dialogue in front of an engaged audience and served as an example of a new kind of net native event. Now that the event itself has finished the Cyposium web site serves as an important record of an important aspect of online creativity.
This essay will appear in the forthcoming Cyposium book.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
It has been almost five years since Roger Bernat, a renowned artist of the experimental theatre scene of Barcelona, premiered ‘Public Domain’. The piece, still on tour, has been performed in public spaces around the world. This audience-centred show invites individuals to participate in this engaging experience that emerges as a sociological choreography. The audience gathers in a public square and they are given a pair of headphones. Nothing warns that a performance is about to take place despite the two signs located at the edges of the square that mark the right and the left. Through this simple but effective setting the piece starts. Welcoming words and introductory instructions are broadcasted to the audiences that immediately understand that the action will be mediated by the voice that is talking to them through the headphones. ‘Would you mind if I ask you some questions’― inquiries the voice. ‘Did you come alone because someone recommended the piece to you? If so go right. Did you come on your own initiative? Go left. Did you go to the play due to work related reasons? Go to the centre. Do you think there are questions that should never be asked? Put your hand in your mouth. Do you call home the place where you live? Put your hands together on your head.’ Through this mechanism, wrapped in the relative anonymity that the group offers, the audience reveals details of their intimacy or of their fictionalized intimacy. Are there supermarkets stealers among the audience members? Have they ever followed strangers? Did they study in public or private schools? Thus, the piece explores bodily narratives playing with the sociological aspects that the audience reveals through their answers.
The development of the piece is constructed through questions that trigger the actions and drag participants into an immersive experience. Groups among the audience members are created and what starts as an entertaining proposal turns into a reflective exercise that interrogates our opinions, beliefs and experiences. Some members of the audience are on our side while others become our enemies; and then war bursts. The piece never loses its playful side although participants become aware of how the categorised distribution of individuals, without nuances, leads to a situation of confrontation. This is of course a simulation, but is this piece a transduction of reality? The theorist Shannon Jackson calls these pieces ‘social works’[i]. From her point of view, these pieces state some of the paradoxes of our systems and as experiments they contribute to discuss the nature of our public engagement. They unfold some of the contradictions of the agencies that operate in our systems while they give evidence of the relational parameters that we assume and accept to construct our social beings. In this case, the sample of audience members is taken as a small sociological study that through continuous dichotomies performs organisation and operation.
The emergence participatory theatre and performance has brought significant changes that basically related to the fact that the audience members have become the raw material of the piece. This change clearly alludes to the aim of artists to incorporate innovate disruptive actions to discuss the matters affecting the current social arena. As Claire Bishop states, there are also tensions that emerge within the performance of these works; ‘quality and equality, singular and collective authorship, and the ongoing struggle to find artistic equivalents for political positions’[ii]. From my point of view, most of these tensions appear due to the game-work nature of these pieces. In a way, labour structures are enacted through instructions that often reproduce some of the basic rules of capitalism; the use bodies to make the system work. To which extent these practices subvert the traditional working relations? Is participation a necessary tyranny for creators to produce social changes? What are the affects and effects of these practices?

‘Public Domain’ also creates an appealing mobile bodily landscape. It is interesting to think about the relationship between the show and reality. The theatricality of the piece interacts with the social reality blurring boundaries, as one is part of the other. The piece is a social event that occurs outside the convention of a gallery, exhibition space or theatre. Thus, the citizens that are not part of the show assume this theatrical intervention as part of their reality, as part of the current social matters. The integration of technologies into the arts have widely contributed to perform new experiential practices. In this regard, technology plays an important role in triggering participation. Technology helps to distribute and operate instructions but also produce a specific aesthetics that appears thanks to the creation of hybrid practices.
The interaction among disciplines and fields has given birth to fruitful collaborations and cutting-edge practices in the arts. The current convergence of the fields of nanotechnology, cognitive science, biotechnology and communications (ITC) has given birth to the most prolific period of inventions and findings in the history of science. The possible intersections between the arts and sciences are gaining day by day a bigger interest but most of its potential is yet to be imagined. In which ways will these practices will contribute to social change? Is participation the key for a major public commitment in matters that affect our daily lives? ‘Public Domain’ proves that through a rather simple system significant concerns can be addressed in a playful but effective manner in a project that has already engaged audiences from over the world.
Roger Bernat – After studying architecture, he discovered theatre and at the age of 25 he entered the Institut del Teatre in Barcelona to study directing and dramaturgy. Soon after, he founded and directed, with Tomàs Aragay, the company General Elèctrica. Well known in Catalonia for their daring and engaged projects, General Elèctrica (1997-2001) created a dozen remarkable productions. Roger Bernat often concentrates on a variety of social groups (heroes, transsexuals, cab drivers, etc.) in his ongoing search for new theatrical forms. His best-known plays include Que algú em tapi la boca (2001), Bona gent (2003) in collaboration with Juan Navarro, Amnèsia de fuga (2004), LA LA LA LA (2004), Tot és perfecte (2005) and Das Paradies Experiment (2007). Apart from his stage work, Roger Bernat also directs videos. http://rogerbernat.info/en/
First off, some claims, some general, some particular. I’m going to use these to speak about the work under consideration and in turn call upon that work to support the claims. A kind of virtuous critical circle.
General: works of art are not messages but objects. They don’t say things nor ask questions, nor assert, nor investigate. Neither do they as objects have messages somehow encoded or embedded within them. To assert otherwise is a massive category error.
As objects they may of course be brought in evidence, copied, become conversation pieces, be described well, be described badly, be described perversely, be seen, be half seen, be missed, be lost, be found, be written about, point to things, be compared and many other things, some of which have not yet been imagined.
Further, artworks are fuzzily-bordered and not necessarily of a physical or temporal piece – the object is not simply the object (and ‘the object’ might not be physical but words, a concept, a sound recording, a protocol) but everything that accretes as a result of it – commentary, jokes, other artworks made in response. If mathematical terminology wasn’t so regularly and toe-curlingly abused in the arts, we might refer to them as manifolds, not necessarily connected.
Even the historical is not immune. There’s a reaching back in time where an established work is transformed retrospectively by homage – ‘Las Meninas’ an obvious case in point.
Also: the work of art is finite – it was born and it will, one day, cease to exist (and it will be forgotten, or there will be no-one to remember it). Everything changes, everything dies.
This implies, too, that although the individual author matters, as product of a unique formation and a unique set of locations in time and space, every artwork is socially authored.
Particular: Abraham’s work represents a new conjunction of technology, collaboration and performance as a generator of moving image. It has precursors (freely acknowledged, indeed celebrated) but it is qualitatively new. The moving image work comes in two flavours, fresh and preserved, both with their own particular and delicious savour. Abrahams conducts live performances on the internet. These performances occur singly, as pieces in themselves, or form part of the programme of events accompanying exhibitions. The moving image pieces in this show are all derivations of this kind of performative event. Except derivation has an air of the hierarchical and the types of piece form no hierarchy any more than fresh or smoked salmon do.
A final general claim: writing about art is not a science but itself an art. Sometimes the brush will be delicate and sometimes broad. There is no recipe or rules or template. One can be too delicate – sometimes confusion is good, particularly in the matter of the affective. Crude thinking sometimes gets us further, paralleling, not dissecting, the richnesses of work. There are some mysteries one should leave as such.
OK. Onwards and upwards…
Performative is currently a much used, some might say overused, word. One quite common usage is to suggest that a work contains visible or at least trackable traces of its own making, a kind of archaeological or sedimentary record, and that perhaps this might have been to varying degrees intentional.
Of course it’s arguable any work of art is performative in this way and that it’s quite hard to erase the trail behind you whether what you make is time based or photographic, sculpted or made with hand applied pigment of one sort or another. Continuous looking and thinking about art for any length of time, especially allied to making stuff oneself, whether dabbling or something more serious, hones an increasing sensitivity to these questions. And this matters; particularly when it comes to over-nice distinctions between close relatives such as the still and moving photographic image and esoteric arguments about how time is differently present or presented in each of these and in other further flung practices too. The new scholasticism feeds on ever finer such distinctions.
So it’s a relief to come across work, which is genuinely performative, enough so that even someone undrenched in theory can see it, can get it and can be delighted and exalted by it. Furthermore work that smells unmistakably of the human, that abuts the high and the low, the crude and subtle, that blurs boundaries, that borrows and echoes the work of others not with the pinched expression of someone with a theoretical framework but in a spirit of ‘why?’ and ‘let’s play’ – the two childish precursors of grown up science and art.
Annie Abrahams’ show at the Centre Régional d’Art Contemporain Languedoc-Roussillon in Sète is a graceful and elegant dog’s dinner of a show. Physically it’s odd, exiled to the upper floor (still a generous space) whilst Catherine Gfeller, someone altogether more easily glossed and hence exhausted (though not without merit) gets the more conventional downstairs galleries (and attracted the lion’s share of the press on the opening night.)
Said upper floor comes in two instalments – a lovely hangar type space, where a game of golf seems distinctly possible, with a kind of tail leading off it, a long thin corridor which fattens a little towards its farther end maybe 100 metres away.
The layout of the show utilises this peculiarity nicely. In the big room a very large two projection installation, Angry Women, spans one corner and takes up a considerable portion of the two adjacent walls.
In the far corner, diagonally opposite, a monitor, with two chairs and two sets of headphones, of which more later.
Leaving the larger space, two more monitor based pieces at junctions where it’s possible for an individual to sit and others to pass. Five chairs arranged in a circle with copies of two books of interviews on each (one with Abrahams, and one with a selection of other cultural figures) and highlighter pens. In the middle of the circle, a pile of blankets. A larger wall piece of rough and ready cardboard placards with texts (“mutuellement vulnérable”, “euphorie communicative”, many others) in various hands.

At the far end, a number of framed photo and images based pieces plus a work consisting of a single photograph and headphone delivered audio (it’s a snapshot – snapshot size, snapshot aesthetic – of husband and wife volunteer fire fighters. The audio is manipulated audio of texts on the subject of fear read by them. Let’s not try and place all this into any sort of context yet. Let’s set out our stall, enumerate, account, describe.)
A final deft touch is the symbolic linking of the two areas by a ribbon of text occupying the 15 or so centimetres above the floor, skirting board height, the topic of which appears to be mental illness (and all elegantly lettered except for one point where a letter had been omitted and is inserted with a caret symbol.)
Most of the pieces employ texts or performances – both gestural and textual – by others – often created according to some seed question or protocol. The texts often come from questions posed on the internet but sometimes from workshop or outreach type (type –this is to tentatively and provisionally locate the thing – it’s outreach Jim, but not as we know it) activity.
The performers in the moving image pieces are geographically dispersed but brought together at a single time by webcams and some custom software that Abrahams has used on a number of occasions where the web-cammed-in participants occupy a space in a rectangular grid (aficionados of seventies UK quiz shows such as Blankety Blank will get it immediately).
There’s a fragility, a delicacy, a tentative hold on existence, a testing of our belief, about these works that so many works of fine art – as opposed to design – have. The sense that what we have incorporates the idiosyncrasies, indeed the weaknesses of the support materials and media, into a final object (the same sense as when an artist wilfully uses something manifestly not intended for art, or allows mistakes to stand, or omits, or makes all too evident repairs; this is not new. Think pentimenti, or the hasty addition of an extra panel of canvas or paper to take account of expanding ambition or vision, or the aestheticized unevenness of Japanese tea-ware.) This sense of object-hood rather than message or statement is key. An objecthood which in retrospect could not have been other, but equally could not have been proposed, foreseen, except in its protocols of playfulness.
The pixellation, dropout, glitching, concomitant upon the pushing of the current state of the network to its limits in the multi participant pieces (and this reminds one of how flicker and roll and a general fuzziness become now part of the Acconci piece Abrahams draws upon in her Theme Song After Acconci – which reasons of space preclude too much detail about here – suffice it to say Abrahams honours, compresses, feminizes, satirises and intensifies the original. If Acconci could have had access to a “better” technology, one where the speed was constant, where no flicker or roll appeared, would he have then felt it served his purpose better? Did what he saw even look fuzzy or worn to him? Probably yes, compared with the film standards of the day, as does Abraham’s work compared with high end digital video [and even the current, rather good, quality of You Tube].)

To offer participants a protocol is paradoxically both to assert and to cede control, to know and to not know how things will turn out (an analogy is the use of chance in the works of Polish composer Witold Lutosławski, where the mechanisms make the generality of the sound, its broad texture, predictable but any particular instance impossible to predict or even fully imagine [but all, please note, a matter of degree because the finer the grain, the greater the level of magnification, the more we can find such uncertainty in anything unfolding over time – it’s a question of our norms – what is the difference between the Stockhausen piano pieces where the performer can choose the order of segments and a Mozart sonata where the tempo may be quite widely varied? – in principle, none])
The piece Pourquoi avons-nous des difficultés à ouvrir un ordinateur et en changer le disque dur? plays on a single monitor with the screen divided into two areas. In each we see, sometimes with difficulty and ambiguously, parts of a computer, screws, connections and hands.
We hear two voices, one that of Abrahams and the other her co-performer, discussant, what have you, Eliza Fantozzi, speaking in French. In the version at Sète there are English subtitles which even for non English speakers provide a kind of functionality, meaning, in that the words tend to be positioned on a line from left to right according to who is speaking. When both speak suggestive gaps appear, though these cannot be read definitively).
The subtitles are in a strange (for a native English speaker) near-English (the title, for example, is translated as “Why do we have difficulties to open a computer and change its hard disk?”).
This is, it must be said, cute, amusing and engaging and it underscores the altogether naughty childlike quality of the entire interchange. The characters (for I think one should mistrust the assumption, however tempting, that we have here unmediated access to the actual participants) are playful – amused and amusing. At the same time they ruthlessly anatomise the roots of their difficulties with technology (but the performativity avoids being on–message in any sense and makes for something strange, complex and even uncomfortable. At one point Fantozzi complains of the lack of colour variety inside the machine and starts painting the components with nail varnish to “create a much merrier circuit” – Je crée un circuit beaucoup plus gai).
Later Abrahams lays into a ribbon connector with a pair of scissors and then starts apparently fringing it with regular cuts half way across … There is an association of the decorative, the playful and a rejection of the serious which is somewhat too close to many gender stereotypes to be entirely comfortable. (The piece was originally performed on international women’s day 2011) And yet, and yet – the end result is complex, for there is a steeliness to the play and a self respect and assertiveness. Perhaps (I don’t know. I don’t think there is a definitive answer. I don’t think close reading or theory can bring us it either) it is the very truthfulness, the richness of the incorporation of the world as it is and not as we might like it to be from which this springs.
Before we get to the physically largest and most imposing presence in the show we’ll look at its neighbour, comprising two chairs, a monitor and two sets of headphones.
Double Blind (Love) is a record of a 264 minute telematic performance by Annie Abrahams and the US artist Curt Cloninger which took place on November the 29th 2009. Annie Abrahams was in the Living Room (Espace de création contemporaine) Montpellier, France and Cloninger in the Black Mountain College Museum and Arts Center, Asheville, North Carolina, US.

Both wore blindfolds for the entire duration of the performance, which was a joint telematic musical (and I use the word advisedly; though Abrahams describes Cloninger as a musician she appears to reject the description for herself. I think she is mistaken) performance taking the form of an improvisation, largely vocal but with some keyboard input from Cloninger, around a short musical cell from the track Until the End of the World by U2. The section in question has a repetition of the word “love” for its sole lyrical content and occurs just over midway through the song. It would perhaps ordinarily be described as a chorus but in fact appears only once in the song (although it continues as a backing vocal throughout the next verse), one of the first of many tiny idiosyncrasies on our pathway, peculiarities which add cumulative spice and interest to the project. I’d always found U2 banal and full of bombast but going to the song, under the circumstances of researching this piece, with necessarily open eyes and ears was a small epiphany, one of a number occasioned by a systematic engagement with Abraham’s work.
It’s worth noting that much of the structure of this piece came originally from Cloninger. In the previous year he had performed a number of pieces under the title “pop mantra” where in a live situation he repeated a similar pop music cell for a period of hours (“usually blindfolded”).
Cloninger had also video documented these performances though at this point this is documentation and lives no independent life of its own.
Let’s take a look at these proto ‘Double Blinds’. There is as yet no suggestion of interchange, of development. Although this is clearly a more obvious option with two performers, conscious development is not impossible in a solo performance. It does however appear to be consciously excluded. In an echo of the process or systems driven works of the seventies, Cloninger sets something in motion and allows it to unfold. He attempts to repeat the phrase many times. Presumably his arms start to ache and his voice to tire. This trial of endurance becomes a principal motor of the pieces. What does this evoke? For me, and you might share this, there are the dance marathons of the twenties, the notion of sport, especially individual sport, of pitting oneself against oneself; there is ritual repetition – Sufi whirling, or that carrying out of repetitive, gruelling and apparently pointless tasks sanctified in some Buddhist traditions; the pilgrimage; there is a kind of practical prayer through ritual, suffering or self-abnegation.
The motoric unwinding and associated characteristics obtain in Double Blind, too. What is new, what comes from Abrahams, is the telematic – the fact of separation by an ocean and the fact of collaboration. Indeed there is an inbuilt sharper contradiction as the collaboration separated by so much physical distance is of the peculiar intimacy that attends musical partnership, improvisatory or not. (A couple of years before Abrahams had performed a telematic kiss for three hours with the US artist Mark River.)
Despite Abraham’s denial the finished performance falls entirely within the established parameters of the musical. Precedents such as the work of Meredith Monk could be cited for Abraham’s compelling vocalisations – song, whisper, shout, scream, cry of pleasure, cry of pain – whose musico-dramatic logic and sensitivity to her performing partner, this listener at least, finds totally satisfying. It’s a touching partnership, with both performers bringing a fierce commitment to the task in hand but also each bearing different gifts – Cloninger, a formed musical sensibility supported by conventional skills and Abrahams a kind of discovery/invention of improvisation (indeed of music) ab ovo.
Thousands of years in 4 and half hours.
There is a formal challenge and satisfaction too, common to both Abraham’s and Cloninger’s concerns – how much transcendence can be mined, discovered, invented, from the small, the insignificant? Can it be exhausted before we are exhausted and what does the transfiguration brought about by the attempt suggest about us as human beings?
Two performers. Two chairs for two spectators only. Likewise, two sets of headphones.
Grace.
Opposite, stretching luxuriantly out, is the exhibition’s jewel in the crown – Angry Women, created by Abrahams and twenty two other women of many nationalities, speaking about anger; acting out, demonstrating, reflecting, on anger, on webcams from their different individual locations and in their native tongues, with the images being sent to the 3X4 grid, in a format that Abrahams has made her own. Because of the limits of even current streaming technology it was necessary to conduct two separate performances (separated by an interval of a couple of months). The length of each performance was determined by a protocol where a minute’s silence by all participants signalled the end. This resulted in pieces of differing lengths which lack of synchronisation adds another layer of fragile grace to the final projections, projected large on adjacent walls around the corner joining them with sound from the left images fed to the right speaker and vice versa.

The effect is visceral – we face what feels like a wave of humanity, not so much in numbers, although 23 is impressive, but in the infinite malleability of the face, hands and of gesture and expression and of how these things can occupy the frame. Sometimes that frame will resemble a Giacometti portrait, with the subject appearing to recede into what seems to be endlessly deep space. At others red lips or an open mouth, sensual and terrifying by turns, occupy the whole of the space – and furthermore each cell is constantly in flux (because these are living, breathing unpredictable human beings). There is something both of portraiture and of the dance at work, and a species of found poetry too, which the moving image work has in common with the collaborative texts at the other end of the exhibition. The combination of iron control, planning, foresight (the grid, the protocols) with a letting go and a trust elsewhere – the phased lengths, the blank space for the person who didn’t turn up, the performative possibilities – makes for something of great richness.
Additionally it’s clear that those of the performers who have previous experience are consciously playing with and against their fellows – gestures are mirrored, sounds echoed, the fiction of looking elsewhere (to the side, or above) in the grid is impressively deployed.
The angry women turn out to be at one and the same time very particular –unique – women and women in general too; the women in general turn out to be human beings in general (and general en masse because each so particular) and the human beings in general turn out to live in this, one, our, very particular, world – that mysterious, frightening and wonderful place.
In keeping with the cheering on of lack of clarity, of mess, of crudity I’ve espoused so far in this piece (and will continue so to do, here and elsewhere) I want to say we need to take the exhibition (and the world) as a whole. Offering us the video and the still image pieces and audio means we cannot but think of them together (we can choose to artificially isolate pieces but we cannot undo our knowledge of that whole). So to the extent that I have selected topics here I have done violence to Abraham’s art, which has no message, is not confined to any one medium, collaborates in multiple ways, borrows, steals (and gives) and presents us with a set of marvellous and mysterious objects which afford us a spectrum of entirely new pathways to the world, to seeing it, talking and thinking about it, ourselves, after we have gone to the bar or got on the train north to Paris and thence homewards, happy and somehow a little changed.
—-
Training for a Better World – Annie Abrahams
Centre Régional d’Art Contemporain Languedoc-Roussillon, Sète, France
28/10/2011 to 01/01/2012
Millie Niss was known, first and foremost as a net artist. Her works tend to have interactive characteristics in them, with thought-provoking writing and the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh is exactly that, an interactive poem with a strong message.
A poem written for an interactive platform can be labelled many things, including ergodic literature[1], electronic literature[2], interactive fiction[3] and hypertext[4] to name but a few terms. ‘Writing, exterior to the mind requires equipment culturally constructed[5]’ to communicate it, and so in this case, the interactive platform is the equipment relevant to the cyberculture of the early twenty-first century. Interactivity is to cyberculture as typography is to traditional writing[6]. Initially, it may seem to be a simple task to read this poem that is laid out completely in one-screen that appears to have a fixed amount of words (seventy), but as we begin the journey of reading this interactive poem, we realise the potential it holds and the complexity of the work. It ‘requires that we understand electronic literature not only as an artistic practice (though it is that, of course), but also as a site for negotiations between diverse constituencies and different kinds of expertise[7]’.
This case study will be an exploration of how the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh can be understood and read in its various potentials, from the surface, looking at the interface and reader experience, to the text, as a reading exercise and finally to the core, exploring the source of its creation through technology.

The Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh welcomes readers with a looped instrumental soundtrack and the first highlighted sentence of ‘this is the title of the poem’ (see image below). The soundtrack, though Asian sounding, has more of an Oriental influence to it than Bangladesh, but it is still effective. With a strong rhythm and a clear tune played by a stringed instrument, the music sets a light mood for the reader. Catchy and short, the never-ending loop of music hooks the reader in.
As one explores the poem by moving the mouse around the page, it becomes obvious that mouse-movements over certain words trigger changes in the highlighted words. Certain words also trigger verbal sentences or oral commentary[8].
The speed in which a reader explores the poem through mouse movements will create different experiences. Slow movements will allow readers to read and take in the various highlighted sentences in ‘an apparently random order[9]’, whilst fast movements will create a sort of chaos where more than one oral commentary may be triggered at the same time creating audio overlaps whilst the pink highlighted words will seem to randomly light up the page.
The simplicity of the colour scheme works very well to complement the poem itself. With just the colours pink and grey, it creates a pleasant atmosphere for the reader, whilst being serenaded by the non-intrusive exotic music. Since the triggers require only the movement of the mouse and do not require any clicking, the reader experience can be a simple one. There are also no pause periods required for page loadings during reading where there would usually be in hypertext. As Millie Niss tells us,
‘My goal was to make a textually-based work that uses techniques other than ordinary hypertext. So instead of clicking to get to a new part of the poem, all the text is presented on the screen at once… The content is revealed by mousing over a word which highlights words scattered across the field which combine to form a sentence.[10]’
This calm and pleasant atmosphere the poem creates for the reader in its visual and audio stimulations creates a juxtaposition to the message and meaning the poem itself brings. We will explore this in the next section.
Before moving on though, it is important that we acknowledge that this poem may be appreciated in the genre of concrete poetry as well, due to it’s visual nature where ‘the object is to present each poem as a different shape[11]’. The shape in this case, is a square, with seventy words listed within it. ‘It is… a matter of pictorial typography which produces ‘visual poetry’’ and ‘it may be on the page, or on glass, stone, wood and other materials[12]’. If the interactive element of the poem is to be removed, leaving only seventy words on the page, it would still stand to communicate the same message albeit in a slightly different manner. It would also serve to ‘bombard the user with all the data at once[13]’, rather than presenting the arrangement of lines of poem to the reader. The interactivity takes in elements of generative art ‘whereby an algorithm is used either to generate texts according to a randomised scheme or to scramble and rearrange pre-existing texts[14]’. In this case it would be the latter, a rearrangement of pre-existing texts.
In a detailed reading of the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh, it becomes apparent that every word listed on the page represents a sentence that appears highlighted or is an oral commentary. See Appendix A for a transcription of the entire poem.
In its basic literary form, it is a surrealist poem. Millie Niss tells us this directly in the lines ‘the surrealist did this without all this technology’ and ‘to understand is not the point’[15], describing it as ‘a combinatorial excursion into the textual possibilities of rhinoceri and other matters[16]’. Surrealist artists loved the iconic rhinoceros and used it as a muse in writing and in art. Salvador Dali was obsessed with the rhinoceros’ horn as he thought that it was ‘divine geometry because it grew in a logarithmic spiral[17]’. Eugene Ionesco, a surrealist playwright famously wrote Rhinoceros, a play about a French city, where the people slowly turn into rhinoceros, until only the protagonist is left as the only human[18]. A more subtle but bizarre use of the rhinoceros is perhaps by Roald Dahl in his book James and the Giant Peach, where James’ parents were eaten by ‘an enormous angry rhinoceros which had escaped from the London Zoo[19]’. Not only is the context surreal, it is also contradictory as the rhinoceros in its true nature is an herbivore.
The surrealists attempted to express in art and literature the workings of the unconscious mind and to synthesise these workings with the conscious mind. The surrealist allows his work to develop non-logically (rather than illogically) so that the results represent the operations of the unconscious.[20]
The non-logical development of the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh can probably be seen in the lack of structure, which itself is non-conforming towards poetry. The apparent random nature of the highlighted selection of words coupled with the uncontrollable force that is the reader and mouse movements create the synthesis of the unconscious and conscious mind, mimicking the way our eyes and brains would pick words out of a paragraph when we read or glance at writing to gauge the meaning of the text quickly, creating a ‘charming piece of stream of consciousness[21]’. In fact, it is what Lev Manovich says is ‘the very principle of new media… [it] objectifies the process of human thinking which involves connecting ideas, images, [and] memories[22]’.
The poem, as in any piece of art, carries a message or meaning. Where much of electronic poetry ‘can focus too much on the look of the poem and not the meaning[23]’, Millie Niss ‘tried to evoke a mood and some plot elements so that the poem had some core context and was not merely a random assortment of sentences[24]’. This can be seen from the direct hints that Millie Niss leaves us in the following lines:
they won’t like this in Bangladesh
it sounds like newspaper headlines
you shouldn’t glorify bombers
From these, we know that the poem is about bombers in Bangladesh that have recently (in reference to when the poem was published) been reported in the news. This aggressive and violent topic juxtaposes the visual and audio display as mentioned earlier.
Tracing these points back to the historical, cultural and political references, we can see that in 2001, the Islamist organisation, Jamaat-Ul-Mujahideen became noticed widely in Bangladesh due to bombs and documents being discovered[25]. Also, 11 September 2001 saw international fear and paranoia of terrorism, especially in America when the World Trade Centre in New York was attacked. Millie Niss then published the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh in 2002[26].
The poem gives us some indirect hints as well in the following lines:
are the rhinoceri from the zoo
is this a modern plague of frogs
isn’t the rhinoceros an herbivore
tyrannical rhinoceri disturb peace activists
book this abstract suspect socialist poem
These suggest that the rhinoceri represent bombers, questioning if the bombers portray animalistic behaviour, questioning the actions of killing when assuming that the basic nature of humans are good and kind (in the herbivore reference). The plague of frogs suggests a biblical reference of a tyrannical power, creating further unease in the poem by placing Christianity and Islam together.
From here, we can see that irregardless of how the poem is read and what order a reader may move the mouse in, the core meaning of the poem remains the same. This is the case, even if as mentioned in the earlier section, the poem is read without the interactivity and just as a concrete poem; the words laid out will suggest and bring across the meaning intended.
Although the poem may seem surreal and random at first, we know now that meaning was fully intended and in the next section, we will see how technology is used to create exactly what Millie Niss wanted the poem to do.
Technical terminology for writing in media has been discussed heavily in the last twenty years or so, amassing various names and genres that may mean the same thing, or may be slightly or even drastically different. Some of these terms were listed in the introduction of this paper and when explored, create a problematic area of definitions. This can be seen from Espen J. Aarseth’s introduction in Cybertext, Perspectives on Ergodic Literature where he spends a considerable time defining the differences in terminology and areas of subjectivity. The key area that I would like to highlight from it is the focus on what the literature is being read from[27]. As Jessica Helfand puts in bluntly, ‘the rectangle of the computer monitor frames everything we see on screen.[28]’
In the context of the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh, the term electronic literature is probably the most appropriate. It is exactly what it says, literature that is presented and thus read from an electronic platform. And in most electronic literature, it is ‘texts that can only be read in a virtual environment[29]’. The characteristics of new media as described by Lev Manovich[30] and Martin Lister et al.[31] will be used below to help describe what the term electronic means for the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh.
The Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh was created with Macromedia Flash, which is now known as Adobe Flash. It is a multimedia platform software that is used to add animation, video and interactivity to web pages. Though Millie Niss started computer programming since the age of eight, she says that her becoming a net artist was accidental and due to the fact that she had bought ‘a copy of Macromedia Flash in 1999 without knowing exactly what it was[32]’ which she then ‘realised almost immediately that the software’s multimedia capabilities allowed (her) to create an immersive experience… instead of a flat description[33]’.
In order to manipulate this software to be able to create the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh, Millie Niss would have needed to have the complete layout planned, including how the words were to be arranged on the screen, what effect each mouse movement would have and all the design characteristics. What seemed random to the reader would have been organised at creation. This was misrepresented in a review of the poem where it was said that ‘it is not a poem that was written first then put into an electronic setting[34]’. Due to the detailed programming required in Flash, it would not be technically possible for Millie Niss not to know what sentences or poetry lines she was going to use from the start. The triggers and layout may have perhaps been developed or manipulated during the programming phase but the poetry lines would have had to have been written or decided together with the seventy words.
As we know, there are seventy words distributed across the screen. When each sentence is highlighted, it is clear that the arrangement of the words were carefully placed, to allow a somewhat equal spread across the screen. This allows the reader to read the sentences from top to bottom (left to right) comfortably and that the sentences are never too bunched up in a corner. This represents digital and digitisation where each word can be seen as a discrete unit where all digital things are made of discrete units that are put together to create it.
Although mouse actions clearly create movements within the poem, this is a new media trick, where every movement is actually accompanied by a still image and the idea of change is one that is simulated in our mind or thought process. Every still image is fixed and programmed by Millie Niss, accompanied with clear instructions as to what (movement) triggers each image. ‘With the help of a mouse,… a computer can be transformed into an intelligent being capable of engaging us in dialogue.[35]’ The sound track, which itself is a loop that is continuously repeated, helps create the illusion of seamless movement. ‘The computer can seamlessly generate both text and sound because both are ultimately represented in binary code[36]’ which is digital. This phenomena can be compared to what is known as modularity or fixity and flux, which describes all digital things to be in a fixed state at all times. It is the manipulation of the user, through programmed instructions in each case that affects a change, represented by modularity or flux, but at every point of modulation or flux, they are still fix states.
The mouse movements also represent automation where triggers automatically bring up images that have been pre-programmed. This is similar to hypertextuality, but where hypertext would require the reader to actually click on each trigger point, the automated triggers make this more interactive. Although in this case, the highlighted texts are not randomly generated and are purposely programmed, it still references both cognitive modes of human thinking and machine execution, in which Stephanie Strickland emphasises on in ‘Writing the Virtual: Eleven Dimensions of E-Poetry’ in what she calls recombinant flux. Millie Niss, together with Martha Deed later wrote Oulipoems in which randomisation is fully adapted[37].
Like hypertext, interactivity in the poem creates non-sequential writing and creates variability for the reader. Every reading experience, by different or similar people will be different. The order in which the sentences are read or heard will differ. Further, depending on what hardware and software the reader uses to access this poem, the reading experiences are heavily affected. For example, a reader who do not have speakers on or attached to the computer may miss the soundtrack and oral commentary. Some computers may not have Adobe Flash player installed, so readers may need to do the installation themselves before reading, in which case, some readers may not even bother, either due to tediousness or computer illiteracy issues.
This is the computer layer that is the master of the poem. The cultural layer can be seen as the context and message of the poem itself, but without the computer layer, it cannot be accessed, as ‘Alexander Galloway in Protocol puts the case succinctly: “Code is the only language that is executable”. Unlike a print book, electronic text literally cannot be accessed without running the code[38]’.
This is a crucial issue for electronic literature when compared to traditional print literature. The lifespan and view-ability of electronic literature is completely dependent on accessibility and promotion. When Millis Niss wrote and published the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh, Macromedia Flash was the latest technology for interactive web applications. Most web platforms supported it. However, today, although Adobe boasts that the Adobe Flash Platform can ‘provide everything you need to create and deliver compelling applications, content, and video to the widest possible audience across screens and devices[39]’, it is not actually as accessible as it says due to recent developments on mobile platforms, costs and licensing factors. It was only earlier in November 2011 that the company announced that they will not be continuing with Mobile Flash developments, which allows their closest competitor, HTML5 to overtake them in the lead. This is also driven by the fact that Adobe Flash requires a private paid license whereas HTML5 is a shareware, with open networks of developers. This news also raised the question of lifespan for Adobe Flash for computers, suggesting that it won’t be long before Adobe Flash would be obsolete[40].
What happens to the Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh when Adobe Flash becomes defunct? Whilst we ponder on that question, the accessibility of it is slowly reducing and less people will not only not know about the poem, but even if they did, may not be able to access it.
“The problem exists for both software and hardware. Commercial programs can become obsolete or migrate to new versions incompatible with older ones, and new operating systems (or altogether new machines) can appear on which older works will not play. With a foreshortened canon limited to a few years and without the opportunity to build the kinds of traditions associated with print literature, electronic literature risks being doomed to the realm of ephemera, severely hampered in its development and the influence it can wield.[41]”
***
The Dancing Rhinoceri of Bangladesh is more than just a poem. As with all electronic literature, it requires more than just literacy to access, understand and appreciate. It is a piece of art, which carries in itself, cultural, historical, political and technological implications and meanings. Though it is a literary genre that is starting to gain recognition in the mainstream, the future of electronic literature depends on the future of technology and how old technology is archived and preserved, for in its core, it is ultimately a form of new media and net art.
[1] Espen J. Aarseth, Cybertext: Perspectives on Ergodic Literature (Baltimore, USA: John Hopkins University Press, 1997)
[2] Electronic Literature Organisation, http://eliterature.org/ Accessed 30/12/11
[3] N. Katherine Hayles, Electronic Literature: New Horizons for the Literary (Indiana, USA: University of Notre Dame, 2008) p.8
[4] Various
[5] Ellen Lupton and J. Abbott Miller, Design Writing Research, Writing on Graphic Design (London: Phaidon Press, 2006) p.5
[6] ibid.
[7] Hayles, Electronic Literature p.38
[8] Millie Niss, Why I Write for the Web, http://www.secretsaunasirens.com/2009/10/spork-was-born-in-arctic-as-all-good.html Accessed 30/11/11
[9] Niss, Why I Write
[10] ibid.
[11] The Penguin Dictionary of Literary Terms and Literary Theory, 1999 ed. p.171
[12] ibid.
[13] Lev Manovich, The Language of New Media (USA: Massachusettes Institute of Technology, 2001) p.77
[14] Hayles, Electronic Literature p.18
[15] see Appendix A
[16] Lynda Rutledge Stephenson, Literature in Cyberspace http://lowres.uno.edu/classes/cyberlit/papers/roadtrip/roadwaye-essay.pdf Accessed 30/11/11
[17] Biography of Salvador Dali, http://www.biographyonline.net/artists/salvador-dali.html Accessed 30/12/11
[18] Rhinoceros by Eugene Ionesco, http://www.rhinoionesco.cjb.net/ Accessed 31/12/11
[19] Roald Dahl, James and the Giant Peach, (London: Puffin Books, 2001) p.7
[20] The Penguin Dictionary of Literary Terms p.882
[21] Appendix B, Response 4 from Ksenia Scherbino
[22] Lev Manovich, On Totalitarian Interactivity, http://manovich.net/TEXT/totalitarian.html Accessed 28/11/11
[23] Lauren Ramstad, Electronic Poetry as Literature, 2009 http://www.uweb.ucsb.edu/~laurenramstad/Untitled-3.html Accessed 30/11/11
[24] Niss, Why I Write
[25] Jamaat-Ul-Mujahideen http://globaljihad.net/view_page.asp?id=993 Accessed 30/11/11
[26] Sporkworld http://www.sporkworld.org/webpub.html Accessed 30/11/11
[27] Aarseth, Cybertext p.1-23
[28] Helen Armstrong (ed.) Graphic Design Theory, Readings from the field (NY: Princeton Architectural Press, 2009) p.121
[29] Ramstad, Electronic Poetry as Literature
[30] Manovich, The Language of New Media
[31] Martin Lister et al. New Media: A Critical Introduction, Second Edition (UK: Routledge, 2009)
[32] Niss, Why I Write
[33] ibid.
[34] Review, Rhinoceri and Faith http://april-litresponse.blogspot.com/2010/02/rhinoceri-and-faith.html Accessed 30/11/11
[35] Manovich, The Language of New Media p.94
[36] Hayles, Electronic Literature p.145
[37] Millie Niss and Martha Deed, Oulipoems http://collection.eliterature.org/1/works/niss__oulipoems.html Accessed 01/01/12
[38] Hayles, Electronic Literature p.35
[39] Adobe Flash Platform, http://www.adobe.com/flashplatform/ Accessed 31/12/11
[40] Charles Arthur, Adobe killed mobile Flash, giving Steve Jobs the last laugh, The Guardian Technology, 9 November 2011 http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2011/nov/09/adobe-flash-mobile-dead Accessed 31/12/11
[41] Hayles, Electronic Literature p.40
Books and Journals
Helen Armstrong (ed.) Graphic Design Theory, Readings from the field (NY: Princeton Architectural Press, 2009)
Espen J. Aarseth, Cybertext: Perspectives on Ergodic Literature (Baltimore, USA: John Hopkins University Press, 1997)
Haskell M. Block, ‘Surrealism and Modern Poetry: Outline of an Approach’, The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism, Vol.18 No.2 (Dec 1959): 174-182
Roald Dahl, James and the Giant Peach, (London: Puffin Books, 2001)
Rachel Greene, Internet Art (London: Thames & Hudson Ltd, 2004)
N. Katherine Hayles, Electronic Literature: New Horizons for the Literary (Indiana, USA: University of Notre Dame, 2008)
Martin Lister et al. New Media: A Critical Introduction, Second Edition (UK: Routledge, 2009)
Ellen Lupton and J. Abbott Miller, Design Writing Research, Writing on Graphic Design (London: Phaidon Press, 2006)
Lev Manovich, The Language of New Media (USA: Massachusettes Institute of Technology, 2001)
Hamlet on the Holodeck, The Future of Narrative in Cyberspace (NY: The Free Press, A Division of Simon & Schuster Inc., 1997)
Christiane Paul ed. New Media in the White Cube and Beyond – Curatorial Models for Digital Art (US: University of California Press, 2008)
Reference Materials
The Penguin Dictionary of Literary Terms and Literary Theory, 1999 ed.
Web Articles
Charles Arthur, Adobe killed mobile Flash, giving Steve Jobs the last laugh, The Guardian Technology, 9 November 2011 http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2011/nov/09/adobe-flash-mobile-dead Accessed 31/12/11
Lev Manovich, On Totalitarian Interactivity, http://manovich.net/TEXT/totalitarian.html Accessed 28/11/11
Millie Niss, Why I Write for the Web, http://www.secretsaunasirens.com/2009/10/spork-was-born-in-arctic-as-all-good.html Accessed 30/11/11
R. D. Pohl, Millie Niss (1973-2009), Buffalo News ArtsBeat, 7 December 2009 http://blogs.buffalonews.com/artsbeat/2009/12/millie-niss-19732009.html Accessed 30/11/11
Lauren Ramstad, Electronic Poetry as Literature, 2009 http://www.uweb.ucsb.edu/~laurenramstad/Untitled-3.html Accessed 30/11/11
Scott Rettberg, Dada Redux: Elements of Dadaist Practice in Contemporary Electronic Literature http://eleven.fibreculturejournal.org/fcj-071-dada-redux-elements-of-dadaist-practice-in-contemporary-electronic-literature/ Accessed 30/11/11
Lynda Rutledge Stephenson, Literature in Cyberspace http://lowres.uno.edu/classes/cyberlit/papers/roadtrip/roadwaye-essay.pdf Accessed 30/11/11
Biography of Salvador Dali, http://www.biographyonline.net/artists/salvador-dali.html Accessed 30/12/11 Jamaat-Ul-Mujahideen http://globaljihad.net/view_page.asp?id=993 Accessed 30/11/11
Review of Rhinoceri and Faith http://april-litresponse.blogspot.com/2010/02/rhinoceri-and-faith.html Accessed 30/11/11
Web sites
Adobe Flash Platform, http://www.adobe.com/flashplatform/ Accessed 31/12/11
Electronic Literature Collection, Volume 1 http://collection.eliterature.org/1/ Accessed 01/01/12
Electronic Literature Organisation, http://eliterature.org/ Accessed 30/12/11
Netpoetics.com, http://netpoetic.com/ Accessed 30/11/11
Rhinoceros by Eugene Ionesco, http://www.rhinoionesco.cjb.net/ Accessed 31/12/11
Sporkworld by Millie Niss and Martha Deed http://www.sporkworld.org/ Accessed 30/11/11
APPENDICES are available upon request. Please email yen(at)yenooi.com
This paper was initially written for a postgraduate assignment. As this is a working version, please note that it should not be cited yet unless the author is contacted first. To do so, please email yen(at)yenooi.com.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
Featured image: Urinal, 2011, 3D printable digital model. Model by Chris Webber, commissioned by Rhea Myers
Rhea Myers is an artist and programmer and keen advocate of the Open Source Software culture and community. Much of the work he creates and the ideas he explores are rooted in sharing; making works that are available for others to use in their own way. This concept can be something of a paradigm shift for a traditional art world – where the notion of an artist as someone visited by the muse and given divine insight into some aspect of the world around us reigns supreme. We imagine said artist sharing their visions through one-off artefacts that become valuable in the competitive marketplace of the consumerist commercial art world.
The Shareable Readymades project works within the realms of Net art, but Shareable Readymades are output as a real-world object. Using a downloadable, freely licensed 3D model of the art work, Shareable Readymades can be printed using modern 3D printing technology wherever the equipment is available. The code for creating the 3D models is available on several websites including Rhea Myers’ own Github account. The artefacts are scalable, which gives the option of deciding what size – up to that of the original item – they print at.
Beyond the idea of a ready-made artefact is the thought, lingering in the air between creation and conception in this work, of the digital blueprint for it: the Blender file (Blender is the 3D software used to model the work). Given the digital and mechanical process involved in creating the work and the tightly wound connection between them, it might seem difficult to know where in the process the work actually comes into existence? Perhaps it is easier to think of the entire process as being the product itself. With 3D printing another possibility emerges: that 3D printing isn’t the total artefact in itself. In industrial design, pieces are created to give real form to objects and allow designers to have a tangible example of what they are trying to develop. They become a step in the production and act as a conceptual point in a longer process. Rhea Myers’ Shareable Readymade Urinals are close to the conceptual nature of Duchamp’s ‘readymades’ – specifically Fountain – because they will never become functioning objects. In our understanding, they increasingly come to represent ethereal objects removed from function, or a discussion about the increasingly fuzzy line between everyday objects and objects defined as ‘art’.
There’s a process of induction into ‘being’ involved and part of this is the commissioning. Myers commissioned the 3D models from Christopher Webber and then made them publicly available for download so that anyone can own an original piece of art.
In Abstract Hacktivism, Otto Von Busch and Karl Palmas lay out an argument for reconfiguring the way we think about the world around us. Tracing a path from Michel Serres through to Manuel DeLanda, they argue that new developments in technology change the language and by corollary, the way we frame our thoughts about the world. As DeLanda has said:
“He [Serres] sees in the emergence of the steam motor as a complete break with the conceptual models of the past. […] When the abstract had been dissociated from its physical contraption [the actual motor] it entered the lineages of other technologies, including the “conceptual technology” of science.”[1]
The essays in this all-too-short book end with the personal computer and how we think about society in terms of hardware. The authors only briefly touch on the emergence of software as a means for constructing metaphors for contemporary life, and Rhea Myers’ ‘readymades’ take this even further, encountering the idea of production.
The digital production and mechanical output perfectly summarise so much about life in the 21st Century. Our understanding of consumerism itself is gradually changing thanks to the growth of Internet shopping. We select our produce from a database of text and imagery. Yet we still believe in the freshness and perfection of the perfect apple – selected according to standards and criteria set by an army of corporate non-entities. The artificiality of the image of the apple could be taken as a reflection of the artifice of the marketplace shopping ‘experience’ we’re led to believe still has some semblance to our forebear’s means of hunting and gathering. Sometime later we take delivery of a perfectly formed apple. The difference between the database version and our own is so insignificant that they may as well be the same thing.
The urinal – the ‘original’ Duchampian urinal – appears in the art history continuum like the database image of the apple. The perfect version waiting to be analysed (read: consumed) by potential shoppers (read: art historians). Every version is now perfect and exactly what we ordered, in exactly the colour we requested. There is little opportunity for malfunction and serendipity in the process. Art becomes exactly what we ordered it to be. Fresh, ripe and leaving no bad taste in the mouth afterwards.
Sadly, what Duchamp missed out on was the final phase in the act of converting everyday objects into art. He should have realised that the real act of art-world transmutation was to then convert them back into everyday mass-produced objects. Thereby proving that art is merely a phase that things can pass through as and when the artist says they do. However, perhaps contextualising Rhea Myers’ project within the marketplace lends itself too easily to the idea that the artworks are for sale? It would be a mistake to imagine that the point of this project is to create a new way of purchasing and owning art. An intrinsic aspect though, is the Open Source and unrestricted dispersal of the idea and ability to create your own version. Ownership, in the traditional sense of that word, isn’t being claimed by Myers. Creating your own version means that you outright own that object. In a more traditional art environment, even though you may have contributed to a piece of work (some Fluxus projects might come to mind. Yoko Ono’s art, to name just one) you still won’t be credited with ownership or creative partnership status. The market relies on the single authorship model. Multiple unnamed authors would just get confusing and complex when copyrights start to be discussed. Locating the project within Open Source means that ownership is not claimed, but credit should be given where credit is due. When art collectors talk about merely looking after a work for the next generation, they’re talking about a continuum of ownership running through the decades. But art reduced to a commodity is saying nothing of any real value, surely?
By choosing to download and print a version for yourself you have the opportunity to own the work and be a part of that disruptive process. Owning a piece of art that comments on the past, present and future of the art world and marketplace must surely be something to desire and possess?
You can find Mark’s original article on Collaboration and Freedom – The World of Free and Open Source Art http://p2pfoundation.net/World_of_Free_and_Open_Source_Art
Part of the Furtherfield collection commissioned by Arts Council England for Thinking Digital. 2011
Featured image: Internet Cache Self Portrait, 2012, Evan Roth
In an essay for the catalog of Collect the WWWorld: The Artist as Archivist in the Internet Age, an exhibition installed most recently at 319 Scholes in Brooklyn, Josephine Bosma announces that the wilderness is back. Though modernity provided the means for humans to sequester themselves safely in comfortable houses, sheltered from nature’s seasons and its bad moods, Bosma points out that the boundaries between the indoors and outdoors, between the private and the public, have been broken down by digital technologies. As data slips into our most intimate spaces, the way rain and wind once ripped through primitive shelters like caves and huts, we return to “a rather basic form of humanity”―an uncanny “21st century version of ancient cultures and traditions.” Sorting through an “erratic, uneven mess” of information, human beings are once again hunters and gatherers. [1]

Yet if hunting and gathering are back in digital form, the foraging is not taking place in a scarce economy. We are not looking across vast space for some edible calories, stalking after evasive prey. Instead, we are flooded with resources in an official archive that grows at almost unfathomable speeds. In his catalog essay, curator of Collect the WWWorld, Domenico Quaranta writes,
“Every time we access a web page… the browser memorizes certain data on our computer… whatever we don’t deliberately delete, we keep. In the cache era, accumulating data is like breathing: involuntary and mechanical. We don’t choose what to keep… but what to delete.” [2]
The artists in the 319 Scholes exhibition appropriated and manipulated images, data, animated gifs, video, clip art, and blogs to create screen projections, net art, prints, and installations. Often they transferred foraged data into sculptural pieces, such as the series of pocket bikes by Jon Rafman and the photocopier run amok in Jason Huff’s Endless Opportunities, suggesting that online information moves in and through our material world. Moving through the gallery made me feel like I had spent too much time online, overwhelmed by too much information. There were hundreds of polaroids in Alterazioni Video’s Olbania, hundreds of images in Evan Roth’s collage Internet Cache Self Portrait: July 17, 2012. The title of the seemingly nonsensical Etsy purchase by Brad Troemel, displayed on the gallery wall, captured the detailed randomness of the internet space: Art Smells Why Wait Grab An Unusually Decadent PINE air freshener with a HOTTOPIC pink to black hair extension attached. The sounds of Eva & Franco Mattes’ My Generation dominated the gallery’s front space. In a pile of smashed computer hardware, a screen displayed videos of hormonal teenage boys freaking out, screaming, and convulsing in front of their computer cams. The collage captures the overflowing, hysterical emotions of adolescents in their now private-public bedrooms but also the frustration that we can feel about life amidst so many networked devices and so much data.

Since many of the works at 319 Scholes made me feel psychologically unsettled and dispersed, the same way I feel after staring at a screen all day long―a feeling that I can fix only by unplugging and taking my dog for a walk―I asked Quaranta how he differentiates Collect the WWWorld artists from the larger population of people interacting with data as simply just hunter-gatherers on an everyday basis. How did he imagine the exhibition representing something beyond what we all do continually, as naturally as breathing? His response:
“Everybody stores, but just a few collect. Storing means downloading (or tagging, pinning, posting, etc.) something and forgetting about it. Collecting means taking care of what you stored, selecting and ordering it according to a personal criterion, applying a human filter to the inhuman, impersonal archive. If the collector is an artist, his collection may be sometimes understood as art.” [3]
If we keep with Bosma’s ecological metaphor, Quaranta’s exhibition, then, presents artists who are also collectors and archivists who, having explored the digital wilderness, have done some weeding in order to plant a garden of cultivated, nurtured, looked-after data. Their art is a gesture toward trying to make some sense or order out of the wildness. In his catalog essay, Quaranta writes,
“Collect the WWWorld takes as its point of departure the very moment an incoherent mass of ideas turns into a hypothesis.” [4]
Yet ever since digital media emerged on the contemporary art scene, artists have been appropriating found “objects” from the internet’s ever-growing archive, remixing them to create new content. But there is a significant way in which Collect the WWWorld captures a new cultural current. Traditionally, archives were protected spaces, governed by authorities, institutions, the state. They were private, physically and politically remote from the public at large, inaccessible except to sanctioned experts who were able to pass through the proper channels of bureaucracy. Digital technologies upended this sanctified space, producing an unofficial endless archive of internet data, and more recently, with ubiquitous mobile networked devices and social networking applications, anyone can upload any random aspect of their mundane private lives into the public archive. Quaranta explains,
“If in the past, and still in the late Nineties, appropriation and remix were dealing mostly with commercially produced culture, now most of the cultural content we access, consume and remix is produced by so-called amateurs.”
In the Web 2.0 world of YouTube and Facebook, brokers, editors, and even curators are no longer indispensable. There are no intermediaries between public and private in the digital wilderness. Furthermore, Quaranta adds, early generations of digital artists were pioneers. Now, the born-digital artist-collectors are “residents dealing with the stuff left by their ancestors.” [5]
In this exhibition of second-generation digital art, the most intriguing works in the show were those that did not simply repeat and represent the experience of hunting-gathering in the wilderness but rather intervene in this process to suggest the ways that media technologies rewire our culture, our public/private spaces, and our imagination. In Kevin Bewersdorf’s Google Image Search Result for “Exhausted” Printed onto Blanket, an image of an emotionless father holding a passed out son in his arms. (I’m guessing at their roles; the situation could be much less innocuous.) With the printing of this random, private scene onto a blanket, someone could actually sleep in with this odd couple, laying his skin next to theirs. The networking of such intimate moments is at once ludicrous, meaningless, and meaningful―and something that those of us with web access experience all the time.
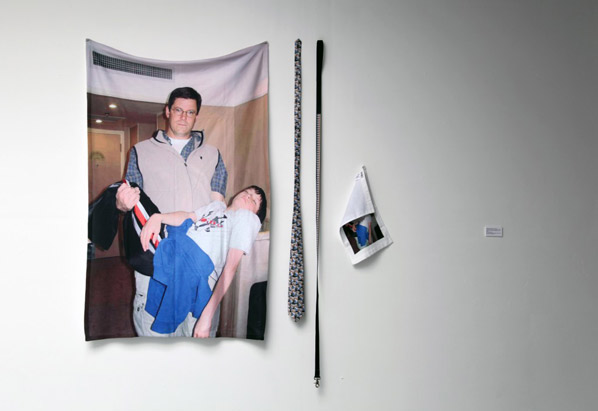

In need ideass!?! PLZ!!, Elisa Giardina Papa has collected online video of mostly teenage girls excited to make new video content except they have one major problem: they have no ideas. The projection at 319 Scholes showed them speaking intimately into their video cams, begging their viewers to help them, confessing their willingness to do anything asked of them:
“Hi YouTube, Hi you guys, Hey um YouTube…. I wanted to start a web show and I need ideas for it but I don’t know like any ideas. I have the web show maybe an upcoming website, who knows… Hey YouTube. I’m behind my kitty cat right here. If you guys can give me some ideas I’d greatly appreciate it… Hi you guys I’m Vanessa I’m wondering if any of you can give me any ideas….”
need ideas!?!PLZ!!, Elisa Giardina Papa, 2011
One girl sits on her bed in her pajamas, another stands in front of a shower curtain. Most play with their hair, some have done their makeup, one provides a close up of her glossy pink lips. The kids repeat their willingness to “do anything… crazy stuff.” We often hear laments these days about how new media generate a culture without substance. Papa’s collage―or rather, her collection―deepened this question: the kids turned loose in the digital wilderness seemed to be aimless, armed with advanced technologies but with no ideas about what to say or what to do. At the same time, they perform Bosma’s “21st century version of ancient cultures and traditions.” Papa’s anxious teenagers seek attention, community, and space away from their probably boring parents, a rite of passage of American kids; one girl has to yell into her cellphone at her mother, “Mom! I’m in the middle of a video!” But though they are in the privacy of their bedrooms, they are also begging strangers for engagement and uploading themselves into the public space of the internet, where presumably annoying Moms can check on what they are doing.
In environmental theory, the wilderness can be a spiritual refuge, a space of healing respite from the frenzied modern world. But being out there, exposed, in the wildness of the mountains or the woods is comforting only once we have our biological needs met, once we are safe and ecologically emancipated by adequate shelter, clothing, and food. Social ecologist Murray Bookchin explains this well: “without a sufficiency in the means of life, life itself is impossible, and without a certain excess in these means, life is degraded to a cruel struggle for survival.” [6] With Bosma’s language in mind, I have to ask if Collect the WWWorld represents our ecological emancipation and our freedom to play in a mysterious forest, or if the group exhibition represents our desperate grasp for the basic anchors of cultural subsistence? Evan Roth’s Internet Cache Self Portrait: July 17, 2012 asks who we are in the eyes of our computers, in the accumulated images stored in our cache capturing our travels through the web. Are we the sum of our clicks and searches? Are we the archivists or are we the archived? Are we in control here, or are we engaged in a “cruel struggle for survival” in the digital wilderness?
Collect the WWWorld is a show first produced by the Link Center for the Arts of the Information Age and already presented, in different versions, at Spazio Contemporanea, Brescia (Italy) in September 2011 and at the House of Electronic Arts Basel (Switzerland) in March 2012. The presentation at 319 Scholes, Brooklyn, open from 10/18-11/4, 2012, featured a number of new artists and works in a brand-new arrangement. The show relies on an ongoing research project that can be followed online at http://collectheworld.linkartcenter.eu.
Participating artists include at 319 Scholes included: Alterazioni Video, Kari Altmann, Gazira Babeli, Kevin Bewersdorf, Aleksandra Domanovic, Constant Dullaart, Elisa Giardina Papa, Travis Hallenbeck, Jason Huff, JODI, Olia Lialina & Dragan Espenschied, Eva and Franco Mattes, Oliver Laric, Jon Rafman, Ryder Ripps, Evan Roth, Ryan Trecartin, Brad Troemel, Penelope Umbrico, and Clement Valla.
THE CRYSTAL WORLD
The White Building, London
3 August – 30 August 2012
The Space’s White Building cultural centre is within walking distance of the 2012 Olympic stadium in post-industrial, post-regeneration London. As I walked down the steps that lead to it I saw a diesel locomotive pulling a train of cargo containers across an old railway bridge over the canal nearby. Millions of these rational forms will be in transit around the world at any given moment, arranged in two or three dimensions like crystalised capital on trains and docks and ships.

The logistics of their production and distribution are determined by computing machinery using algorithms that operate with inhuman speed and complexity. This same economic logic warps the architecture of the area around The White Building, with old factories and warehouses retro-fitted as office space and as gallery space.

Inside the White Building’s project space the computational enabling technology of the global economy is the subject of a show by Martin Howse, Ryan Jordan and Jonathan Kemp. It takes the title of J. G. Ballard’s novel “The Crystal World” as its starting point. In Ballard’s novel a virus progressively turns all life – vegetable, animal and human – into crystal forms frozen in time. It is a Cold War allegory of the catastrophic imposition of rigid order.

For Howse, Jordan and Kemp these imaginary crystals become the very real minerals refined in the production of the computing machinery used to structure our contemporary world. Inside every digital computer are wires, circuit boards, integrated circuits and other components. They are made from iron, copper, phosphorous, boron, tantalum and other rare earth elements. The central processing unit of a computer keeps time using a quartz crystal. The products of deep geological time are suddenly unearthed and set to pulsating millions of times a second.

Computers are crystal engines. They are mineral fetishes that we use to manipulate powerful unseen forces that we believe we have mastered, like crystal healers working with a patient’s energy grid. But they are so invisibly familiar to us as our smartphones and laptops and their use in logistics and media is so pervasive that it takes an effort for us to perceive their operation or their implications.

It takes almost two tonnes of raw materials to make a desktop PC. Unlike “Tantalum Memorial” (2008), by Harwood, Wright and Yokokoji, “The Crystal World” focuses on these raw materials geologically and temporally rather than geopolitically. But computing waste is toxic and valuable. The former makes disposing of old computers a growing problem, the latter makes recycling old computers a growing business. The minerals that computers contain can be recycled where they are valuable enough, or left to leach into the water supply in e-waste dumps where they are not.

Or in the case of “The Crystal World” an open laboratory and the resultant art installation can re-extract them from their components and printed circuit boards using acid, water, electricity and heat in order to re-crystalise them and return them to geological time. The gleaming silent boxes that organize and mediate our lives are returned if not to the earth from whence they came then at least to their raw materials.

Tables edge the White Building project space, covered with the equipment and results of five days of workshops (and one with books, including Ballard’s, giving any spectators unsure of what is happening a conceptual framework to proceed from). Table after table of crystals, circuit boards, jars, electical equipment, and wires are overwhelming in the details of their appearance and implication. These traces of human activity and inquiry frame the flow of water and electricity in the center of the space, convincing the viewer of the creative intent of its production and drawing them in to its logical universe.

The centre piece of the show is a favela chic water feature that drips acid-loaded water through calcinous rock fragments, over e-waste, into two cut plastic-drum tanks. Next to it an array of smaller plastic containers contain circtuit boards having their copper leeched from them by acid, fungus growing on the by-prodcucts of the project, and other watery deconstructions of computing machinery. It looks dangerous and uncertain, deconstructing both the physicality and the meaning of computers. Seeing the innards of an IBM ThinkPad computer becoming encrusted with calcium like a digital stalagtite, or CPUs branching feathery crystals, returns computing machinery to its raw mineral state. FLOPS give way to eons once more. Neither is a human timescale, yet we must live between them at the moment.

The most fantastical artifact along the walls of the project space is the “Earth Computer”. It’s a battery-like construct of recycled copper and zinc in a tray of silver nitrate attached to lightning conductor-style copper strips. Sitting in earth on a plastic sheet and surrounded by the left-over materials of its creation for the duration of the show, it will be buried nearby afterward. Such a device can function effectively, but not literally. It is more likely to spring to life in the mind of the viewer than if it is struck by lightning. It is effective art, psychic engineering rather than technological cargo culting.

Acid, water and electricity mixed together with e-waste look and feel dangerous. The recycled ad-hoc materials and equipment containing and channeling them reinforce this feel and leaven it with an aura of creative investigation. The form of the show is timeless, the workshop of the alchemist, outsider scientist, or mad inventor. Its content is very contemporary, from Ballard’s rising cultural stock and the social and environmental costs of e-waste to Long Now deep time and posthuman philosophy. Art symbolically resolves the gaps between ideology and reality, and computing is so pervasive and key to society that most people don’t even regard it as ideological never mind conceptualise its failings as such.

The water and abandoned human artefacts of some of the installations is more “Drowned World” than “Crystal World”, and the broken machinery is more “Crash”. Ballard’s catastrophes provide a modern mythology that is a more useful resource for art than its literary roots might suggest. It achieves the defamiliarising and critical impact of hauntological art without requiring its supernaturalism or nostalgia. There is a Ballardian attitude at play here.
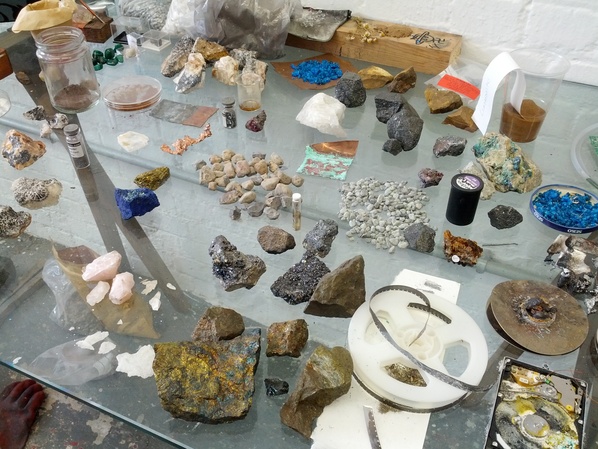

I found “The Crystal World” mind-blowing. It relates the tools of our human existence to non-human substances and timescales, providing the kind of corrective to anthropocentric vanity that object-oriented philosophy aspires to. It achieves this profound insight and presents it in an accessible way precisely because of the modesty of its materials and aesthetics, and because of the resonances of the cultural materials chosen as its starting point.
http://spacestudios.org.uk/whats-on/events/the-crystal-world-open-laboratory-exhibition-
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
Dual
Nottingham Playhouse
5 September – 30 October
After a glorious false start in the 1990s, the previously over-hyped technologies of virtual reality have been quietly reclaimed in a more sustainable and democratic way through Free Software and Open Source hardware. The show “Dual” at Nottingham Playhouse showcases art that mostly uses these new technologies. A theatre is the perfect setting for the reality play of virtual reality. Curatorial collective The Cutting Room (Clare Harris and Jennifer Ross) have organized the funding, production, and presentation of artworks that mix the virtual and the real in creative ways.

Michael Takeo Magruder’s “Deconstructed Metaverse” (with Drew Baker and Erik Fleming), 2012, is installed on the upper landing of the theatre. The windows on the landing have been glazed with images of warmly coloured softly undulating colours. On closer inspection they are pixellated and have endless lines of computer code superimposed over them in small white type. The code is XML representing a virtual world, and that virtual world can be seen and interacted with on monitors in front of the windows. They display a ceiling-less ultra-modern rotunda with windows glazed in images of the views that could originally be seen through the real windows that are now glazed with images of the site-specific virtual world.

The first, smaller, monitor sits on a plinth alongside the circuit board that runs the virtual world using OpenSim under GNU/Linux from a single USB memory stick. You can use a keypad to explore the world, your presence there represented by a generic default human avatar that walks and flies around the island. Or you can visit the virtual world over the Internet. In either case, a large screen further along shows a rotating view of the island, its architecture and inhabitant(s).
Magruder has worked with virtual environments since the VRML era, and “Deconstructed Metaverse” continues some recurring themes while bringing them to a new level. There are multiple layers of reality and presence to this work that the viewer can find themselves looking into and out from, relating to other onlookers as part of the audience or part of a performance in the virtual world themselves.

Brendan Oliver’s “Particulation” uses a Microsoft Kinect to capture the poses and motion of pairs of patrons walking through the Playhouse’s ground floor bar. A laser-scanning motion tracker and the software to process its input would have been unobtainable for most artists a decade ago. Oliver makes good use of hardware that was liberated against the wishes of its manufacturers and of software frameworks that are shared more freely.
Oliver uses them to capture and evoke the movements of two people who may not realise that they are the inspiration for the visual art on the wall. They are translated into a particle system of bubbling circles of light projected just far enough away from the sensor that monitors them that the connection between captured movement and animated image is not immediately obvious from all angles. Particulation has the feeling of joyous discovery and exploration that the best interactive multimedia art can bring to a space.
Below ground, “Mirror On The Screen” by Charlotte Gould and Paul Sermon uses similar technology to Deconstructed Metaverse to create a pocket universe of symbolic scenery and objects from children’s stories. In order see the screen presenting the virtual world and use the keypad to move your avatar around it you must stand in front of a printed backdrop where you are watched by a webcam. The resulting video stream is fed into the virtual world and superimposed onto cracks in its reality.
In addition to seeking the highest place in the forest, the edges of the world, and all the objects and characters within it, you find yourself hunting your own reflection. The tables are turned as the avatar you are watching starts watching you, and your purpose becomes seeking out further reflections. The setting of the theatre puts the viewer in a frame of mind open to the drama of the virtual world and its looping back on reality. Far from jolting you out of the experience, suddenly being faced with your own image in the virtual world draws you in further.
Finally, Kim Stewart’s “Sigma 6” is a 3D computer animated film set in a dystopian high modernist moonbase-like environment of harsh architecture and harsher treatment. The virtual world-like quality of the animation, and the avatar-like quality of its persecuted protagonist have their reality punctured in a way that continues the theme of mixed realities in a way that turns towards body horror.

These common themes of blurring virtual environments with real bodies and places allow the works to complement and distinguish themselves from each other artistically and technically. The Cutting Room are to be applauded for assembling such a thematically tight and technologically competent show that both serves and is served so well by the context of the institution that it is staged in.
http://www.nottinghamplayhouse.co.uk/about-us/the-cutting-room/
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
12 Remixes, by Michael Szpakowski
From August 2011 to July 2012, the video artist and musician Michael Szpakowski entered a remix competition every month, and compiled his remixes (some of them with accompanying videos) on his website. “I’m 54 years old,” he explained at the beginning of the project, “and although I’m musically reasonably deft I know little about the culture in which I’m attempting to intervene. I know none of the specialised vocabulary, can’t distinguish genres and although I understand what is being said, just about, I don’t speak the language in which posts or comments on this kind of work are framed.” The project, in other words, was a deliberate step outside his “comfort zone”.
The results are often startling. It’s worth comparing the remixes with the original tracks from which they derive, because it provides some insight into Szpakowski’s working methods, and makes you realise the extent of some of the transformations he has achieved.
One of the most striking examples is the remix of “Sandwiches” by the Detroit Grand Pubahs. The original track is a grotesquely overstated hyper-lecherous rap. A synthesised-drum-and-bass arrangement underpins a chipmunk-style speeded-up vocal, warbling lyrics of such obvious symbolism that they hardly qualify as suggestive: “I know you wanna do it/You know I wanna do it too/Out here on the danceflo’/We can make sandwiches…/You can be the bun/And I’ll be the burger, girl…/Make your thighs like butter: easily spread…” The effect is quirky, irritating and compulsive; tongue-in-cheek, deliberately outrageous, blatantly sexist and borderline pervy all at the same time.
Szpakowski’s remix has an entirely different feel. The vocals have been slowed right down from warbly chipmunk to entombed Darth Vader; correspondingly, the bassline has slowed too, from a prefabricated booty-shaker to something subterranean and slightly menacing; and in the space above there are echoey keyboard-notes floating and pulsing like luminous jellyfish. The effect of the lyrics is no longer leeringly voracious, but mournful, obsessive and introspective. There is an instrumental coda with a vaguely Scottish Highlands flavour to it. The feel of the track has changed completely, and so have its texture and geometry. We find ourselves in a darker, much larger space.

Another good example is “OK good stand clear”, based on “110%” by Laura Vane and the Vipertones. The original song is efficient, well-assembled funk/soul, complete with a punchy horn section and a sassy female lead vocal. It’s slick, sharp and professional, but hard-working rather than inspired. Szpakowski’s remix dispenses with almost everything except the rhythm section, which is slowed down slightly to give it more depth and a thumping creaky quality like an elephant in new walking-boots. To this he adds a sampled American voice saying “OK? Good” and “Stand clear of the closing doors!”, and a hammering piano-figure. Again the effect is to open the track out, to give it a more three-dimensional feel, and also to make it much less derivative, much less obviously the product of a particular genre.
In almost every instance Szpakowski’s remixes have a more resonant and spacious feel than the originals; the sounds are dirtier, fuzzier, more textured; and the rhythms are more complex. These changes may not always be entirely to his advantage. As he admits himself, “I don’t dance (or haven’t for twenty years or so), which actually makes a big difference in how one experiences popular music…” Certainly there is one track – a remix of “Paradisco” by Charlotte Gainsbourg and Beck – where Szpakowski’s version has a spiky, angular, echoey jazz feel, but loses out to the original in terms of finger-clicking compulsiveness. It’s true that his remix puts a stronger focus on Gainsbourg’s voice and lyrics than does the original; but whereas Gainsbourg and Beck’s version stays within the disco format and gives it an iconoclastic indie makeover, Szpakowski’s remix takes us beyond that format altogether, and comments on it from the outside.

In some of the tracks there is a move from the USA to Europe in terms of feel. One example is the remix of “What happens in Vegas” by Chuckie ft. Gregor Salto – a histrionic slab of USA club music. Szpakowki’s version (“Shit happens in Vegas”) has a distinctly Kraftwerk-esque, European-techno slant. Also, because the remixes are often crackly, fizzy and hissy, they tend to feel “older” than the originals. At times we seem to be listening to badly-tuned radios in the pre-digital era, or to vinyl LPs smothered in dirt and played through a fluff-laden needle. But this “distressed finish” effect is in keeping with a broader sense that Szpakowki’s remixing technique involves a kind of deconstruction or breaking-apart of the tracks on which he is working. They become less smooth and shiny, less self-contained. The original tracks are often tightly-focussed in terms of their musical styles, with a narrow range of subject-matter, and often with manipulative designs on the audience – wanting to make them feel like dancing, wanting to make them feel sexed-up, or trying to tug at their heart-strings (“Try to Stay Awake” by Frank Friend, “Trojans” by Atlas Genius and “Jigsaw” by Mimi Page are all relationship-based heartstring-tuggers). The remixes, on the other hand, aren’t looking for such straightforward reactions. Their subject-matter is less easy to pin down, and their ingredients bespeak a mixing-together of disparate materials, different cultures, and even different eras.
Non-musical ingredients are one noteworthy feature. In “OK good stand clear”, the voice saying “Stand clear of the closing doors!” comes, as Szpakowki explains, from “New York subway recorded announcements… grabbed, I think, from YouTube”. He is also fond of introducing a voice intoning random numbers – this occurs in several of the tracks. Usually the voice has a foreign accent, and sometimes the numbers are spoken in a foreign language. These number-sequences, says Szpakowski, come from “the so called ‘numbers stations’ which are believed to have been used by various intelligence agencies… they’re available at the internet archive“.
On “I’m getting a cat” the words come from mashed-up Tweets which have been run through a voice-to-text synthesiser. “I am that I am” borrows its vocal from the painter and sound poet Brion Gysin – a voice-sample which, until it begins to distort, sounds rather like a 1950s announcement on the BBC. “Speaking in Tongues” reverses the vocal on a hectoring soul track by Colonel Red called “Rain a Fall”, so that it ends up sounding as if it’s in some unspecified European or possibly Middle Eastern language. And “Sugar Plum Fairy on the Dancefloor” introduces the chiming melody from Tchaikovsky’s Sugar Plum Fairy into a rap called “Disco Technic” by Stan Smith, to surprisingly good effect. There is a genre-busting transgression of boundaries, a throwing-together of cultures, a jumbling-up of eras, and a deliberate use of incongruous material.

The videos Szpakowski has produced to accompany some of these tracks show similar traits. Again his admission that he doesn’t dance is relevant here, because the starting-point for many music videos – a very tight and emphatic synchronisation of visual effects with the beat of the track – is not a particularly dominant feature in his work. The one which succeeds best in this respect is the video for “OK good stand clear”, which projects text versions of the words onto the screen in big letters precisely as we hear them. There is also a lovely moment in the video for “I’m getting a cat” where, in a bit of old black-and-white footage, some youngsters sitting on chairs on a stage start to sway from side to side, apparently in time to the music.
But synchronisation to the beat isn’t Szpakowski’s priority. “I’m getting a cat” provides a good example of the kind of effect he achieves instead. The synthesised vocal for the track first announces that it’s getting a cat, then starts to ask absurd questions about cats and cat-care – “Does your cat try to style your hair?”; “What is your funniest and yet painful cat story?” – which are gradually infiltrated, first by other subject-matter – “Become a big brand on Facebook!” – then by symbols – “Poundsign poundsign poundsign” – and sequences of numbers. What starts off as funny, ironic and nostalgic develops or breaks down into a kind of digital fragmentation, and eventually into wordlessness. The end of the track is a wistful instrumental coda, embellished with piano and strings. And the video follows much the same path. It starts with old footage from the 1960s White House, in which President Lyndon B Johnson seems to be announcing his intention to get a cat to his slightly-bemused aides. Then there are some outtakes from what seems to be an instructional video in which a troubled youngster is being given helpful advice (presumably cat-care advice) by a reassuring and helpful older man. By the end of the track – the coda – we are watching teenagers playing music, drinking coffee and dancing. Again, humour and irony have been replaced by something more wistful and hard-to-define.
“Found” materials, often quite disparate materials spliced together by digital means, are just as important to the videos as they are to the remixes: they feature archive footage of the Whitehouse; shots of groovy teenagers from the Fifties or Sixties; Japanese Noh theatre; imagery based on Little Red Riding-Hood; square-dancing American kids; old claymation footage of teeth wearing boxing gloves; big black lettering; jumbles of coloured pixels; and images of Las Vegas captured from Google Maps, reconstituted into a long sun-baked backwards drive from the middle of town into the desert. Like the musical tracks they accompany, these videos cull their materials from many disparate places; they are full of little jolts of incongruity, slightly-bizarre juxtapositions; they lead us not only inwards towards the music but outwards towards different cultures and different eras; and they also call our attention to the digital medium itself, the Web on which all these materials are available, and the computer software which slices and splices them.

Perhaps most remix artists are more influenced by the work of their immediate peers than by art theory, art history, or inspiration drawn from other cultures. Not so with Szpakowski. As mentioned before, one of these remixes (“I am that I am”) uses a vocal track from Brion Gysin; and the words “OK good”, from “OK good stand clear”, are sampled from a recorded talk by William Burroughs. Burroughs and Gysin were the first proponents of cut-up and fold-up techniques in literature: Gysin was also an experimental painter and sound artist. This link with the two of them hints at a connection between Szpakowki’s remix style and modernist or post-modernist art. Remix culture itself is closely related to mash-ups, which in turn (whether remix artists are aware of it or not) can trace their ancestry not only to cut-ups and fold-ups but to the collages, bricolage, decalcomania and other mixed-media, mixed-genre experiments of the Modernists: experiments which reflected not only an urge on the part of Modernist artists to break free from received genres and formal conventions, but a feeling that the modern mind did not belong to a single era, a single unified body of belief or a single point of view – instead it contained many disparate perspectives, and ideas or images from many different eras and cultures, all thrown together into a jumble. For the modernists, this jumble was itself both one of the joys and one of the symptoms of modernity.
For modernist and post-modernist artists, formal perfection is often a secondary consideration, compared with the excitement of putting things together in new ways, seeing things from new angles. T S Eliot (in “Tradition and the Individual Talent”) described the mind of the artist as a “medium…in which special, or very varied, feelings are at liberty to enter into new combinations”. He made the same point in “The Metaphysical Poets”: the artist, he argues, “is constantly amalagamating disparate experience”; and modern art is bound to be more complicated than the art of earlier centuries, because modern life itself has become more complicated: “Our civilization comprehends great variety and complexity, and this variety and complexity… must produce various and complex results.” It was also argued, by various theorists, that modern artists found it increasingly difficult to belong wholeheartedly to a particular tradition, or to stick to a particular working method or lexicon of forms, because mass reproduction had made so many different traditions and examples, from so many different eras and cultures, available to them. If these observations were true at the beginning of the twentieth century, they are most certainly true now, at the beginning of the twenty-first, when life is characterised not just by “variety and complexity”, but by information-overload, and when the work of other artists, other eras and other traditions is available not only in museums, libraries, books and prints, but online at the click of a mouse or the blink of a Google query-screen. So one way of understanding Szpakowski’s remixes – his particular take on what a remix ought to be like – is to look at them in the light of modernist, post-modernist and digital-modernist aesthetics.
Another neo-modernist aspect of these remixes is their reluctance to woo the audience. There are moments when the arrangements are slightly unsympathetic to the listener. One example of this is “I’m getting a cat”, where the voice-over stops asking absurd questions about cat-care and starts coming out with fragmentary nonsense about Facebook, number-sequences, and “poundsign poundsign poundsign” instead. The “poundsign poundsign poundsign” sequence, in particular, goes on to a point where a lot of listeners might find themselves wishing it would stop. Similarly, on “I am that I am”, the voice-over, which starts with a sequence of variations on the theme of identity –
I AM THAT I AM
AM I THAT I AM
I THAT AM I AM
THAT I AM I AM
AM THAT I I AM
– soon gets speeded-up and distorted into an incomprehensible babble, and this babble is so loud and frenetic that it’s quite hard to hear the music. Again, some listeners may find themselves wishing that the voice-over would stop.
As already mentioned, the vocal track in “I am that I am” is based on an original piece by Brion Gysin, and Szpakowski has actually cut it down in order to re-use it – so although Szpakowski’s track may seem a little bit tough on the audience, it’s actually quite a bit less demanding than Gysin’s original. But the link with Gysin provides a clue to the aesthetics which are apparent throughout the whole “12 Remixes” project. “I am that I am”, as a text, is based on the idea of reordering a five-word line into all its possible variations, as can be seen from the extract above. As such, it has a mathematical quality. It resembles “ordinary” poetry in the same way that a peal of bells resembles “ordinary” music, and its structure and length are determined, not by any particular ideas about what may sound good to an audience, or what may provoke a certain emotional effect, but by the need to run through all the possible variations of a certain sequence in a certain order.
As a sound-poem the piece progresses in a similar way: Gysin takes his sequence of statements, and gradually adds echo to them and speeds them up until they become a frenzied babbling noise. In other words he performs a set of mechanical distortions on them, and increases or redoubles those distortions until they have reached a logical conclusion. Again, he is not particularly thinking about what will grip, entertain or move his audience: his attention is fixed on the materials, the medium and the process. This is not to say that “I am that I am” does not have any affect. It is delivered in the ringing tones of a self-important orator, and when the first layer of echo is added we imagine that the speaker might be addressing a rally in a great hall, like Citizen Kane, Mussolini or Hitler. But the self-assertion of the words is then turned into nonsense as the layers of distortion pile up. We feel firstly that great leaders and orators and being mocked, and then that identity itself is being called into question. But we also feel, as listeners, that these reactions may belong to us at least as much as to the piece itself: it has not been designed primarily with the purpose of producing them, and if we failed to experience them the piece would still have a purpose and meaning of its own beyond them, as a peal of bells has its own purpose and meaning whether we enjoy the sound of it or not.
This concern with sequence and process, with breaking things down into their constituent elements and then reorganising those elements according to mathematical rules, can again be related to the experiments of modernism – to the modernists’ determination to question and rearrange the materials and media from which works of art are made – but as the example of the peal of bells indicates, it can also be linked to much older forms of art; and at the same time it has a particular relevance for artists who are working with computers and code. Five words being reorganised into every possible sequence will produce a flicker of recognition in anyone who has every attempted code-poetry. It’s the kind of experiment which sits very naturally in the digital environment and the new media art genre.

Szpakowski’s remixes cannot be described as mathematical sequences or coded music, but they certainly do show evidence of a Gysin-like interest in variations and logical progressions. This may make them seem a bit unsympathetic in places, but it also gives them a certain air of toughness and detachment. As already mentioned, if they are compared with the original tracks on which they are based, one difference to emerge is that they don’t seem to have such obvious designs on their audience. But it’s also true that they don’t tend to follow such obvious paths in terms of musical development. If we look at “In Paradiscos”, for example, the original track has a very strong feeling of moving up a gear when it comes to the chorus, whereas Szpakowski’s remix doesn’t follow the same pattern. Another example is “the moon is inside the snow”, a remix of “Blindsided” by Luke Leighfield and Jose Vanders (which is itself a cover of an original track by Bon Iver). In Leighfield and Vanders’ version, there is a definite sense of drama and progression, as the female vocal is joined by piano and violin, and then by a male voice singing in harmony. By the end of the song, we feel that we have been taken on an emotional journey. It has a narrative arc. Szpakowski, on the other hand, dispenses with the male harmony altogether, and also with large sections of the song’s lyrics. He cuts up and rearranges snippets of the female vocal to create quite a different impression – more of a Haiku than a romantic poem – and he alternates the original vocal with a second female voice talking in Japanese. The end result is just as beautiful as the track on which it is based, but in a quite different way. It’s more austere and contemplative, less narrative and dramatic. It seems to be less about recounting a personal experience, and more about organising disparate elements into an aesthetically satisfying pattern.
Modernism, cut-up techniques, digital experimentation – perhaps these are big perspectives from which to view what is essentially a fairly modest project. Szpakowski didn’t set out on this series with any particularly grandiose ambitions: he set himself the task of producing one remix a month for a year because he thought it would be something interesting to do: it would build on his strengths as a musician and technophile, but it would also set him a series of new challenges. As it turns out, he has risen to those challenges to great effect and produced something really special – a collection which shows variety of tone and pace, wit and inventiveness, along with unity of design and a distinctive “voice”. Whether it’s a digital-modernist take on remix culture or not, anybody who is interested in experimental music could do a lot worse than put their headphones on and give it a try. It certainly repays close attention.
Featured image: Jon Satrom (left) and jonCates at Intuit, Sept. 20, 2012 (right). image: Shawne Michaelain Holloway
Post-Static: Realtime Performances by jonCates and Jon Satrom @ Intuit, the Center for Intuitive and Outsider Art (Chicago). September 20, 2012. Programmed by Christy LeMaster
“Alchemy; the science of understanding the structure of matter, breaking it down, then reconstructing it as something else. It can even make gold from lead. But Alchemy is a science, so it must follow the natural laws: To create, something of equal value must be lost. This is the principle of Equivalent Exchange. But on that night, I learned the value of some things can’t be measured on a simple scale.”[1]
In 1966, Bell Laboratories scientists and engineers collaborated with artists to construct several performance-based installations under the title 9 Evenings: Theatre & Engineering. Works included Variations VII by John Cage and performance engineer Cecil Coker, in which a sound system pulled sounds from radio, telephone lines, microphones and musical instruments, and Carriage Discreteness by Yvonne Rainer and performance engineer Per Biorn, a dance event controlled by walkie-talkie and TEEM (theatre electronic environment modular system). Critic Lucy Lippard was wrote that the event was filled with technical problems and that the artists involved allowed the technology to take precedence over the art. She pointed out that no theatre people took part in the event and suggested that while this event did not offer a specific design for a new approach to theatre, it revealed the possibility that new approaches to theatre might be born from the combination of art and technology:
A new theater might well begin as a non-verbal phenomenon and work back towards words from a different angle. Departing from Samuel Beckett’s highly verbal, single-image emphasis, it could move into an area of perceptual experience alone, its tools a more primitive use of sight and non-linguistic sound. Such a theater would not necessarily be the amorphous carnival of psychedelic fame but could be as rigorously controlled as any other.[2]
She also observed that it was often impossible to understand the relationship between the technology and the events it triggered without reading the program, mentioning one such missed connection in Open Score, by Robert Rauschenberg and performance engineer Jim McGee. In this piece, tennis rackets were wired such that each impact of the ball on a racket turned off one light in the performance hall. Lippard wrote that this connection was not noticeable and thus the conceptual framework of the piece was lost to the audience.
To artists working at the intersection of art and technology more than forty years after this event, it is disturbing to note that the same issues Lippard pointed out —the subjugation of concept to technology, the failure of the technology itself and the lack of a radical approach to the intersection— are still all too present in many works taking place in the worlds of new media art [3]
. None of these were issues for jonCates or Jon Satrom as each presented a performance intersecting with the exhibition “Ex-Static: George Kagan’s Radios” at Intuit, the Center for Intuitive and Outsider Art in Chicago, IL. Their performances serve as examples of new media employed as a tactic in support of art rather than “new media art” as a condition represented by infatuation with expensive devices. Instead of yet another demo of “cool” tech, the audience experienced a rigorously controlled blast of chaos.

The lights go down completely and we are illuminated by a large amorphous video projection behind a table stacked with equipment. The video is black and white as is the video monitor facing us from the table. jonCates moves between the back and front of the table, with purpose. While the equipment stack is familiar, multiple mixers and cases, this is no DJ set. Much closer is the image of a few men in long sleeves and ties tending to tables full of equipment for John Cage’s “Variations VII”. With several nondescript devices on and adjusted, the air around us has become alive with a noisy drone that, by this date and to this audience, is very familiar (parallels extend back to sonic attacks from Peter Christopherson and Chris Carter with Throbbing Gristle) but now the sound is comforting, an aural field that is neither alien nor distracting.
A droning, machine sound, or the droning machine sound, has become a ridiculously common element of a contemporary “experimental” sound and video work. It is thus all the more surprising to be instantly drawn into jonCates’ audio, to take pleasure in it and to lose track of time completely. We are watching him control the mixer and occasionally speak into the microphone that is set in front of a conspicuous security camera. Again, jonCates uses the most expected situation —the camera faces upward toward the video projection screen, creating a counter-clockwise tilting feedback loop. And again, we are not distracted by this, it is familiar yet beautifully framed and we are drawn in. We have been invited to a field constructed by a tactician expertly employing simple situations.
The raw quality of both the droning audio and the feedback loop combine with jonCates’ humble appearance to remove the expectation of a spectacle and we return to the real situation with questions: who is this man and what is he going to do? He keeps speaking into the microphone, his eyes look desperate, and, despite seeing him perform a similar (although much less engaging) performance at the 2011 Gli.tc/h festival, we are surprised as we realize, as it is nearly two-thirds complete, what he is doing: giving a lecture.
jonCates has been speaking for some time but only a few echoed fragments are reaching out beyond the drone. It has been an incantation without purpose, a repetition of the meaningless words one says when one is presenting something to an audience. Finally, jonCates drops the distortion and the volume on the droning sound and his voice becomes clearer. It is obvious that some communication is going to happen and everyone shifts slightly as we strain to remember how to listen to a voice. Are we here to see another performance or hear something important?. The voice is not strong and it has no authority. It is perfectly ordinary, slightly academic with a hint of vulnerability. It’s the voice of a mad scientist who has begun to understand that his experiments may be his undoing. At this point the piece could collapse and jonCates has not propped himself up with his technology. Instead, he’s used it to lead us to key moments and obliterating everything else. Still, he seems not so much frightened as curious to see where this will end, if what he needs to say can be given a short lifespan in this space. This is where performance lives —in the unfolding present. And jonCates says:
“…and I thought [?] … I thought [?] about how I should remix something in realtime for you that I should reflect upon the past, I should reflect upon [?] …patterns so I thought that I should probably do this as a remix and render it in realtime for you but then I found … from 1997…and it was sitting right next to the first tape … it was sitting right next to the first tape, had the same title as the first one, that also said “Flow” and right next to it had another a label that said “Remix” and I thought ‘I already made that piece’ [sampled voice droning: ‘oceanic waves upon waves upon waves upon waves’] and that’s almost too good to be true so I put the tape called ‘remix’ into the VCR, not this VCR. I had to buy a new VCR that VCR broke and … called ‘remix’ .. rendered in realtime for you … and I watched it, and almost [? ] [?] decide … I had already … [sampled voice droning: ‘we can stay in the spell of the laser lights’] … and I’ve been thinking about these things … [sampled voice droning: ‘we are all together … in the time space continuum of … of … of …’ and the drone continues.]”[4]
“The peculiarity of the time bounce, as he mulled it over, was that the resumption of the earlier state of being not only set physical objects back to their former positions, it actually wiped out the events of the lost hour. Like daylight saving indeed! With the lost hour unhappened, even memories of the time were obliterated…They might be reliving a given moment for the fifth time, the fiftieth, the five millionth, and never notice it!”[5]
“A representation is the occasion when something is re-presented, when something from the past is shown again —something that once was, now is. For representation it is not an imitation or description of a past event, a representation denies time. It abolishes that difference between yesterday and today. It takes yesterday’s action and makes it live again in every one of its aspects —including it’s immediacy. In other words, a representation is what it claims to be —a making present.”[6]
“For every organ-machine, an energy-machine: all the time, flows and interruptions. Judge Schreber has sunbeams in his ass. A solar anus. And rest assured that it works: Judge Schreber feels something, produces something, and is capable of explaining the process theoretically. Something is produced: the effects of a machine, not mere metaphors.”[8]

They are called radio buttons because on old car radios you pushed one button and the other popped out. The performances of jonCates and Jon Satrom were developed as an intersection with the exhibition Ex-Static: George Kagan’s Radios at Intuit, the Center for Intuitive and Outsider Art, on display until January 5, 2013, curated by Erik Peterson and Jeremiah Hulsebos-Spofford.
“In the wee, wee hours your mind get hazy / Radio relay towers lead me to my baby / The radio’s jammed up with talk show stations / Its just talk, talk, talk, talk, till you lose your patience”[9]
jonCates makes Dirty New Media Art, Noise Musics and Computer Glitchcraft. His experimental New Media Art projects are presented internationally in exhibitions and events from Berlin to Beijing, Cairo to Chicago, Madrid to Mexico City and widely available online. His writings on Media Art Histories also appear online and in print publications, as in recent books from Gestalten, The Penn State University Press and Unsorted Books. He is the Chair of the Film, Video, New Media & Animation department at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago:
http://systemsapproach.net/
Jon Satrom undermines interfaces, problematizes presets, and bends data. He spends his days fixing things and making things work. He spends his evenings breaking things and searching for the unique blips inherent to the systems he explores and exploits. By over-clocking everyday digital tools, Satrom kludges abandonware, funware, necroware, and artware into extended-dirty-glitchy-systems for performance, execution, and collaboration. His time-based works have been enjoyed on screens of all sizes; his Prepared Desktop has been performed in many localizations. Satrom organizes, develops, and performs with I ♥ PRESETS, poxparty, GLI.TC/H, in addition to other initiatives with talented dirty new-media comrades.
http://jonsatrom.com/
Sam Renseiw and Philip Sanderson’s Lumière & Son project is a near perfect and altogether exhilarating sequence of moving image lyric poetry (though lyric here does not exclude humour or the grotesque) and a demonstration of how seriality and fragment – an unfolding over time, the diaristic – has quietly become one of the fundamental modes brought stage centre by the network (so much more than the rather dull ‘interactive’ which has so quickly become the standby of the monetised digital). Impossible to watch one of these pieces without the desire to watch just one more.
The set (which lives online but has been shown offline in whole and part) and its component pieces, moreover, are studies in various interesting things: the liberating effects of constraint and collaboration and what those both demand and imply; also of randomness, or perhaps better, the loose, the dashed off, differing degrees of accuracy in such collaboration (also the apparently dashed off, the apparently loose [also the apparently synchronised or ordered]).
To start with, a little history. In 2007 two young members of the digerati, Andreas Haugstrup Pedersen and Brittany Shoot, invented a form and threw down a gauntlet. The form, in fairness, was not exactly new – over 100 years old, actually – but its re-contextualisation within the digital realm and more particularly on the network was, without exaggeration, a stroke of genius[1]. It involved taking precisely the constraints affecting the films of the cinema pioneers, the Lumière brothers, and applying these to contemporary online video work. Films or videos of exactly one minute, fixed camera, no sound, no zoom, no edits. Such videos dubbed, naturally, ‘Lumières’. There was clear recent precedent in the constraints of the Dogme movement of Von Trier and others but the project also drew on the various little-bit-art-little-bit-geek, young, playful cultures which abutted and intersected the more formal area which we called, for a while, ‘net-art’, and which thrived on a sparky and often competitive and showy overcoming of the early net’s limitations of file size and bandwidth – projects like 5k.org, 10secondfilm.com spring to mind.
Additionally, because the start of modernism still does not really seem all that far away, early film was a natural reference point for many wrangling the early internet as art tool and channel both.
We responded viscerally to the sheer, almost willed-into-being, expressivity of the ad hoc devices and solutions of early film and this fitted snugly with the bodges we ourselves were employing. It gave us confidence, too, that our ducking and diving too could be expressive but also it confirmed a certain tendency to lo-fi-ness there in the zeitgeist. (I speculate – a lo-fi-ness which helped to define and declare art – useless, beautiful and human – as against the slickness of corporate design, communication and advertising… This has persisted remarkably – note the thriving on-going cult of the animated gif)
That was the form. The challenge – make some. Embrace that 100+ year old limitation and do something engaging with it. Push the form as far as it will go.
Pedersen and Shoot set up a web site where all contributions would be aggregated and indexed (in retrospect, somewhat unfortunately, by links rather than copies held on their server – much work of historical significance has already vanished. Shoot and Pedersen themselves have moved on and the site has a Marie Celeste feel). In addition to the site itself, there was a Lumière manifesto which, personally, I found a little narrowly focussed. Shoot and Pedersen seemed to invoke a near ethical dimension to the return to first principles and in their own moving image practice confined themselves to work (much of it very good) entirely within this discipline. It was clear from the huge response of other artists and film-makers though that the form clearly answered a diverse set of pressing needs. For some it was a cleansing activity, for some a sketchbook, for others a spur to invention and for others still, a challenge in the sense of “How can I observe the spirit of the rules whilst actually driving a coach and horses through them?”
Although the Lumière made next to no impression on the ‘official’ world of art video (one speculates – cynically, perhaps – too democratic and available to anyone with a cheap camera, too ontologically opposed to the expensive grandeur of high concept, too hands-dirty in a world where artists aspire to hire videographers and editors to realise their art; in short, too lacking in the conspicuous consumption that validates much contemporary work), it was enthusiastically taken up by a mixed bag of videobloggers and artists excited by the idea of video specifically made for the net.
An immediate adopter and one of the most enthusiastic and prolific makers of Lumières was the Danish architect, educator and thinker, Thomas Wiesner, who operates in online video as Sam Renseiw and maintains a quirky and engaging site called Spacetwo: Patalab. Renseiw (as he prefers to be known in a video context) is a maker of numerous very singular small video works, which evince his keen interest in space and movement within spaces. (He teaches not only architecture but also a course for dancers involving approaches to conceptualising movement in space). I’m not sure Renseiw completely understands how original his work is. It is characterised by a joy in careful, quizzical looking (and a spontaneity in finding or being gifted subjects for such looking, assisted enormously by the continual development of more portable and discreet video cameras). It is, in terms of the formal art world deeply unfashionable. Personal and diaristic, it eschews the grand concept and extravagant and expensive execution and is all the better for this.
Renseiw has a profound sensitivity to space and to how people and objects move along variously restricted and open trajectories but he is mindful too of what the ‘actors’ in these found scenarios, set out to do and in fact achieve as human beings. The gap between aim and reality provides fertile ground for Renseiw’s dry and humane sense of humour, which is never far distant.
Significantly his prolific Lumière making (337 at the time of writing) sits side by side with longer (though still lapidary) works with music, editing and the other things the Lumière eschews.
Renseiw’s Lumières are characterised by a number of quite distinctive things. Something that unites them all is a quite extraordinarily heightened sensitivity to both colour and composition, which formal feature hits us forcefully in the moments even before we begin to decode any content or action. Formally striking too is the way in which a number of the pieces are composed so to as to allow for action in the near, middle and far distance, sometimes in different sectors of the frame, sometimes simultaneously in a kind of layered visual counterpoint and sometimes spread out temporally. My imputed intentionality here is somewhat problematic, though Renseiw confirmed to me that he shoots much more material than he uses and that he will select a particular minutes worth of material from longer sequences so on two counts there is a rudimentary (though nominally forbidden) editing process occurring. A quick comparison with Lumières by other film-makers will however confirm that Rensiew’s singular vision distinguishes each of his pieces from the off.
Other signatures are extremely low, oblique or occluded camera positions, into the fields of which parts of human bodies mysteriously intrude. This sounds clinical. Curiously it is the opposite. Redeeming it is a genial humour which allows the part to stand for the whole – we perforce imagine the entire human being whilst smiling at the V-effekt with which we are presented – for example a pas de deux for a pair of woman’s black leather boots (on the ends of beyond-the- frame legs) and the four paws of a black dog – randomness, clumsiness, near misses, narrow escapes and – we just know because we are human – purposeful activity. Human life, in short.
Another defining stamp is a musician’s sensitivity to rhythm and tempo – rhythm as manifested both as near metronomic regularity – someone’s gait, traffic flow, a hammer, for example, with either disruptions – slowings down, speedings up, pauses, stutterings – to that regular pattern, or polyrhythms created by other simultaneous independent near regularities and variations therefrom.
There are three loose categories into which Renseiw’s Lumière work could be said to fall (of course they’re by no means entirely mutually exclusive) – we’ll call them the loop-able, the documentary and the performative. The loop-ables are kin to the still photograph, are often of natural phenomena or repetitive but irregular human engendered activity where one could imagine the minute’s imaging infinitely, hypnotically extended – the flashing light patterns in Belisha Code for example. The documentary tag applies where the topic itself might be assumed to have some independent interest, for example the workers transporting away in a sling Copenhagen’s Little Mermaid for a trip to Shanghai’s 2010 expo in Speaking Voice or Michelle Obama’s motorcade in Rite of Passage. In what I’ve called the performative, richest of all in my view, an amazing amount of stuff happens. And everyday stuff happening and rendered vital by keen eye, framing and selection rather than something we might have known to look out for, is key. The differently distanced layers referred to earlier partition the frame physically or the piece temporally and unexpected things happen against and within them. We participate in these dynamically as viewers – we view this strange jigsaw world and complete it mentally; sketch a world beyond which is not simply our lived world but that world somehow leavened with Renseiw’s odd and warm sensibility.
I’ve written pretty glowingly about these Lumières – constrained, silent but surprisingly un-austere and you could well think that to add sound, music or both and several layers of these to boot might be over-egging it all somewhat. So one would think, but I have complimentary things yet to say about skill, tact, panache, flair and sensitivity and they are heading the way of Philip Sanderson, Renseiw’s musical/sound collaborator in the extended Lumière and Son project.
Renseiw’s Lumières are, I hope I’ve established, rich, dense, multi-layered but remarkably uncluttered works. A number of these pieces approach as closely as possibly the condition of music whilst remaining wholly without sound. It might seem superfluous or an act of hubris to add sound to them, the consequence of which could be to render leaden, stiff and fixed what is light, playful, complex and turns on a sixpence.
With the exception of a couple of near misses Philip Sanderson’s sound and music additions triumphantly avoid this trap and indeed deepen those rich and quicksilver qualities.
It’s important to note that what Sanderson contributes is all found or appropriated material – it’s possible he’s added original material in, I don’t know, but it’s not a significant chunk if he has – he certainly reworks much of it intensively, usually in the form of a mix of several layers of sound, some musical, some textual. (And we should note that Sanderson’s wit and deftness is literary as well as musical).
The deployment of sound gains enormously from Sanderson’s huge and eclectic range of knowledge, reference and enthusiasms. There’s a cooking metaphor in here – mixing the ingredients, finding just the right, perhaps almost imperceptibly present flavourings, knowing the qualities of things and how to combine them well…
Elsewhere I have asserted that the key feature of the most successful short form video work is a combination of intense poetic compression with a huge range of suggestion. I called this opening-out – a universe from a speck of dust. An ability to evoke the range of connectedness of many disparate things by well-chosen images, sounds, texts, whatever can pertain to moving image. Certainly Renseiw’s work has this in spades. Sanderson’s sound opens-out the movies still further. It adds, almost literally, an extra dimension, as if enabling new angles of view. It provides paths, bridges, vistas, tunnels, maps, balloons, telescopes, and sonar.
The guiding methodological principle seems to be a species of metonymy and one moreover which suggests an, in practice entirely non-existent, explanatory or illustrative dimension. The flashing beacons in Belisha Code are accompanied by a recording of a numbers station where one’s immediate impulse is to construct entirely absent meaning in the correspondence of the binary on-off of the four beacons and the German numbers from zero to nine heard on the soundtrack. Let’s be clear that this is not a criticism – a rigorous correspondence would be leaden – closed-in – but what we do have is a rich package of suggestion and affect. The correspondence that does exist is formal and temporal, between the flashes of the beacons and the articulation of the words and where the same sort of rickety polyrhythms that we’ve observed within the original Lumières themselves ensue.
Although comparison of some of Sanderson’s sources with their use in the pieces evidences, on occasion, some quite detailed cutting, mending and buffing-up there is an inescapable sense in his deployment of sound of the somewhat aristocratic tradition of the modestly dashed off. It’s partly his clearly extensive knowledge of his sources and his evident skill with a huge variety of genres but it’s also to do with a certain ambiguity in how the sounds are placed – not four square upon, but athwart the images, the sound often only fading or vanishing well after we’re into Renseiw’s end titles. Sometimes the sound is clearly not cut to shape in the way one might at first expect – an introduction, for example proper only to the original sound itself and not to any clear visual motivation might be left standing. The imperfections, noise, oddities and glitches contained within each block of appropriated sound intensify this sense of informality as does the slightly culinary air referred to previously. On the other hand, often enough to matter, the sound directly lines up in a spine tingling way with a particular action. It’s a master class in expressive ambiguity.

Renseiw – physical poetry, the occlusion, constraint. The careful choice of footage (variety and kind of motion within a narrowish range). Humanism: we don’t see faces, we don’t hear voices, we are amused but we recognise ourselves, youth and age &c.
Sanderson: The music found but could have been composed. The artfulness of placing it just thus. We will never know whether the way it ends with the action, the running off, taking place just after the repose of the final minor chord was deliberated or found. For me this placement implies a universe beyond the letterbox. It has a commonality with the treatment of time in many photographs and paintings – this is an instant, a fragment, but there was a before and an after.

Note that there are four beacons. The sound (a numbers station, one can almost track the archaeology of impulse!) draws on the numbers 0-9, in German. It’s worth noting there is no obvious mathematical mapping between the pattern of the beacons and the numbers but the character in sound of the numbers is close to that of the beacons in light. Suggestion, metonymy.
This forces our attention very strongly on that area of the screen, with the concomitant effect that when we force our attention away it is as if our eyes have been suddenly opened. There is a world out there.

There is a hint of the transcendent in the title – how is this realized? Unless we know Denmark it takes a few moments to realize we are on a train rather than a boat or plane – we are clued into this by the close objects we clearly pass at speed and the reflection of passengers and seating in the windows. One speculates that the sound track is comprised of two elements – one the rhythmic and metallic pulse which somehow rhymes with the passing object (a kind of pseudo-diegesis) and the second an (Open University?) lecture on relativity.
Here, not exactly metonymy but something more fragile, delicate chains of suggestion and subtle resonance. No argument (to see an argument in any of this would be to commit a category error) but a complex and suggestive …um…thing. One should also note that this piece (in both its silent and extended versions) is extremely beautiful.

Let’s talk about the sensibility and taste of the makers. Renseiw offers something simple, a kind of tour de force – we perceive it as such although given the fixed camera constraint any virtuosity belongs to the seagull.
A banal seasoning of music would involve simply the seven note modal motif which hails, I’m almost certain, from American popular song of the 70s big country type – Wichita Linesman, you know the sort of thing. (I checked with Sanderson –it’s Bobby Goldsboro’s Summer The First Time) By itself it would be too perfect, too parallel to the floating bird (it seems to give way to a crashing wave sound in its looped form; interestingly the Goldsboro video I found on YouTube begins with a shot of gliding seagulls). With too much parallelism nothing extra arises but Sanderson spices the mixture by the addition of dialogue from what sounds like an American film of the forties or early fifties. It disrupts the idyll but only so as to make us more aware of it. There is a kind of musical V-effekt here (which could have been so badly handled and so isn’t). This is its ‘meaning’ – these things! Here, now!

There is something of the dance about this. The music beautifully picks up both the nervous, sudden gestures of the cook but also suggests the process of cooking itself. The music has a funk component. One might say that it cooks.

Visually – the low angle, the fragmented view of the body, the person here and not here. The focus on that person which permits and invites its opposite, in particular the framing of the sky and trees. The rhyme between the black-booted two legs of the woman and the black four legs of the dog. Their pas de deux. The music here subordinate, properly so. Ambient sounds, on the one hand, with odd vocal snatches on top. The strangeness doesn’t demand our attention because we are so focused on the visual.
Until the last moments we simply hear a fitting (slightly arch) accompaniment to the skating – we surmise that it is intended to pastiche the kind of accompaniments used in professional skating. At the last moment we realize this is exactly what it is, as the commentator’s voice breaks through. There is also a ‘skate’, ‘friction’ or ‘traveling’ noise which exactly underpins the final move we see, just before the humour of the juxtaposed text, which continues after the movie has gone to black, strikes us: “Delightful, skating of the highest quality” delivered in classic plummy BBC tones…

A hugely rich piece: visually there are a number of layers – the far left street background where distant people and vehicles process. The game of Petanque: – the actual participants (although glimpsed corporeally only twice: fleetingly at the very end and as one set of typical Renseiw-y legs) and the balls themselves (and the metonymic link between these and the planets). Thirdly, the large shadows. (And the apparent size of each of these layers allows for very clear visual interaction). Sound – the ‘light’, jokey, playful music. The University Challenge soundtrack, here unusually clearly cut up – questions – astronomy; replies – painters. A risk for Sanderson, but one that works.

A little detective work indicates the level of detailed truffling about by Sanderson – part of the sound, the text, is grabbed from a YouTube video about French patisseries in London and cut up considerably – in particularly yielding the repeated incantation “cream cakes, tarts, macarons” the latter word in a considerably overheated French accent following the sloaney first three, to deeply comic effect. Comic maybe but, repeated, as in a dream; this mood is reinforced by a rather beautiful waltz time solo piano loop of the opening line of The Associates’ Party Fears Too. Here’s another piece where the visuals, here also dreamy and wistful, set in a looking glass Copenhagen (and the disjuncture between the London-location heavy narrative and the visuals is simply ignored, taken for granted, part of the deal), support quite a complex sound assemblage. Utterly haunting and quite difficult to say exactly why.
If one didn’t know it wasn’t one would surely assume this was carefully planned, and our knowledge it was not adds to our pleasure in it. Visually the rhyme between the woman and the near foreground statue is perfect – at one point she seems to mirror it exactly. Maybe she knows the area well and there is some unconscious mental echoing…we’ll never know. The other sharp visual pleasure is the smallness of the area of focussed distant activity, which again feels like a sort of directorial chutzpah, except, except…
Sanderson’s contribution is razor-sharp – the pseudo dialogue hits the mark precisely but doesn’t outstay it’s welcome – or at least there’s other stuff going on to detain us, not least the way the model’s preliminary warm-up shimmy becomes a perfect piece of minimal dance when set against the music.
Right of Passage/Speaking Voice

I wonder if when the content has it’s own ‘documentary’ interest, when the filming becomes a case of “Look at this remarkable thing not because of its intrinsic interest but because it happened”, the final result is somehow less engaging?

Again a dance related piece – the regular beat of the calling of the numbers one to eight sets up an aural grid against with which the implicit rhythms of the movement in, out and across frame interact in a sophisticated but subtle polyrhythm. Part two of the sound, with actual step instructions, ups the tension and the effect (especially the late entering ‘spinning’ man). Note how often in these pieces the sound fades out slightly later than the visuals, over Renseiw’s titles, thus emphasising its separate existence in an independent channel or dimension.

Beautiful found synthesis. Funny. Funny and truthful and touching.
The moving image is packed with incident at both different spatial levels and at different points in the piece. The Portsmouth Sinfonia version of Dance of the Sugar Plum Fairy underpins like a grid, as with Square Dance but in a more complex way, the visual rhythms of the film. Enough coincidence of rhythm to feel planned, enough ‘pull outwards’ to feel open… Again humour… Why does the Portsmouth Sinfonia track, in particular, work so well – atmosphere? the conjuring of a sort of raggedy clockwork ? – can we imagine in its place a more conventional rendering of the Tchaikovsky? Yes, but…

Prime example of Sanderson mind set – metonymy, suggestion – the trees are hair, the water appears exactly on cue (worked? Hmm – the audio appears to be cut to make the word ‘rinsing’ and the water jet coincide)

A one liner, but, given its place in the sequence, none the worse for it.
Brass band/Dancers.
*The pieces loosely divide into ones where either sound or vision predominate and some where they have equal roles.
* Not only does dance appear a couple of times explicitly as a subject but the spirit of dance pervades the project.
*The question of the success of individual pieces and of the sequence – a piece that seems less effective in isolation can well form an effective point of relaxation or reflection in the sequence as a whole…
*There are three pieces which, if one ‘re-removed’ the sound, would not strictly be Lumières – Check Out Art Fairs (speeded up), A Beauty Overblown (slowed down) & Sucked In (reversed). Sanderson performed the first two operations for reasons he felt the sound he used demanded. (To which one can only say: yes, this is right, a constraint is there for the sake of art, not art to be constrained.) Sucked In remains a mystery.
*The titles matter (note the re-titling of the composite works). They provide yet another dimension and illumination too.
*The prevailing tone is light, warm and playful. The darker side of life is largely absent, at least explicitly (though there are trails we could pick up to find it). Humour is everywhere. Only a philistine or fool would judge the work as a consequence to be less ambitious, significant or universal.
Featured image: Still from performance of Structure M-11
You would measure time the measureless and the immeasurable.
You would adjust your conduct and even direct the course of your spirit according to hours and seasons. Of time you would make a stream upon whose bank you would sit and watch its flowing. – Kahlil Gibran
Algorithms only really come alive in the temporal time-frames that they move through. Their existence depends on being able to move freely along time’s arrow, unfolding and expanding out in to the universe, or reversing themselves backwards into a finite point. Every form and structure that the universe creates is the result of a single step along that pathway and we’re only ever observing it at a single moment. Those geological steps can take millions of years to unfold and we can only ever really look back and see the steps that happened before we chose to observe them. Computational algorithms break down that slow dripping of nature’s possibilities and allow us to become time-travellers, stepping into any point that we choose to.
Paul Prudence is a performer and installation artist who works with computational, algorithmic and generative environments, developing ways to reflect his interest in patterns, nature and the mid-way point between scientific research and artistic pursuit. The outputs from this research are near cinematic, audio-visual events. Prudence’s creative work, and his blog, Dataisnature (kept since October 2004), explores a number of creative potentials as well as documentating the creative and scientific research work of others that he finds of interest. As the blog’s bio states:
“Dataisnature’s interest in process is far and wide reaching – it may also include posts on visual music, parametric architecture, computational archaeology, psychogeography and cartography, experimental musical notational, utopian constructs, visionary divination systems and counter cultural systems.”
Paul himself feels Dataisnature, and his other blogs, are by their very nature ordering systems, trying to create some kind of structure on information. “Yes, it’s true [that they are ordering systems], but the ordering is sometimes a little bit oblique. I am not interested in ordering systems such as categories or tags, for example, as each blog post has the potential to generate many of its own categories.”
The blog and perhaps all blogs, shouldn’t be an end in themselves then? Should they be a starting point for a deeper investigation? “Well, I’m more interested in substrate and sedimentary structuring – specific fields existing in layers and sometimes overlapping and interacting rhizomatically.”
Blogging for Paul and many bloggers who don’t operate within the ‘monetization of blogging’ sphere that has grown up in the past few years could almost be considered a documentation and ordering process for the creative process. The process and interaction between the theory and the blog as textual artefact becomes quite complex. As does the theory and creative output of the blogger. Paul would argue that this isn’t always something that can be even as straightforward as theory to practice though.
“The posts at Dataisnature are not confined to theoretical relationships between art and science projects, but also take into account metaphorical ones. I never wanted the posts to be so pinned down that they disable the opportunity to make entirely new connections at any level.”
So the chance to see what happens inbetween strict disciplines and an openness to the potentials that may arise out of relaxing the barriers? Shouldn’t that be the way that everything else that is ‘not of academia’ operates anyway? And for that matter, outside of the possibilities of arts/science/research funding.
“I applied the term ‘recreational research’ to Dataisnature in its early days,” Paul explains. “This is still to some degree important – the notion that research doesn’t have to be tied down by the prospect of peer review or academic formatting. This kind of interdisciplinary research can be highly addictive – its the new sport of the internet age. It can generate blogs that become chaotic repositories of interconnectedness – linearity becomes infected with cut-up and collage. In my own mind I have an idea of what Dataisnature is trying to say but I get people approaching me with completely different, and amusing theories of what they believe the blog is about.”
In digital arts (or let us call it digital creativity, to avoid the complexity of art versus design versus technology) the breakdown between the equipment used and the research of the creator has become almost at times indistinguishable. A painter is often only one step away from being a chemist, a sculptor closer to an engineer than a painter. The tools used define and form some of the output. Digital creativity only makes this more implicit. So when using technologies and researching, the scientist and the creative often walk hand-in-hand towards the finished artefact. As Prudence says: “Collaboration among artists and scientists exists through time as well as space.”
“A great part of an artist’s task is to be a researcher. It’s important to remember that any idea you have has already been tackled in the past with a different (want to avoid the term lesser) technology.”
The blogging process offers a chance to gather information and allow some of the artist’s own influences and present interests to manifest themselves into a rough-hewn structure. “For me, blogging facilitates a medium for an archaeology of aesthetics, technology and conceptuality. All this fragmented information is gathered then reconstituted, and fed back into the artistic practice. Of course my personal work blog is more about supplying supplementary material to anyone interested in my work.”
Taking an arguably typical example of Paul Prudence’s work, for example Structure-M11, the sense of a becoming and developing is in the way it attempts to reconnect with what (for want of a better phrase) could possibly be called our lost industrial heritage.
Looking through Prudence’s flickr stream documenting the research trip, there are numerous industrial landscapes empty of human life, where only the machines have been allowed to remain, static and poised, ready to begin work again. If only someone would employ them. These machines perform simple tasks, but they do it elegantly, time after time after time, never complaining and never asking for any recognition. Perhaps that’s why it is so easy to abandon them? And these machines are not only a monument to the way we discard unwanted technologies, they also reflect the changing fortunes of the town as it has moved from production-based economy to one centred mainly on tourism and smaller businesses. It is fitting in a way that the soundscapes and visuals that Prudence has brought to life from these landscapes have such a contemporary, sci-fi industrial feel to them. As though the clean, slick lines and geometric perfection had emerged, phoenix-like, from the unbearably hot, oil soaked environments of the factories and the monotonous repetition of working within them.

The soundtrack that accompanies the performance was made from field recordings at the site. From these, Prudence generated real-time visuals that reflected some of the sonic activations and echoes throughout these landscapes. The final pieces look like ‘robotic origami contraptions.’ The steady throb and crash of the audio reflects the repetition of the machine and its operator’s lives while also suggesting some of the dehumanising effects working in a factory can have on a person. There’s also the beauty, of course, if you shift your own perception a few degrees away from the machines, there is always a window looking out at a natural landscape. And those same slick, geometric shapes of the machines begin to reflect some of the elegance of the world of nature. Nature, like humanity, loves to repeat itself infinitely until something breaks that pattern. Isn’t that a fundamental part of mutation and evolution? Structure-M11 seems to be constantly mutating and growing new rhizomes, but nothing complete ever emerges. Paul Prudence’s work isn’t here to save us from the monotony of the machines though, its task is to remind us of how important nature is to our lives, no matter how entangled in the machine those lives may begin to feel.
Prudence’s interest in the natural spaces emerges from his own theory-based interests. As he says, “My interest in generative systems and procedural-based methodologies in art lead to a way of seeing landscape formations and geological artefacts as a result of ‘earth-based’ computations.”
“The pattern recognition part of the brain draws analogies between spatio-temporal systems found in nature and ones found in computational domains – they share similar patterns. I began to think of the forms found in natural spaces more and more in terms of the aeolian protocols, metamorphic algorithms and hydrodynamic computations that created them.”
“Some of these pan-computational routines run their course over millions of years, some are over in a microsecond, yet the patterns generated can be amazingly similar. I like the fact that when I go walking in mountains my mind switches to [the] subject of process, computation and doWhile() loops inspired by the geological formations I come across.”
This connection and flowing from one space to the other, gives the viewer the feeling that they recognise the shapes and patterns from something they’ve seen before. Attending a performance of Prudence’s work might make you feel as though you’ve been to one already. But it’s just the reconnection of interconnection that you’d be experiencing. And that’s always a good place to start, when experiencing any artwork, isn’t it?
21 Sept 2012
Scopitone Festival, Nantes, France.
24 Sept 2012
Immerge @ SHO-ZYG, London
17-25 October 2012
VVVV Visual Music Workshops at at Playgrounds 2012, National Taipei University of Art, Taipei & National Museum of Art, Taichung, Taiwan
Prank sombody with the fake Windows 10 upgrade screen which never ends. Open the site in a web browser and go full screen with the F11 key.
Featured image: Still from Me and Mrs Sloan (Susan Sloan (2007). Motion-captured animation of artist’s mother.
Susan Sloan’s exhibition of motion captured portraits on The Wall at The Photographers Gallery raises issues in terms of data object relations and computer animation – or ‘animatography’.
In critiquing the work by Susan Sloan, currently on show on The Wall, what emerges is the artist’s concern with the essential qualities of the data space that she is utilising. What has become apparent is the distinct new medium of animatography, as used in virtual reality art works like Sloan’s, as well as in the more ubiquitous moving image; a language which is not composed uniquely by the author/animator, but also by the apparatuses of computing and software development which are then engaged with by artists and other individuals, “they [photographs] are produced, reproduced, and distributed by apparatuses, and technicians design these apparatuses. Technicians are people who apply scientific statements to the environment.” [1] In this way, a piece of proprietary software like SoftImage, can be seen as an apparatus much like a camera or an easel.
In answer to the Photographers Gallery’s questioning of the impact the digital is having, I would argue that the critical and theoretical discussion of computer animation use in virtual art works should focus on the creative exploration of data object relations. I am also suggesting that the term animatography be applied when talking about the medium of computer animation, and the following discussion focuses on the development of an awareness of how this language is utilised in art in virtual space.
The medium of animatography can be explored as an essentially synthetic medium which extends the languages of animation into one of data object descriptions; the use of data to describe virtual objects, and the complexity of these descriptions. Sloan’s work very much explores the nature of applying data to ‘objects’ or rather, as it means in psychoanalytic terms, subjects. The work is composed of complex object descriptions, comprising 3-D modelling techniques as well as motion capture data.
First it is necessary to look at data object relations in terms of psychoanalytic theory, then its applicability to animatography. Susan Sloan’s work, highly explorative of this as it is, is looked at to further elucidate the relationship between data, psychoanalytic theory and animatography.
To understand this approach it is first necessary to outline a theory of object relations as explored by Peter Fuller in relation to art works. Fuller applied D.W.Winnicott’s major psychoanalytic concept of the ‘potential space’ [2] and found that he could relate this theory to his study of aesthetics, and it has informed the development of a theory of animatography, which is based on our relationship with ‘data objects’, in aesthetic and cultural terms.
Winnicottís theory describes a baby’s gradual development and awareness of herself as a ‘separate autonomous human being’ [3] in relation to, at first, her mother. While up until that point she has felt at one with her mother, several months after birth, at a key moment, this recognition of autonomy starts to occur. Fuller writes, “This process of discovery seems to be a vital period of human growth. During it, the baby, necessarily posits the idea of a ëpotential space.” [4] He quotes Winnicott’s definition of potential space as: “the hypothetical area that exists (but cannot exist) between the baby and the object (mother or part of mother) during the phase of the repudiation of the object as not me, that is at the end of being merged in with the object.” [5]Fuller then points out that “Much in Winnicott’s view, depended on this ‘potential space’ between the subjective object and the object objectively perceived, between me-extensions and the not-me.” [6]
Potential space, Fuller explains, is important to creativity and to understanding aesthetic experience. The ‘location of cultural experience’ is derived from the ‘potential space’ where ” – if he has sufficient trust in his environment – the individual can explore the interplay between himself and the world, not as mere fantasy, but as cultural products which can be seen and enjoyed by others.” [7]
Similarly the cultural products of computer animation and therefore the aesthetics of animatography can be seen to derive from a relationship to the potential space, as transitional objects of meaning and value generated through a type of work and/or play. For Winnicott, “play is the paradigm of cultural activity” [8] and “cultural activities are those in which the experiences of the potential space are still operative.” [9] If we take Winnicott’s and Fuller’s theories, the potential space exists for artists, animators and a participating audience in which a play of separation; where a perception of what is me and what is ‘not-me’, takes place. There is no essential difference here between traditional media and animatography, apart from the specific differences of the nature of data itself, and therefore how we relate to data object descriptions.
If we add to this theory of ‘potential space’ with feminist psychoanalytic theory, which, in contrast to a generally masculine approach sees positivity in closer connectedness: “Chodorow herself suggests that care and socialisation of girls by women produces attributes which could (and should) be regarded positively; a personality founded on relations and connection, with flexible rather than rigid boundaries, and with a comparatively secure sense of the non-hierarchical nature of gender difference.” [10] We can see Sloan’s work as a carefully constructed interplay between artist and subject. Also, what does it mean to be described by data, which has automation at its heart, and yet requires a lot of skill to achieve this level of detail?
In virtual environments, the avatar is a key aspect for enabling a realisation of the ‘world’ to take place through human-computer interaction. In the works currently on show, Sloan looks intensely at the animated portrait, which inevitably relates to the condition of the avatar, while raising questions of perception to do with notions of reality and authenticity. Portrayed through animatography, the data object of the portrait model is related to as a me-extension, as well as sometimes being felt to be not-me, but a representative of the self, in terms of the freedom of self portrayal in this genre. In this sense, Sloan’s work suggests avatars ‘which really look like you’, through which the complex psychological reaction of what is me and not-me can be apprehended.
As such animatography could be said to have a physicality, in terms of the data it is composed of. Projecting the imagination into a notional space, the artist can at the same time make that space pragmatic in symbolic terms. A fantasy, and yet a data driven reality. This paradox between perceiving the physicality of data and the perception of the animatographic illusion as simply a fantasy lies at the heart of this relationship.
Susan Sloan’s Me and Mrs Sloan (2007), explores data object relations in the form of a motion captured portrait of her mother synthesized with motion captured movement by herself. It is a work about the potential space itself. In this instance, the artist has modelled the head and upper torso of her mother, in 3-D animation software, and then animated the head and shoulders, based on subtle motion captured material of herself. In this way, the data object is her mother combined with herself in terms of the motion captured material. It is Sloan’s work, and therefore the dialogue with what is ‘not-me’ is a fascinating one. The motion captured material is also ‘not-my-mother’, and instead it is a record of Sloan’s slight movements. In terms of locating ‘cultural experience’ (Fuller, 1980) this is a study of whether and how the potential space exists, when working with animatography. What is isolated or exposed, is that we relate to the ‘data object’ in the form of Sloan’s mother, as if the essence of potentiality in the relationship is somehow captured, in a way that explores what it means to relate to data that is ‘all-there-is’. This helps to establish that there is a cultural experience in the work, by the subject of the work itself.
The work explores synthesis in data terms, the portrait model with the motion captured movement used to animate it. In this sense identity is blurred artificially, and a synthetic effect is created, yielding a potential space in animatographic terms. In this work a synthetic identity, in this case between mother and daughter, becomes possible, which is like an advanced form of the avatar in multi-user platforms.
The concept of ‘potential space’ can be used to understand the nature and significance of data object relations in animatography, the me-extensions and the not-me, through programming a computer or manipulating a computer program to make animation is what this work points to in technical terms.
Animation is principally iconic, which means that there is more me-ness in its structure and execution than the traditional film image, which is partly composed of the indexical. [11]It can be argued that the engagement animatographers have with the portrayal of data object relations is precisely what identifies the need for animatography as a separate discipline, one which can culturally embody the unavoidable relationship we now all have with data objects in a more ubiquitous sense.
Data object relations in terms of Sloan’s work, has been considered in relation to psychoanalytic theory and its applicability to animatography. Through analysing a preoccupation with object relations, and specifically ‘the potential space’ as found in Winnicott’s theory, evidence of the potential space is found to exist as subject matter within Susan Sloan’s work. This is potentially an important aspect in critiquing art which explores subtle synthesis as an aspect of data object relations.
Dr Stephen Bell and Susan Sloan at the NCCA (National Centre for Computer Animation) in Bournemouth, United Kingdom
An interview with Katrina Sluis, Digital Curator at the Photographers’ Gallery By Marc Garrett
http://www.furtherfield.org/features/interviews/interview-katrina-sluis-digital-curator-photographers-gallery
“Human Readable Messages_[Mezangelle 2003-2011]” is a book published by Traumawien containing almost a decade of Mez Breeze’s “Mezangelle” writings. Mezangelle is hand-crafted text with the aesthetics of computer code or protocols. What marks Mezangelle out is how deep its use of those aesthetics go and how effectively it uses them.
Computer programming languages have their own logic, and it is not captured by holding down the shift key and bashing the top line of the keyboard to add what looks like a cartoon character swearing or random line noise to text. It’s true that programming languages can look incomprehensible to the uninitiated. This Perl code:
y/A-Za-z/a-zA-Z/
will swap the case of lower and upper case English letters. But the conciseness of this notation hides a clear informational structure only in the same way that mathematical or musical notation do.
Likewise the markup language HTML that this article is written in:
<p>looks “<em>gnarly</em>”</p>
and a computer protocol such as email transmission via SMTP:
220 smtp.example.net ESMTP Postfix EHLO someone.example.org 250-smtp.example.net Hello someone.example.org [192.0.2.201] 250-SIZE 14680064 250-PIPELINING
is incomprehensible without reference to detailed technical documents. But all express clear semantic structures and instructions to the computer systems that have been programmed to understand them.
These notations have been created to express data and concepts in structured ways that are possible for computers to work with. They may look typographically arbitrary but they do involve aesthetic choices and historical precedent. They have associations, they have resonances.
We do not usually see the codes involved in our use of computers and the Internet when they function effectively, but they are always there. When they successfully empower or coerce us they become invisible. In the age of social networking, ecommerce, and mobile devices they are pervasive.
What, then, are we to make of Mezangelle? Human written, but intentionally structured in the style of computer code, it recreates the expressive, communicative underpinnings of software syntax rather than simply its surface aesthetics.
To read Mezangelle is to parse it. Parsing in computer software is the process whereby a computer breaks down textual input into smaller and smaller but more and more closely related chunks of meaningful information. Parsing Mezangelle requires the human reader to group and regroup word fragments into shifting webs of meaning. It takes time to do this, and different textual characters and formatting take different amounts of time, adding rhythm and pacing to the meaning of the text.
The history of literary typography, of mathematical notation, and of programming language design has lent a rich range of often contradictory precedents both to software and to writing that draws on its aesthetics. A dot can mean a fraction or a part of an object. A square bracket can instruct a computer to construct a list in memory, to access an element of an array, or to send a message to an object. As can a colon or two, or various arrows. Hashes can indicate comments, identifier numbers, or other entities.
The raw typographic aesthetics of character glyphs spring from their visual form (smooth, straight, long, slanted), size, and relative visual complexity. A full stop or a vertical bar is simpler than a hash or an ampersand. These factors affect how long it takes to perceive them and the effect they have on the eye as we look across them. The glyph-level and code level visual arrangement of code affects the pacing of our reading, building pace and meter. The more semantic aesthetics of the way these glyphs are used to structure code build on and interact with this. And it affects the relations and meanings that we build as we read the text.
Like computer program code, Mezangelle structures its content in order to communicate to and invoke the resources of its parser. Crucially this is a human parser rather than a software one so those resources are aesthetic and cultural. As well as pacing the experience of the text as spoken performance would, these destabilize and expand its meaning as the attention of critical writing does.
The intrusion of quoted plain English text such as an Alan Sondheim piece or an email from a mailing list that have been the inspiration for an answering piece of Mezangelle serves both to show how different Mezangelle is from written English and how effectively it can be part of a conversation.
Here is a line of Mezangelle (broken by the format of this page):
.. my.time: my time: it _c(wh)or(e)por(ous+h)ate_ _experience____he(u)rtz___.] [end]
Read as code, the underscores mean private data and variables, the square brackets mean list construction, message passing, references to individual elements of data structures. The full stops are decimal fractions or references to data or functions that are parts of larger objects. They do not decorate (in the sense of being frivolous), they evoke.
They also semantically structure and pace, allowing reading and re-reading as poetry. Underscores creates distance, brackets group and shift the meaning of words and fragments of words. Addition signs and colons combine concepts and further disrupt the parsing of language as a flat, linear, structure.
Mezangelle is distinct from much historical code poetry in its structural and semantic mastery of the aesthetics of code. It is distinct from concrete poetry in its semantic, destabilizing, temporal rather than merely structural use of typography.
Mezangelle is net art, it is produced and encountered in the environment of the Internet. Mezangelle lives in blogs and on mailing lists. But it does not die on the printed page, far from it. “Human Readable Messages” is typeset in Donald Knuth’s Computer Modern font, a beautifully spindly artifact of the early days of computer typesetting, with the occasional intrusion of Courier-style monospaced teletype/typewriter fonts. This gives the printed text a digital, online feel retaining a genetic link to the environment it originated in.
Mezangelle surfaces and integrates the hidden aesthetics of computer mediated human activity, setting computing and human language in tension and synthesizing them. It expands the expressive possibilities of text and is a form of realism about the conditions in which human reading is currently flourishing. “Human Readable Messages” provides an ideal opportunity to familiarize ourselves with Mezangelle in the depth that it deserves and rewards.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
Anonymous, untitled, dimensions variable is the title of a show by 0100101110101101.ORG (Eva and Franco Mattes) at Carroll/Fletcher gallery in London from 13th April to 18th May 2012. Or at least it was. The title changes each day based on submissions to a blog (http://exhibitiontitlechange.tumblr.com/). The new titles have been printed out and displayed on the wall to the left as you walk in to the gallery.
You don’t expect this kind of playful intersection of the virtual and the real in a gallery off of Oxford Street, across from Soho, opposite other new galleries. Carroll/Fletcher’s glass-fronted welcomingly brutalist interior says “serious contemporary art space”. Inhabiting such a space presents a challenge to net and digital art that must be met with careful presentation and considered curation.
Through the glass front of the gallery, and as you enter, you see a sculpture or assemblage of a (stuffed) cat trapped in a birdcage by a (stuffed) canary (Catt, 2010). The cat has suffered Epic Fail as the Internet would say, and did in the meme image that the sculpture is based on. It’s a comic and unnerving object even without the extra layers of reference provided by the original meme and the knowledge that it was originally presented as a fake Maurizo Cattelan sculpture. It is art with its roots in the net that can stand on its own without that context. Its companion piece, Rot, 2011, is a fake Dieter Roth sculpture consisting of detritus in a glass jar on a plinth against the far wall. 0100101110101101.ORG briefly inserted it into the Wikipedia page on Roth, and the fact that its materials were all ordered via the Internet drives home just how commonplace this has become.

Both are given the room they need to work as objects in a gallery. Neither originates in itself as net art, more in 0100101110101101.ORG’s history of tricksterism and transgression. These are concerns that are easily linked to net culture, possibly too easily on the part of the reviewer, but it is telling that they are the works that the show opens with. They physically establish the playful appropriation and hyperreality that is the basis of much of 0100101110101101.ORG’s work.
Pride of place in the first room of the gallery goes to the projection The Others, 2011, 10,000 digital photographs (supposedly) copied without authorization from the folders of computers used by people on a peer-to-peer filesharing network that 0100101110101101.ORG used to distribute their own work. These are private images, projected at an angle and slightly across the corner. Configure your peer-to-peer filesharing client wrongly and it shares all the files in the folder you share. Including the images of you naked, drunk, lonely, partying, or whatever else you wouldn’t post anywhere a future employer might find them.

In the next, smaller, room is Colorless, odorless and tasteless, 2011. It is an old-fashioned car racing video arcade game retro-fitted with a petrol engine that starts up when you insert a coin and revs as you press the pedal to accelerate the virtual car on the screen, filling the (sealed…) room with carbon monoxide. Combining the virtual made physical of Catt and the moral impact of The Others, it is the most immediately dangerous artwork I’ve ever had to review.
Moving into the larger room at the back of the ground floor of the gallery, the video No Fun, 2010, is the most shocking piece in the show. Franco Mattes pretending to hang hineself on the random Internet webcam video chat switchboard Chatroulette is one thing, but the reactions of other Chatroulette users as they connect and see him apparently hanging there is quite another. Some laugh, some jeer, only one I watched displayed any lasting concern. This is the moral and aesthetic flipside of The Others.
Reenactments, 2007, is my aesthetic and technical favourite piece in the show. Videos of canonical performance art pieces being re-enacted by Eva and Franco’s Second Life avatars are displayed on CRT monitors arranged at floor level surrounded by the cables and adapters used to play back the video from SD cards. It’s much easier for an avatar to remain still as a “Singing Sculpture” than it is for a human being, making it even stranger, and Marina Abramovic’s “Imponderabilia” works much better with impossibly buff avatars than with mere naked human models stood in a doorway. It exquisitely foregrounds the social mediation of Second Life and its players self-presentation. A large cartoon wolf squeezes through between the naked avatars, their polygons intersecting. A vampire attempts to fly over them but hits the bounds of the architecture. The crowd in the background chat and bide their time. The virtual intensifies the real, out-doing and critiquing its appropriated source material.

Stolen Pieces, (1995, made public 2010) claims to move beyond fakery and unauthorized copying to physical appropriation. Stolen physical fragments of canonical postmodern artworks (Duchamp, Warhol, Koons, Rauschenberg) are displayed like forensic evidence, protected in small plexiglass containers, accompanied by large photographs of them and by documentary evidence of their theft. There’s no statute of limitation on theft in the UK, and damaging artworks shouldn’t be applauded. But it’s a daring performance and a concrete critique of the fetishism that lies at the heart of the art market and the institutions that help drive its value.
Following the brutalist concrete staircase to the basement reveals My Generation, 2010, a smashed but still working early-2000s PC lying on the floor. On its monitor, that appears to have fallen on its side, show video clips of computer game players giving in to and venting their frustration at the games they play. This isn’t the kind of image of yourself you want as your lasting monument on the Internet. Gathered together, like the images in The Others and the videos in No Fun, they again form a summation of an aspect of society and our visual environment that could not be achieved with such immediacy by other means. And the clear space and architectural solidity of the gallery again help to put a different emphasis on the material than if it was encountered on the web.
The wall-filling video projection of Freedom, 2011, records Eva’s attempts to plead with the players of networked First Person Shooter computer games not to kill her character. Touch-typing might have helped, but even when Eva manages to type long enough to explain that she’s an artist, or to ask people not to shoot, the social and game logic of the virtual world mean that her character is executed again and again, the screen shifting to third person as her avatar moves out of her control in death. Like No Fun, there is a core of callousness to these Internet interactions, and like My Generation they are unexpectedly preserved and presented for contemplation.
The final piece in the show is the documentary Let them believe, 2010, a video record of 0100101110101101.ORG’s Tarkovsky-haunted journey into Chernobyl’s “Exclusion Zone” in order to recover part of a fairground ride to turn into Plan C, 2010. Bringing part of the ride to life in a place where people can enjoy it is an effective and resonant symbolic resolution of the kind that art more than any other mode of human endeavor can provide.

0100101110101101.ORG’s work presented physically has more than enough presence to fill the gallery and benefits from the space and the considered curation afforded it here. Some of the work is more physical than virtual and vice versa, sometimes the ethics of the work place 0100101110101101.ORG as the villain sometimes as the victim, and sometimes the work is performance whereas other times it is assemblage. I mention this to point out both the strong themes to the work and how individual the effect of each piece is.
Net art in the gallery might seem a category error, like museum postal art. Or it might seem a commodity, like auctions of land art documentation. But net art is transitioning from being the contact language of artworld emigrants learning the net’s protocols to the contact language of net emigrants learning artworld protocols. 0100101110101101.ORG have made art of these encounters from the start, and have always been as at home in the gallery as on the net.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
There’s a splendid exhibition currently on at Manchester’s Cornerhouse. Entitled Subversion, it presents a selection of artworks, a good number of which are moving image pieces, from various artists who are united by a strong connection to the Arabic speaking world. We’re already in loaded territory, for all sorts of obvious reasons. Those reasons could give rise to a long discussion which I’m not going to approach directly here, instead simply quoting a programmatic statement from Glaswegian Egyptian-Turkish writer Omar Kholeif, the show’s curator:
‘Like many of the artists I was looking at, I felt that collectively curators and writers associated with the politically unstable Arab world were being asked to step up and perform to an identity that the world wanted us to play. With Subversion my aim was to do just the opposite. I worked with artists who referenced this very language but who wanted to dissent, poke fun, critique and re-define themselves as artists of the imagination, and not of any specific social or political condition.’
And, in case you’re wondering, he succeeds richly in this aim and, I think, more.
If you can get to Manchester with at least a couple of hours to spare before 5th June your life will be enriched thereby.
I’ve already written a short piece on the show, with a couple of video clips, on DVblog and I’ll be writing a longer review, including consideration of some of the thornier question alluded to above, for MIRAJ 4, out in June 2013.
What I’d like to do here is to look in some detail at one particular piece from the show, a short video by Khaled Hafez. I don’t mean to suggest that it is somehow best in show although I do love it – the show is too diverse for that kind of simple-mindedness. I do think a careful examination of it will yield support for Kholeif’s position. What we have here is a complex work of art, which bears repeated viewing, which doesn’t bend or break but thrives under that hard scrutiny and which, although inevitably stamped with the experiences, background, the moment in time, the physical location of its creator – what isn’t! – is universal (Problematic term! Of course we can’t know what 100 years will make of it but we can assert its current universality and adduce evidence that it is a work which promises to be of some long-term interest too.)
Hafez is probably better known as a painter of striking mash-ups of ancient Egyptian gods, comic book heroes, bodybuilders and models set against richly textured, feverishly beautiful and largely non-perspectival landscapes of the imagination. His paintings are characterised not only by this content (and of course what we lose in a run down of content is the aftermath of the act of painting, facture’s narrative, the play of line, geometry and colour. I’ve seen none of his pieces ‘in the paint’ but I’d bet money they’re good enough to eat.)
Furthermore, series, numbers, line-ups, multiples and queues of those Gods, comic book figures, bodybuilders and hybrids thereof seem to be important to him (and I don’t think I’m wrong in perceiving an echo of hieroglyphs and their implied grid and of pre-Arabic Egyptian art too).
There’s a strong sense of directionality and of motion arising from these lines and groupings and even if one knew none of the background it wouldn’t be surprising to learn of Hafez’s deep interest in moving image.
OK – to the piece itself. Let’s stay zoomed-out for a while and point out first that it was made in 2009, two years prior to the revolution which brought down Hosni Mubarak, exemplifying the ‘storm petrel’ effect whereby artists, who can often be infuriatingly ditzy as politicos, nonetheless, in virtue of their trade – their looking, their seeing, their empathy, empathy often of a strangely disinterested variety except for the can-I-make-art-from-it question, which question perhaps even makes their antennae the sharper, their sensitivity to society’s emotional weather, their readiness to make apparently random or intuitive connections – can be uncannily prescient about impending social change. Artists often ‘get it’ before the key actors begin to have the confidence to move.
So, you need to know that the piece contains so much reference to social conflict that, at first sight, to the outsider at least, it could have been made in the last year.
We start in darkness. Titles: “Anubis productions presents”. A number of soundtracks sewn together in a kind of faux short wave radio polyphony which resolves to a solo piano playing something doomily romantic which I don’t recognise (on subsequent listening it appears to be of a piece with the up-tempo stuff that follows, so I assume it’s especially composed). Over this we hear an extract from the resignation speech given by General Gamal Abdel Nasser in the immediate aftermath of the defeat in the six day war against Israel in June 1967. (He resigned for a day, coming back to office surfing a wave of popular support and grief and then ruling until his death in 1970).
I presume that to quote Nasser is a potent gesture in Egypt. I assume, despite any criticisms anyone might make of him he carries a ‘father of the nation’ type weight and that an allegorical comparison between him and Mubarak would come naturally – here is a flawed but somehow heroic figure, indubitably at the least a genuine anti-imperialist – offering his resignation, but, now, in stark contrast, his pale epigone, his inheritor as dictator but not as hero, clings grimly on by force and brutality and mired in sleaze.
The audio continues and we see more titles:
“The A77A Project (On Presidents and Superheroes)”
Hmm – presidents. In the plural.
Also: you don’t strictly need to know this, but it was gleefully explained to me by the artist that A77A is Egyptian blogger ‘slang’ in that it represents Arabic characters difficult to transliterate directly to Roman for the Arabic word for ‘Fuck’. Of which more soon.
The next thing we see is a detail of the lower centre of a painting by Hafez from the previous year, “Outside Temples”. We focus in on three figures seen in profile. They are almost identical except that whereas the two outer ones have the jackal heads of Anubis the central one wears… a Batman mask. They stand in profile, in body builder pose, right arms raised above and in front of the head forming a sinuous S curve to mirroring left arms behind the lower back.
We zoom into these figures as music changes to a metronomically regular disco drum and cymbal rhythm and the two rightmost figures ‘detach’ themselves from their background and walk forward out of frame to the right.
This detaching happens five times – series in time as well as space.
Three sets only of the figures then parade past us with the arms that had been set in the raised arm pose pumping up and down (crudely animated by pivoting at the shoulder, a similar device setting the legs in motion) in what I surmise is an offensive gesture. It is certainly charged with a raw and vulgar vigour. At this point the figures march against a plain white field – slowing the piece down reveals stray blocks of pixels generated in the animation process. This lack of polish, the retention of rougher edges, feels like a Brechtian distancing. It certainly helped to sharpen my attention as well as endowing the piece with a kind of elephantine grace.
We move to a landscape, I’m guessing a poorer or outlying area of Cairo, with a building site before us. Two of the figures continue their rightwards motion across the frame. They loom large against the background and even allowing for distance, dwarf the human figures behind them. Interestingly the background imagery appears to have been shot from a vehicle moving across the frame to the left, which further cranks up the energy level.
We cut to a 3D software generated mannequin walking in the same direction in a similar landscape. The two painted figures catch up and merge with it – by the somewhat clunky use of a split screen – giving birth to a single Anubis headed mannequin who is our protagonist for the rest of the piece.
The figure continues into a landscape dominated by a still of the Sphinx of Giza, ( Abū al Hūl, in Arabic, translating into English as The Terrifying One) which, in a move straight from Terry Gilliam, picks up the next words of the Nasser speech, ‘mouthing’ with a detached and hinged lower jaw . In the background, the ‘sky’ – in fact simply the background where the image has been cut out in Photoshop – cycles through various colours from a fierce red through multiple greys to black. As you might have surmised realism is not the key term here… except…except …there is a kind of higher realism going on… A pastiche of the stuttering effect so overused in popular music in the early days of sampling is applied to the ends of words in the speech – and here, in Nasser’s Arabic translated as ‘I decided to step down’, the bloggers’ A77A appears, repeated and repeated, a splendidly childish and satisfying equivalent to shouting ‘Fuck! Fuck! Fuck! Fuck! Fuck! Fuck! Fuck! Fuck!’
From now to the end every background image is a still and our Anubis – visitor from another realm, mostly an observer, bemused God in a world gone insane, who intervenes only once and then as a kind of trickster, stepping backwards to change a banner in English reading “Presidential Elections” to “Presidential Erections” ( and then the Arabic banner too – Hafez told me that, strangely, a small change will accomplish precsely the same transformation in both languages) but who pauses politely to allow a photographer to snap five women with cheesy shutter noise and all – processes inexorably rightwards through a number of frames of varying character: some, surreal collage: a man on a bike with a wheelbarrow on his head; some whose strangeness arises from a sophisticated deployment of the warped perspective arising from the lo-fi animation technique – another man-on-bike whose movement at an apparent 70 degrees ‘through’ the frame emphatically underlines the constructed nature of what we are watching followed by a subtle but delicious section where the background image is smaller than full frame size and Anubis steps decorously up into and then down out of it; some, more serious – confrontations between demonstrators and riot police, with the arm-pivot device once again deployed to enable a middle aged women make our putative vulgar gesture repeatedly to the cops.
Anubis finally vanishes into what I take to be a polling booth.
This is such a rich work. It is both enormously local and particular and at the same time hugely general. It is full of ‘content’ but at the same time driven by smart, knowing and dextrously deployed formal devices, which reside not in the background but near to the surface and greatly add to the pleasures of the piece, which presents weighty and serious matters, but does so with great geniality, a geniality and humanity I for one wish to firmly identify with the awakening oppressed as they genially, but definitively and unsentimentally, sweep aside and settle accounts with their former oppressors.
—–
This review is a collaboration between Furtherfield and DVBlog.
Watch the film on the DVBlog website

Featured image: Artist Suguru Goto discusses his work.
London 2012: there is of course one event which springs to mind when we think about this city and the year we’re in, but there is also another significant event happening in London right now, one which is very important for the digital and media arts world. It is the year that Watermans Arts Centre is holding the International Festival of Digital Art 2012.
As well as showcasing an array of digital art by internationally renowned artists, the programme also offers the opportunity for members of the public to get involved in discussions around themes that the Festival touches on through the seminar series accompanying the shows. These are in collaboration with Goldsmiths, University of London. Nearly three months in, the Festival has launched two exciting shows,Cymatics by Suguru Goto and UNITY by One-Room Shack Collective.
The first show, Cymatics, is a kinetic sound and sculpture installation that expresses Goto’s vision of nature. To enter it, the audience step through a door into a boxed, dark room within which they are presented with a touch screen interface, a shallow metal tank holding water and a screen showing a video feed of the water in the tank. The piece invites the audience to move the water in the tank by manipulating sound waves via an interactive screen. The result of the interaction is a stunning variety of geometric shapes, demonstrating the distortion that sound waves can have on a substance. This occurrence reveals the bridge between technology and nature, which fits into Goto’s re-occurring theme within his work of the relationship between man and machine.
The seminar which coincided with the show, Interactivity and Audience Engagement, was chaired by Régine Debatty and featured on the panel Tine Bech, Graeme Crowley and Tom Keene, all who which explore audience engagement in different ways within their work. Tine Bech is a visual artist and researcher whose installations invite audiences to engage in playful interactions, from chasing a motion reactive spotlight in Catch Me Nowto sound triggering shoes in Mememe. Tom Keene is an artist technologist whose focus intersects participation, communication and technology. His work is multidisciplinary, investigating the way we communicate, mediated by technology. His practice is diverse, from exploring the potential relationships between networked everyday objects in Aristotles Office to inviting a community to comment on their local issues through signs in Sign X Here. Graeme Crowley is a designer and artist who has created installations for prominent public areas, including The Wall of Light, commissioned by Arrowcroft Plc for the centre of Coventry and Spiral/Bloom commissioned for a hospital in Rochford by the NHS.
I found the juxtaposition of these three practitioners very interesting as each of them explore the interaction between audience and technology in varying ways. Bech’s work is very tactile and sculptural, almost making people forget the technology behind it. She likes to look at technology as something we can mould and which can be used to explore the wider issues which art can bring up, rather than just focussing on the tech itself and how ‘shiny’ (to use her own term) it is. In contrast to this, within Keene’s practice technology feels very prominent, visually as well as conceptually. Crowley’s focus is different again as it mostly operates within the commercial sphere. It therefore is produced for greater public consumption and needs to withstand being a permanent exhibit, becoming part of the architecture it is planted on rather than something which is temporary. The talks given by each panel member and discussions which accompanied them were all diverse and brought up interesting points around the idea of audience engagement and interactivity. Members of the audience entered into these discussions with ease, creating an open dialogue which itself was participatory and engaging.
UNITY, by One Room Shack is the current exhibit as part of the International Festival of Digital Art 2012, bringing a piece of work to the gallery which aims to embody the Olympic spirit, visually as well as conceptually.
Design for Unity
The installation takes the form of a transparent maze, angular in its structure and illuminated with different coloured LED lights in each section. Each illuminated section of the structure forms a different letter, all together spelling the word ‘unity’. As the audience navigate their way through the installation, their movement is picked up by motion sensors, triggering the LEDs at each point to turn on. These each represent a particular colour of the Olympic rings.
The ideologies of the Olympic Games linked with an immersive space explores the value of ‘being together’, something which the African humanist philosophy Ubuntu also speaks about.
UNITY is effective in exploring the theoretical concepts embedded within it through a playful and simple interactive structure. As an individual you step from section to section with the different groups of LEDs individually illuminating you as you go through the work. When a group of people interact with the piece at the same time however, the piece lights up as a whole, echoing the values of being together that UNITY invites us to explore. It is through enabling this experience, that the work celebrates and explores human connections.
I do find it interesting how the piece has such a strong stance towards the more idealistic ideologies of the Olympics, especially when taking into account the anti Olympics sentiment present in London. The event does bring people together, but unfortunately as we’ve seen in East London and also at previous Olympic locations across the globe, they also have the ability to put local communities at risk through rising rents and eviction [1]. UNITY looks at ‘…understanding the implication of UNITY on humanism in a neo-liberal world where hyper-capitalism and love of excess trump compassion and selflessness.’ [2] but in reality, the Olympics have unfortunately become something which arguably embody these traits. This said, I do think that UNITY is an incredibly beautiful piece in its visual execution and that its interaction compliments the theoretical idea which it is looking to address.
I look forward to the remainder of the International Festival of Digital Art 2012 and the eclectic ideas within media and digital art which the programme explores. I interviewed Irini Papadimitriou, Head of New Media Arts Development at Watermans, about the Festival:
Emilie Giles: First of all, can you tell us what the premise is behind the International Festival of Digital Art 2012?
Irini Papadimitriou: The idea behind the Festival started from a decision to develop a series of shows that could form a discussion rather than being one-off exhibitions and help engage more people in the programme. In the last year we have been focusing more in participatory and/or interactive installations so I thought it’d be interesting to dedicate this project and discussions in exploring more ideas behind media artworks that invite audience engagement as a way of understanding our work in the past year.
Since this was going to take place in 2012 we felt it would be necessary to open this up to international artists so this is how the open call for submissions came up last year. We received so many great proposals it’s been very hard to reach the final selection, but at the same time the opportunity of having a year-long festival meant we could involve as many people as possible and hear many voices not only through the exhibitions (this is just one part of the Festival) but also with other parallel events such as the discussions, presentations of work in progress by younger artists and students, the publication, a Dorkboat (coming up in June with Alan Turing celebrations), as well as collaborations with other organisations or artists’ networks and online.
EG: Touching on your last answer, the Festival has a clear aim then to engage people in discussion rather than just being viewers of a show. Do you think that within media and digital art there is a particular need for this approach?
IP: I think that hearing people’s thoughts and responses and enabling discussion is important for all exhibitions and art events but specifically for the Festival (since the aim is to question & explore audience participation). It was very relevant to hear ideas and views from other artists, technologists, practitioners etc but also audiences, rather than just the participating artists.
Also, and this is my view, I think as media and digital art use technologies that many of us are not particularly familiar with or if we use technologies it will be most probably as consumers, it’s important to talk about and discuss the process (as well as impact of technologies) both for the artists as well as for audiences.
EG: The themes chosen for the programme are diverse and each relevant to media and digital art in their own way. What are the reasons for each focus and why?
IP: The themes explored in the Festival result mainly from the selected proposals and discussions with the artists. There were so many things to talk about so having these themes was a way to start from somewhere and help understand better the installations shown throughout the year. The seminars that we are organising are an opportunity for the artists to talk about their work and share their ideas with both audiences but also with other artists invited to take part in the panels. It is also a way of discussing these themes and presenting other work that raises similar issues. The seminars are shaped around the themes such as perception and magic in digital art, sound and gesture, geographies, virtual spaces as artistic mediums and of course participation and interaction. We are currently working on a publication with Leonardo Electronic Almanac which will be coming out in the next couple of months and will include essays from artists, academics and students as well as interviews with the artists behind the selected proposals. Again the catalogue has the Festival themes as a starting point but we tried to combine different content and ways of communicating these.
EG: How do the pieces featured in the exhibition question audience engagement, participation and accessibility ?
IP: The artists presenting work are exploring participation and audience engagement in different ways and I think we will have also interesting outcomes from the seminars and the publication which will allow us to explore these ideas further.
In the current installation, UNITY, One Room Shack collective are using the playful structure of a maze (in the form of the word UNITY with each letter lighting up in the colours of the Olympic rings) inviting people to walk inside to reflect and draw upon the complex nature of human reality and ‘difficult’ aspects of human existence.
Michele Barker and Anna Munster who will be showing HokusPokus later on are interested in exploring how we perceive actively in relation to our environment, how we see, what we see and how this makes us ‘interact’. HokusPokus inspired from neuroscience examines illusionistic and performative aspects of magic to explore human perception, movement and senses. The tricks shown in HokusPokus have not been digitally manipulated; they will unfold temporally and spatially, amplifying and intensifying aspects of close-up magic such as the flourish and sleight of hand.
The Festival will close with an installation by American artist Joseph Farbrook, Strata-Caster, which was created in Second Life mirroring the physical world, exploring positions of power, ownership, identity and drawing parallels between virtual and physical worlds. An interesting and important part of the installation is the use of a wheelchair by visitors to enter and navigate Strata-Caster.
EG: How have the 2012 Olympic and Paralympic Games inspired the Watermans International Festival of Digital Art?
IP: As we are trying to explore what participation is we thought it would be an interesting link (rather than inspiration) between the Festival and the Games/Cultural Olympiad since they are meant to symbolise, promote and inspire values like creativity, collaboration, participation, engagement etc. The Festival isn’t about the Olympics and participating artists didn’t have to propose work that linked to the Games, but we did receive many proposals that reflected on the Games, what they represent and the meaning of participation, so some of these proposals are being shown as part of the Festival, such as One Room Shack’s UNITY and Gail Pearce’s Going with the Flow.
It’s a bizarre thing when you stumble upon the “new art movement” filtering through discursive chatter. Is it actually a movement, or is it simply a bunch of like-minded individuals telling me its a movement?
Behold The New Aesthetic then – a new art meme in visual culture whimsically constructed by James Bridle, which manifests itself in a Tumblr blog, a presentation for Web Directions South, Sydney and an original blog post. Recent attention to it has reached feverish proportions coming off the back of a SXSW panel in March and a generally positive endorsement by Bruce Sterling in Wired, plus some group responses on the creators project. More recently, the computational media scholar and philosopher Ian Bogost has posted his own thoughts for The Atlantic.

As a meme should do, “the New Aesthetic” has fulfilled its role – it has a lot of people talking about it. Like any meme which dices visual culture with some sort of research element, it has artists, writers, even media and aesthetic scholars measuring their own opinions on it in rank order without anyone knowing exactly where it’s going, what it really is or who exactly is doing it. In our noisy and crowded “I can’t believe I got 50+ retweets” over-networked epoch, this is quite an achievement even if you don’t take it that seriously.
But here’s the question: can the new aesthetic be more than a meme? More to the point, does it want to be? Is it capable of a direction? Can it be serious?
That said (and as Bridle avers) this isn’t really a prominent “movement” of ideas as such. Neither does it present material which it would deem ‘arty’. Instead, it’s an extremely broad and oblique orientation which seeks to document the subtle (and sometimes explicit) changes within our information saturated existence. It simply contextualises the contingent manifestations of computational activity, and how they are reversing and revising computational and human activities back in on themselves. Bridle’s tumblr simply presents the new aesthetic for what it is, much akin to perusing through pictures in a Facebook profile, a Reddit top ten list or clicking on Stumbleupon – simple snapshots of “stuff” which echo a blurring between the world of networks, machines and everything outside of it (with a particular emphasis on where it goes a bit wrong, hence a certain infatuation with glitchyness). Quoting Bridle’s Tumblr page;

“It is a series of artefacts of the heterogeneous network, which recognises differences, the gaps in our overlapping but distant realities.”
In another video presentation ‘We fell in love in a coded space‘ at Lift12, Bridle terms this ‘network realism’ – instances where the amalgamation of computational networked activity blurs with non-computational activity, to such an extent that it reduces any observer to nothing but a curious, passive node, gleefully whittling through instances of vaguely creative stuff. For Bridle, this occurs not just in industry but also architecture, finance, storage, fashion and now an attempt at aesthetic understanding. It’s an infatuation with the alterity of bots, algorithms, pixels and realised fictions. In this presentation however, Bridle is largely concerned with how one can respond or understand the ‘desires’ of bots, unaware that anthropomorphising the situation may not reap the rewards required. In this interpretation the new aesthetic is charged with the task of asking how we can think and orient ourselves computationally, whether it be designers, thinkers, writers, scholars or artists.
Sterling himself, mostly issues praise with a pinch of amusing impatience, as if the New Aesthetic movement should progress faster than it actually is doing, with more ideas and more focus. Kyle Chayka states that artists are already embracing it as a ‘contextual seedbed, rather than a label’. Jonathan Minard understands it as a new method of reflection concerning cultural tool-making, where the ‘dumb tools’ of machinic interface scream images back at us.

Digital Humanities scholar David Berry has blogged a similar view echoing that the new aesthetic is tapping into what he calls ‘Computationality’, a historical paradigm frame-making of sorts, which constructs specific meaning-making practices. Visualisation revolves around processes and patterns and so the list making exercise of Bridles’s Tumblr blog would seem apt in this regard, as it issues unparalleled amounts of pattern making not just as content, but as form. The archive is a jamboree of other pattern recognising events; security face recognition, retro 8bit encapsulation, satellite visuals and generally messing about with an Xbox 360 Kinect. James George mentions something similar but suggests that the new aesthetic should question the critical distance between artistic activity and technological use. It resembles a massive screen dump from a digital artist’s delicious account. Quoting Bridle again in an interview with The Design Observer Group;
“The New Aesthetic is not criticism, but an exploration; not a plea for change, rather a series of reference points to the change that is occurring. An attempt to understand not only the ways in which technology shapes the things we make, but the way we see and understand them.”
To most of the established readers here, it’s easy to criticise the “newness” of the New Aesthetic, in the same way the 90’s trope “New Media” has been quickly bundled away as if it never existed (Marius Watz makes this point). For those of you who have been studying such issues concerning hacking, play, enumeration, collecting, remixing, glitch-ing, (see Rosa Menkman in particular) in the broader realm of the computational arts, there really isn’t anything novel to gawk at: this is more of a rearrange or a rebadge. Indeed, internet discussion has been rife with such criticism, from the triteness of using Tumblr as the ‘official site’, to quick dismissals concerning the New Aesthetic’s distinct lack of any historically serious ‘substantial practice’ – not that it wanted it in the first place (Indeed it’s a pity that it has contingently replaced an identical term for a movement unrelated to Bridle’s own, coined by arts writer Michael Paraskos and realist artist Clive Head. Moreover, depending on how one looks at it, Paraskos and Head’s own movement has similar views espoused by Bridle’s version, including perhaps a direct opposition to conceptualism and foregrounding art as a material practice).
If Bridle were not so sincere about the whole affair, one would be mistaken that this was a too-cool-for-school strategy straight out of a Nathan Barley episode. But thats an easy misread. As Bogost states, Bridle is just curious about the weirdness of the network we all rely on and revel in. But there is a point where fascination with creativity turns into ADHD. The New Aesthetics tumblr site, already does just that, without any hint of standing still. “What’s going to come next? What can we do next? What are the limitations? What happens if I click that? What is that doing there?”
However both Bogost and Greg Borenstein issue a different view about the new aesthetic. They both discuss it in relation to a recent trend in philosophy called Object Oriented Ontology (OOO), a movement to which I am extremely sympathetic to. Bogost explains OOO succinctly enough;
“If ontology is the philosophical study of existence, then object-oriented ontology puts things at the center of being. We humans are elements, but not the sole elements of philosophical interest. OOO contends that nothing has special status, but that everything exists equally–plumbers, cotton, bonobos, DVD players, and sandstone, for example. OOO steers a path between scientific naturalism and social relativism, drawing attention to things at all scales and pondering their nature and relations with one another as much as ourselves.”
The link to OOO is fairly self-evident. If one of the most prominent aspects of the new aesthetic is an obsession with how a machine “sees” the world, OOO is a commitment to the seeing of things in widest possible sense. But while Borenstein generally aligns OOO to the new aesthetic with exuberant equivalence, Bogost’s view is one of general optimism, but not broad acceptance. For a start, the new aesthetics is based on a continual divide and repair between two opposing realms; the physical and the digital, each coming together and breaking apart endlessly, like throwing a box of magnets.
One of the main stipulations of being an OOO advocate is the realist eruption of what counts as a thing, and how that thing contingently relates to different types of entities. This is why Bogost decenters computation in the new aesthetic, and emphasises the multitude of things that escape the physical/digital divide. Their adventures are always-already strewn across the ontological landscape. One of the other main stipulations involves us lacking secure knowledge in fully understanding discrete units on their own terms – we can never experience their being in the same way we experience our being.

If one has read Bogost’s latest publication, Alien Phenomenology (and if you haven’t, I’d urge you to do so immediately), one would understand Bogost’s view that the new aesthetics misses out not just speculating on the hidden lives of objects other than computers and humans, but it also hovers on the inescapable problem of anthropomorphising machines and objects to within an inch of their lives. The alien aesthetics challenge is provocative.
“[T]his Alien Aesthetics would not try to satisfy our human drive for art and design, but to fashion design fictions that speculate about the aesthetic judgments of objects. If computers write manifestos, if Sun Chips make art for Doritos, if bamboo mocks the bad taste of other grasses–what do these things look like? Or for that matter, when toaster pastries convene conferences or write essays about aesthetics, what do they say, and how do they say it?”
There is an interesting discussion to be had in OOO about the usefulness of anthropomorphising the infinitesimal non-human relationships between the properties of things. Whilst others (including Bogost) see it as an inevitable factor of being one finite human entity amongst a crowd of other finite entities, I see it as a hinderance.
In particular, I’m interested in the way the new aesthetic never manages to access computation ‘just’ as it is. It only takes computation seriously when it functions as a qualitatively intelligent system, which meets or surpasses rational intelligence, or, it directly flips into “dumb tools” of (mis)communicative manipulation for the whims of human mental acts.
But I digress. Last year Bridle released a book called “Where the F**k Was I?”, which accurately sums up the mentality of the movement. The really interesting element of the new aesthetic is that it presents genuinely interesting stuff, but Bridle’s delivery strategy is set to ‘gushing disorientation’. At present, it’s the victim of the compulsive insular network it feeds off from. It presents little engagement with the works themselves instead favouring bombardment and distraction. Under these terms, aesthetics only leads to a banal drudgery, where everything melts together into a depthless disco. Any depth to the works themselves are forgotten.
Memes require instant satisfaction. Art requires depth.
The Glitch Moment(um)
Rosa Menkman
Institute Of Network Cultures, 2011
ISBN 9789081602167
Rosa Menkman’s book “The Glitch Moment(um)” is a comprehensive study of the theory, practice and social context of contemporary digital Glitch Art. Glitch Art is similar to the ironisation of the noise of old media into cultural signals seen in Trip Hop and that is the basis for the nostalgic image-making of Lomography or Instagram. But it is based on current digital technology, rather than past analogue technology.
Glitch Art is growing in popularity and critical attention, and is already being recuperated by the mass media (for example in a recent Calvin Klein perfume television advertisement). Analogue glitches have been part of art and popular culture for decades, for example in Nam June Paik’s television-based art or the titular character of the cyberpunk TV show “Max Headroom”. Digital glitches and their simulation featured in the postmodern graphic design of the early 1990s created by groups such as Designers’ Republic. But between a history of analogue media and a future of mass media recuperation there is the current Moment(um) of digital glitch aesthetics that Menkman identifies.
Menkman begins by explaining the basics of Shannon/Weaver information theory as the basis for a theory of what glitches are. In information theory, messages are sent as a signal from a transmitter to a receiver over a channel which is disrupted by a source of noise. This “noise” is the crackle on analogue telephones or on vinyl records, the static on analogue TV and radio, and the corruption that sometimes affects digital images or audio streams (nowadays notably Skype chats).
Where kinds of noise are associated with a particular we can recognise them as particular “noise artifacts”. We can also recognise compression artefacts in digital media such as those seen in over-compressed lossy image and video files (JPEG and MPEG artefacts). These noise and compression artifacts are experienced by the users of communication media as glitches. Menkman describes these phenomena in detail, providing the reader with a firm foundation in the sources and expression of Glitch phenomena.
How artists can deliberately create these phenomena is the subject of the next section of the book. Titled “A Vernacular Of File formats” it is a condensed adaptation of Menkman’s 2010 artwork of the same name. It is a thorough and accessible resource for both understanding the production of and creating visual glitch aesthetics. Each picture demonstrates a technique for modifying the data of an image file format so that a computer can still parse and render the file but it will appear corrupted to a human viewer. Starting with an uncorrupted (but unnervingly contrasty) “RAW” image, Menkman explains the production and principles of corrupted digital images in sufficient detail that the reader can recreate and build on these techniques themself, or use this knowledge as the basis for understanding and appreciating the work involved in the Glitch Art produced by others.

The next two chapters cover the phenomenology and philosophy of Glitch. The theories of Paul Virilio and Alan Liu are usefully deployed here to give Glitch a philosophical grounding. But there is also a recognition that Glitch is an inherently open concept that is difficult to define. Menkman rightly considers the work of Beflix (Ant Scott) as a leading Glitch Art figure. The diversity of Beflix’s work illustrates the problem with categorizing Glitch neatly, or at all. 5VOLTCORE, JODI, and others provide alternative views of what Glitch can be. This builds to Menkman defining “Glitchspeak” as the vernacular, or in possibly the creole, of Glitch Art.
In “From Artifact To Commodity”, Menkman turns to Glitch aesthetics in music, particularly the glitches created through circuitbending, and the precedent this has set for the creation of standardized tools for glitching visual media. As such tools have been created for images, Glitch aesthetics have found their way into the artistic mainstream and into music videos and other mass media. Glitch may be impossible to categorize but it is all too easy to commodify. This marks its emergence as a genre, and Menkman finishes this section by considering Glitch as a recognizable but still problematic genre that relies heavily on spectators’ technical, aesthetic and theoretic literacy.
Having given the reader a solid grounding in the theory, practice and philosophy of Glitch, Menkman finally moves on to its sociology. Using a tool that looks like Gephi but isn’t (Issuecrawler), Menkman models the social network of relationships between Glitch artists that exist on the Internet. Clustering blogs and other Internet expressions by the number of links between them allows the tools of social network analysis to be used, revealing who is central to the Glitch artworld as judged by the clicks of their peers.

Finally Menkman sums up Glitch aesthetics in a section called “The Emancipation of Dissonance Glitch”. Starting with a quote from Jackson Pollock:
“I don’t use the accident. I deny the accident. There is no accident, just as there is no beginning and no end.”
Menkman concludes that “Like the best ideas, glitch practices are dangerous because they generate awareness”. By which point the reader is perfectly placed to understand just how and what kind of awareness Glitch generates, and how they can appreciate or produce Glitch art themselves.
Glitch Art has been long overdue serious critical attention. I cannot remember the last time I read a book that so thoroughly and concisely presented the theory and practice of a contemporary art movement in as does “The Glitch Moment(um)”.
You can download a PDF or order a print copy here
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
DoggieWoggiez! PoochieWoochiez! is a new video work (2012) by Everything is Terrible!, a self-described “found footage chop shoppe”. DoggieWoggiez! PoochieWoochiez! is an active catalog which describes, invents and destroys concepts as it arranges video footage into flows of multiple cuts that map the use of dogs in cinema and television. The structure of this review takes hints from the work it overlays. We dispensed with “original” writing and didactic detailing of what we as critics experienced. Instead, we unraveled multiple threads left hanging after watching DoggieWoggiez! PoochieWoochiez! We neglected to offer an appraisal of the worth of the work, and add to the number of words already in the world. Instead, we traced the flows passing through the video and developed a program of citations that provide a map of exit and entrance points-a map, as any map, that is as much about those making as about the territory described-which we hope will provide openings for a reader who has not yet watched the work, and provide expanded intersections for those who already have.
“This is the scenario: You are terminally ill, all medical treatments acceptable to you have been exhausted, and the suffering in its different forms is unbearable. Because the illness is serious, you recognize that your life is drawing to a close. Euthanasia comes to mind as a way of release.” 1
“Success consists of simply getting up one more time than you fall.” 2
“From whatever angle you approach it, the present offers no way out. This is not the least of its virtues. From those who seek hope above all, it tears away every firm ground. Those who claim to have solutions are contradicted almost immediately. Everyone agrees that things can only get worse. ” 3
“A positive anything is better than a negative nothing.” 4
“I think it’s because dog movies and dog footage tends to be the dumbest. It’s like the lowest common denominator amongst everything we’ve found, the most mediocre footage imaginable. I think that was a big motivator, and we just like dogs. It’s a nicer way to deliver horrible things about humanity. Instead of watching people be racist, which makes you feel terrible, you get to watch dogs be racist, and you’re like, ‘That’s a little better.'” 5
“Americans spent $50.96 billion on their pets in 2011. That’s an all-time high, and for the first time in history more than $50 billion has gone to dogs, cats, canaries, guppies and the like, the American Pet Products Association reports. Food and vet costs accounted for about 65 percent of the spending. But it was a service category one that includes grooming, boarding, pet hotels, pet-sitting and day care that grew more than any other, surging 7.9 percent from $3.51 billion in 2010 to $3.79 billion in 2011.” 6
“So we have a corpse on our backs, but we won’t be able to rid ourselves of it just like that. Nothing is to be expected from the end of civilization, from its clinical death. In and of itself, it can only be of interest to historians. It’s a fact, and it must be translated into a decision. Facts can be conjured away, but decision is political. To decide on the death of civilization, then to work out how it will happen: only decision will rid us of the corpse.” 7
2:39 . Black and white footage of a clothed dog sleeping in hay.
2:41 . Saint Bernard laying on the floor trying to drink champagne out of a bottle.
2:42 . Black and white footage of a dog holding a bottle labeled “Hard Cider” in his mouth and drinking.
2:43 . Dog with bandana sitting at table licking the foam from a beer.
A hand pouring beer into a dish filled with dog food.
2:44 . A club. Multiple young women filling the face of a puppet dog full of liquor bottles.
2:45 . A dog wearing a jersey with the number one peeing on a referee’s ankle.
2:47 . A dog lifting its leg on a pants suit leg.
A bulldog in a spiked collar peeing on a floor mat that says “I [heart] Acting.”
2:48 . A dog peeing on a metal catwalk, shot from below.
2:49 . Jack Nicholson holds a small dog up and away from his chest as the dog pees.
A man lying on a floor is shot below and through a dogs legs, the dog’s urine stream is hitting him in the face.
2:51 . A similar shot, reversed. Another man, wearing a fur hat, is buried to his neck in sand and ice. A dog urinates into his mouth.
2:51 . The same bulldog in spiked collar lifts his leg to pee. A small rocket comes out of from beneath him.
2:52 . A similar shot from the other side, a different dog is urinating flames.
“I am for an art that embroils itself with the everyday crap & still comes out on top.” 8
“Trash collection is the business of public sanitation; its recycling, the very height of capitalist alchemy, turns everything into grist for commodification’s mill. But it is also a strategy of aesthetic sublimation that, according to Thomas Crow, is internal to modernism (he has analyzed the cyclical aspect of this in terms of the incorporation of the ‘low’ by the ‘high’)” 9
“Classification in the widest sense is, along with astronomy, probably one of the oldest scientific pursuits undertaken by man. In the most general terms classification is the process of giving names to a collection of objects which are thought to be similar to each other in some respect. The ability to sort similar things into categories is obviously a primitive one, since it would seem to be a prerequisite of the development of language, which consists of words which help us to recognize and discuss the diSerent types of events, objects and people we encounter; each noun in a language is a label used to describe a class of things which have striking features in common. Thus for example, we name animals as cats, dogs, or horses and such a name collects individuals into groups.” 10
“I am for an art that imitates the human, that is comic, if necessary, or violent, or whatever is.” 11
“What is it that moves over the body of a society? It is always flows, and a person is always a cutting off [coupure] of a flow. A person is always a point of departure for the production of a flow, a point of destination for the reception of a flow, a flow of any kind; or, better yet, an interception of many flows.” 12
“I am for the art of things lost or thrown away, coming home from school.” 13
“Cluster analysis, also called data segmentation, has a variety of goals. All relate to grouping or segmenting a collection of objects into subsets or “clusters,” such that those within each cluster are more closely related to one another than objects assigned to different clusters. An object can be described by a set of measurements, or by its relation to other objects.” 14
“And now, we have to start from scratch with this movie and go through thousands of VHS tapes and find those three minutes and put them in a pile until we have enough to make an hour-long movie. And yeah, it made it harder because we just fucking hate those movies.” 15
“Central to all of the goals of cluster analysis is the notion of the degree of similarity (or dissimilarity) between the individual objects being clustered. A clustering method attempts to group the objects based on the definition of similarity supplied to it.” 16
“[Claes Oldenburg] quickly saw that it didn’t take anything to make a Ray Gun: any right angle would suffice, even blunted, even barely perceptible. The Ray Gun is the ‘universal angle’: ‘Examples: Legs, Sevens, Pistols, Arms, Phalli-simple Ray Guns. Double Ray Guns: Cross, Airplanes. Absurd Ray Guns: Ice Cream Sodas. Complex Ray Guns: Chairs, Beds. Mondrian didn’t need to reduce everything to the right angle: everything is already a right angle. During the time of The Store, Oldenburg made huge numbers of Ray Guns (in plaster, in papier mache, in all kinds of materials in fact), but he soon saw that he didn’t even need to make them: the world is full of Ray Guns. All one has to do is stoop to gather them from the sidewalks (the Ray Gun is an essentially urban piece of trash: Oldenburg produced their anagram as Nug Yar:New York). Even better: he didn’t even need to collect them himself; he could ask his friends to bring them to him (he limited himself to accepting or refusing the find’s addition into the corpus, according to purely subjective criteria). Finally, there are all the Ray Guns one can’t move- splotches on the ground, holes in the wall, torn posters-but which one could photograph. The “inventory”is potentially infinite. And what should be done with this invasive tide? Put it in the museum.” 17
“I am for the art out of a doggy’s mouth, falling five stories from the roof.” 18
2:54 . A dog and man lay side-by-side. The dog’s legs are up and its belly is exposed to the camera. Voiceover: “Being a thief isn’t bad enough, you have to be a lush too.”
2:56 . A golden retriever puppy faces the camera with a drunken expression. The dogs lips move as he says “That’s the weirdestest grape juice ever.” He laughs.
3:02 . A dog jumps off a large desert rock onto another rock. He yells “Hasta la vista, kitty.” A mountain lion is shown launching into the air.
3:05 . Maniacal laughter is played over footage of a tree frog sitting on the top of a dog’s head.
3:06 . A Weimaraner sleeps under a blanket. Voiceover: “Do dogs dream? She dreams she’s a dear”
A ripple dissolve into the same dog with her head stuck through a tapestry of deer so that it appears that there is a deer with a dog head.
“Are there Oedipal animals with which one can ‘play Oedipus,’ play family, my little dog, my little cat, and then other animals by contrast draw us into an irresistible becoming? Or another hypothesis : Can the same animal taken up by two opposing functions and movements, depending on the case?” 19
“Writing about the dog who befriended him and his fellow-inmates in a concentration camp, and whom they named Bobby, Levinas says that this dog was ‘the last Kantian in Nazi Germany,’ because his joyful greetings reminded the prisoners of their human dignity. Yet, when questioned closely about the ethical status of nonhuman animals, Levinas is reluctant to ascribe to animals that ‘ethical face’ which he elsewhere has called (as Martin calls Sylvia’s face) ‘an epiphany.’ By contrast, says Levinas, the animal face is merely ‘biological,’ incapable of demanding the ethical response. Levinas denies that the dog can have a face in the ethical sense: ‘the phenomenon of the face is not in its purest form in the dog,’ he writes. ‘I cannot say at what moment you have the right to be called ‘face.’ The human face is completely different and only afterwards do we discover the face of the animal.’ In an article subtitled ‘Levinas Faces the Animal,’ Peter Steeves, with gentle irony, stages another face-to-face encounter between Levinas and Bobby, asking the philosopher: ‘What could Bobby be missing? Is his snout too pointy to constitute a face? Is his nose too wet? Do his ears hang low, do they wobble to and fro? How can this not be a face?'” 20
“We’ve always had a thing with how people treat little people at Everything Is Terrible!, like it’s really weird and creepy. Anybody who’s like a second-class being, when they’re used in videos, it comes across very creepy and gross. I think it’s the same thing with humans and dogs. They’re weirdly sexualized, they’re weirdly turned into little kids at the same time.” 21
“…individuated animals, family pets, sentimental, Oedipal animals each with its own petty history, ‘my’ cat, ‘my’ dog. These animals invite us to regress, draw us into a narcissistic contemplation, and they are the only kind of animal psychoanalysis understands, the better to discover a daddy, a mommy, a little brother behind them (when psychoanalysis talks about animals, animals learn to laugh): anyone who likes cats or dogs is a fool.” 22
“I think that’s a big reason why people use dogs the way they do, because I think we kind of hate ourselves so we dress up dogs like ourselves to mock ourselves. So you dress a dog up like a drunk human, and then you laugh at how ridiculous it is, but I think it’s therapeutic. We’re letting off steam about how much we hate ourselves.” 23
3:13 . A close-up of a shaggy dog who speaks. “It’s not a dream”.
3:16 . A large dog outside a car tells a small dog inside a car, “Bitches ain’t got no business being inside your head” The voice is or is similar to Samuel Jackson’s.
3:17 . A bloodhound with an ice pack on its head also has cartoon dream bubbles floating around it. The woman inside the bubbles says, brightly “Wake up!”
Another dog, turning his head to the camera, says “Who are those jokers?”
Return to the bloodhound, the floating woman says “It’s me, Jan.”
3:20 . A dog dressed as a pauper is grabbed from above and dragged to the side.
A dog wearing a bandana says “Great danes! This is terrible. But what can I do…”
This trails into a golden retriever saying “…I’m a dog.”

“What difference does it make if someone is terminal? We are all terminal.” 24
layla commented: 4-21-2008 9:01 PM “In 2007 Guillermo Vargas Habacuc a so called artist took an abandoned dog from the streets tied him to a very short rope to a wall in an art gallery and left a kettle of food on the other side of the room beyond his reach and left him there to slowly die of hunger and thirst. The socalled artist of such cruelty and the visitors of the gallery of art watched the agony of this animal. The dog finally died of famine surely after a painful absurd and incomprehensible torture. The prestigious Centralamerican Biennial of Art decided that this horrible act committed by this guy was art and Guillermo Vargas Habacuc has been invited to repeat his cruel actions in said Biennial in 2008. i seen this post on facebook and a few pictures of the poor innocent dog starving to death it broke my heart and i had to see if peta was aware of this sick man who thinks this i some great at creation.” 25
olivia commented: 5-10-2008 5:35 PM “i hate you. you should be put in the poor dog’s possision. you can’t imagine how many people hate you. almost more than a million. just so you know thats not art. the dog died because of you. you should go to prison because of this. you broke peoples’ hearts. i am really upset at you i could write all day long if i have to because you just waisted a life i wish i could waiste youres!!!!!! do you wish all the animals should die? you just made my day so so so horrible. im going to tell everyone what you just did. just so you know i’m cring. i hate hate hate hate you. you should be ashamed of your self. so listen to this just because you think your all that doesn’t mean that you can kill an other animal. i have 7 animals and you are not going to touch them! that dog did nothing to you. if heshe did doesn’t mean you should kill him! please don’t touch any other animal!!!!!! you suck!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! P.s i hate youuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuu” 26
Renate commented: 5-5-2008 1:34 PM “Here’s a thought let’s tie up Guillermo Vargas at one of his own exhibits and starve him to death!” 27
Rainie M commented: 4-28-2008 2:59 PM “Oh Gods! How can anyone be so bloody heartless? Dead or dying animals are NOT art…things like this only come from sick minds. Is the human race devolving so much that we have come down to this as entertainment? If you want Art go to a Museum . Geez this is just sick…” 28
Tucker commented: 4-26-2008 10:43 AM “THIS IS DOWN RIGHT UNCALLED FOR DIGUSTINGCRUEL AND THESE PEOPLE NEED TO BE LOCKED UP AND CHARGED BIG TIME!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! I AM CRYING SO HARD RIGHT NOW IT IS UNBELIEVABLE WHAT $IN PEOPLE DO TO ANIMALS AND THIS ALL NEEDS TO STOP NOW AND BIG TIME CHARGES AND JAIL TIME NEED TO BE STRONGER AND LONGER IN ALL STATES AND AROUND THE WORLD!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! SAVE THE ANIMALS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!” 29
Angie commented: 4-24-2008 12:55 PM “I am so sickend by this whole so called art.. I am a artist myself. ! And i think someone need to tie this guy up and not feed him any food and have people watch him starve . Then he will realize how it feels. He gives a bad name to other artist out there!” 30
yf commented: 4-22-2008 2:32 PM “you know he really shoudl have starved himself and then do a ‘selfportrait’.. much more apt.. silly stupid man.. so pointless.. so banal.. people KNOW what skeletal skin and bones animals look like .. we have seen them.. we know what skeletal starved humans look like too infact.. we dont’ need a dumb dimwit 12 brained idiot to INTENIONALLY starve a dog in ORDER to produce his pointless ‘artwork’.. what a dumb stupid peabrained twit !” 31
Kristin Gleeson commented: 4-22-2008 1:29 AM “Yeah I’ve seen something like this before but what was it? Oh yeah the HOLOCAUST. Thousands of people collected subdued and starved to death. Was that an artistic masterpiece? If you call this art you’d have to call Hitler an artist I mean after all he was trying to make a culturally altering statement as well. It’s not art it’s sadistic immoral and completely disgusting. This poor creature did not deserve this and neither does any other animal on the planet.” 32
“Do not imitate a dog, but make your organism enter into composition with something else in such a way that the particles emitted from the aggregate thus composed will be a canine as a function of the relation of movement and rest, or of molecular proximity, into which they enter.” 33
“Its efficiency is striking. There is nothing extra, superfluous or obscure about Mr. Kulik’s performance. For all intents and purposes, he is a dog: he can be scary and unpredictable and territorial. After all, he’s in his prime, about 5 dog years old; visitors who wish to enter his cage may do so one at a time and must put on the quilted overalls and arm-guards that hang near the chained and barred door to his cage.” 34
“The choice of the term ‘pack’ for this older and more limited kind of crowd is intended to remind us that it owes its origin among men to the example of animals, the pack of animals hunting together. Wolves, which man knew well and from whom many of the dogs he uses derive, had impressed him very early. Their occurrence as mythical animals among so many peoples, the conception of the were-wolf, the stories of men who, disguised as wolves, assailed and dismembered other men, the legend of children brought up as wolvesall these things and many others prove how close the wolf was to man.” 35
“Saying it would be too confusing, a judge has denied the petition of a so-called ‘furry’ to legally change his name to Boomer the Dog. Forty-four-year-old Green Tree resident Gary Guy Mathews says he filed for the name change in June because he’s a fan of a short-lived 1980s NBC television series called “Here’s Boomer,” which featured a dog that rescued people.” 36
Where’s Waldo, #1.5 – Sun Aug 15, 2010 10:31 PM EDT “This boy ain’t wired right. I’ve heard of men wanting to be a women and women wanting to be men but this is a new one on me. Mom and Dad must have raised the poor kid in a kennel instead of a crib. Wonder what his favorite pup food was? Of course maybe he’s smarter than any of us thinks……or maybe not.” 37
dave-735909, Thu Aug 12, 2010 10:21 AM EDT “Why can’t we just respect people’s constitutional right to be crazy?” 38
Susi-Oh, Thu Aug 12, 2010 12:10 PM EDT “My sentiments exactly but how far do you want to take this? Should we just let him bark back when you ask him a question? Can you introduce a guy like that with a straight face? He’s big for a dog and might scare little children. Actually, even without the name change he looks a bit scary.” 39
Janet A., #15 – Thu Aug 12, 2010 10:59 AM EDT “If this idiot was truly a dog, we’d put him to sleep for being insane. Just a thought.” 40
wchall1949, #2 – Thu Aug 12, 2010 10:15 AM EDT “OMG – the really frightening thing here is that this guy is allowed to marry & reproduce!!! Truly scary!! What a moron!!!” 41
Sues-343312, #2.1 – Thu Aug 12, 2010 11:22 AM EDT “Well he is 44 yrs old has managed to not procreate up to now. Let’s just hope he meets up with a spayed female” 42
3:26 . A close-up of a crying child, with a dissolve of snow over his face. He says “Daddy…”
Close up of an adult man, he says “I don’t have a daddy.”
A girl wears a party hat. Lying on her bed, she talks to her brother, also wearing a party hat. She says “I just miss him so much…”
Cut to a different girl in pigtails addressing a bloodhound wearing a king’s crown and fur cape. She says “I miss him too.”
3:30 . Close-up of a crying boy. “I miss him, mom.”
Angry-looking farmer standing under a tree. He says “Your mother passed on.”
3:32 . A woman lays on a bed with a girl. “…to join the angels.”
A man looks up to the sky and gestures upwards “She’s in heaven.”
A woman with a party hat “watching over you right now.”
3:37 . A boy addresses a dog. “My dad used to do that.”
A boy and his mother talk as she drives. The boy says “He wants a dad.”
A woman sits next to a boy outside with a rocky hill behind them. He is looking through binoculars. She says “You remind me a lot of your dad sitting there.”
“When they’re your best friend it turns into this weird, gross, furry pile where you can’t tell where the lines are between human and dog, master and slave, and sex, and it’s just ugh.” 43
“Bestiality lowered a man to the level of a beast, but it also left something human in the animal.” 44
“A man has appeared before Limerick District Court charged with ordering his Alsatian dog to have sex with a 43-year-old mother of four, who died from an adverse allergic reaction to the intercourse.” 45
“Addressing the consent issue, Daniels writes, ‘[T]he truth is that animals, particularly domesticated ones, don’t consent to most of the things that happen to them.’ Animal sexual autonomy is regularly violated for human financial gain through procedures such as AI. Such procedures are probably more disturbing physically and psychologically than an act of zoophilia would be, yet the issue of consent on the part of the animal is never raised in the discussion of such procedures. Should the day Bentham speaks of arrive when animal rights are recognized by society and the law, an argument which speaks only to the zoophile’s right to fair exercise of his property rights in the animals he owns may prove an insufficient legal justification for acts of zoophilia.” 46
“In 1812 in a similar case in strongly Federalist Seneca County, New York,William Moulton, a fifty-eight-year-old veteran of the Revolutionary War and a prominent Democratic-Republican, was accused of buggering a bitch, which then delivered a litter of puppies that ‘had large heads, no hair on them nor tails, and on the side of their head they had small ears.'” 47
“I am for the majestic art of dog-turds, rising like cathedral.” 48
“The right of sovereignty was the right to take life or let live. And then this new right is established: the right to make live and to let die.” 49
“Though a single gull had already struck Melanie on the forehead the day before, the choice of the children’s party for this first fully choreographed attack suggests the extent to which the birds take aim at the social structures of meaning that observances like the birthday party serve to secure and enact: take aim, that is, not only at children and the sacralization of childhood, but also at the very organization of meaning around structures of subjectivity that celebrate, along with the day of one’s birth, the ideology of reproductive necessity.” 50
“Death is outside the power relationship. Death is beyond the reach of power, and power has a grip on it only in general, overall or statistical terms…death now becomes, in contrast, the moment when the individual escapes all power, falls back on himself and retreats, so to speak, into his own privacy. Power no longer recognizes death. Power literally ignores death.” 51
“Physician assisted suicide is fundamentally inconsistent with the physician’s professional role.” 52
“Even worse their comments continue to make no distinction between hierarchical and non-hierarchical organizations and institutions — simply rejecting all organization — which is tantamount, if you think about it for a minute, to proposing a future that lacks workplaces, religious centers, families, any kind of assemblies, and so on — a future in which lone individuals or small groups fend for themselves (a vision seemingly not too far from what they propose).” 53
‘It is critical that the medical profession redoubles its efforts to ensure that dying patients are provided optimal treatment for their pain and other discomfort. The use of more aggressive comfort care measures, including greater reliance on hospice care, can alleviate the physical and emotional suffering that dying patients experience. Evaluation and treatment by a health professional with expertise in the psychiatric aspects of terminal illness can often alleviate the suffering that leads a patient to desire assisted suicide.” 54
“Their vision of a commune offers very little guarantee of its own basic existence. There are no proposed methods for deciding what will be produced or consumed nor how much of each or its distribution in a socially responsible way.” 55
“The euthanasia of animals has been acknowledged by most animal protection organizations, including [The Humane Society of the United States], as an appropriate and humane means of ending the suffering of an animal in physical distress. It is also used widely to end the lives of animals who have severe behavioral problems, including aggression, and cannot be adopted into an appropriate new home because they pose a threat to the health and safety of people or other animals.” 56
“Once we know where it is we want to go, we can then act with the urgency needed to organize and build institutions and movements able to win change and create the necessary foundations for a future society.” 57
“Those who demand another society should better start to realize that there is none left. And maybe they would then stop being wannabe-managers.” 58
“This is the dog’s real trick, the height of animal acting. Not surprisingly, the imitated action is one of violence and must have been somewhat complicated; because all pet dogs, and dog performers most of all, must be nonviolent and cooperative, the animal actor here must go against its ‘nature’ in order to successfully set up the final tableau. That animals can be domesticatedmade to forego violence in order to serve peopleis the triumph of human culture over nature. That they can then be trained to appear violentto attack humansis the ironic confirmation of this subjection.” 59
“Should you battle on, take the pain, endure the indignity, and await the inevitable end, which may be days, weeks or months away? Or should you take control of the situation and resort to some form of euthanasia, which in its modern-language definition has come to mean ‘help with a good death’?” 60
“At the final stage of this evolution, we see the first socialist mayor of Paris putting the finishing touches on urban pacification with a new police protocol for a poor neighborhood, announced with the following carefully chosen words: ‘We’re building a civilized space here.’ There’s nothing more to say, everything has to be destroyed.” 61
3:43 A montage of eerily smiling children’s’ faces. Audio is the word “dad” played over and over as it overlaps and becomes “dog”. The words dad and dog are repeated in a loop. The video becomes a distorted montage of psychedelic faces of children and dogs. Eventually the words dad and dog becomes god.
4:03 The montage audio and video end abruptly.
A small dog says “I know something we can do.”
A shot of a Bernese, who says “Poop” then winks.

DoggieWoggiez! PoochieWoochiez! $20
http://www.everythingisterrible.bigcartel.com/product/doggiewoggiez-poochiewoochiez
http://www.everythingisterrible.com/
How can designers and programmers work more harmoniously? How can the tools being created better meet the needs of users? There is a need for designers to have a greater role in the production of the tools that they use, aside from just reporting bugs, requesting features or designing logos for open source projects. This is where the Libre Graphics Research Unit comes in. The Libre Graphics Research Unit (LGRU) is a traveling lab where new ideas for creative tools are developed. The unit has grand aims, looking to bring aspects of open source software development to artistic practices. The programme, sponsored by many organisations in Europe, is split into four interconnected threads:
The first meeting, Networked Graphics, took place in Rotterdam from 7-10 December, 2011 and was Hosted by WORM. This second meeting, Co-Position, for which I was present, took place at venues across Brussels from 22-25 February 2012. Co-Position is described by LGRU as:
[…] an attempt to re-imagine lay-out from scratch. We will analyse the history of lay-out (from moveable type to compositing engines) in order to better understand how relations between workflow, material and media have been coded into our tools. We will look at emerging software for doing lay-out differently, but most importantly we want to sketch ideas for tools that combine elements of canvas editing, dynamic lay-out, networked lay-out, web-to-print and Print on Demand.
The meeting saw the coming together of many international artists, theorists and developers for four days of work around this subject. As some of the sessions of the meeting took place simultaneously I’m unable to give a full synopsis of the event. Instead, what is presented below are some of the key issues raised at the meeting.
The subject of copyright cannot be avoided when discussing digital art and collaborative practices. There is a definite need to foster a safe and welcoming environment for artists and designers to produce, share and remix their work. Licensing of artwork under Copyleft licences – such as Creative Commons – helps to create this environment.

In his presentation, entitled “Libre Workflows – A Tragedy In 3 Acts”, Aymeric Mansoux was quick to point out that Creative Commons licences do not cover the source of the artwork. To put it into context, a JPG is covered by a Creative Commons licence but is the XCF/PSD file? Mansoux also considered what is actually a finished piece of artwork? In a remix culture is an artwork ever finished? Mansoux refers to this quote from Michael Szpakowski for further elaboration:
I’ve found it helpful to think of any artwork, be it literary, visual art or music as a kind of fuzzy four dimensional manifold. So the “complete” artwork is the sum of all its instances in time, and all epiphenomena. The entire artwork, seen this way, is a real and precisely enumerable sum, a concrete, not imaginary, set, which could be knowable in its entirety by something long lived and far seeing enough.
From their home town of Porto, Portugal, Ana Carvalho and Ricardo Lafuente produce Libre Graphics Magazine with ginger coons who is based in Toronto, Canada. For the production of the magazine they use Git, with their repository being hosted on Gitorious. As a tool for sharing files between collaborators Git is very useful. However, they explained that they feel they are not making effective use of all that Git has to offer. Part of this comes from the complexity of using Git. There are more than 140 commands in Git, each with their own unique function. These are usually entered via the command-line, but there are a number of programs with a Graphical User Interface (GUI) available. Programs with a GUI are usually favoured over command-line programs as they remove some of the complexity. Carvalho and Lafuente have found, however, that many of of these GUI programs simply replace commands with buttons, which doesn’t remove any of the complexity in using Git. What is needed is an easy to use specialised tool for the production of art.

In this work session, presented by Ana Carvalho and Eric Schrijver, the work group imagined how to adapt existing version control tools to meet the needs of artists and designers. The session began by taking a look at how people currently implement version control. A common practice is to manually make backups, renaming files to differentiate between stages. This can be an effective way of making different versions, but it doesn’t address other issues such as making comparisons or merging changes. The ineffectiveness of these manual methods is soon very apparent. The work group was introduced to the Open Source Publishing (OSP) Visual Repository viewer, which begins to respond to some problems with current version control systems by providing thumbnails of files in a repository.
Using this as a basis we began to look at other functions that the OSP Visual Repository viewer should have, such as the ability to compare graphical files in different ways and to revert back to previous versions or merge versions. Although there was no time to produce working code we did seek to address the complex task of merging and comparing not only the ouput file but also the working files (svg/xcf/psd).
Every good work of software starts by scratching a developer’s personal itch.
This quote from The Cathedral and the Bazaar by Eric Steve Raymond could not be more accurate in describing the motivations behind the development of Laidout, developed by Tom Lechner, a comic artist from Portland, Oregon. Perhaps one of the most impressive software demonstrations of LGRU, Laidout is a program for laying out artwork on pages with any number of folds, which don’t even have to be rectangular.


In an attempt to devise new tags that can be added to the SVG specification, Michael Murtaugh and Stephanie Villayphiou presented a work session that looked at the different ways language is interpreted by both humans and computers. To address this the work group took part in a task that saw them act as an interpreter of commands. With nothing more than a list of tags used in SVG files the work group would attempt to construct shapes.


The results varied from person to person and highlighted an important question: How can computers interpret ambiguity

Using the Richard A Bolt “Put that there” demonstration, Murtaugh showed how human-computer interaction is still based around using very clear, unambiguous commands that can be easily interpreted by computers. In SVG only the most basic of shapes – rectangles, circles and lines – are represented. But, as the work group participants asked, could there be tags to represent more complex shapes, such as a horse?

On the final day of the meeting I took part in a roundtable discussion, chaired by Angela Plohman and featuring myself, Stephanie Vilayphiou, Camille Bissuel and Ana Carvalho. The discussion first went over all that we had achieved over the four days at the meeting, and then the discussion focused on how and why we share our artwork. Expanding on the earlier quote from Szpakowski, how can we make sharing all of our artwork – including the early stages and inspirations behind it – an easier and integrated part of making artwork? In addition to sharing our final, “finished” artworks do we want to also share our processes and ideas behind the artwork? More importantly, can software easily aid this?
Other topics debated in the discussion revolved around opening up our artwork and processes to others. By opening up the development process of our artwork do we do so to invite collaborators and contributions or just observers? The Blender Open projects, for example, are highly regarded as an example of the work that can be made using open source software. The files used to make these projects are are released upon completion of the project, but the development process remains closed to the team of artists and developers. Would opening up this process to contributors add any value or could having too many ideas dilute the original vision of the project.
Although no conclusions around these topics were made, it was nonetheless important for everyone at the meeting to think critically about their practice
A concern of mine is that research is not always acted up on and exciting possibilities exist only as theory. However, I feel that the approach of Libre Graphics Research Unit, which combines research and practice, will ensure that the work undertaken at the meetings is implemented. It is actively working with developers and users to try and create solutions.
At the Co-Poistion meeting not one final product was made, but the initial vision for the future of layout was formed.
The next meeting, Piksels and Lines, takes place in Bergen, Norway and is organised by Piksel.
MONODROME: Art’s debt in times of crisis
AB3 Athens Biennale 2011 Monodrome
Curated by Nicolas Bourriaud and X&Y
23 October-11 December 2011
Athens Biennale 2011 was the third edition of this institution and was entitled “Monodrome”, meaning “One way street” after the 1928 text “Eisenstrasse” by Walter Benjamin. The concept of the title is obvious; after the first Athens Biennale in 2007 prophetically entitled: “Destroy Athens”, the second Biennale “Heaven” in 2009, “Monodrome” comes as a closure to this trilogy. Why Walter Benjamin? Because he was a “defeated intellectual”, according to the curators. German-Jewish philosopher, an emblematic figure of 20th century thought, gave an end to his life at the french-spanish border while trying to escape the Nazis. “He was unable to overcome his personal dead-end as a subject”, says Poka-Yio of X&Y and he continues: “The title of this exhibition after Benjamin’s text refers to a collective dead-end” currently at stake and it’s only possible fate: a cloud of doom. “Monodrome” aimed to provoke debate around “something that has fallen apart, but to also offer the possibility of a glimpse at something new to come”.
Indeed, this Biennale took place at a specific moment in Greek and global history, where all 20th century utopian narratives (i.e. modernism, ecology, metaphysics) are crashing, introducing to the whole world a humiliating and disturbing, both socially, as well as nationally, dystopian non-future. Athens, the cradle of democracy was – at the time – “rocking the world”, by suffering the experimental imposition of a non-democratic supernational regime stamped with the mark of over-privatization, a situation that immediately started spreading all over Europe. Now – that the exhibition has come to an end – nearly everyone on this planet feels that “the time” {our world – as we know it – has come to} “is out of joint”, “the very place of spectrality” (Jaques Derrida, “Specters of Marx: The State of the Debt, the Work of Mourning, and the New International“ Routledge, 1994: 82).

What’s art got to do with this? “Artists usually have premonitions of what’s going to happen, it is often that artists precede with their work social changes; artists are mostly intuitive, it’s at the core of their existence, this how they create” Poka-Yio says. Nicolas Bourriaud and X&Y had to deal with a situation that can be called no less than a “crisis management”. The exhibition was organized practically with no funding and was based mainly on the contribution of all participants and volunteers. The social events that were taking place during the very opening of the show were probably amongst those of the most significant importance in Greece’s postwar history. The energy and emotional vibe caused by this historical moment were the background of the Biennale and made it both a great challenge and a responsibility for the curatorial team.
Despite these critical financial and social circumstances, the Biennale was successfully realized against all odds and it can be said, that it was well received by the audience – an accomplishment on behalf of the curators who selected the works, planned and organized it. The curators of the 3rd Athens Biennale 2011 felt that “the widening situation for which Greece is a much derided yet overexposed case-study must become the focus of cultural investigation, in a way that it is no longer poignant – or even moral – to simply keep making exhibitions in the way that had become the norm in previous years”.
In order to address these issues, besides investigating the exhibition’s conceptual framework, the curators decided “to experiment with the Biennale exhibition format itself, by transforming it into an invitation to create a political moment rather than stage a political spectacle by making a call to a sit-in of collectives, political organizations and citizens involved in the transformation of society”. At another level, as the exhibition was designed and produced, its various stages of development were providing the basis for a feature film directed by Nicolas Bourriaud. Social media also played an important role in the communication strategy of this Biennale, as every event, talk, happening or performance was recorded and presented at AB3 youtube channel and one could follow it via facebook, twitter and other social platforms, as vimeo, flickr and tumblr.
The conceptual framework, upon which the theoretical thread was build, was a deep dive in the folds of Greek history. The curatorial strategy chose “to represent an ongoing crisis through historical fragments, a Benjaminian technique”. Walter Benjamin, provided with his text “Eisenstrasse” the tools for looking at history in a fragmented way, for he, according to the curators, introduced theoretical tools for looking into history with terms of “here and now”, by often making references to the city and to the popular culture of his time. “One way to talk about history is to include history”, says Nicolas Bourriaud. “The exhibition was structured as text; its narrative unfolds as one searches in the ruins and tries to read their meaning”, as one “tries to find out about new possibilities of giving meaning”.
Walter Benjamin, as a character, for the needs of this exhibition’s narrative concept was brought in a paradox dialogue with another character, a fictional one: Saint Expery’s Little Prince. This narrative plot brings this real life character, the emblematic intellectual, to meet the hero of a children’s novel, because: “a child can pose questions in an intelligent manner representing the inner child to be found in everyone” says Xenia Kalpaktsoglou of X&Y team of Athens Biennale co-founding curators. Little Prince poses all fundamental questions of “being” to the philosopher and the intellectual strives to give back the right answers. This imaginary dialogue took place in the form of sketches spreading like a graffiti-comic all over the walls of the exhibition’s main venue building. “As the intellectual retreats defeated in the face of the escalated distress, the Little Prince keeps questioning this condition with the disarming innocence and the plainspoken boldness of a child”.
The real protagonist of the exhibition, however, was Diplareios School, the main venue, a nearly disused old building located at the heart of downtown Athens in an underprivileged area, right across the City Hall and the old big open market. The local color and the smells of the market square, crowded with immigrants, ethnic shops and – especially at night – the presence of junkies, dealers and prostitutes was part of the exhibition’s “aura”. This building was literally used as a “panopticon” of both contemporary and ancient Athens and has a long history. It was built for the purposes of housing a School of Design, meant to be “the Greek Bauhaus”. Among many of its uses, it was requisitioned during the German Occupation and during the time when Athens was so badly over-built, it was hosting the offices of Urban Planning public service. The second exhibition venue was “Venizelos Museum”, a former military basis also used during the Greek dictatorship as the headquarters of torture investigating anti-regime citizens (former ΕΑΤ – ΕΣΑ).“The space is the artwork”, Bourriaud says. “Not just a venue. It’s previous functions manifest its character; it is a real protagonist”.
Diplareios School is an allegory of modern Greece surrendering itself to abandonment. Looking around all one sees is worn walls and graffiti, all one hears are the voices of protests and the ubiquitous noise of the city. The curatorial strategy for this Biennale was quite different from the two previous exhibitions, “Destroy Athens” in 2007 and “Heaven” in 2009. No big names of the international art market to be found among the artists. No self-referential patterns in this exhibition, other than “questions on the reasons behind the political crash, the crisis of moral values, the dead-end”. It was in fact a much more “introvert” exhibition, focused on the local scene, featuring mainly emergent Greek artists. The exhibited artworks in their majority came form Greece: “to include the local, to talk about local artistic production was one of our aims for this exhibition” according to Bourriaud.
Only to mention a few, Spyros Staveris, an emerging Greek photographer with a video art photo-documentation following the “Aganaktismenoi” social movement in Athens at its very birth. In the same room, “Ηommage a Athenes” a sound installation by Vlassis Kaniaris, with recorded sounds of the recent Athenian protests. One could not but mention the remarkable work of young Greek sculptror Andreas Lolis who is making cartboard boxes and felizol sculptures out of marble. “In my artwork, I try to make time stop. The reason why I am using marble, is because I want to make these fragile objects eternal”. “We all use cartboard boxes. People sleep in them. When I looked down from the windows of the Biennale venue and saw people on the terraces sleeping in cartons, it only came to me as a natural thing to co-exist with this situation – not to record it”. “This is the best time for Art. Not the art market, Art. When I recently saw the artworks of Athens Fine Art School graduates, I realized that the bubble-effect’s gone, now. These young artists, living this situation have grown into reality. There’s so much truth in their artworks”.
Another captivating artwork featured at the Biennale was “EXIT” by the Greek collective “Under Construction”, an installation of old rusty worn office desks; “in fact we present an allegorical image of Greece, using old equipment of public services, eroded now from abandonment. The hard to distinguish faded “EXIT” ‘statement’ does not exist, at least not literally”.

Rena Papaspyrou’s “Photocopies” is another stunning installation, where phone numbers printed on fragments of paper are posted on the wall. “Extending the decay of the wall, this piece secretly interacts with the graffiti notes on the wall waving alternative histories of the numerous uses of the building”. Thus the interaction between Papaspyrou’s installation and the Diplareios building creates a sense of dialogue, both in concept as well as in form.

One may wonder whether any international artists were presented in this exhibition. Lucas Lenglet, Jakob Kolding, Norman Leto, Caroline May, Josef Dabernig, Józef Robakowski only to mention a few, and of course, Julien Prévieux’s “A La Recherche du Miracle Economique”.
“This is a fragmented exhibition”, Bourriaud says: “one can see in this exhibition various media, film, collages, photographs, sculptures, drawings, paintings”. Amongst the artworks, the visitor would encounter several objects that have nothing to do with art but were used as tools for the exhibition narrative: a time lapse, a trip down to memory lane. For example, an object used for this purpose was a placard, that the curators found discarded after a recent protest in Athens. On the placard was written: “WAKE UP BANANA REPUBLIC”.

Also, the lost opportunity of Greek design; some of the works of students of Diplareios School were exhibited; they had been left in the old School. Posters by Greek National Tourism Organisation by Michael and Agnes Katzourakis. Pictures of Andreas Papandreou with Gaddaffi during the “good old days”. Air stewart and pilot uniforms from The Olympic Airways. In the attic of the old School, the crescendo of the exhibition’s narrative: as one faces the image of the ancient monument of the Acropolis through the dirty windows of the old School, a dead pigeon that was found there and was respectfully kept by the curators as a symbol, an omen.
The 3rd Athens Biennale 2011 was a double project; in both the form of an international exhibition and a feature film. The return of Walter Benjamin as a ghost that comes to haunt the city of Athens during this crisis period is the theme of a film directed by Nicolas Bourriaud. “It is a feature film, a film as an exhibition, a documentary based on actual characters, a docu-fiction and an experimentation with the platform of the Biennale”, says Bourriaud. “The film will be a work of fiction albeit based on real events. This is the first time that the relationship between contemporary art and filmic language is investigated in this way”. A catalogue will document the whole process of the 3rd Athens Biennale, and a DVD edition, including the movie and documents on participants’ works, will be published. Following the completion of the Biennale, the film in its final format will be distributed both in the art world and the cinema circuit. The executive producer of the movie is Kino Prod (www.kino.fr) in Paris.
Ironically, and sadly, “Monodrome“’s TV trailer was censored by the Greek National Broadcaster (ERT), who was also the major communication sponsor of the Biennale. The director of this 26’’ spot, Giorgos Zois, a talented young Greek filmmaker who has already won several international distinctions and prizes – according to his official statement as an answer to this act – attempted to “deliver the theme of the 3rd Biennale MONODROME (meaning one-way) in a series of slow-motion images of a forcibly accelerated reality depicting the one-way contemporary condition. Instinctively and suspiciously the national Greek television judged the content to be against the law that forbids “messages that contain elements of violence, or encourage dangerous behaviors, or insult human dignity”. “Apparently the daily transmission of aggressive porn-like governmental policies, does not count as an insult to viewers”. You can watch the trailer here:
White Heat Cold Logic
British Computer Art 1960-1980
Edited by Pal Brown, Charlie Gere, Nicholas Lambert and Catherine Mason
ISBN 9780262026536
MIT Press 2008
This is the third and last in a series of reviews of the results of the CACHe project. The first review was of the V&A’s show and book “Digital Pioneers“, the second was of Catherine Mason’s “A Computer In The Art Room”. Where “A Computer In The Art Room” concentrated on the history of art computing in British educational institutions up to 1980, “White Heat Cold Logic” gives voice to the individuals who made art using computers in that period more generally.
Charlie Gere’s introduction explains the source of the book’s title, referring to the British Prime Minister Harold Wilson’s famous 1963 speech that a new Britain would be forged in the white heat of the scientific and technological revolution. Gere provides an overview of the history of art computing in the era that may be familiar from “A Computer In The Art Room” which is much needed, for it provides useful context for what follows in this volume. He also argues for the value and interest of the history of art computing, in terms that make it clear for academia.
Roy Ascott describes the emergence of pre-computational art informed by cybernetics, systems theory and process against the background of the emergence of “Grounds Course” art education. Adrian Glew documents Stephen Willats’ use of computing in the processes of his art of cybernetic social engagement, the first but not the last more mainstream British artist to appear. John Hamilton Frazer describes the unrealised interactive architecture of the 1960s “Fun Palace” and 1980s “Generator” and of the technology and social legacies of these nonetheless influential projects.
Maria Fernandez puts the figure of Gordon Pask centre stage. As John Lansdown (to whom this book is dedicated) emerged as a major figure behind educational arts computing in “A Computer In The Art Room”. Gordon Pask also emerges in this volume as the cybernetic prophet of the 1960s, mentioned by many in the early essays in this book. His own interactive theatre and robotic mobiles complement his involvement in planning the Fun Palace and as a source of ideas and support for more projects.
Jasia Reichardt provides a theoretical and practical insight into the genesis of her foundational “Cybernetic Serendipity” show at the ICA in 1968 and considers what came next. Brent Macgregor provides an outside view of the same. Neither attempts to mythologize this much mythologized show, the reality of its achievements is more than impressive enough.

Edward Ihnatowicz is the subject of two essays, one with tantalising images of preparatory and documentary material by Aleksandar Zivanovic and an insightful but more personal essay by Richard Ihnatowicz. Hopefully his reputation will continue to increase towards the level it deserves.
Richard Wright follows the ideas of Constructivist art into Systems Theory, which alongside cybernetics is one of the guiding ideas of the art of the period overdue for rediscovery both within art computing and more generally.
Harold Cohen remembers the origins of his “AARON” painting program in a tale of the struggle of art against bureaucracy. Tony Logson’s tale is surprisingly similar, although his systems-based art is very different from Cohen’s cognitively-inspired forms. Simon Ford reveals Gustav Metzger’s involvement with early computer art and with the Computer Arts Society (CAS). CAS also feature large in Alan Sutcliffe’s description of his computer music compositions, one of many essays that left me wishing I could see the code and experience the art as well as reading about it.
George Mallen also touches on CAS, and on Pask’s System Research Ltd. as he explains the art and business of the production of the unprecedented environmentalist interactive multimedia of the “Ecogame”. The Ecogame is one of many works in the book that people simply need to know about. Doron D. Swade makes the idea of the “two cultures” of art and technology that came together for the Ecogame more explicit in an attempt to recover the art of the Science Museum’s first computing exhibit.

Malcolm le Grice and Stan Heyward each describe the institutional travails of making some of the first computer animation in the UK. Catherine Mason draws together the history of many of the institutions already mentioned in what is both a recap and an extension of the history she presented in “A Computer In the Art Room”. Stephen Bury and Paul Brown bring the influence of the Slade to the fore in their chapters, revealing the Slade as an important piece in the puzzle of British Computer Art.
Stephen Scrivener, Stephen Bell, Ernest Edmonds and Jeremy Gardiner each describe their personal artistic journeys through the era of FORTRAN and flatbed plotting, illustrated by images of their work that again made me wish I could also see the code. Graham Howard describes how conceptual artists Art & Language didn’t use a university computer to generate the 64,000 permutations of one of their “Index” projects of the 1970s, instead gaining access to a local produce distribution company’s mainframe across several weekends.
The different strands of technology, institutions, ideas and economics are all drawn together in John Vince’s history of the PICASO graphics library, which spread from Middlesex Polytechnic to many other educational institutions and the successor to which, PRISM, was used to make the first logo for Channel 4.
Brian Reffin Smith makes clear, artists were as affected by the idea of computing as by computers themselves, especially when they didn’t have access to them. The Fun Palace was influential despite never being realized, Senster was influential despite being lost. It is important to realize just how limited access to computing machinery was in the era covered by the book, and to recognize how ideas of computing and its potential were part of the broader intellectual environment of the time.
Finally, Beryl Graham’s postscript covers the history of UK arts computing after 1980. I lived through some of the period covered and I recognise Graham’s description of it. The critical irony that she identifies in UK net.art and interactive multimedia is of key importance to its art historical value. Although I would question how uniquely British this is, the UK certainly took it as a baseline. As with Gere’s introduction, Graham presents the case for art computing in a way that the art critical mainstream should not just be able to understand but should be inspired by. Cybernetics, systems theory, environmentalism, socialisation, the content of conceptual art, and the political concerns and developments of the Cold War all illuminate and are in turn illuminated by this history.
For a book about art computing it is frustrating how little art and source code is illustrated in the book. Much work has been lost of course, and “Digital Pioneers” does illustrate art from this period. But for preservation, criticism and artistic progress (and I do mean progress) it is vital that as much code as possible is found and published under a Free Software licence (the GPL). Students of art computing can learn a lot from the history of their medium despite the rate at which the hardware and software used to create it may change, and code is an important part of that.
White Heat, Cold Logic presents hard-won knowledge to be learnt from and built on, achievements to be recognised, and art to be appreciated. Often from the people who actually made it. What was previously the secret history or parallel universe of art computing can now be seen in context alongside the other avant-garde art movements of the mid-late 20th century. I cannot over-emphasise the service that CACHe has done the art computing community and the arts more generally by providing this much needed reappraisal of early arts computing in the UK.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
Blue Sausage Infant is the solo electronic project from Washington DC’s Chester Hawkins. Active on the live scene since the late 1980s, he’s shared the stage with touring and local luminaries, whose stylistic echoes radiate his own productions. Hints from prog, industrial, dark ambient, and noise all come across on BSI’s first LP release, Negative Space. Issued on Zeromoon in gorgeous packaging and colored 180-gram vinyl, Negative Space’s three tracks combine into a diverse snapshot of Hawkins’ musical creativity and expertise using a fair number of electronic and other diverse instruments (including electric toothbrush), all helpfully enumerated on the inner sleeve.

Side one is the single solo track “Motion Parallax,” a drifting space music riff that evolves through increasingly soupy accompaniments. From the Berlin overtones that emerge from the opening swirling white noise to a tribal electronic rhythm that reminded me of the proto-noise-punk band Chrome, BSI creates a diorama of timbral and harmonic landscapes. A distorted voice just out of comprehension earnestly and repeatedly strives, but fails to make herself meet and fuck understood, channeling an obscure Samuel Beckett character. Perhaps because of its murkiness, present even in the background of the rhythmic passages, Motion Parallax carries a lulling quality, a hard-edged long-form ambient work.
By contrast, side two opens considerably further towards krautrock with the title track, thanks to the assistance of a guitarist, a drummer, and a fourth performer on percussion and electronics. For all that side one referenced ambient, “Negative Space” draws from post-rock, with sustained guitar textures, rhythmic bass riffs, four-bar phrase structures, and a continuous dramatic build over the fourteen-minute performance. The side concludes with the shorter solo track “Subferal,” dense electronics dotted with sirens and alarms, led by an obsessive oscillation that starts on an intense single note and dissolves into swizzling distortion.
Originally posted on Furthernoise: http://www.furthernoise.org/index.php?url=page.php&ID=430&iss=96