




Recently I was approached to conceive and run an outreach project to accompany a solo show of work by Eduardo Kac at Furtherfield Gallery in North London’s Finsbury Park.
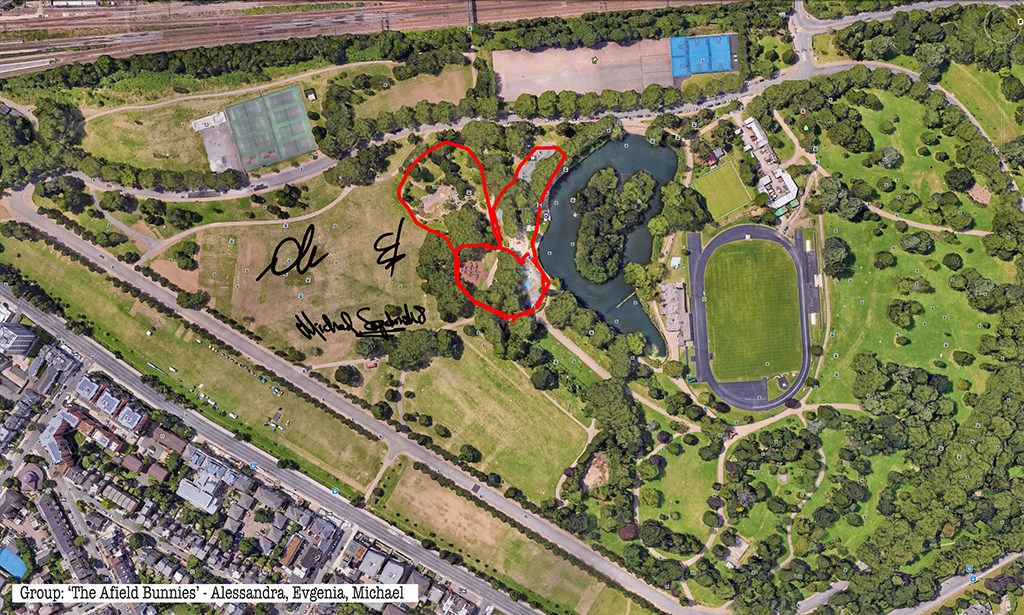
Among the works on show was one of Kac’s Lagoogleglyphs, large scale stylised representations of rabbits (something of a signature obsession for him) painted in some sort of sportsground emulsion directly onto a section of the park and allegedly of a scale which make it harvestable by the satellites Google rents for its various mapping activities.
Being completely frank, I have to say I entertained a degree of scepticism about Kac’s work—some of it falling within, in my view, one or both of two entertainment based metaphors—the ‘one-liner’ and the ‘theme park’—neither particularly positive elements of my critical lexicon.
Be that as it may, some of the work, particularly the less grandiose pieces (that delicate bunny flag flapping above the gallery!) were touched enough with real poetry to make me want to take up the challenge.
I say ‘challenge’ advisedly for I’m only ever interested in doing anything which in some sense challenges me and I also felt that my ambivalence about Kac would result in anything I ended up making containing a return element of ‘challenge’ or, perhaps more gently put, practical critique.
The word challenge also described the sense I had of wanting to counterpose collaboration, the collective, the everyday, to the artist with a capital ‘A’; of going some way to claiming art as a way of seeing and feeling and thinking together for All ( also with a capital ‘A’).


Reaching back in memory I pondered two remix/homage projects from the noughties which somehow straddled, in a pleasantly clunky fashion, practices both cutting edge digital (at least in their original moment) and time honoured too.
Apposite and practical stimuli for my 2018 purposes, they suggested elegant pathways to both honour previous work and to gently…um… stress-test it.
Both evinced rich humour, a warmth and a concomitant refusal to take themselves too seriously, qualities lacking in much contemporary art and both had a kind of performative klutziness I found entirely engaging.
Both were made in the first years of this millennium when digital and particularly online art was a wild west with a few fragile homesteads scattered here and there and not the orderly space it is today colonised almost entirely by the mainstream art world or commerce or both.
I recalled first a project by Nathaniel Stern where he hired South African billboard sign writers to paint physical representations of various, mostly art related, web pages.
The second was artist duo MTAA’s remix of Tehching Hsieh’s One Year Performance project, an endurance piece where Hsieh had forced himself to punch a timeclock on the hour, every hour for a whole year.
Reversing the premise MTAA’s Whid and River posted a database of video clips of themselves sleeping, eating, inhabiting the space and left it to the online viewer to watch these being digitally assembled (by Flash—remember that?) into a simulacrum of the original over the assumedly continuous period of a year.
Armed, fortified, prepared thus, I set to work—but I still needed a concrete plan and methodology.
Being a keen runner and the project taking place in a London Park in which I had run a 10k not long before (and now having endurance floating near the top of my mind) I felt some kind of park related physical activity would be an element and this would be a way of coming closer to those who loved the park but for whom the art gallery might not be their first association.
But still I lacked the concrete rabbit themed activity which would offer genuine practical, meaningful and autonomous artistic engagement and creation to participants.
I did not want to control what those participants would do but give them a clearly defined (clearly defined enough that all inputs from three separate days of activity could be brought together into a final unified work) and interesting task within which they would need to deploy creativity, focus and skill.
The fad for exercise related GPS devices had previously passed me by but one day whilst running with my daughter, who uses her phone and GPS enabled software to document her running in data and map form, I had a small epiphany—here there (might) be rabbits.
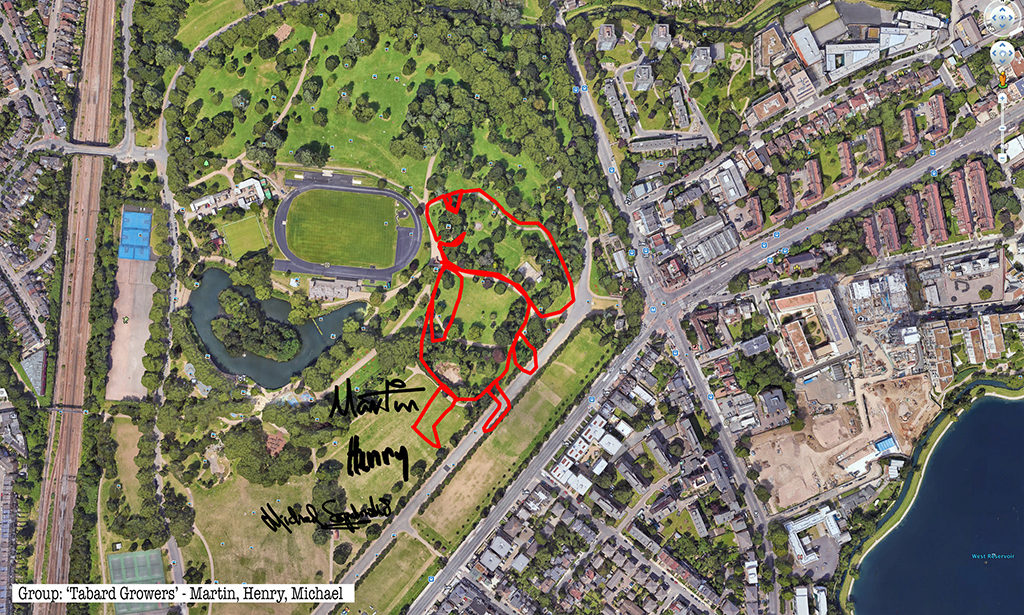
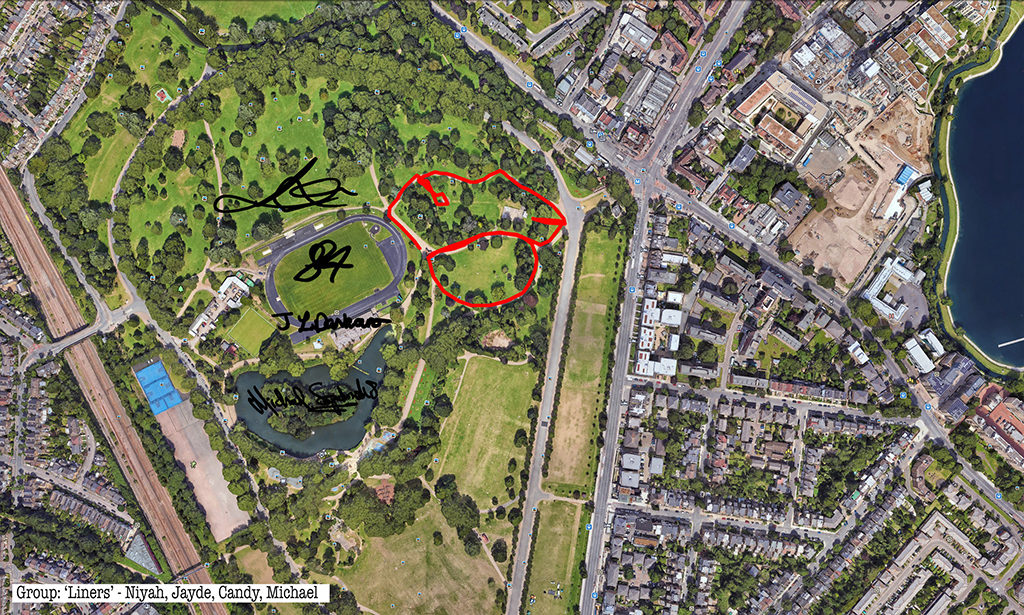
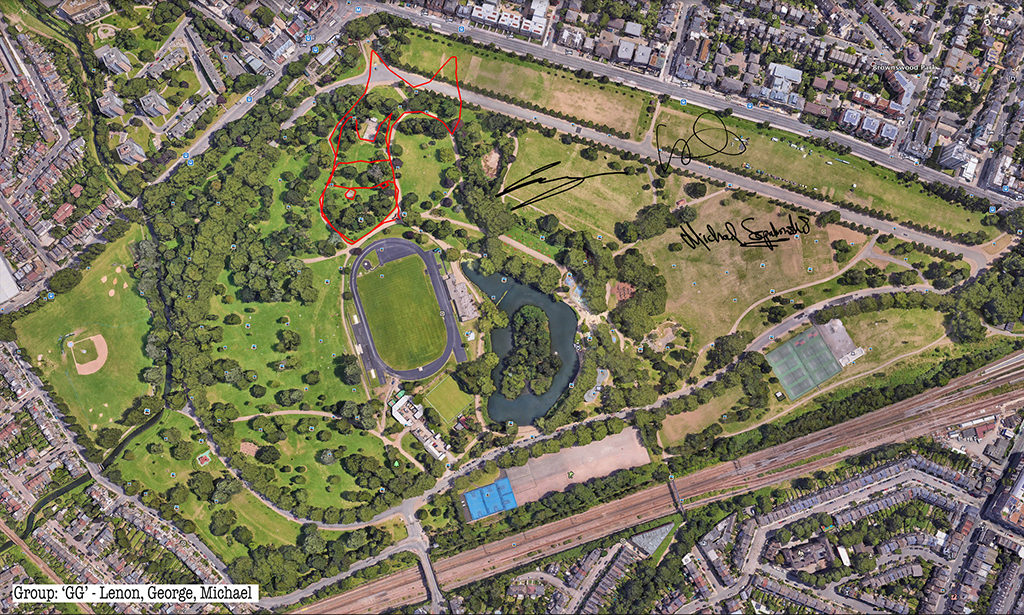
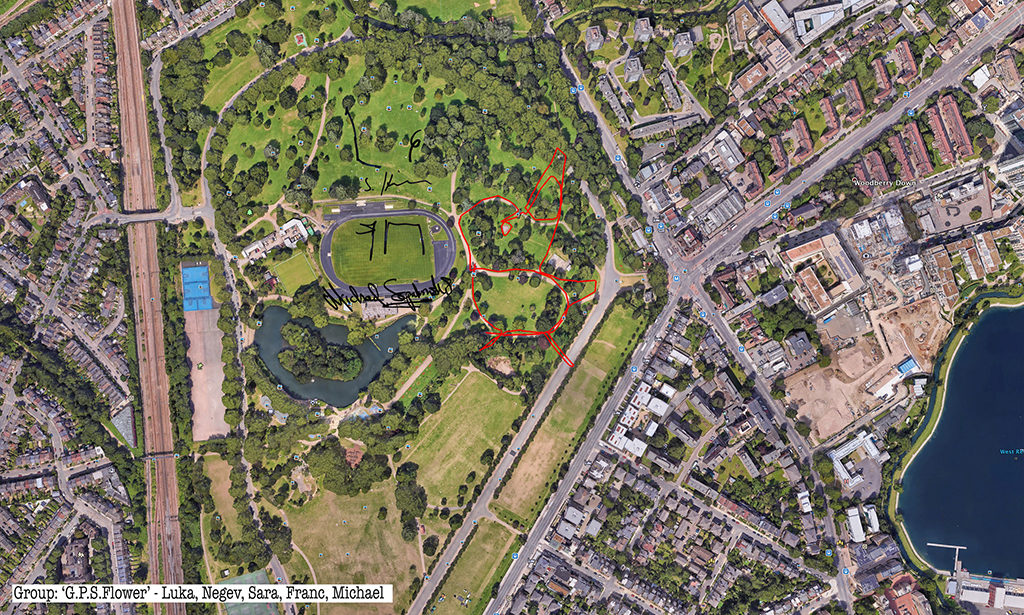
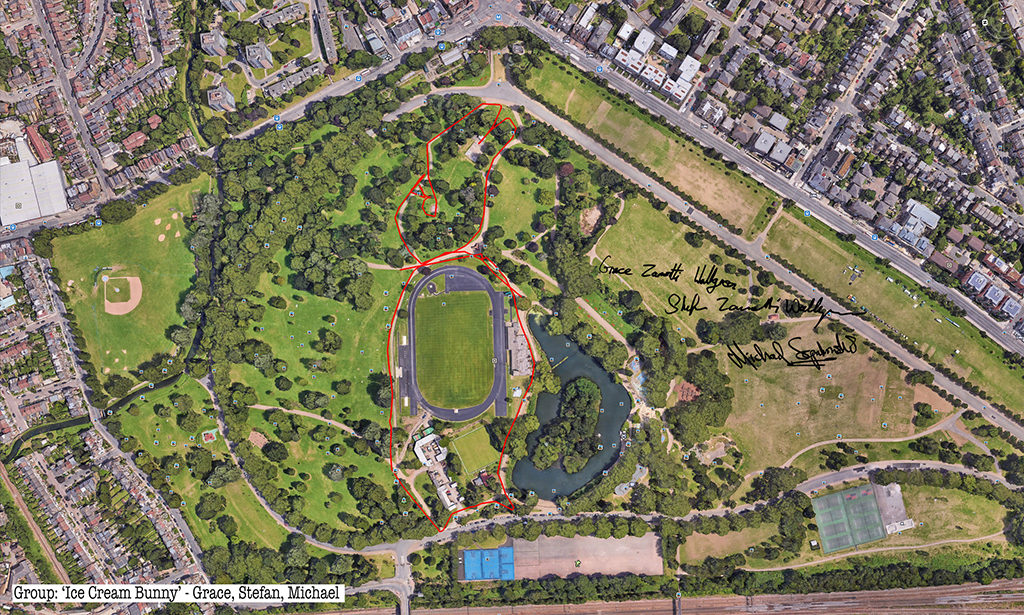
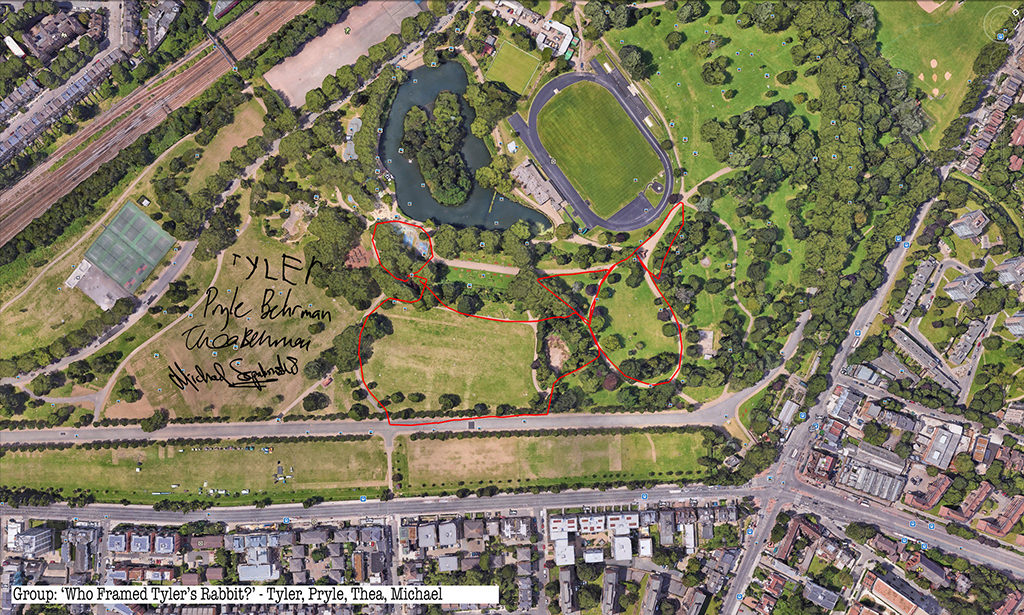
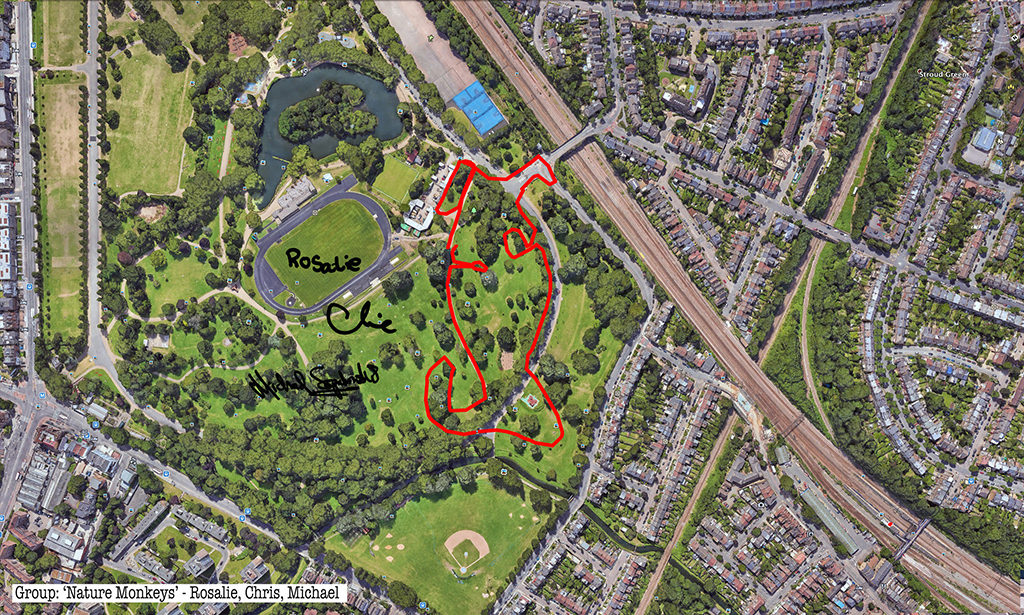
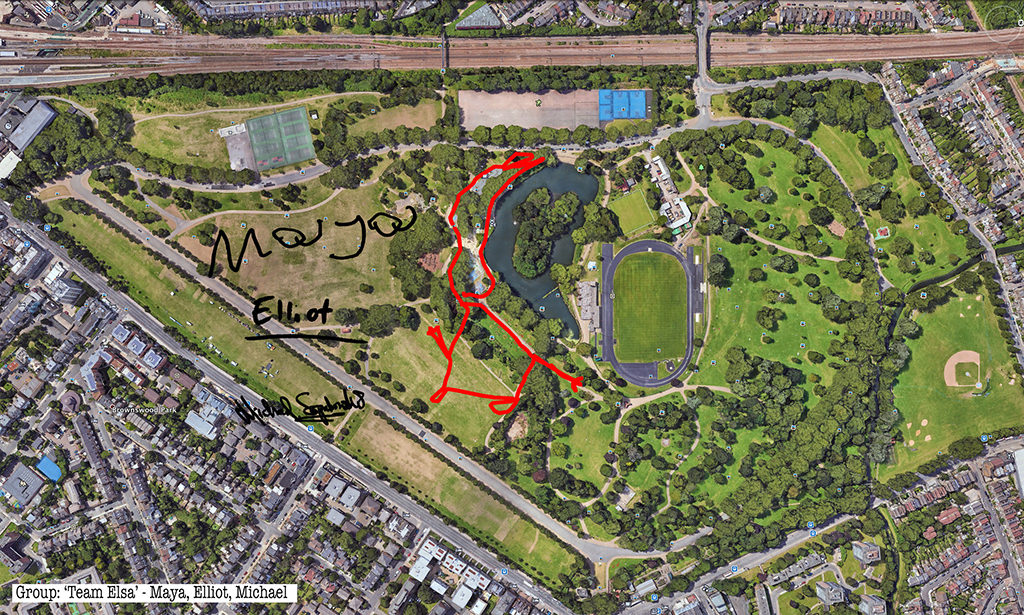
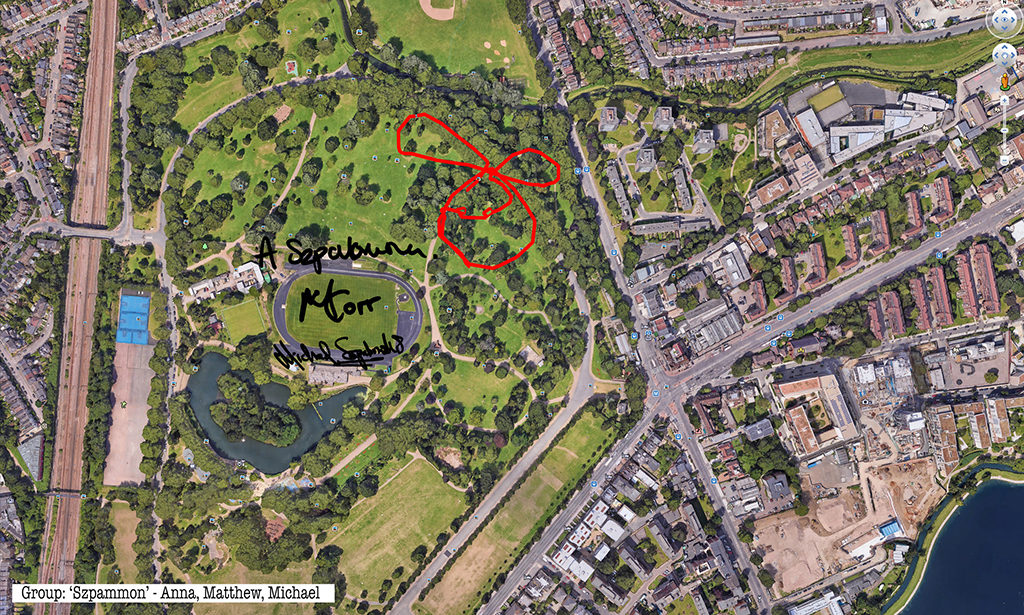
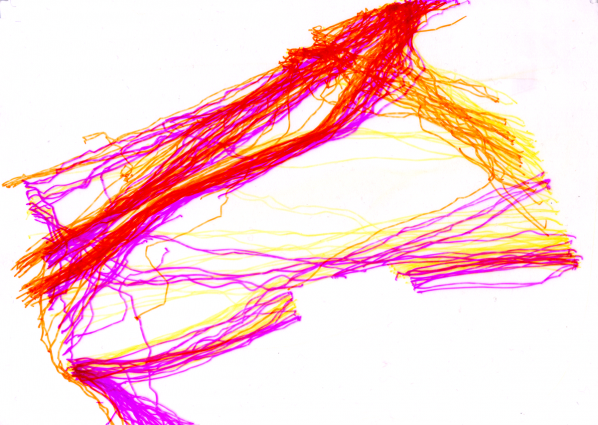
Rabbits, giant GPS rabbits, first planned and sketched by participating teams in marker pen over a satellite image of the park—ears, eyes, paws, body, fluffy tails emergent within its various paths and trails and features and obstructions.
And then, using these maps, we would carefully and attentively walk-out each monster rabbit trapping and freezing it as a succession of data, a series of co-ordinates in the memory of the GPS watch I would wear, finally to be reconstitututed as a continuous line drawing in turn fed back into a fresh satellite view of the park.
But that succession of co-ordinates, actuated by the actual movements of the human body (like a giant pencil lead or nib or brush) will resolve itself into something ancient—line, preconceived and then drawn out by human beings.
Being, together, both the very oldest form of mark making and something blink-of-an-eye recent too (well, as recent as the noughties efflorescence of so-called locative media which I shamelessly pillaged here.)
Inaccuracy in some measure a feature of both ancient and modern—the error margin of even GPS and GLONASS together, two sets of four satellites working in concert; the mix of will and skill and the fallibility and triumph too of flesh and bone and sinew which is part of what thrills and moves us in the arts.
This is what I had in mind.
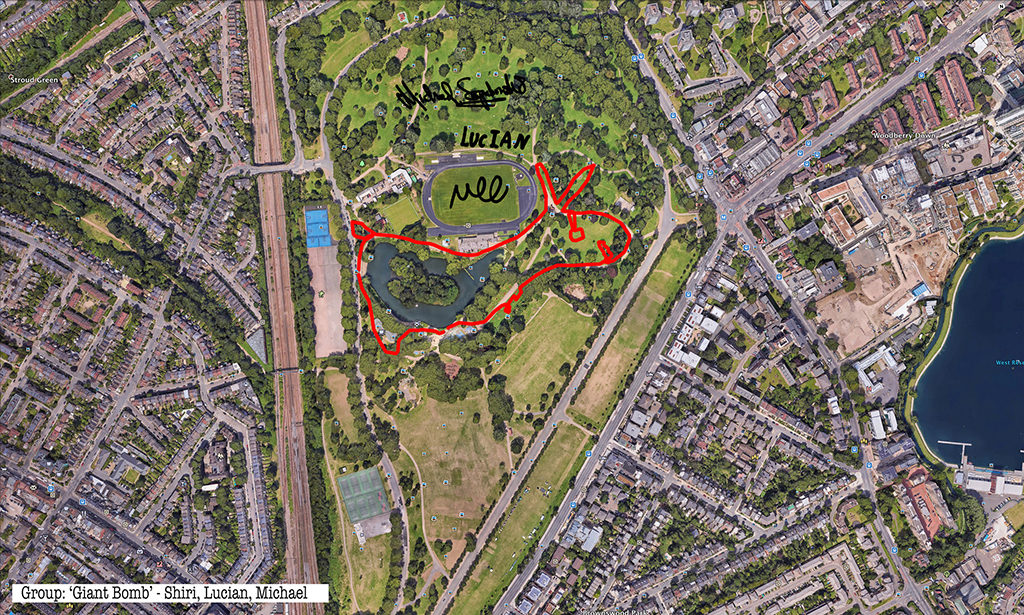
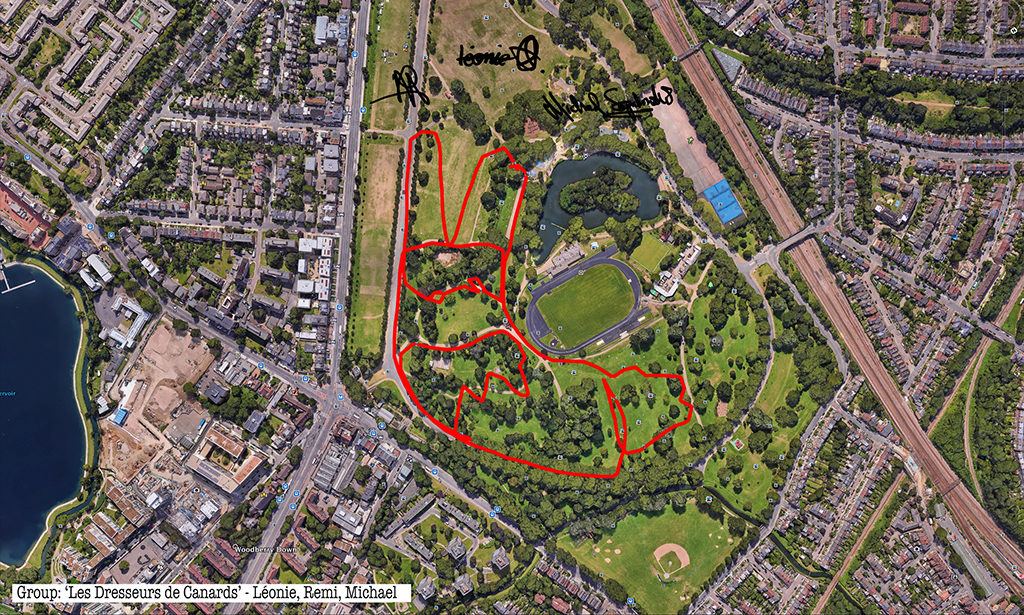
Repeatedly outlining then co-performing an activity which I learned to summarise simply and precisely, almost automatically, one might have thought boredom or a dozy, parroted, routine might threaten.
And how anxious I was each time as to whether and in what way each new team would engage with—buy into—adopt as theirs, as ours—the task.
But how striking the variation both in the simple, basic act of depicting in continuous line each new rabbit-of-the-imagination and the forty minutes lively sociability surrounding that initial sketching and subsequent walking-out.
Balancing the competing claims of making something serious, something with some kind of weight, some satisfying end product, whilst making space for others’ fun and dreams and and will and whimsy is neither easy nor is it trivial.
In the end people seemed to have a good time, they seemed at ease, went at it with a will and—it seems to me—something rich and affecting emerged.
Thanks to all at Furtherfield and thanks—no, not thanks, but credit—to my fellow artists: Alessandra, Anna, Candy, Chris, Elliot, Evgenia, Franc, George, Grace, Henry, Jade, Lenon, Léonie, Lucian, Luka, Martin, Matthew, Maya, Negev, Niyah, Pryle, Rémi, Rosalie, Sara, Shiri, Stefan, Thea and Tyler.
Roger Malina is a physicist and astronomer, Executive Editor of Leonardo Publications (The M.I.T. Press), and Distinguished Chair of Arts and Technology at the University of Texas at Dallas. Dr. Malina helped found IMéRA (Institut méditerranéen de recherches avancées), a Marseille-based institution nurturing collaboration between the arts and sciences.
Mariateresa Sartori and Bryan Connell are two artists recently based at IMéRA. Their work connects with human movement through the city, and addresses the intersection between technology and perception. Recent work by Venice-based Mariateresa Sartori has encompassed drawing and video. Bryan Connell, Exhibit/Project Developer at San Francisco’s Exploratorium, works especially with landscape observation devices and mapping.
Lawrence Bird interviewed Roger Malina, Mariateresa Sartori, and Bryan Connell about the intersection of their work with the city. Images above courtesy: Roger Malina, Rita Gambardella, Bryan Connell.
Lawrence Bird: Roger Malina, in your recent writing you make the case that science is no longer just a field of positive knowledge. Scientists are increasingly open to engagement with the arts — for example artists’ residencies at CERN. You’ve even argued that we’re in a crisis of representation as profound as that of the Renaissance or the 19th century, and this is “driving a new theatricalisation of science.”
Urban life has often been understood as performative – display, performance of social roles, presentation of oneself before others are all part of the public life in cities. How would you say that crisis of representation plays out with regards to this performative dimension of urban life? How is science implicated alongside art in the city, in these conditions?
Roger Malina: One of my arguments for the ‘crisis of representation’ really looks at Renaissance systems of representation — first driven by what the eye could see, and then the eye extended by microscopes and telescopes. These systems of representation were developed that led to a deep contextualising of the viewer in the world.
Today we are in a new situation because so much of our perception of the world comes not through extended senses but, in a real way, through new senses. This has been happening over a number of decades; the first wave of this was at the end of the 19th century when there was a cultural shock with the introduction of x-ray images, infra-red and later radio — which didn’t extend existing senses but augmented them.The most recent series of triggers maybe comes from the nano-sciences and synthetic biology — we now perceive phenomena of which we have no daily experience of (eg quantum phenomena). Field emission microsopy or MRI or some of the other new forms of imaging really don’t build on our existing experience — there are discontinuities and dislocations. Another element is of course the hand held device that leads to techniques for ‘augmented reality’ — I have a phone app that I can point at an aeroplane overhead and it tells me what the plane is, where it came from, and where it is going.
Coming to your question about the city — there is clearly a shift in map construction and reading — from the Cartesian map that we have been acculturated to. The ability to toggle between the bird’s eye view and the “street view”, and the ability to view maps that have multiple layers simultaneously are driving artists and others to develop new forms of representation.
Someone whose work is interesting in this regard is Bryan Connell in San Francisco, he just finished an art science residency at IMéRA in Marseille. He was working on a large urban trail project called GR13 — 300 miles through industrial, urban, sub urban, and wild landscapes (the city had a hell of a time getting right of way through these areas). Bryan is currently working on a web site for the Marseille European City of Culture events, where he’s working on some of these questions of representation. The project involves a collective of ‘artist-walkers’ that I think fits right into this question of performativity.

LB: There’s currently a great deal of interest in the connections between representation, digital technology, and politics, for example the current Hybrid City II conference in Athens. As you’ve pointed out, these often underline the connections between what digital media mean for artists and what they can contribute to citizens — what’s emancipatory about them. What can art offer civil life in this context? Are there any conflicts or contradictions in that relationship?
RM: One pertinent example is the work of Bruno Giorgini, a physicist, and Mariateresa Sartori (visual artist) who work on the “physics of the city.” They were recently in residence in the IMéRA Mediterranean Institute of Advanced Study which hosts artists and scientists in residence who want to work with each other. We now have access to incredible amounts of data on human mobility (pedestrian and various forms of transportation) so it is now possible to study human behaviour quantitatively. Sartori discovered that she could tell many things about a person just through the morphology or topology of their movements through the city. Girogini discovered that people’s movements could be predicted at the 80% level, but 20% of the time he had to introduce what he called ‘social temperature’; in discussions he also referred to this as a ‘free will’ parameter. Barabasi has found similar results analysing cell phone GPS data of individuals. So its interesting to think of the development of cities as 80% predictable and 20% serendipitous. This of course then highlights the role of the arts and culture in making cities part of the cultural imaginary that drives people to make choices. Recently Max Schich here at the University of Texas has analysed very large data bases looking at where prominent people are born and where they die over the last 500 years. Immediately you can see how suddenly certain cities become cultural ‘attractors,’ say the way Berlin or Hong Kong are now. And of course cities are now trying to ‘design’ this into the development of cities. Here in Dallas there has been a huge investment in the ‘arts district’ and in institutions of higher learning in the belief that healthy cities require such investments. See for instance the US National Endowment for the Arts Program; there are many similar programs in Europe.

This doesn’t yet address your ’emancipation’ question. One of the things that is happening is that we are becoming a data taking culture (see the recent literature on ‘big data”). The cell phone has transformed every citizen (that has one) into a data taker. Of course much of this data is used by companies for marketing objectives. But many citizen groups are now able to take data for their social objectives. Some of this is captured by the ‘citizen science’ movement ( one example is here). There have been good examples of citizen’s taking data (on pollution, on illegal activities etc.) and then being in a position to challenge ‘authorities’ of various kinds whether scientific, political or economic (see for instance the way citizen groups have mobilised to collect data after man-made disasters such as oil spills, or illegal logging in forests).
A few years ago I wrote an open data manifesto which argued that I would like to advance a new human right and a human obligation:
1. Each of us has the right to the data that has been collected about ourselves and our own environment.
2. Each of must contribute to the knowledge construction by collecting and interpreting data about our own world.
Most scientific data collection is funded by public tax payer funding. The public has a fundamental right to all data collected and funded by public tax money.
LB: How do you imagine an artist’s training will change as these conditions evolve? And a scientist’s — could we foresee any kind of convergence?
RM: One interesting development is a cohort of hybrids, who have one degree in science or engineering and one in art and design ( for example J.F. Lapointe, a researcher at the National Research Council of Canada with degrees in molecular biology and dance) or degrees in Science or engineering and employment in art or design (like myself or Paul Fishwick, a key figure in the field of aesthetic computing). There’s been an emergence of art/science Ph. D. programs that take students from art or design or science or engineering. I suspect this cohort will grow over the coming years.
LB: Mariateresa Sartori, your IMéRA research project with Bruno Giorgini focused on mobility in the city. Can you tell us a little bit about how your work and Dr. Giorgini’s work complemented each other? What kind of evidence did you bring to the table as an artist?
MS: The project I worked on with Bruno Giorgini developed an exploration that began with earlier work in Venice. There I created a series of drawings using a rudimentary, even crude procedure: I traced out the movements of each pedestrian in the Piazza San Marco, drawing their paths with a felt-tipped pen on a transparent sheet placed over the computer monitor. I then faithfully transferred the results onto ordinary large sheets of white paper. The lines thus drawn in different directions created a space, drawing a St. Mark’s Square that is actually not there. As well as the actual physical space, it is also a drawing of our individual and collective manner of relating to space. Each single path determines the route of others, in a continuous and reciprocal game of influences that makes our collective progress.
At IMERA we developed this method for a new environment, a city more ethnically and culturally plural than Venice. Together we set up procedures and tools for collecting data about mobility networks there: nodes, links, chronotopi. These drew on the work of Bruno Giogini’s Laboratorio di Fisica della Città of the University of Bologna. We shot videos focusing on specific behavioural patterns where strategies of shifting, approaching and distancing play a decisive role; and we were also attracted by the places and situations of pedestrian congestion. Using the same technique as in Venice, I translated these into drawings of movement. These again created a space that marks out squares and places which are actually not there, each synthesizing space, time and humanity in a single image.

LB: Is there an emancipatory or governance-related dimension to this work? Degrees of mobility have human rights implications. How does your work as an artist connect with these rights, especially the notion of the right to the city?
MS: The first goal when I work as an artist observing reality is observation, i.e. a way of observing that implies a new attention. The result is always instructive because I do not have particular expectations. After lines have been traced following my process, something always emerges and what emerges can be a useful and indicative element for the emancipatory dimension of the urban condition. I would say that Bruno Giorgini is more involved in that dimension than me, especially in the notion of the right to the city.
LB: There’s a current preoccupation among researchers in a number of fields with the relationship between representation, often engaged with/through technology, and urban life. How has your latest work connected with this relationship?
MS: My way of working with technological instruments such as computers is very particular and limited. I use the computer as a technical tool strongly mediated by the senses, i.e. by human perception. I am very interested in modalities of perception: they are so imperfect, yet sufficiently perfect to make our existence possible.

LB: You described the way you work with technological instruments as “particular and limited.” Another way to look at this is that you make the technological system slow down by inserting yourself into the process… and the result is your drawings, which still movement. Might this be one role for art — to insert the human into the machine? Much net art focuses on flows of information, virtual movement, and representing that. While not quite glitch art, do your representations of movement in some sense intentionally put a brake on the machinery?
MS: I find your words enlightening, you describe my way of working better than me….. Actually I insert myself into the technological process…..but this is not a statement of a position against technology.
I can say that what interests me the most (and art’s relation to science is just one instance of this) is the thread of connection between specific cases and general theory, between subjective and objective. Between, on the one hand, the singularity of events and, on the other, general theory. The individual’s experience is singular, unique; but there is always a thread, even if fine, that leads each individual case to a wider generalisation. What interests me is this incessant – indispensable as much as concealed – mental activity that every day leads us to search for generalisations and regulating principles. What interests me is the human tendency to comprehend phenomena, even the most complex, via schematic representation, via a generalisation that leads to the identification of organising principles. I mean “Comprehension” in very wide sense, where emotions and feelings participate too in embracing reality, including reality. Maybe in this sense I put the human in the machine…
There is a discrepancy between how we perceive reality, mediated by our senses, and the truth decreed by science. On a rational level we recognize the truth, but we cannot internalize in a deep way this knowledge; this is beyond our human capabilities. I think that in my artistic research I find myself in this deep discrepancy.

LB: Bryan Connell, your work in Marseille addresses, among other concerns, technology and its relationship to nature. Do you see the urban environment as playing any particular role in that relationship — of having a particular status in our negotiation of it?
Bryan Connell: One of the things that intrigued me about the metropolitan hiking trail in Marseille is the way it plays with our sense of meaning and value in the exploration of contemporary landscapes. Most long distance hiking trails are designed to lead out of urban environments, not into them. We don’t usually think of carrying a field guide that illustrates the taxonomy of fire hydrants, electrical pylons, or urban weeds on an extended city or suburban walk. That kind of engaged, systematic attention is usually reserved for wild natural terrains. From a traditional environmental perspective, the less altered a place is by human technology, the more scientifically interesting, ecologically exemplary, and aesthetically rich it’s going to be. Without undermining the validity of ever-present environmental concerns, the trail functions as an invitation into a more challenging and complex relationship to the emerging para-wilds and novel ecosystems that are arising at the intersection of the natural world and the technological infrastructure of the built environment.
Similarly, the Marseille trail doesn’t really focus on the kinds of urban sites that are traditionally thought of as having significant historic, architectural, or cultural interest. Instead, the trail route incites visitors into an exploration of the everyday environments and working landscapes of the contemporary urban transect – a world of parking lots, freeway overpasses, suburban developments, abandoned railways, and semi-rural wildlands.

Landscape ecologist Earl Ellis argues that to better navigate our way through the current geohistorical epoch, the Anthropocence, we must expand the traditional ecological concept of regional biomes into the parallel notion of “anthromes” – biomes that are complex interconnected melds of human technology and natural systems. In a sense, the GR 2013 Marseille trail is a sketch or system of exploratory paths into what a publically accessible, anthrome based urban ecology observatory might look like.
LB: A similar question is in relation to the image, especially sequential images. What does it mean for our negotiation of the relationship between nature and technology? Between science and art?
BC: We increasingly live in a networked digital metropolis with an image and information density that both mirrors and exceeds the high population densities of the physical metropolis. One topic of particular interest to me is the role these images play in transfiguring the quality of our desire. To what extent do scientific or aesthetic images that increase our ability to find meaning and satisfaction in observing and understanding urban landscape phenomena mitigate our need to physically alter the landscape to conform to an idealized image of what it should or shouldn’t be?
For example, the Marseille metropolitan trail didn’t require much physical alteration of the terrain – it’s a conceptually designated network of pre-existing roads, paths, streets and highways. The trail’s function is not to alter place, but alter the cognitive landscape of trail users so they have a richer sense of place. If you are fascinated by the diversity of ways a para-wild plant population has adapted to a technologically modified environment, do you need to engage in an energy and material intensive re-landscaping of that environment with a palette of conventional horticultural plantings to make it more “beautiful”? In this sense, constructing interpretive images of landscape is more than a way of augmenting a recreational hiking experience, it’s a way of shifting and re-configuring what we think we have to consume and alter to find meaning and vitality in contemporary landscapes.
http://uranus.media.uoa.gr/hc2/
Hybrid City is an international biennial event dedicated to exploring the emergent character of the city and the potential transformative shift of the urban condition, as a result of ongoing developments in information and communication technologies (ICTs) and of their integration in the urban physical context. After the successful homonymous symposium in 2011, the second edition of Hybrid City has grown into a peer reviewed conference, aiming to promote dialogue and knowledge exchange among experts drawn from academia, as well as artists, designers, researchers, advocates, stakeholders and decision makers, actively involved in addressing questions on the nature of the technologically mediated urban activity and experience.
The Hybrid City 2013 events also include an online exhibition and workshops, relevant to the theme
Hybrid City Conference 2013: Subtle rEvolutions will take place on 23-25 of May 2013.
The Hybrid City II events will take place at the central building of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens.
This document was edited with the instant web content composer. Use the online HTML editor tools to convert the documents for your website.
Someone said to me ‘To you football is a matter of life or death!’
and I said ‘Listen, it’s more important than that’.
Bill Shankly
Drawing is one of the two oldest purely cultural – in the sense of playful, not directly concerned with keeping body and soul together like cooking or hunting or shelter – activities that comes down to us today directly in the form of artefacts from between 25 – 35 thousand years ago [1] (the other is music [2]). There is no known human culture that has not made representational and other marks with something, on something, for both fun and survival. Furthermore, as Patrick Maynard demonstrates in his steely eyed and magisterial Drawing Distinctions [3], it can be shown to be the practice which more than any other underpins not only all of present day visual culture (including photography, which, following Maynard [4], we read as a species of drawing) but also the technical developments of our advanced industrial age. With satisfying circularity, drawing, a fundamental tool for engineers and architects, scaffolds the level of production which (by guaranteeing surplus product) is the prerequisite for the very existence of our substantial caste of artists and designers, those useless and indispensable dreamers.
Arguably, then, in a perfect world its study might be counted, with literacy and numeracy, as a genuinely key skill to be studied by all. Certainly, perhaps a more realistic demand, it should be a practice both underpinning and overarching any systematic education in art and design. What concrete shape might this take within the Babel of practices which current art education encompasses?
A couple of years ago the two of us, both from a background in digital art/moving image, started teaching on two consecutive courses – a Foundation degree in Digital Art and Design and its top-up, a BA (Hons) degree in Art and Design Practice. Much of the formal documentation of the courses specified the use of particular kinds of software and allegedly real-world reasons for deploying them (many involving the demands of “industry”). From the start we were antagonistic to this approach. We wanted to “artify” the course – introduce as much experimental, speculative, exploratory, pleasurable and downright pointless (in the way that the best art is both pointless and hugely important) activity as possible. We didn’t abandon the idea of teaching design, but we did decide that the core course programme would henceforth be art/design agnostic – it would deal with ways of making and thinking about images (as well as sound, performance, interactions or concepts) that could be used with profit by students moving in either or both or other directions. It would not be training; work would be driven by the imagination and shaped by the ambitions of students. Teachers would introduce new technical processes, but these would be embedded in thematically organised investigations of historic and contemporary precedents. Help with technique or software might be part of what teachers did, but this would be part of an organic investigation/development by student and teacher together. If a teacher knew something they would help; if they didn’t, they might know where to look; if neither knew, they might search together; if the student knew, they could teach other students and the teacher too. In short we identified a peer-learning process as the only sensible approach sufficient for developing the necessary skills, knowledge and flair in a rapidly-developing field.
Moreover we wanted a course that integrated the digital with every other sort of visual (and conceptual, performative and sonic) practice. We were both impatient with the idea that work made using digital tools, or work created within and distributed across a network, was somehow qualitatively different from all that had preceded it (a not uncommon view often allied to a species of digital mysticism). Indeed we realised we both sensed, and gradually came to articulate clearly, that there was a continuum – a chain – from the cave painter to the contemporary artist. Not to say that social and historical concreteness plays no explicatory role, but that there is some still human centre to mark making (and to allied practices – singing, the telling of tales, etc.) which has persisted and will persist and is part of the territory of being human. ’A chain’ is no loose metaphor, but a precise account of the reality. Inspiration and technique pass continuously from generation to generation. And this is cumulative – making much of the past of art available to its future. In a sense the terrain of art accretes, expands, as time passes. Even what is lost to famine or war, proscription, taste and changes in technology leaves traces, the possibility of reconstruction and re-use (and, often most creatively, misuse). This is what we wanted to instil in our students.
Our drawing sessions link to and are inspired by earlier instances of art powered pedagogy that place cross-form conversation at the heart of learning together. Joseph Beuys made drawings throughout his artistic life – often enigmatic constellations of media, concepts, entities, political figurations and material properties. However of particular relevance here are his extended works, Office of the Organization for Direct Democracy by Popular Vote for 100 days at documenta 5, 1972 and Honey Pump in the Workplace for documenta 6 in 1977, in which he demonstrates his expanded notion of art that is exactly congruous with his philosophy of teaching – ‘to reactivate the “life values” through a creative interchange on the basis of equality between teachers and learners.’ [5] Both pieces required the involvement of many people in processes outside of the realms of ordinary action (such as the maintenance of the plastic pipes of the honey pump as it circulated 2 tonnes of honey through the building) in order that they might connect with unfamiliar concepts and experiences. The artworks integrated many different categories of work (some, but not all, associated with art making) including performance and the practice of various disciplines (of dialogue, rhetoric, democratic processes of exchange and decision making). And yet, in an interview with Achille Bonito Oliva, Beuys makes it clear that he has no interest leading audiences towards an “activism devoid of content” [6]. The liberation of humankind through art (Beuys proposes that everyone is an artist and society is to be sculpted by everyone) depends on a more deliberate engagement of individual energies.
Drawing was particularly important to both of us. It was something Ruth had always done from an early age. Collections of drawings made by her between the ages of six and thirteen depict public street scenes of everyday social groupings and activities (a group of kids running with a dog, two mothers with two prams, businessmen waiting for a bus). The figures are too small to carry facial expressions. Nevertheless their interactions, mood, social status and relationships are expressed by their outfits, gaits, their gestures and their proximity to each other and other elements of the scene. Ruth now looks back on these as evidence of an early growing fascination with sociality. Through school she learned that ‘drawing well’ meant producing an image as much like a photograph as one might render. Praise and grades were awarded accordingly. Later, at art school, drawing became a liberating process of discovery. She generated abstract marks, as traces of energies within the body, rather than to create a deliberate composition within a pictorial plane. In this way she produced surfaces such as might be produced by soot covered animals (think monkey, gazelle, seal, tiger, crow) thrown together into a white room. This surface would then serve as a mirror (or crystal ball) from which entities, gestures and forms of light and shadow emerged to be drawn out in further explorations of aspects of her unconscious.
Drawing was something that Michael aspired to. Because he had come to moving image work – to “being an artist” – by a strange route through theatre, maths and music, he had both a fascination with and a terror of drawing. He had been the kid in the class who couldn’t draw, and yet had loved the feeling, the deep engagement with both the act and with what it awoke inside him –his mind’s eye – that it brought. In his moving image work he had attempted to confront this. The inverted commas that came with a certain species of conceptualism were a great help because he could frame himself performatively, comically almost, as an uncertain but oh-so-willing draftsperson, one with no eye or dexterity, a technical schlemiel.
In his secret heart, though, he knew he wanted to do this thing without (or at least largely without) irony.
Arising out of this obsession, in the early years of the new millennium, Michael had launched a little provocation where he challenged digital artists, as they were then still called, to create self-portraits, on the sole condition that this be done using non-digital means, and subsequently to photograph them for display in an online archive. Those who didn’t baulk at the task produced a touching and intriguing panorama, of pen and paint and pencil but also of bathroom tile, egg tempera and iron filings… [7]
As part of a discussion about this Michael had opined on some listserv or other that the barriers between artistic practices were porous and that the true measure of anyone aspiring to be an artist (musician, film maker, poet) was that, if lost in a deep forest or desert isle, with only a rock to make some marks on and another rock to make those marks with, the putative artist would eventually produce something of interest, depth and value.
Early on we introduced chunks of drawing as an occasional workshop – Ruth introduces, and then builds on familiar art school, Bauhaus type exercises that attempt to separate process from outcome-anxiety, allowing students to engage with an inner dialogue about their looking and representation un-disrupted by fears of inadequacy. These include:
drawing without looking at the paper; from memory; without removing pencil from paper; drawing with the “wrong” hand; drawing in five minutes or five seconds; drawing only negative space; having the pencil trace the movement of the eyeball as the drawer observes an object, etc.
Michael felt the centrality of drawing calling him but these sessions still felt like a slightly naughty holiday, an activity that did not necessarily link to his background and formation as an artist. The teacher, like the student, was still exploring.
The big epiphany came with the introduction of a weekly drawing session for all three years of the course. It happened and happens every Monday of term, without fail, and everyone in the room takes part, staff included. As many days as possible where more than one member of staff is present in the room, to make for debate, thus modelling civilised disagreement and forcing students, ultimately, to make up their own minds; there are usually two members of staff and occasionally more present. Each drawing session is led by a student who brings in an object, procedure or puzzle for the rest of us to address.
What happened is that we were rapidly out-Bauhaused by our students. Byzantine sets of instructions for tasks that we as teachers would have rejected out of hand as overly complex, impractical or confusing were carefully explained by students and then carried out by all of us in utter silence.
Half an hour elapses, we place our sets of images on the floor and we process around them all, discussing them. The important thing is that everyone has drawn. Everyone is both vulnerable and admirable. Teachers are not privileged. For students, it is understood that although the process carries course credit, what is being marked eventually is a series of drawings – some “good”, some “bad”, most neither – and that technique – whatever that is – is not the focus. There must be room for play in creative education; hence, for this part of the course, taking part in all of the sessions is enough to secure a pass.
With respect to collective feedback, our experience has been that perceptive kindness predominates. We search for the wonderful things, speculating on why they are wonderful, maybe asking questions of the person who has made this thing, trying to elicit that week’s secret or lesson. The drawings are a pleasure to behold. We have no intention of reproducing any of them here, though many would bear reproduction – we do not want to betray the egalitarian, labouring-together ethos of the thing by selecting outside the sessions and group. We are not sentimentalists – it is precisely because we understand the necessary element of brutality involved in the fair administration of an assessed course that we want to create oases, visions of how things could be other. It is the collective production of shared work that matters – it is not, let us emphasise though, a privileging of “process over production”. The production matters – desperately so. [8]
Over the weeks, our drawings are diverse in category, style, media and technique including: illustrations of the set task, abstractions, naïve figurations, diagrams, signs; some are performances of processes made in pencil, pen, paper, wood, charcoal, paint, collage, arrangements of plastic objects, paper-constructions; they reveal our choices and learning. Some students advance arguments in their drawings either with each other or with their own earlier work. As new tasks are set we each decide in the moment whether we understand the activity we are to involve ourselves with is mundane, ritualistic (perhaps even sacred), mad or wise, pointless or significant – our conclusions shape our drawings. In this way collective drawing has become central to the ethos of our courses as an integrative practice for negotiating a shared studio culture and shaping our learning together, our movement towards collegiality. Doing the drawing means the week has a start to it – we affirm ourselves as folk with a common interest, different but equal. The sessions have helped to provide a social glue, too, across the three years of the course.
There are areas where we as teachers know more than the students; both of us have track records of work in the art world, but the drawing sessions level us all – they enable a mutually supportive but acute look at progress on a common task. Since the drawing started we have also incorporated its lessons to other disciplines; staff and students share their photography work in a more horizontal way than the demands of the course would normally allow. We use new forms of social media, and have Flickr accounts in which all participants are contacts.[9] We comment on and “favourite” each other’s works as equals and collaborators.
Both drawing and photography in these contexts devolve to something similar – filling a blank space by mark making, with valuable, experiential knowledge accrued: repeating processes many times over to find out what constitutes skill and when (often, it turns out, much more often than is often acknowledged) to accept the gifts brought by chance; discovering that the art happens in a social space between the maker, the wider world and the viewer; understanding the work of others because we do it side by side; and, finally, coming to grips with the question of personal style and the diversity of ways of doing things well and meaningfully.
Each week reveals both artistic phylogeny and ontogeny – we solve the problem here and now, as if for the first time ever and this illuminates the historical chain, the intertwining of theory and practice, our mutual dependence, all of us artists and all of us nourished by art too.
—-
Originally written for Drawing Knowledge (2012). Tracey, The Journal of Drawing and Visualisation Research, Loughborough University.
Revised and republished Miller, A & Strong, J. (eds). (2012) Research-Led and Research-Informed Teaching. CREST Publishing.
Contact: info@furtherfield.org
DOWNLOAD FULL PRESS RELEASE HERE
See images from the opening of Invisible Forces on Flickr.
Scroll down for the video of the exhibition.
An exhibition about why contemporary life is so difficult for so many
Invisible Forces features the work of artist-visionaries: Kimathi Donkor, Laura Oldfield Ford, IOCOSE, Dave Miller, Edward Picot, and YoHa with additional game events, talks and workshops with Class Wargames, The Hexists, Olga P Massanet and Thomas Cade Aston.
Our social, economic and cultural institutions are being dismantled. Control over the provision of social care, urban and rural development, and education is being ceded to the market facilitated by unseen technological and bureaucratic systems.
Undeterred, the artists in this exhibition meet the challenges that ensue with clear eyes, spontaneity, experimentation and a sense of adventure. This selection of installations, digital video, net art, painting and drawings deal with conspiracy, money, politics and hidden signals.
As part of Invisible Airs, YoHa (Graham Harwood & Matsuko Yokokoji) attempted to read 20,000 comma separated lines of Bristol City Council’s apparently open-data. After which they understood that power reveals itself through multiple layers of boredom. They constructed four pneumatic contraptions which reveal the relations contained within the fields and the people affected. A video made by Alistair Oldham documents their art project Invisible Airs, Database, Expenditure & Power. Invisible Airs was commissioned by The University of the West of England’s Digital Cultures Research Centre (DCRC) in collaboration with the Bristol City Council’s B Open data project.

This is shown alongside Data Entry, a video that investigates how databases operate on us and through us by looking at the work of midwives and women in labour. “Databases move through us, allowing new forms of power to emerge… [they] order, compare, sort and create new views of the information they contain. New perspectives amplify, speed-up and restructure particular forms of power as they supersede others.”
Edward Picot is an artist and writer who also works as an administrator in the UK health service. His seriously funny soap-gone-wrong, Dr Hairy In…, chronicles the trials, tribulations and cogitations of an ordinary (but slightly hirsute) general practitioner – with hilarious results!* Dr Hairy’s struggles with NHS bureaucracy are brought to life in a series of satirical video shorts, featuring puppetry performances given by a child’s doll and screened in a doctor’s waiting room, as an installation. “It was like watching Team America set in the NHS” says Ian Hislop (broadcaster, editor of Private Eye and NHS patient).
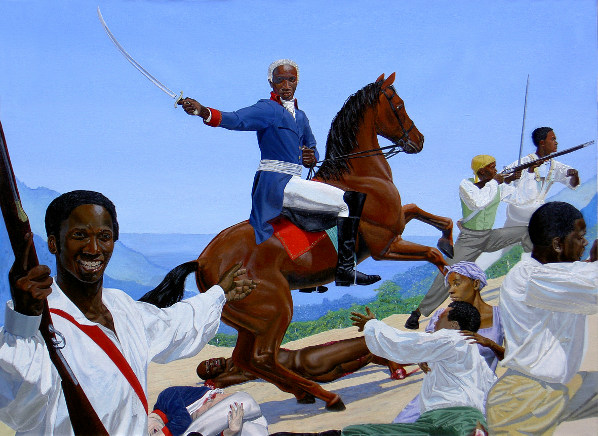
Kimathi Donkor‘s Toussaint Louverture at Bedourete is a history painting made with oils on canvas that depicts an icon of anti-slavery struggles who, in his lifetime, was smeared as a reprehensible war lord. Created to mark 200 years since the independence of Haiti, the image shows the leader of the Haitian 1791-1804 revolution in a pose reminiscent of the Jacques Louis David’s Napoleon Crossing the Alps, surrounded by inspired revolutionaries in a battle that led to the creation of Haiti as the first slave free nation in history. In a short film by Ilze Black, Dr Richard Barbrook and Fabian Tompsett of Class Wargames interview Donkor about the work.

Laura Oldfield Ford‘s recent drawings are the result of walks (or ‘Drifts) through deserted urban spaces in the part of East London being prepared for the 2012 Games. They depict layers of failed utopias of the past and present and imagined futures. Known for her poetic and politically tuned ink drawings produced in print and online in her zine Savage Messiah, Oldfield Ford documents her psychogeographic explorations, in text and image, of the city as a site of social conflict, melancholy and political resistance.

Net artist Dave Miller presents two agitprop posters and a pamphlet of images reproduced from his interactive, multi-layered, online narrative bankers_bonuses. Miller worked with software he created himself to combine hand drawn illustrations with images gathered from Internet searches, and provocative (sometimes preposterous) statements made by powerful people about the ethical questions arising from the economic crisis.

Italian artist group IOCOSE has created A Crowded Apocalypse, a net art project that exploits crowd sourcing tools in order to simulate a global conspiracy. The “crowd” assembles its own conspiracy and then protests against its protagonists and effects. A Crowded Apocalypse is commissioned by AND Festival and Furtherfield.
As we scan our cultures for maps, role-models, possible ways of living in today’s world, we often encounter images of society that are created by its hidden, controlling forces. By naming, revealing, tracking, playing, making, subverting and transforming tools, circumstances and figures that give rise to current crises we enlarge the debate and extend our freedoms. And the artists in this exhibition offer examples of just some of the ways in which this might be done.
* Important note. Dr Hairy In… is NOT a critique of socialised medicine and so we include a disclaimer: “The creators of this piece would like to point out that they all work in the National Health Service and are completely devoted to it.”
Free public play, games, making and discussion run alongside the exhibition.
Led by Dave Miller, The Hexists, Class Wargames, Olga P Massanet and Thomas Cade Aston. See HERE for details.
Rachel Baker (The Hexists)
Rachel Baker is a network artist who collaborated on the influential irational.org. Her art practice explores techniques used in contemporary marketing to gather and distribute data for the purposes of manipulation and propaganda. Networks of all kinds are “sites” for Baker’s public and private distributed art practice, including radio combined with Internet (Net.radio), mobile phones and SMS messaging, and rail networks.
Kayle Brandon (The Hexists)
Kayle Brandon is a inter-disciplinary Artist/researcher, whose work is sited within the public, social realm. She predominantly works in collaborative and collective fields; a working method which informs much of her ethos around the making of art. Her main areas of interest are in the relationships between the natural and urban worlds and Human/Non-human relations. She investigates this field via physical intelligence, provocative intervention, observation, self-guided exploration and collective experiences.
Class Wargames
Class Wargames is an avant-garde movement of artists, activists, and theoreticians engaged in the production of works of ludic subversion in the bureaucratic society of controlled consumption.
The members of Class Wargames are Dr. Richard Barbrook, author and senior lecturer in the Department of Politics & IR at the University of Westminster; Rod Dickinson, artist and lecturer at University of the West of England; Alex Veness, artist and co-founder of Class Wargames;Ilze Black, media artist and producer; Fabian Tompsett, initiator of London Psychogeographical Association and author; Mark Copplestone, author and figure designer; Lucy Blake, Software developer; Stefan Lutschinger, lecturer, artist and researcher; and Elena Vorontsova, World Radio Network and journalist.
Kimathi Donkor
Kimathi Donkor lives and works in London. He attained his B.A. at Goldsmiths and an M.A. at Camberwell College of Art, both in Fine Art. In 2011 he received the Derek Hill Award painting scholarship for the British School at Rome; and, in 2010, his paintings were exhibited in the 29th São Paulo Biennial, Brazil.
IOCOSE
IOCOSE has been working in Italy and Europe since 2006. It organises actions in order to subvert ideologies, practices and processes of identification and production of meanings. It uses pranks and hoaxes as tactical means, as joyful and sound tools. IOCOSE thinks about the streets, Internet and word of mouth as a battlefield. Tactics such as mimesis and trickery are used to lead and delude the audience into a semantic pitfall.
Dave Miller
Dave Miller is a South London based artist and currently a Research Fellow in Augmented Reality at the University of Bedfordshire. Through his art practice Dave draws out the invisible forces that make life difficult. His work is about caring and being angry, as an artist. His art enables him to express feelings about the world, to attempt to explain things in a meaningful, yet subjective way, and make complexed information accessible. Recurrent themes in his work are: human stories, injustices, contentious issues and campaigning. Recently he’s been very bothered by the financial crisis.
Laura Oldfield Ford
Laura Oldfield Ford lives and works in London. She studied at the Slade School of Art and completed her MA Painting at the Royal College of Art. She has exhibited extensively including Rokeby and Hales galleries in London, Savage Messiah takes over Late at Tate Britain, The Arnolfini, Bristol , De Appel Amsterdam and the Goethe Institute, New York. She has also recently been commissioned by Art Review. She is currently working on new projects for the Shenzhen Sculpture Biennial in China, the 2012 Gwangju Biennial and the show ‘Desire Paths’ at the Caja Madrid in Barcelona. A compilation of her zine ‘Savage Messiah’, which documents her psychogeographic drifts through London, is available on Verso books.
Edward Picot
Edward Picot was born in 1958. He lives in Kent with his dog, wife and daughter, not necessarily in that order. He earns his living as a Practice Manager in a doctor’s surgery, and in his spare time he does creative things – usually at the low-tech end of the new media spectrum. He started the Dr Hairy series – humorous short puppet-videos about a fictional doctor, closely based on his own experiences of working in the NHS – in 2010.
YoHa
Graham Harwood and Matsuko Yokokoji (YoHa – English translation ‘aftermath’) have lived and worked together since 1994.
YoHa’s graphic vision, technical tinkering, has powered several celebrated collaborations establishing an international reputation for pioneering critical arts projects.
Harwood and Yokokoji’s co founded the artists group Mongrel (1996-2007) and established the MediaShed a free media lab (2005-2008). In 2008 they joined Richard Wright to produce Tantalum Memorial shown in 9 countries and 15 cities over 4 years. In 2010 YoHa produced Coal Fired Computers before embarking on a series of works about the lived logics of database machinery including Invisible Airs, Data Entry in 2011 and Endless War in 2012.
Furtherfield Gallery
McKenzie Pavilion, Finsbury Park
London N4 2NQ
T: +44 (0)20 8802 2827
E: info@furtherfield.org
Furtherfield Gallery is supported by Haringey Council and Arts Council England
Dave Miller’s bankers_bonuses is supported by KAY MOUNTING.
‘Living’ is the result of a six month residency at the V&A by Christian Kerrigan – from January to June 2010 – and it is part of The 200 Year Continuum. The 200 Year Continuum is the title of a project by the same artist that explores the relationship between nature and technology. Interestingly ‘Living’ was exhibited in the same space where it was created: in the digital studio of the V&A. This was a small room with dim light and crowded with rarities. It felt like one was penetrating the secretive and magical space of experimentation of some sort of mad professor.

Once in the space my gaze wandered around a series of oddities. On the right, a table full of raw materials; in the middle of the room, a fish tank with algae floating in high pH waters; on a wall, a real time video projection showing the evolution of the algae; on a different wall, a slide projection showing some drawings; in some shelves, notebooks with notes by the artist; above the sink, chemical products piled up on a shelf; and on each and every window a semi-transparent drawing. No explanations, no titles, nothing. It’s you and the objects. Luckily Christian Kerrigan was always about, meeting visitors and discussing the work. We started looking at the materials on the table. Christian told us those were unprocessed rocks and crystals that he used as the starting point for his drawings. He scanned pieces of amber, moss, fiber glass, volcanic rock or resin and produced a model using 3D software. Then he manipulated that model to create his drawings and printed them on semitransparent paper. He eventually placed them on the windows of the space. This routine allowed him to explore the different stages of a process that makes real matter and virtual space intermingled. It is a practice that explores where the process of creation begins, and what it does to reality. ”The drawings, he tells us, become extensions of the physical material which I started with.” Although we have become accustomed to discuss the hybridity of our nature-culture, the way Christian carefully interwove materialities and virtualities was very evocative. The fact that the drawings were placed on the windows gave yet another layer of complexity to the mixture. The colours of the printings morphed natural light into a hybrid light turning the atmosphere of the room into a creative and ongoing process.
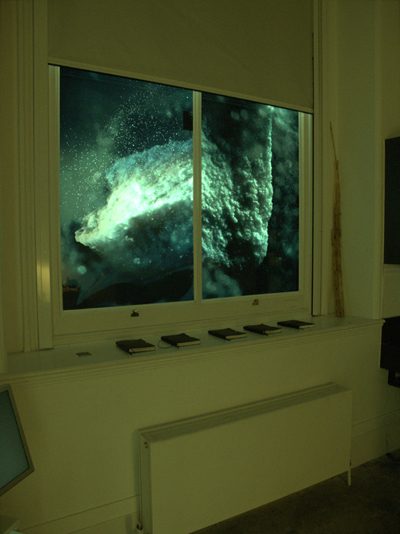

Next I wondered about that mysterious fish tank in the middle of the room where algae lived (and died) in high pH waters: Encased Nature. Apparently the algae reacted to the elevated pH creating a protective coat that eventually killed them. At the bottom of the tank: a graveyard of coated dead algae showed the consequences. I instantly loved the idea. Again an experiment about the hybridity of natural and controlled habitats. I thought it was a particularly dystopic illustration of the environment we inhabit where control works on the conditions of the environment, dictating the way reality unfolds. This is an emerging tendency in our most-discussed societies of control, what has come to be called soft control. And we could take it even further, and see it as a great illustration of today’s climate of fear. In such a habitat, the threat has become virtual and all-pervasive, it has become poisonous in itself, just like high pH. The nightmare of security measures that this artificially produced environment justifies links quite well to the ‘lethal-protective’ coat. What this allegory leaves out, though, is the power of imagination! The capacity of conditions to be turned around, the potential for intervention and deviation from the pre-programmed chain of (re)actions. The idea of projecting a live video recording on the wall was to intensify the experience and highlight the importance of mediation. As Christian argued, we are now more used to experience nature through a lens than to experience its presence. However, the quality of the footage seemed to work against the intentions of the artist and rather than intensifying the experience of that enclosed nature, it tended to obscure it. The particular texture that the webcam gave to the recordings turned that hybrid habitat almost into an abstract movie. On a different corner there was another video projection made out of a series of drawings. Interestingly they had been created using a ‘living technology’ and recorded at a nano-scale. For Living Drawing, the artist had collaborated with Martin Hanczyc from the Department of Physics and Chemistry at the University of Southern Denmark. They had manipulated some protocells that inhabited chemical gradients and reacted to ultraviolet light. When UV light was applied to the fiberglass where these protocells ‘lived’ their motion left traces of colour that were recorded. This technique, although still in its early stages, allowed the artist to ”explore the spontaneous event of drawing by using organic systems”, he told us. Kerrigan’s rather cryptic exhibition proved to be an inspiring and very personal exploration of the blurring between nature and culture in its absolute physicality. Paying particular attention to the materiality of the creative process, from the composition of the materials used, to the chemistry of the drawing process or to the laws of electromagnetism that inform light in its interaction with his work, his methodologies show a passion for unfolding reality in its many scales. His work is that of someone who’s starting to explore rather than someone who’s making an assertion; it is tentative rather than conclusive, it is interesting for its questions rather than its answers. However, even if sometimes vague, it is at points pleasingly dark and sometimes inspiringly intense.