



Artist and designer Ling Tan talks about the SUPERPOWER! workshop that explored ways to empower young women through a creative exploration of wearable technology in public space.
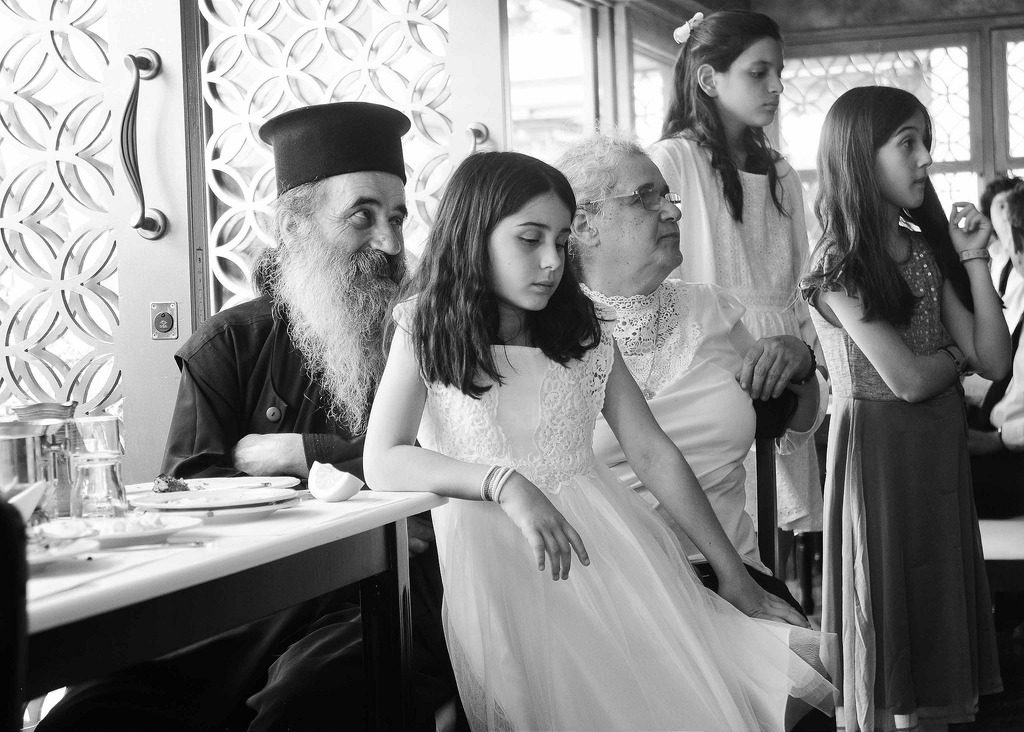
Last summer, artist and designer Ling Tan worked with young peer leaders from All Change Arts, and the Furtherfield team to devise a project called SUPERPOWER! Finsbury Park. It brought together young women from different walks of life to discuss their relationship with the city. The project explored the ability for technology to bring about female empowerment, and question the participant’s role as female in regards to decision making about our city.
Three common themes by the participants were collectively identified, and linked to a place in Finsbury Park. Using the themes to co-create a series of wearable devices that enabled them to record their subjective perceptions of the city using gesture sensing technology. These were: Cultural diversity and inclusivity in our community; Safety of individuals in the London Borough of Islington and; Wheelchair accessibility around Finsbury Park area
It was all co-scripted and used for an exploration walk, involving the team walking around a specific area of Finsbury Park, performing and recording their subjective experiences using the wearable devices that catalogued their gestures. During the workshop, participants designed body gestures using the wearable technology which track their body gestures and communicate remotely with each other through haptic/audio sensors.
Marc Garrett: Where did the idea for the workshops come from and how did the concept of superpower shape what participants did with your wearable technology.
Ling Tan: In SUPERPOWER! Finsbury Park, the participants were young women aged 15-25 years old and almost all of them have no prior knowledge of electronics and coding. Instead of the workshop being about coding and making, I wanted it to focus on empowerment, challenging them to go beyond their comfort zones. Hence the term “superpower” became a powerful concept to get them to think about technology as a form of superpower that extends their perception into the environment. The idea for the workshop built upon a couple of projects I was doing over the past few years; WearAQ and Fakugesi Social Wearables. The projects use wearable technology to enable different communities to actively record and map out their relationship with their cities through individual subjective perception in the form of body gestures. For example, perception of air quality in London, UK and perception of safety on the streets in Johannesburg, South Africa.
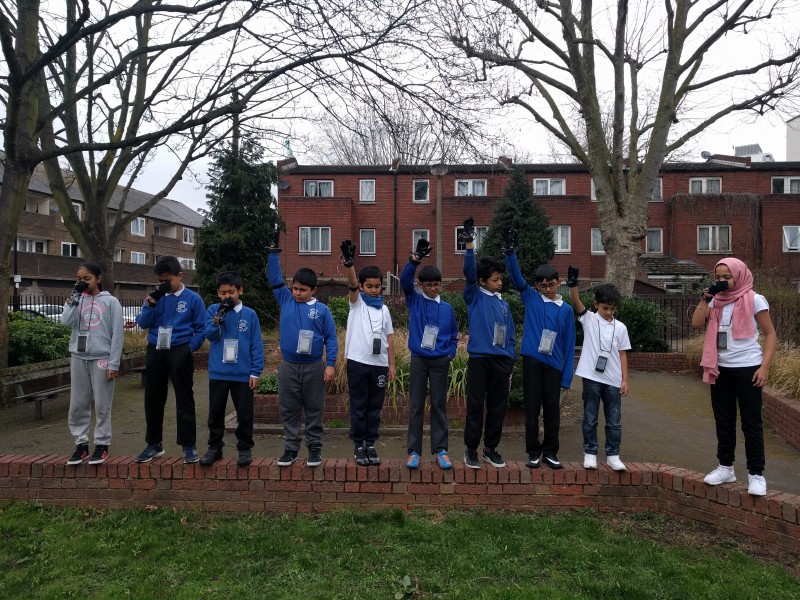


In the workshop, participants discussed about their relationship with Finsbury Park, designed experiments and body gestures to map out their own relationship through the use of an existing set of wearable devices, went out into public space and run with experiments with strangers, park users. For me, learning about what they want to do with technology is more important than picking up skills like coding or fabrication.
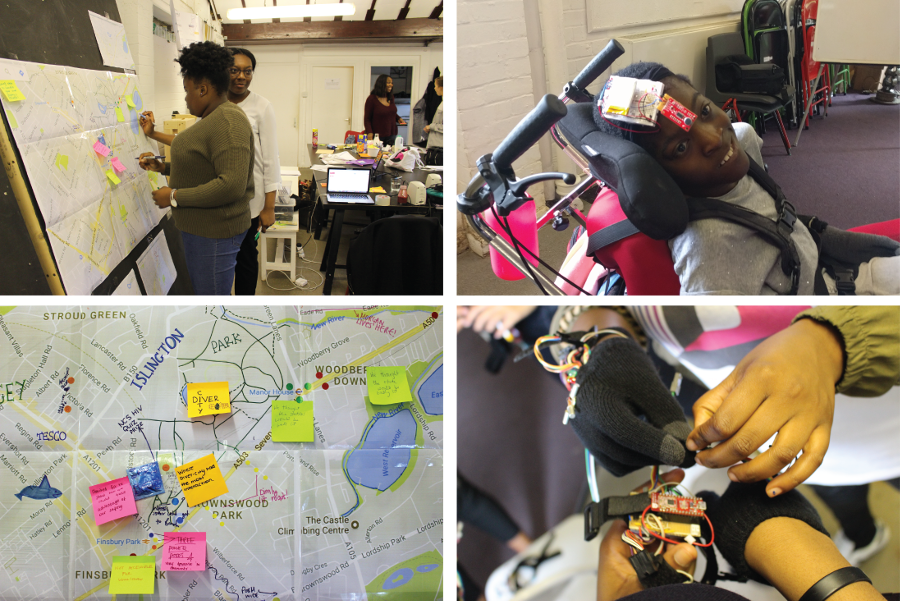

MG: We were surprised to hear how much the young women had appreciated being taught in depth about how the wearable technologies worked as part of this workshop. Do you think this informal workshop format offers a different way of supporting learning about and working with technology? What most surprised you about the way that the young women responded?
LT: I wanted to steer away from a conventional technology workshop where participants would focus on coding and fabrication, than design, because these are skills that they can pick up themselves through on-line documentation and support. For me, what is more important is to figure out what their own interests are with technology, by learning it through hands on design activities with ready made wearable technology. That way, it makes them feel comfortable with tackling complex technology and it also gives them the opportunity to learn about issues that might occur when technology is tested in the real world, checking it out when it does not work and why.
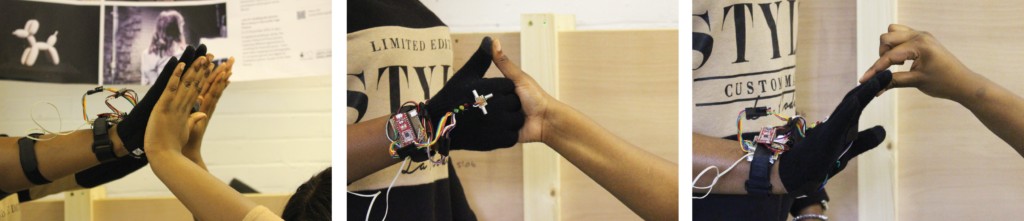
I was most astonished by their speed of learning and how well they picked up the tech knowledge. For example, one part of the workshops involved learning about the body gesture and what the wearables can detect through decoding “1” and “0” read via the body gesture sensors. I was very surprised that they were able to quickly translate that into their own body gesture design.
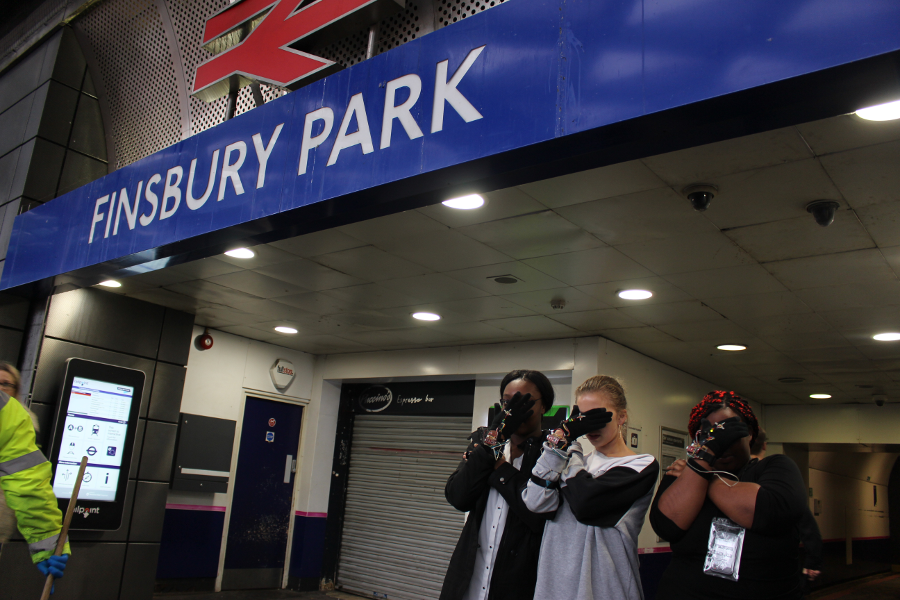

MG: Your workshop addressed questions of value in technology innovation, in the particular context of working in the public space of the park. Please tell us about how you approached these questions and why this is important to you.
LT: I think its is important to demystify technology especially given that we are living in an era where technology is so embedded into our everyday life that we take it for granted and do not notice its impact. It is important for the younger generation to learn about ethics of technology, to be curious about who and why companies are designing specific types of technology, and most importantly, to learn that technology does not always work, that technology cannot solve all our problems. They need to learn to be proactive and have a sense of agency in tackling issues concerning their own environment. For example, issues such as safety on the streets cannot be solved entirely by technology, it also needs other input such as citizen vigilance, policy and law changes.
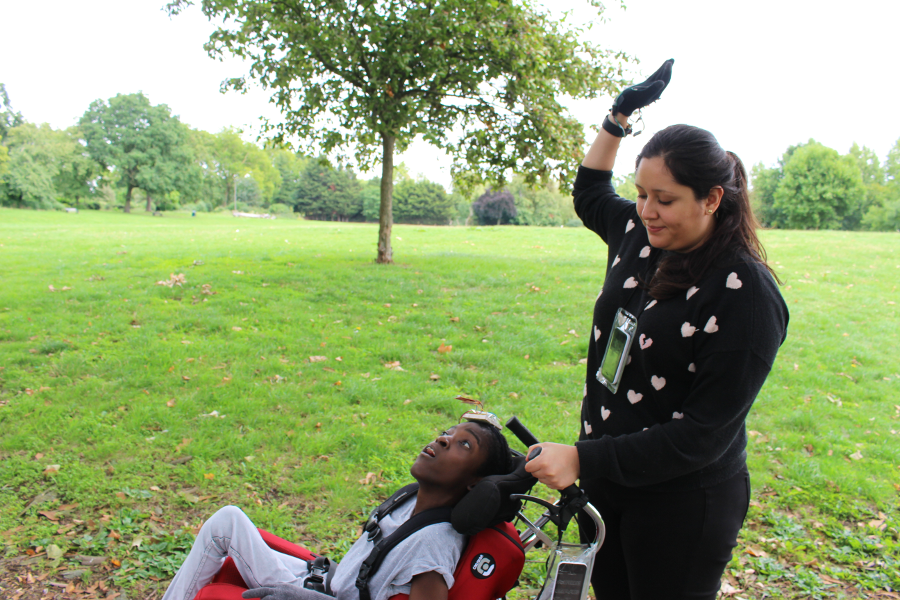

SUPERPOWER! Finsbury Park was a part of the B Creative Summer School, a programme of arts projects created by young women for young women aged 16 – 25 in Islington.
Special thanks to:
All the participants involved in the project
Peer leaders from All Change
Ella Medley Whitfield
Commissioned and supported by: Furtherfield and All Change
This project has been funded with the support from the European Commission. This communication reflects the views only of the author, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein.
This is the third of three pieces on people who are posting work to the photography sharing site Flickr [1].
In this final article I look at the work of Karin Rudolph
. Rudolph is a Belgian photographer, currently living in Athens, where she works as a wedding and event photographer and raises two teenage sons. In addition to her work for pay she makes an ongoing series of ‘personal’ images which she regularly posts to the photo sharing site Flickr.
I ask her to send me some images from a wedding job and she does.
It is a job she is clearly good at—everything is beautifully shot, nicely framed, sharply in focus (when sharp focus might be thought necessary), but there is that extra something that comes with a good portrait photographer, which I can only describe as fellow feeling. A fellow feeling which elicits transparency and a willingness to risk vulnerability from the subject. I’ve never met Rudolph but it’s clear that her personality, her way of being, is a player here.
There’s also a sharp curiosity at work—a hunger for the way the world looks and with Rudolph this seems to become attached to particular objects, creatures (some human, some not) and roles. There was a dog at the wedding in the images she sent me. The wedding took place outdoors and the clearly much loved animal figures in a number of the shots. It’s as if at one point R becomes fascinated by it and we get shots where the all humans are cropped (in the shooting; she doesn’t crop after the fact) down to the waist and the dog becomes central (although a small child has a supporting role here too since he necessarily evades the crop/frame wholesale). We get a dog narrative. Then a bouquet catches her eye and we get a bouquet narrative, the wedding filtered through a non-human being or an object. Motion—a sense of the moment before and the moment after being necessary, if hidden, components of this still image—is a key underpinning of so many of these images, particularly in relation to these micro-narratives.
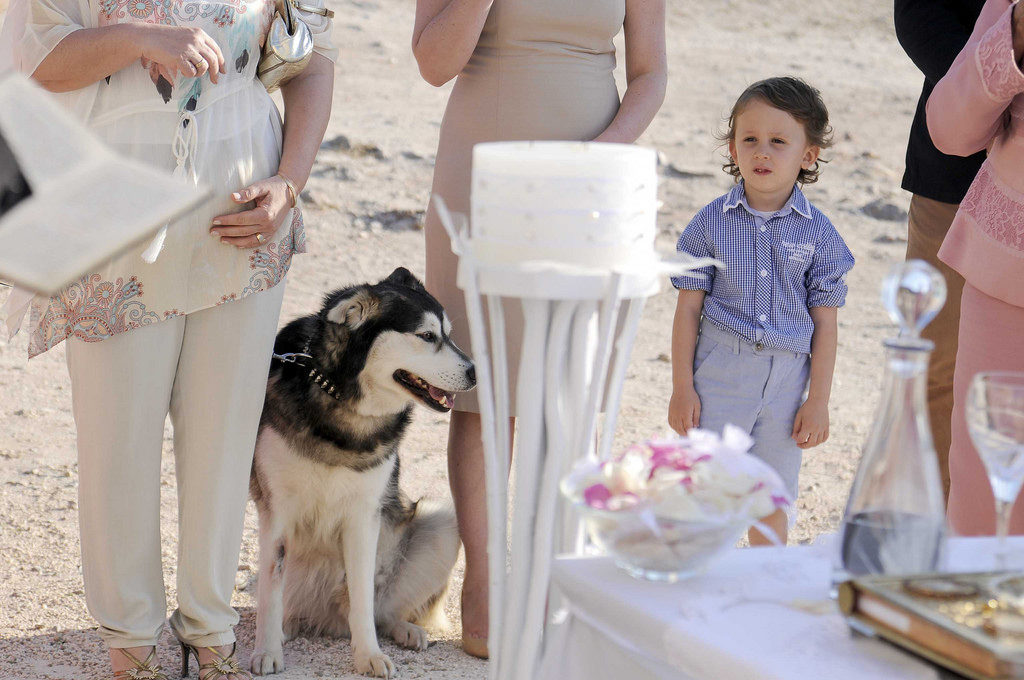
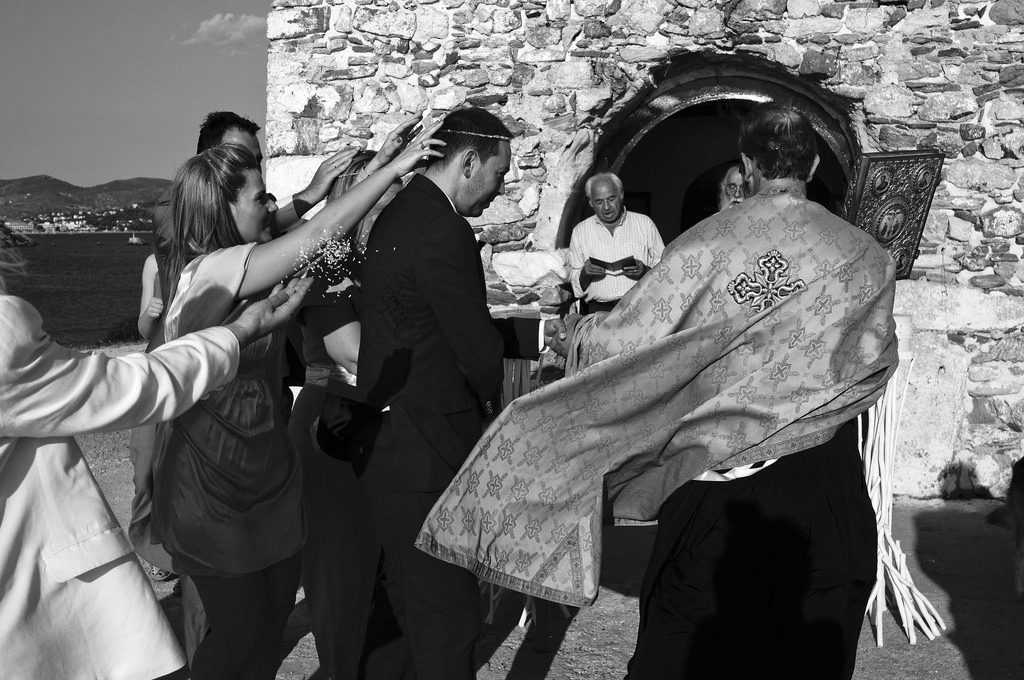


In a photographer less manifestly gripped by the facts of our fragile human being and ways in the world one might call some of her approaches formalist. It is certainly true that rhyme, echo, geometry, continuities and disruptions of line, shape and colour play a highly significant role in the structuring of her images but one of the driving forces of R’s work is that it constantly moves to dissolve any artificial divide between content and form. Yes, her eyes seek pattern; yes, this or that organising device might order an image but this never obscures our awareness of the facts, feelings and relationships portrayed or implicit there. Also—we humans are formalists, aren’t we? We’re pattern seekers. We play. Were you never fascinated as a child by mirrors, by the world turned upside down by hanging from your legs or by the cropping or heightening, or focus) achieved by looking through the cracks in your fingers? Of course you were. As we grow we perceive the whole world through a complex dialectic of what is presented to our senses on the one hand and our burgeoning sorting and structuring principles on the other. We are of necessity creatures of content and form together and one surmises that this is what makes us creatures of art too.

I’d been writing and thinking about this piece for a few months, on and off, and I’d got to a second or third draft when it hit me with a thud, a jolt, that hardly any of the recent images have titles.

The fact had just sailed under my radar, curiously, since I’ve argued and will again, that insofar as we can talk about meaning in a photo (or any visual artwork) this possibility lies in a network of references and comparisons which ineluctably involves talk, writing or both. Language. Further, that visual art is best seen as something humans do (emphasis on both words) than as the usual set of isolable ‘in and of themselves’ objects (which isolation is a fiction, at best an analytical convenience). And then it struck me ( I was being struck a lot that day) that there is something about these images that fights back against language—they’re often cross genre and resist categorisation and there’s a sense in which the easiest approach to what’s in them is simply to list it, and finally to say that this image had these things in it under this kind of light from that angle but, of course, this is far from satisfactory and at root there is something far transcending taxonomy or description going on. But –dammit! –I can’t help feeling it is as if the images (placed as they are in the sequence formed by Flickr) are calling out, hailing each other. I don’t know why, but forced rhubarb, a most unlikely image, is the one which springs to mind and persists, as if the absence of the immediately adjacent language of a title somehow forces the set of glorious but hitherto mute images to invent speech.

Anyone who has ever taken an un-posed image of a human being on a fast shutter speed will be cautious about ascribing emotions or characteristics to the subject on the basis of what is revealed. As in so many other ways, the very small, the very distant or unreachable, animal locomotion, the photograph reveals things beyond our normal ability to see or grasp them. One of these things is the curious plasticity of the human expression and how in our interactions we read this in sequence, in time, together with a host of other clues, aural and visual, to make sense of what is going on, to try to understand both what a person is doing and to surmise what they might be feeling . (Of course the opposite of this, the posed image, brings its own problems too.)

When we think hard and soberly we cannot but be convinced that the photograph alone, an impossibly small fragment of time, does not allow us enough evidence, that it is somehow unanchored in the world.
And yet, the desire to draw conclusions, to make comment, is certainly strong in us and each photographic image of a person, especially the striking and affecting ones, comes with a very strong sense that we are able to do so.
What can we actually say about the still photographic portrait, both in general and in particular cases?
One thing we might say is that the single image’s apparently complete account of a human being, based upon a fleeting expression (and perhaps the fleeting expressions in response of others and maybe also the presence of contextualising objects or other clues) suggests at best, a class of possibilities. This single image evokes a range of other possible images and moments in the world at least one of which must correspond to our strong intuitions about it. So even if we were able to establish the facts of the matter in this particular case and it made a lie of our emotional response , nevertheless that response represents a truth and somewhere, perhaps quite often, in the world, situations occur, have occurred, will occur, which correspond to this truth.
And it seems to me that it is this instinct for general human truth, allied to the particularity of light, line, composition, of other things depicted, which manifests in the eye-and-heart-catching-ness of the resulting final image.

A strong way of putting it would be that any portrait is just as much a work of fiction as a novel but that as we would not wish to deny something called ‘truth’ in the novel ( you might—I see no point to the thing otherwise) in the portrait we work our way back to truth.
And at least for me it is the photographer’s—and here, now ‘the photographer’s’ means R’s—capacity for empathy, for narrative, for understanding of the world and the wonder and the oddness of its inhabitants that makes her such a good portraitist (and let’s not forget, too, simply having done the thing a lot —this is often underrated nowadays.)
Do I know whether the Orthodox priest at the wedding table was a kind man? No. I don’t. I cannot. Is kindness manifest in the photo, is the possibility of kindness in the world reasonably asserted in it? Do I know more about kindness thereby? Absolutely.

There’s a black and white image, taken, I think, at the place where her teenage sons practice their footballing skills which feels like a short story or perhaps a collection of short stories, each cued by the various human presences which form at one and the same time a large (in how they capture our attention) and a small (in how much actual area of the image they occupy) part of the entire image.
It also has a most clearly defined geometry—three strips, the topmost being the practice field itself, the middle appearing to be a road like depression running between the photographer and this field and the lowest a pavement of some sort on the other side of that ‘road’. The almost bizarrely long evening shadows of R and a companion (and the horizontal distance between shadows is nicely ambiguous on the exact relationship between those shadowed) stretch forward into the image. The vertical grid adjacent to them, with a gap in the centre picked out in shadow too, suggests they are standing at a pedestrian gate to the place. I imagine the figure at the viewer’s right is R as the arms appear to be raised in a photo taking action.
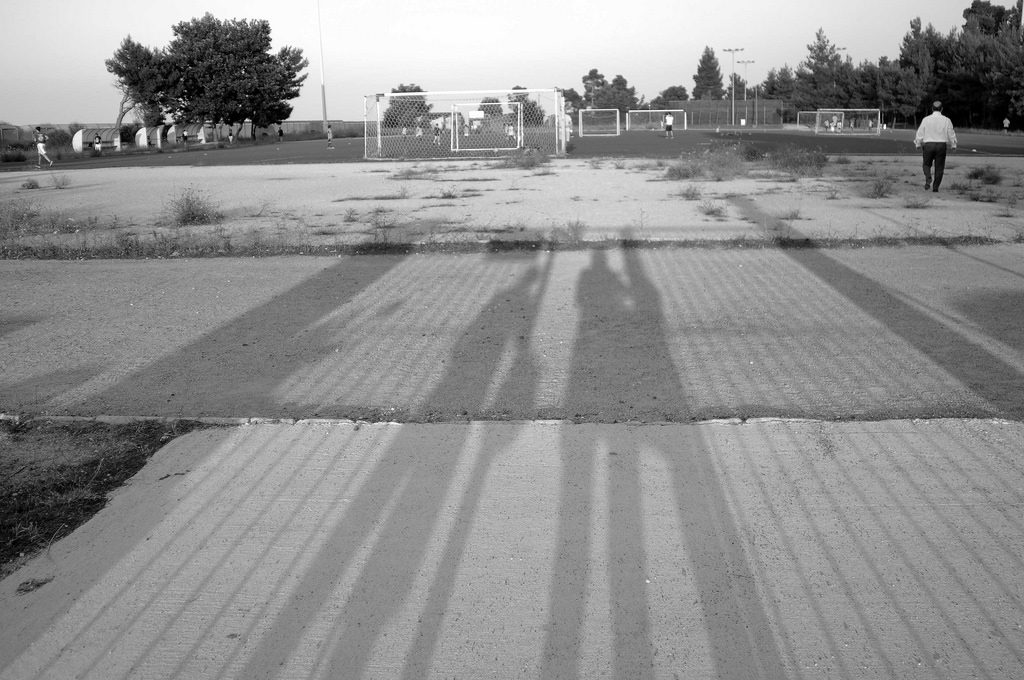

(The image thumbs its nose at genre—it is oblique self-portrait, landscape, social history, portrait and exploration of geometry and structure all at the same time.)
Shadows aside, the figures which catch my eye (what about you, so much to choose from or are you constrained in a similar way to me by something in the way the image is structured?) are the short stocky man in motion, walking away from us at the image’s far right top strip foreground. There’s a delicious swagger and confident openness about him.
Has he passed through the gate where R stands? Did he greet her?
The second key (perhaps because nearest?) figure is the young man, top strip, viewer’s far left, again in movement, this time almost certainly certainly sports related. Is he pursuing a stray ball? Running to greet a friend? Engaged in some sort of running warm up/exercise? As we strain to see, our relationship to the image’s scale shifts and we begin to realise just how many other figures he opens up to us—there are at least six either standing or seated in those little sheds at the field’s side between him and the left edge of the nearest goal net—each an enigma of a small but definite kind—and when we move rightwards from them we realise (and we have to move closer in, look differently, at the image to see this) just how many people there are in some sort of action here. As we move out again we are stuck by the contrast between the contemplative calm of the giant shadows and the anthill busyness of the young men. And here’s another thing. This is such a male photo. (With the exception of the photographer and I think it’s only because I know she is female that I read her as such. Then even as I write this I notice the slight head-cocked-to-one-side quality of aficionado-like attention in the head of the left shadow—and why do I think that might clue maleness? What does that say about me?) Oh! Layers and layers of fact, of presence, of things to enumerate and puzzle over. So much! And this before we take the thing as a totality—geometry, inhabitants, shadows, activity, motivation, time of day, distant trees, weeds and barren ground, a sky whose colour we can only guess from the fact we know there is evening sun. And that totality is the hardest thing to compass in any way other than an intake of breath or shiver down the spine. Enumerating the contents helps (although it’s not essential to the immediate affective apprehension of the whole—that just happens) but it’s the inexplicable (not a value judgement—literally inexplicable—simply, ‘This is what R did’) decision to frame those contents in that way—the bit of the process which defies words—that makes this and so many other pieces by her so powerful.

5.
A ravenous eye.
She has a ravenous eye, constantly tracking the scene in front of her and hungry for detail. This hunger does not distinguish between content and form. Whatever is human, whatever stirs affect or curiosity—whether pattern, rhyme or echo, or ethics, or suggested human warmth or frailty, this is swallowed up and processed by heart and mind in turn

The resulting images bear the strong feel of certain, almost objective, structuring principles—that following of object or creature within a scene, the use of rhyme and echo. Two further categories are geometry and colour (and nothing here is pure, there are no essences, sometimes blocks of colour impose an extra, parallel geometry upon a scene whose first order sense—whether it be human beings in action or traces of interpretable human activity; buildings, signs, the street —apparently lies elsewhere.) The key thing about all these structuring principles is that they are found, excavated, discovered, seen—not made. They happen in parallel with, arise out of the actions and feelings of, human beings in this world, the only one we have.

Because she is someone who has lived, fully, in that world, for a fair time, because her hunger extends beyond the visual (she always has a book on the go and the range of these is impressive), because she has a number of languages and is at home in at least three cultures, she makes images which are connected and re-connected by hundreds of threads to things we ourselves might have read and thought or experienced and talked about. Further, it is impossible to imagine that the fact she is a woman living in a country not of her birth, where she has learned a different script, different ways of talking and being, where she works in part as an image maker for hire and constantly both connects and holds separate that work for pay from own ‘own’ work, at the same time as raising children by herself, that these facts are not also somehow foundational.

For a long time I have struggled with how to attach the word meaning to image. It is too easily and glibly used. An image never ‘means’ a single thing (unless it is the poorest of images and even then the human capacity for/delight in ambiguity sets to work to disrupt this) What is evident in Rudolph’s work is networks of evoked meaning, memories, feelings.

Her way of being in the world, this following her eye and nose, means that there is a kind of metonymy purged of any attempt at system—here is a dog or child or chair or window. Here are the things which necessarily were near it at a moment in time and this is how they were disposed. There was reason and there was randomness. Parts of the disposition were beautiful. (What do I mean by beautiful? They move me, they fill me with a joy that cannot be reduced to words though it perhaps can be limned by various combinations of words, combinations potentially infinite which always nearly but not completely fail.) Parts of the disposition were stark or threatening or at least worrisome. The bringing together of all these parts—worry, beauty, pattern, action—into an image framed, bounded, lit, by the laws of the heart and the laws of the intellect now pulling one way, now the other. The work about the world is itself part of the world. We are not alone. No person is an island. We can read each other’s thoughts. We can feel each other’s feelings.
The words and the image and human heart and human history dance ever outwards and outwards. What does an artist do but always start to write the whole history of humanity in the world?

Featured image: System Map by Andrea Crespo, 2015, image
Fear is easily attributable to a cause—we fear something in particular. Anxiety, however, can be described as fear without the source. Yet, anxiety is also a safety mechanism. Without it, we would walk in the face of danger. In the online exhibition Body Anxiety, curated by Leah Schrager and Jennifer Chan, the disquiet is experienced in the flesh, whether this is as a symptom or sublimation.
Whatever your gender, your body is politicised in ways you cannot control. If you are female, or gender queer, there is also a fight against power. The works in Body Anxiety specifically problematise the image of women in the media and in the art world. Women artists, they claim with good arguments, are powerless; sothe show gives time and space to a group of artists the curators call ‘female painters’. Even though few paint (in fact, probably only Schrager herself does), Schrager puts forward the argument of painting as the highest artistic form, one dominated my males. She recontextualises painting for this exhibition, where most artists use their own bodies as canvases for video performances, sound works, photographs and writing. Perhaps this is peinture féminine to Helene Cixous’ écriture féminine.

Good examples of the symptomatic are Victoria Campbell’s The Penelope Files, an auto-interview video with a reflexive sound monologue where she explores her thoughts on images of herself while browsing through her computer files. We hear her; we only see the screen. Exploring her relation to image, authorship, labour and the body, something about photography is revealed in the repetitive moving of files on her desktop’s finder window. Narrative also inhabits the work of Randon Rosenbohm. She presents a scan of a handwritten diary entry where artistic labour, exploitation and male artists feature. Her other work consists of a tumblr blog of rejected selfies. Both are pieces we should not see. This is also the case in Ann Hirsh’s video. Dance party just us girls shows footage that should be for private consumption, part of a home video, a laugh, documentation of a personal exploration. Using generic distorting video software available in most computers, the two-channel work shows the torso of a woman bobbing away to a song next to an image of moving genitalia, in a feminist version of Courbet’s painting The origin of the world. The two images share a pair of glasses and the genitalia is converted into a talking face, like in Denis Diderot’s libertine novel The Indiscreet Jewels.

Saoirse Walls’ Den Perfekte Saoirse(2012) quotes Jurgen Leth’s The Perfect Human. She replicates some of the famous body poses and music from the classic black and white film, showing us the best of her individual self in a sublimation. She can do a side crow, twerk, walk in heels and, thanks to camera tricks, have a 100% symmetrical face. The work gets more and more bizarre with the appearance of make up and hair extensions. Where has Leth’s serious exploration of perfection gone in her quote? What are we demanding of Saoirse Walls? Another good example of an impossible demand and how this conflict is shown in a work of art is Nancy Leticia’s video. Her youthful, gorgeous self plays piano in her underwear. She plays very well, but how does this relate to the image setting?
Screenshot of Den Perfekte Saoirse by Saoirse Wall, 2012, video, 2:22 mins
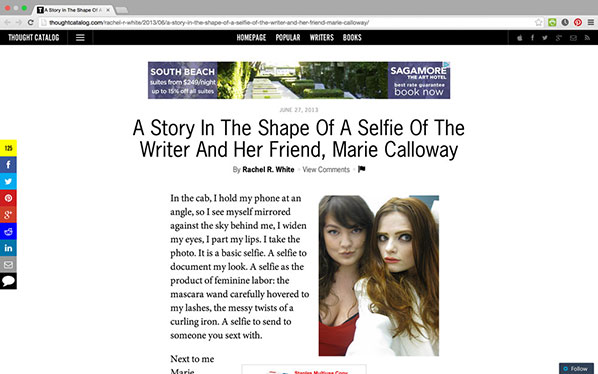
The writer Marie Calloway—an alt lit writer, also a female painter in the way Schrager intends—features in Rachel Rabbit White’s work A Story In The Shape Of A Selfie Of The Writer And Her Friend, Marie Calloway. Her writing with images addresses the issue of anxiety head on. ‘Refresh’, ‘refresh’, ‘refresh’, she writes at the end of a blog post-merging stories about Marie, public events, selfies, feminist writers and artists, and social media.
These diverse works are playful, at times irreverent, and certainly thought provoking. The curation is purposeful, direct and erudite. Yet, I have some issues with the display, with the sidebar prefaced by curatorial statements and with links to the artists’ biographies and websites. It feels more a catalogue than an exhibition. I don’t have a solution, though, as maybe this is a constraint of the medium. A few of the works are hosted on external websites—vimeo, red tube. Some of them even require passwords and this provokes a particular way of looking, a gaze, then a click, a search away from what is presented in front of us. I am an active viewer, often in the position of a Peeping Jane.
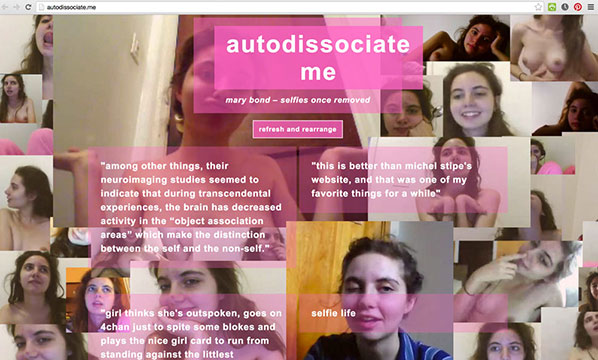
In her 1975 essay ‘Visual Pleasure and Narrative Cinema’ Laura Mulvey examines scopophilia, the pleasure in looking. This is not an innocent act. She argued that the relation between looker and looked is unequal in cinema, with woman as image and man as bearer of the look. If woman is a ‘one dimensional fetish’, as Mulvey writes (a thought which will be later echoed in Nina Power’s 2009 book One Dimensional Woman), the artists in Body Anxiety take this to its hysterical consequences, attempting to break the Master-Slave bond, making woman image AND bearer of the look. Let me return to the title for a moment. Anxiety, Sigmund Freud wrote, is neurotic fear, as distinct from real fear. So one is a reality, something tangible and worthy of our concern whereas the other sounds like is made up, accusation of fabrication (like hysteria). It is this last idea the show is trying to contend. The anxiety felt and displayed in these bodies, the imperative to conform to a certain standard and behaviour, the manipulation of femaleness in pornography, the shutting down of the woman’s voice are indeed neurotic, but not because of it they are less real. As a body of work, the exhibition is convincing and raises clear issues around female empowerment, agency and exploitation, and how these are linked to flesh. Converting the anxiety into an intelligible fear that can be stood up against, as these artists do, might be the first step towards overcoming it.
This conversation follows in a series of interviews with women who work at the intersection of art and technology. Amy Alexander’s work as an artist, performer, musician, and professorapproaches art and technology from a performing arts perspective, often examining intersections of art and popular culture.
Amy Alexander is an artist and researcher working in audiovisual performance and digital media art. She has worked under a number of pseudonyms including VJ Übergeek and Cue P. Doll. Coming from a background in film and music, she learned programming and began making time and process-based art on the Internet in the mid-1990’s with the Multi-Cultural Recycler and plagiarist.org. Amy has performed and exhibited on the Internet, in clubs and on the street as well as in festivals and museums. Her work has appeared at venues ranging from the Whitney Museum and Ars Electronica to Minneapolis‚ First Avenue nightclub. She has written and lectured on software art and audiovisual performance, and she has served as a reviewer for festivals and commissions for new media art and computer music. She is an Associate Professor of Visual Arts at the University of California, San Diego. During summer/fall of 2012, Amy is Artist-in-residence at iotaCenter in Los Angeles.
Rachel Beth Egenhoefer: You’ve taken on many roles as an artist, musician, performer, coder, organizer, professor. How would you explain what you do to the “average Joe” who has not idea what a code artist is?
Amy Alexander: I usually don’t try to explain to people what a code artist is. I generally just tell them about the types of projects I or my students do, (“museum installation,” “club performance,” etc.) and what some of them are about. Then I explain that it’s done by writing software, building electronics, making videos, etc. But the point is more about the projects, not about how specifically they are made.
I also think talking about code-as-art is both less necessary and less difficult than it was five or ten years ago. What motivated me and a lot of other code artists back then was a concern that algorithms had a cultural impact that wasn’t well-recognized. Nowadays, people are familiar with the idea that Google sorts your search results in a particular way, websites you visit develop demographic profiles of you, etc. – they’re already concerned about algorithms. So I think it frees up both artists and audiences to focus on other aspects of the work. Of course, there are definitely some situations in which focusing on algorithms-as-art is important. Just like photographers sometimes focus on the nature of photographs, video artists on video, etc.
RBE: You’ve worked as yourself, as well as other performers such as Cue P. Doll and Übergeek. Can you describe the differences between some of your characters, and how do you see identity as a key element in your body of work?
AA: Some of the online characters just evolved. I tend to anthropomorphize things, and I like to break into characters; I’ve just always done those things. So in some cases when I’m developing a project from a particular perspective, a character emerges who personifies that perspective. For example, The Original Plagiarist.org (1998) website was a collection of projects in which grandiose attempts to opportunistically plagiarize from the Internet always turned out to be transparent. So the character of Plagiarist emerged as the proud proprietor of this site and creator of all its projects – and the only person who couldn’t see the futility of the plagiarisms.
Übergeek is different, since I physically go out and perform as her. She’s both a theatrical character and actual club performer – in varying proportions depending on the context of the show. The theatrical character is a geeky rockstar wannabe. That opens up space for Übergeek to exaggeratedly escape the physical restrictions of performing on a computer – by waving around an “air mouse,” dancing on a DDR pad, etc. The club performer comes from my growing up performing music. I’d never thought about it, but the zone musicians go into to perform is really like playing a character. You have to become someone else. A few years ago I heard Steve Schick explain that when he has to perform a difficult piece of music, he imagines he’s someone else – and that other guy can play the piece. Eventually I realized that any performance of any kind I’d done that I’d been remotely satisfied with, whether music, VJ show, or performance art – I’d mentally become some other person. Going into character is really important, even if the character is just, “the performer.” It can be easy to forget the crossovers between performing arts and visual arts, but there’s a lot we can learn from one another.

RBE: Do you think this happens to us when we interact online, that we become performers? (Some people believe for instance that Facebook is really a performance of ourselves, not our real selves) Do you see any intersections of performance in “online” vs “physical/ in person” interactions? (I realize this gets into an entirely different question, the idea of intentional performance and unintentional, but perhaps you see an overlap?)
AA: I think there’s an overlap, but there’s also an overlap between the kind of “performances” we do online and those we do in “real life.” I don’t buy the dichotomy that the physical world is real/true and the online world is fake. We perform different sides of ourselves in different real life situations – work, friends, family, large group, small group, etc. Sometimes we perform more consciously than others. On the other hand, sometimes we feel less inhibited in online interactions, so we behave more naturally.
That’s not to say there’s no difference between online and offline interactions – but then again, these differences didn’t just suddenly emerge when the Internet came along. Think back to when people sometimes had pen pals by snail mail, for example. The relationships could be friendly, intimate, or performative. When things like immediacy and nonverbal communication disappear, that invites a different kind of behavior – be it more natural, more performative, or a combination.
RBE: What connections do you see between identity, code, and performance?
AA: I guess I’ve responded to identity & performance in the question above. As for code & performance: people have pointed out that code parallels musical notation, in that both are executable languages. If you think about scores by people like John Cage, where scores could actually be diagrams or verbal instructions to the performers, the connection between performance and instruction set becomes even clearer. This is interesting historically and theoretically, but for many of us who use code in performance, the connection becomes self-evident in practice. Code launches processes and actions, and performance *is* processes and actions, and there’s a back and forth between the performer and software. It’s not that much different for me performing software than performing a musical instrument; if I play violin, I finger, bow, pluck in various ways to get various sounds. You can think of the violin as interface, the notes and gestures as parameters, or whatever. But to be honest, trying to create precise analogies is a recipe for disaster. The point is, you perform both of them, and you have to learn how to do it. The difference with software is, you build your own instrument; that’s both a blessing and a curse. So you try to balance playability with flexibility, and so on. Because of my experience playing music, I keep trying to build ones that will accommodate clumsy performers like me!
RBE: Do you see all code as being “performed”? (Or perhaps is saying code is executable the same as saying code is performed?)
AA: It depends on which sense of the word “performed” you’re using. In the sense that means to do some sort of process – like to perform your job duties – yes. You can think of data as nouns and algorithms as action verbs. You “run” code, and though the physical metaphor might be an exaggeration, in general, some sort of an action happens. So in that sense, the processor is performing the code.
But in the other sense of the word – intentional performance, performing arts, performance art, etc. – running code is innately no more of a performance than breathing. People like John Cage have made interesting performances out of breathing, and people like Alex McLean have made interesting performances out of running code. But it’s not that way on its own, except in the Cagean sense of it being performance if you think of it that way. I think that’s interesting, but I’m personally more interested in code’s cultural, rather than formal, implications. In other words, I’m not so excited that processes are dynamic and self-repeating for their own sake. I’m more interested if, for example, that means we have increasing difficulty finding unpopular or obscure information online, because the popular perspectives have formed an algorithmic echo chamber.

RBE: Your newest work is using audiovisuals, performance, solar energy, and the history of dance in cinema. How did you arrive at this combination of ideas?
AA: The project is Discotrope: The Secret Nightlife of Solar Cells. It’s an audiovisual performance – a collaboration with Annina Rüst, with algorithmic sound design by Cristyn Magnus. There’s really two parts to the project: the projection system, and the content and performances that we develop for it. The system is a disco ball where some of the mirrors have been replaced by solar cells. The cells power the motor that turns the ball. We project video onto the ball instead of colored light. The result is, reflected, fragmented video images move around the room. Since the video projections “solar”-power the ball, the speed at which the images move around the room varies with the brightness of the images.

The way this all came about was I’d been interested in the philosophy behind hybrid cars and various other things – that when we “waste” energy, we might actually be creating it. I kept wondering if this idea could be applied to media somehow, and I kept trying various experiments with video: could the talking heads on cable news power an LED? etc. Never quite found the right outlet for this idea, though. At some point, Annina and I came across a disco ball, and we noticed the similarity between its mirrors and small solar cells. Then the idea of projecting videos onto it hit us, and it all came together as a “media-powered” system. Of course, that was just the general idea. After Annina built the initial prototype of ball, it took many hours working with it the studio for the “instrument” to reveal itself – i.e. how exactly does a video-powered disco ball become useful visually and performatively? Figuring that part out was just elbow grease – but getting from rough idea to what-is-this-really always is for me; I have to get my hands on things and play with them.
The content framework we’re working with for at least our initial round of performances is “the history of dancing ‘at’ cameras.” Since it’s a disco ball, we envisioned performing it at community dance parties, etc., and so people dancing seemed like the obvious thing to project. We started from the idea of projecting the people at the party onto it live – but we realized we also wanted to expand beyond that. Again, the elbow grease process: I’d try different clips of people dancing on YouTube, old movies, TV shows. Eventually a connection emerged between early cinema clips and contemporary YouTube clips. In both cases, people dance pretty much like vaudeville performers, directly for the audience – as opposed to cinematic narrative style, in which the viewer is a fly on the wall. In the dancing “at” cameras style, there’s a more direct, intimate connection between dancer and audience. We’ve written some things about this on the Discotrope blog – and I’ll probably write more there soon. Another thing we became interested in is how representation (gender, physical, etc.) does and doesn’t change from early movie camera demos and Hollywood films to YouTube, where people are generally self-cast and self-directed. And I’m really interested in the relationship between all of this and the muddy space between exhibitionism, voyeurism, and surveillance. That’s a theme that’s run through a number of my projects, and dancing at cameras certainly exemplifies that murkiness.
Of course, a lot of the dancing at cameras perspective relates to film history in general – cinema’s origins in theatre and vaudeville, the development of montage, etc. So it’s interesting to see it return with YouTube. Teresa Rizzo has written a really interesting article related to this called, YouTube: The New Cinema of Attractions.

RBE: When you say “people dancing at cameras” I immediately thought of surveillance cameras. Is your disco ball a type of surveillance camera?
AA: I’m really interested in the blurring between surveillance, exhibitionism, and voyeurism. The Multi-Cultural Recycler, SVEN, and CyberSpaceLand all hit on that theme in one way or another; this time it’s cinematic dancers. The cinema/YouTube performers who appear in Discotrope all knew they were on camera, so overtly it’s more about exhibitionism and voyeurism. Glamorous 1950’s female burlesque dancers did their strip tease acts for the camera; sixty years later, not-so-glamorous scantily-clad men proudly stomped through the Single Ladies dance on YouTube. One group does work-for-hire within the Hollywood studio system; the other does what they want. Does that make one voyeurism and the other exhibitionism, or is it more complicated than that? in some cases, we see the performers much differently than they probably saw themselves. Does that make it surveillance? I think it’s all very muddy, and that’s what I find interesting.
The flip side is that there are people in some of Discotrope’s YouTube videos doing things like dancing in Walmart, which gives the video a surveillance camera look even though it’s obviously not surveillance (in the traditional sense, at least.) People turn the tables on surveillance video and make their own production numbers in surveilled/controlled areas – for fun and as a type of resistance. That’s one of my favorite parts of Discotrope. Then we get to recreate those Walmart spaces in the big Discotrope projection. It makes it even more like an old Hollywood production number, and it makes it weirdly immersive. This is fun for us, because Walmarts are not the kind of thing normal people like to recreate immersively. 🙂
RBE: For this piece you are creating something for other people to perform with. Are there any differences for you in creating work that you will perform vs. others performing?
AA: Ah, those pesky multiple senses of “performance” again!. 🙂 I do the visual performances for Discotrope, so for now I’m primarily building the software system for myself to perform. So far Annina is the only other person who performs with the software. Like anything, it’d require some tweaking to be distributed for more general use, though I’ve tried to make it not too terrible in that regard. 🙂 More challenging/interesting might be for performers to get the feel for moving the ball – like anything, it takes practice to get proficient.
But perhaps you’re talking about performers in terms of the audience who can dance to Discotrope, or the parts of the show where audience members can dance on camera interactively. In this case, they’re both performer and audience at the same time. That’s an interesting challenge, because in designing the show, we have to think about them in both ways.
RBE: You are starting a residency at the iotaCenter in Los Angeles, what will you be working on there?
AA: It’ll be mainly exploratory/preliminary research; things will likely be changing/developing as I go along. But my general plan is to explore two threads: gestural and spatial cinematic performance. In performing CyberSpaceLand over the years, I found myself unconsciously developing certain gestural/structural performance techniques that were much different than what I’d consciously designed for the piece. That spawned some ideas about gesture, time and space that I’m going to try to take further. The spatial thread grew out of some things we’ve played with in Discotrope in terms of deconstructing cinematic narrative in a 360 degree space. I’ll be exploring these spatial cinema ideas both in regards to Discotrope and as broader research.
iotaCenter’s a great place for doing research in abstract / formal and experimental cinema, visual performance history, etc. They’ve got a terrific collection of films and texts. I’m hoping to also use the opportunity to get together with other experimental cinema and visual performance folks in LA. It’d be great to organize some fun/intellectually-stimulating/breathtakingly-earthshattering screening/performance events.
RBE: This interview is going to be part of a series of interviews with women working in art and technology. What do you consider to be important today about being a woman working in art & technology? Do you think it is still useful to discuss the female voice as a separate voice in the field?
AA: It’s a tricky subject, because we both need to hear women’s voices and avoid tokenizing or homogenizing them. Women artists working with technology do tend to have different perspectives than men, and there are far fewer of us. So often when the dominant themes emerge, they tend to be the “masculine” themes by virtue of sheer numbers. A corollary is that often women artists feel pressured to focus on gender issues or certain types of social issues. Again, it’s a problem of critical mass and self-perpetuating themes. Since a fair number of women are already involved with those topics and many women’s interests overlap there, they have momentum. But this ends up discouraging women from discussing or doing work on other topics they’re interested in, So, while we need to talk about shared experiences among women in art and technology, we also need to recognize that they have a diverse range of work and perspectives.
RBE: How have you seen perceptions of gender change through the years either in teaching, performing, or working as an artist?
AA: It’s interesting to think that the first programmers were women, and that at the time it was considered clerical work. (See Researcher reveals how “Computer Geeks” replaced “Computer Girls” by Brenda Frink.)
As men started to fill programming jobs, the perception of programming shifted. It became something “technical” that was somehow inherently “man’s work,” even though it had been clerical “women’s work” only a few decades earlier. I’ve seen something similar happen as a female computing artist. I think there are more of us now – at least we don’t seem to be the novelty we were ten or fifteen years ago. And I’ve seen a shift in attitudes and perception among undergraduate computing arts students: by now both the men and women have grown up playing video games and doing a variety of Internet activities that might have seemed like “boys-with-toys” pastimes a decade ago. So their perceptions of what they’re learning to do as computer artists is a little more open and less gendered. But unfortunately, there are still circular perceptions in all age groups that whatever technical work women are doing can’t be too serious by virtue of the fact that a woman did it. It would seem to parallel the current political debate in the US about the pay gap between women and men. There are always arguments that women’s jobs aren’t as demanding, and they usually end up with someone saying, “I can’t believe we’re still talking about this in 2012!” So on one hand, the more things change, the more they stay the same. On the other hand, as more women computing artists emerge, we’ll hopefully soon achieve sufficient critical mass for world domination. Don’t say I didn’t warn you.