



“Tweets in Space beams Twitter discussions from participants worldwide towards GJ667Cc – an exoplanet 22 light years away that might support extraterrestrial life. By engaging the millions of voices in the Twitterverse and dispatching them into the larger Universe, Tweets in Space activates a potent conversation about communication and life that traverses beyond our borders or understanding.”
Marc Garrett: Could you explain to our readers what ‘Tweets In Space’ is?
Scott Kildall and Nathaniel Stern: Tweets in Space is an art project — a networked performance event — which beams your Twitter messages to a nearby exoplanet that might support human-like, biological life. Anyone with an Internet connection can Tweet with the hashtag #tweetsinspace during the performance time, and their messages will be included in our shotgun blast to the stars. The performance is on September 21st, 20:30 – 21:00 Mountain Time (3:30 AM BST / London time).
MG: What was the motivation behind your current collaboration?
SK and NS: We found inspiration from various sources. First, in NASA’s Kepler mission, whose purpose is to discover planets in the “habitable” or “Goldilocks” zone. The project has found over 2000 exoplanets thus far, all of which are “not too hot, not too cold, but just right” for life as we know it. Scientists now estimate that there are at least 500 million planets like this in the Milky Way alone. Our conclusion: extraterrestrial life is almost certainly out there.
![The newly discovered planet is depicted in this artist's conception, showing the host star as part of a triple-star system. Image credit: Carnegie Institution / UCSC. [1]](http://www.furtherfield.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/planet_gj667cc.jpg)
“The latest discovery is at least 4.5 times bigger in size than Earth. Reportedly, the planet exists 22 lightyears away from Earth and it orbits its star every 28 days. The planet is known to lie, in what is being referred to as the star’s habitable zone. A habitable zone is a place where the existing conditions are just perfect for life sustenance. Astronomers, according to this report also suspect that the GJ667Cc may have been made out of earth-like rock, instead of gas.” [ibid]
Another source of great inspiration is how we use social media here on Earth. This is our second, large-scale, Internet-initiated collaboration. In 2009, we amplified the power structures and personalities on Wikipedia, and questioned how knowledge is formed on the world’s most-often used encyclopedia – and thus the web and world at large. Now, we are turning to the zeitgeist of information and ideas, feelings and facts, news and tidbits, on Twitter. The project focuses on and magnifies the supposed shallowness of 140-character messages, alongside the potential depth of all of them – what we say in online conversation, as a people.
We are directing our gaze, or rather tweets, via a high-powered radio telescope, towards GJ667Cc – one of the top candidates for alien life. It is part of a triple-star system, has a mass that is about 4 times that of Earth, and orbits a dwarf star at close range. GJ667Cc most certainly has liquid water, an essential component for the kind of life found on our own planet.
MG: Right from its early years when Jagadish Chandra Bose [2], pioneered the investigation of radio and microwave optics – science, technology and art have had strong crossovers. And it might be worth mentioning here that Bose was not only well versed as a physicist, biologist, botanist and archaeologist, he was also an early writer of science fiction. [3] Which, brings us back to ‘Tweets In Space’, wherein lies themes relating to science fiction, radio broadcasting (commercial, independent and pirate), wireless technology of the everyday via our computers, and ‘of course’ the Internet.
![J.C. Bose at the Royal Institution, London, 1897.[3]](http://www.furtherfield.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/JC-Bose-at-the-Royal-Institution-London-with-his-radio-equipment-The-date-is-1897.png)
But, what I want to pin down here is, where do you feel you fit in historically and artistically with other past and contemporary artists, whose creative art works also involved explorations through electromagnetic waves?
Scot Kildall: The work of JC Bose is incredible and what strikes me is that he eschewed the single-inventor capitalist lifestyle in favor of his own experiments. Isn’t this the narrative that artists (often) take and linked back in many ways to the open-source/sharing movement, rather than the litigious patent-based corporation? And it mirrors in many ways the reception of electromagnetic radiation as well. You can’t really “own” the airwaves. Anyone who is listening can pick up the signal. This comes back, as you point out, to the internet. Twitter is now, one of the vehicles, and, ironically entirely owned by a benevolent* corporation.
Nathaniel Stern: (Agreeing with Scott) and we can’t forget of course Nam June Paik, who played with naturally occurring and non-signal based electromagnetic fields to interfere with analogical signals (as well as the actual hardware) of tube televisions, and more. And of course, there have been other transmission artists, explored in depth by free103point9, among others. I think, like them and others, we are messing with the media, amplifying (figuratively and metaphorically) and intervening, pushing the boundaries of DIY and cultural ethico-aesthetic questions…

MG: What is especially interesting is that all the tweets submitted by the public are unfiltered. How important is it to you that people’s own messages are not censored when going into space?
SK and NS: Absolutely. Tweets in Space is by no means the first project to transmit cosmic messages with METI technologies (Messaging to Extraterrestrial Intelligence). Our fellow earthlings have sent songs by the Beatles, photos of ourselves shopping at supermarkets, images of national flags, and even a gold record inscribed with human forms – controversially, where the man has genitals and the woman doesn’t. These slices of hand-picked content exhibit what a select few believe to be important, but ignore, or willfully exclude, our varied and collective modes of thinking and being.
Tweets in Space is “one small step” with alien communications, in that it is open to anyone with an Internet connection. It thus represents millions of voices rather than a self-selected few. More than that, our project is a dialog. There have been, very recently, a small number of projects that similarly “democratize the universe” but none are like ours: uncurated, unmediated thoughts and responses from a cooperative public. We can speak, rebut, and conclude, and nothing is left out. Our transmission will contain the good, the bad, and the provocative, the proclamations, the responses, and the commentary, together, a “giant leap” for all of humankind – as well as our soon-to-be friends.
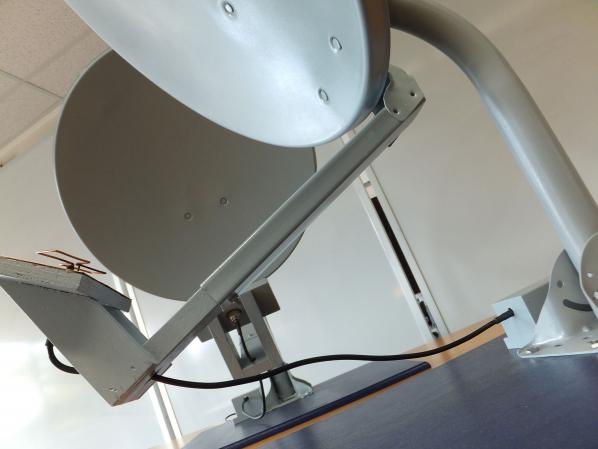
Furthermore, by limiting the event to a small window of only 30 minutes, we are encouraging all our participants to speak then respond, conversing with one another in real-time, through networked space. We are not just sending lone tweets, but beaming a part of the entire dialogical Twitterverse, as it creates and amplifies meaning. Tweets in Space is more than a “public performance” – it “performs a public.”
MG: Now, you will be transmitting real-time tweets toward the exoplanet GJ667Cc, which is 22 light-years away. How long will it all take to get there?
SK and NS: Well, first off, we’re collecting all of the tweets in real time, but only sending them out later in October. The main reason for this is that we have to wait for the planets to align – literally. We want line of sight with GJ667Cc from where our dish is. The added bonus of time, however, is that this will allow us to really flesh out how we send the messages in a bundle. We want to include a kind of Rosetta Stone, where we will not only send binary ASCII codes of text in our signal, but also analog images of the text itself. We additionally intend to choose the most frequently used nouns in all the tweets from our database, then give a kind of “key” for each. If “dog” is common, for example, we can transmit: 1. an analog image of a dog, like a composite signal from a VCR; 2. a text image of the word “dog” in the same format; and 3. the binary ASCII code for the word dog.
In terms of time/distance, when speaking in light years, these are the same thing. A light year is the distance light can travel in one year of Earth time (about 9.4605284 × 10 to the 15 meters). Since radio travels at the speed of light, a big dish on GJ667Cc will pick up the signal in 22 years. We should start listening for a response in 44 – though it may take them a while to get back to us…
MG: Will the code used for the project be open source, and if so, when and where can people expect to use it?
SK and NS: Yes it is! The most useful part of our code is the #collector, which saves real-time tweets to a database, that can then be used for live projections or web sites, or accessed and sorted later via all kinds of info. The problem is that it’s not really user friendly or out of the box – folks need a suped up server (VPN), and to plug into a few other open source wares. The main portion of the backend we used is actually already available at 140dev.com, and then we plugged that into Drupal, among other things. For now, we’re telling interested parties to contact our coder, Chris Butzen, if they want to use our implementation. And we hope to do public distribution on tweetsinspace.org if we are able to package it in a more usable format in the next 6 months.
MG: Are there any messages collected so far, grabbing your attention?
We’ve had thousands of tweets so far – even while just testing the ware in preparation for the performance. We’re anticipating a lot of participation! The tweets we’ve seen have ranged from variations on “hello [other] world” and “don’t eat us,” to political activism and negative commentary, to a whole surreal narrative of about 30 tweets per day over the last 3 months.
go to tweet aliens to add your own words…
Some of our favorite tweets have been those that question how to make our own world better. These speak to both the hope of space age-ike technology, as well as the hope in collective dialog – both of which our project tries to amplify. Such tweeters ask about the alien planet’s renewable energy sources, tax structures, education, art, and more.
We imagine the 30-minute performance will see a much more potent discussion about such things, and hope your readers will participate. The final transmission will be archived permanently on our site once we’ve prepared it for launch.
As part of the International Symposium on Electronic Art in New Mexico (ISEA2012). We will collect your tweets and transmit them into deep space via a high-powered radio messaging system. Our soon-to-be alien friends might receive unmediated thoughts and responses about politics, philosophy, pop culture, dinner, dancing cats and everything in between. By engaging the millions of voices in the Twitterverse and dispatching them into the larger Universe, Tweets in Space activates a potent conversation about communication and life that traverses beyond our borders or understanding. http://tweetsinspace.org/
AND THEY WILL BE SENT INTO DEEP SPACE!!!
Watch the stream LIVE here – http://tweetaliens.org/tweets/tweets.php