



Featured image: @mothgenerator by Everest Pipkin and Loren Schmidt
Taina Bucher interviews artist and bot maker Everest Pipkin about their most popular Twitter bots, how they work and what they mean. Indeed, what are bots, who else is engaged in artistic bot-making, and how will social media bots evolve?
Meet Tiny Star Fields. Several times a day, the Twitter account publishes a field of stars in different shapes to a dedicated 51.000 followers. The latest tweet, published 53 minutes ago, has already been retweeted 151 times and gathered 114 favourites. Tiny Star Fields is a Twitter bot. During the last few years, bots, or automated pieces of software, have become an integral part of the Twitter platform. As some recent reports suggest, bots now generate as much as twenty-four per cent of posts on Twitter, yet we still know very little about who these bots are, what they do, or how we should attend to these bots. Admittedly, star-tweeting bots like Tiny do not belong to the kinds of bots that are most talked about. When people usually think of bots, they mostly have a specific type of bot in mind, which animates feelings of annoyance and disturbance. The spam bot, however, is but one kind of bot.

As Tiny and many others like to attest, bots are just like people. They are different. They tweet for different reasons, have specific audiences and engage with the world in various ways. Guided by their human programmers or taught to learn from existing data in playful ways, bots are legitimate users of platforms. But bots would be nothing without their creators, their makers who have conceptualized and brought these digital personas ‘to life’. So let’s not just meet Tiny Star Fields but also Everest Pipkin, the 24-year-old artist and creator of Tiny Star Fields.
Everest why don’t you tell us briefly about yourself and your background?
I grew up in the woods of Austin, Texas, where I also attended university for my undergraduate degree in studio art. Most of my work there was focused on drawing and installation, but I was also curating internet ephemera and beginning some rudimentary code projects at the time (albeit in isolation from others doing similar work). I also have a history in curation and have run creative spaces for many years. I’m currently pursuing my MFA at Carnegie Mellon in Pittsburgh.
What got you started with making Twitter bots?
I started making bots in the summer of 2014. I moved to a tiny town in rural Minnesota (population 900) for a longer-term artist residency and was quite isolated. I didn’t have a car, there was no bus or train, and I didn’t know anyone there. I was used to being alone on residency, but often I had friends near enough to visit or a local coffee shop to haunt. With no other options, I was at home and online almost constantly. The internet has always been important to my practice (and my social life), but I attached myself to it as a lifeline in that period.
I was already following Twitter bots (@everycolorbot, @youarecarrying, @twoheadlines, @minecraftsigns, @oliviataters, @prince_stolas, and I’m sure many others), but being online constantly shifted how I thought of them, rather than just seeing their occasional statements as charming non-sequiturs in a human space, I started to notice their underlying personalities, the structure of code that differentiated one from another; when they posted, the kind of source materials used, how they interacted with others. With nobody to keep up with locally, I also began sleeping in erratic structures- some nights for 5 hours, others for 14. As a side effect, I would catch off times on Twitter, where everyone but the bots were asleep. These timelines of automation had a striking effect. I was particularly fond of the bot chorus around the turn of the hour- bot ‘o clock, as some call it.
I had been following and aware of @negatendo’s #BOTALLY posts (a sort of # organizing structure for bot-related news and resources) for a while, but I also started following @thricedotted, @inky, @beaugunderson, @tullyhansen, @aparrish, @boodooperson and @tinysubversions (and many others!) in this period. There were new bots almost every day, all unique, and I was really taken by how people interacted with them and how they operated in that social space.
How did you go about making your first bot?
I got node.js set up on my laptop (no small task for me then) and figured out some fundamentals of text manipulation in javascript. After several false starts, I made my first bot, @feelings.js, in the afternoon. I made @tiny_star_field five days later, in the middle of the night, hiding in my basement during a tornado. The power was out, and I’m almost certain I got the structure done in one laptop charge. I deployed it when the power and internet came back the next day.
You waited for the sky to clear and become sprinkled with stars again. In the meantime, you made your own digital sky, that’s cool. Did you do a lot of programming before starting with making bots?
I suppose that depends on what you mean by programming. I had worked in and around browser-based experiences for years but had never taken a structural approach to learning code. Every new idea and project had a particular set of problems that I attacked with utter naivete, writing vast messes that were shocking when they worked. Looking at my source code for those projects now is very much like looking at an outsider-art approach to computer science. Which is, I suppose, what they are.
I still sometimes struggle with basic concepts just because I haven’t run into them before- I learn best when directed at a goal, and sometimes those goals skirt fundamental structures. My knowledge is a funny hodge-podge assemblage of extremely difficult concepts I needed for some project or another, while I may forget the syntax for a basic sentiment. I keep telling myself I’ll read a book or take a course on putting code together properly, but so far I keep learning what I need. I am sure I will feel the same about my current projects in a year or two as I do about my older ones. My first bots are very embarrassing inside and it has only been a year and change.

You’ve said that @tiny_star_field is your most popular bot, but your personal favourite is @feelings_js. Would you care to elaborate?
Neither of those bots came from a particularly well-considered place technically; they were the first I made, and I was learning. I was tickled by the idea of a bot that did nothing but emote; it seemed like a charming inversion of the coldness that often creeps into automata. Tiny was a simple reflection of my Unicode character habit; I have a hobby of making little vignettes or dioramas combining characters and atypical symbols, and I have been enjoying automating them. (I am also now a Unicode Consortium member and am working structurally with these characters.)
That comment about favourites was from a long while back, and my favourite bot is probably now Moth Generator (@mothgenerator), which was a collaboration with @lorenschmidt. It’s different from many of my bots; it’s just a wrapper on an image generator, but it is the first bot I’ve made that I felt used @-replies in a truly useful manner. It takes the text of the tweet sent to it to seed the generator with a unique number; therefore, the ‘moth’ moth will always look like every other ‘moth’ moth, while a ‘bot’ moth would shift in many ways. A ‘moth bot’ moth would share characteristics of both.

How do these bots work?
Feelings.js (and a few others like it) is basically a fill-in-the-blank Wordnik wrapper. It has a variety of possible sentence structures on a switch statement and then pulls parts of speech from the dictionary API. I have a few structural rules that slightly favour alliteration and a few other cute tendencies (blocking offensive words), but it is basically mad-libs.
Tiny is even simpler; it has a large array of star and space options and pulls randomly from the available options. The biggest challenge was finding an ideal balance between character frequencies. I tweak it occasionally and don’t feel it is ideal yet. I am tempted to make it sparser. I am also in the process of making a Tiny Star Fields clone that uses actual astronomical data at varying scales, so the tweets will be a literal patch of sky.
Some of my other bots are a little bit more complicated- Moth Generator is a wildly long drawing routine in Javascript, Sea Change (@100yearsrising), tweets unicode characters mapped to sea-level rise predictions over the next century. Others use more obscure text manipulation techniques and large corpuses. But I think it is important to note for folks just starting that complication does not necessarily make them stronger artistically or more popular socially- the best things are almost always just good ideas.

What has been the response to your bots?
There is certainly an audience of bot appreciators; sometimes, I will see people who follow 30 or 40 bots but none of their makers. Bots also have their own secret lives outside of intention. Tiny auto-followed people back for a while (something like the first 6k) made for a truly wonderful sample! Very few are in the bot community; I think the vast majority are One Direction fans. It is a fascinating slice of social life I would never think to seek out myself.
What is the bot community that you are referring to?
Gosh, what is the bot community, good question. I suppose it seems to be a loosely associated group of folks interested in social bots. People seem to come from all walks- programmers, game developers, linguists, writers, artists, analysts, and poets. Making the skeleton of a Twitter bot is a fairly simple exercise and doesn’t inherently have the high knowledge overhead of some other creative programming tasks. They are also incredibly flexible in content and process, and I think that mutability allows a certain wealth of intent from bot to bot. These two avenues of openness mean they are used for all sorts of things! As entities, they are as unique as the people who make them.
In general, I’ve found folks who are organized around making bots to be nothing but supportive, kind and interested in helping others get started with producing their own work in this realm. Within that community, structure are also all the folks that might not make bots (yet) but know what they are, and are interested in their processes, or write about them, or consider them valid as artworks or creative entities.
What, indeed, are bots?
What are bots? Gosh, this is an even better question than the one about bot communities. So, there are many ways to think about bots, and in my opinion, they are stackable and do not refute one another. But here are my thoughts:
Firstly, they aren’t new automata has been around for a very, very long time. One can look at examples of clockwork machines or candle-powered toys from over 1000 years ago. Even beyond physical examples of automata, the idea of bots is pervasive culturally; stories about golems and enchanted armour or physical objects imbued with personality have been with us since stories began.
Digital bots (especially those living in social spaces) fit into this long history of objects granted almost humanness. They fill in for a part of human action, the slice of person granted to digital representations of ourselves. Just like the golem that guards a passage, their tasks are programmed, but we grant them entity because they do these tasks on their own (guard, tweet). Perhaps this is as much doubt (“Is it /really/ a bot, though? Maybe it’s just a person pretending?”) as it is a gift.
Secondly, I do think there is an aspect of doubling or mirroring that these bots employ. They are widening the reach of their creators; they are automated versions of a specific slice of their creators. Many, many bots fall into this category. Something Darius Kazemi once said first got me thinking this way. It was advice to a want-to-be bot maker who didn’t have an idea for a bot. Darius suggested ‘come up with a funny but formulaic joke and automate it’. This type of repetitive production is not just seen in joke bots but almost all bots that are not attempting to emulate humanness. The maker would have made the joke once; by making a bot, it is made many times (but also, perhaps made better than it would have been once).
To expand, the goal of work-by-generation is a fundamentally similar but shifted process from that of work-by-hand; rather than identifying and chasing the qualities of a singular desired artwork, one instead defines ranges of interesting permutations, their interpersonal interactions and how one ruleset speaks to another. Here, the cartographer draws the cliffs that contain a sea of one hundred thousand artworks. And then, one searches for the most beautiful piece of coral inside of their waters.
So, I suppose this is where bots are truly interesting to me because this kind of making (looking for the best moment in a sea of automated possibilities) is a methodology of construction that feels, in some ways, new.
I like the notion of bots leading secret lives. Are you ever not in control over your bots? Or what does this secrecy entail?
I take a pretty lax approach to keeping up with my bots. I rarely log into their accounts or closely monitor what they are up to. I censor certain offensive words, follow them on my Twitter account, and hope to catch them if they break. This means that their notifications never reach me; the things that are said to them (or their own replies) are often invisible to everyone but them.
In what ways do people or other bots interact with your bots?
Most (although not all) of my bots are non-interactive, meaning they do not @reply back when spoken to. That being said, they are absolutely interacted with. Tiny star fields, in particular, get a ton of messages; lots of people will have conversations in the mentions. I find them pretty charming and will occasionally peek at what people are saying to one another. Since I generally keep @replies off, I don’t get the bot-to-bot eternity loops you’ll sometimes see with the image bots, ebooks bots, or others that reply. But I always like it when spam bots or Reddit bots find mine by keyword search. The best example of designed bot interaction might be Eli Brody’s tiny astronaut (https://twitter.com/tiny_astro_naut), which inserts spaceship emoji into Tiny star fields’ tweets, or its conceptual sibling, tiny space poo (https://twitter.com/tiny_space_poo).
How many of your bot’s followers do you reckon are other bots, and is bot-to-bot interaction different to how humans interact with bots?
I haven’t done the numbers, but it seems like there is a slightly higher percentage of bot-to-bot followers than human-to-bot. I would guess this combines auto-following routines and being manually directed to follow entire lists of other bots. Perhaps also, they are more patient with repetitive or nonsensical tweets and stick around longer.
Most bots now have conversational abandonment built in, but this was not always the case- it was once pretty common to see two replying bots get into a conversation with one another that would last hours or days, to the tune of thousands of tweets, one every few seconds. I once got accidentally caught in mentioning one of these cycles and had to wait for one of the bot’s owners to wake up and reset their servers. It was amazing, and I also had to turn off all notifications on every device I own.
Now, I think most bots use more intelligent replying- just to one person, randomly across their followers, or only every 10 hours, or perhaps replying to keywords or requests. To me, this has made bot-to-bot interactions feel a lot more human.

Do people ever wonder about you, the human behind the bot?
Many people who follow Tiny Star Fields do not understand that it is a bot! Or that bots are even on Twitter. The predominant interaction that seems to occur runs along the lines of “DO YOU SLEEP” or “what is this” or “I love these thank you so much for making them all the time”. I find that disconnect pretty delightful- the assumption of a (very) dedicated human somewhere. I’m also fond of the interpersonal conversations in the comments, often having nothing to do with the original stars; it occasionally functions as a bit of a forum for strangers to connect.
Where do you see Twitter bots or social media bots generally evolving?
I have found myself moving off of Twitter and back into non-social spaces for much of my work. Part of this is probably personal; my interests shift project-to-project. Part of it is intrinsic limitations in the media, the 140-character limit, and the difficulty of keeping up with Twitter’s often evolving terms of service. I am interested in physical robots or the housing of digital spaces- where these bots live- and a lot of my studio practice is now exploring tangible machines. Some of the best bots I’m seeing out of others use neural nets or very clever source material. In my own work, I am looking forward to more physical-digital integration, especially as I pick up some new toolsets required for more complicated work. I am interested in biological emulation and the hidden data that Twitter links to every tweet (perhaps my next bot will not be readable on the Twitter web client but instead comes alive in an API call?).
A small part of me also feels like others have taken up the call (and doing it better than I ever could have). This is to say, Twitter bots are in a kind of renaissance- tools like George Buckenham’s Cheap Bots Done Quick (which uses Kate Compton’s Tracery) and the plethora of tutorials and frameworks have radically democratized the process, and it seems like every day I see someone new to this space building interesting or beautiful things. I am learning as much from newcomers to the form as anything!
In short, for the future- who knows? But now, bots are serving as a fascinating space to test new ideas, construct entities and artwork of generated text and data, and publish those experiments to an audience excited to see them in the world. What more could one hope for?
Finally, what are your favourite bots at the moment?
https://twitter.com/CreatureList – automata bestiary from @samteebee
https://twitter.com/FFD8FFDB – image-processed security cameras by @derekarnold
https://twitter.com/imgconvos – a @thricedotted answer to image-bot loops
https://twitter.com/everycolorbot – The first bot truly dear to me still going strong, thanks to @vogon
https://twitter.com/reverseocr – a @tinysubversions bot that randomly draws until it hits whatever word it is trying to match in an OCR library
https://twitter.com/ARealRiver – the only real way to view this (very clever) bot is in its own timeline, probably on mobile. from @muffinista
https://twitter.com/LSystemBot – l systems by @objelisks
https://twitter.com/INTERESTING_JPG – a bot-form of deep learning, which attempts to describe human images with computer vision, by @cmyr
https://twitter.com/park_your_car – compelling use of google maps highlighting available car space by @elibrody
https://twitter.com/wikishoutouts – shoutouts to the disambiguation pages of Wikipedia
https://twitter.com/soft_focuses – a very quiet mysterious bot from @thricedotted
https://twitter.com/TVCommentBot – attempted image recognition of television, @DavidLublin
https://twitter.com/GenerateACat – procedural cats – @mousefountain and @bzgeb
https://twitter.com/pentametron – a bot that looks for tweets in accidental iambic pentameter by @ranjit
https://twitter.com/RestroomGender – @lichlike’s gendered restroom sign generator
https://twitter.com/digital_henge – This bot by @alicemazzy tweets moon phases, eclipses, and other solar and lunar phenomena
https://twitter.com/a_lovely_cloud – digital cloud watching from @rainshapes
https://twitter.com/the_ephemerides – computer-generated poetry with outer space probe imagery, @aparrish
To find out more about Everest Pipkin’s latest projects, please visit Everest Pipkin
Daniel Rourke: At Furtherfield on November 22nd 2014 you launched a Beta version of a networked project, 6PM Your Local Time, in collaboration with Fabio Paris, Abandon Normal Devices and Gummy Industries. #6PMYLT uses twitter hashtags as a nexus for distributed art happenings. Could you tell us more about the impetus behind the project?
Domenico Quaranta: In September 2012, the Link Art Center launched the Link Point in Brescia: a small project space where, for almost two years, we presented installation projects by local and international artists. The Link Point was, since the beginning, a “dual site”: a space where to invite our local audience, but also a set for photographic documentation meant to be distributed online to a global audience. Fabio Paris’ long experience with his commercial gallery – that used the same space for more than 10 years, persuaded us that this was what we had to offer to the artists invited. So, the space was reduced to a small cube, white from floor to ceiling, with neon lights and a big logo (a kind of analogue watermark) on the back door.
Thinking about this project, and the strong presence of the Link Point logo in all the documentation, we realized that the Link Point was actually not bound to that space: as an abstract, highly formalized space, it could actually be everywhere. Take a white cube and place the Link Point logo in it, and that’s the Link Point.
This realization brought us, on the one hand, to close the space in Brescia and to turn the Link Point into a nomad, erratic project, that can resurrect from time to time in other places; and, on the other hand, to conceive 6PM Your Local Time. The idea was simple: if exhibition spaces are all more or less similar; if online documentation has become so important to communicate art events to a wider audience, and if people started perceiving it as not different from primary experience, why not set up an exhibition that takes place in different locations, kept together only by documentation and by the use of the same logo? All the rest came right after, as a natural development from this starting point (and as an adaptation of this idea to reality).
Of course, this is a statement as well as a provocation: watching the documentation of the UK Beta Test you can easily realize that exhibition spaces are NOT more or less the same; that attending or participating in an event is different from watching pictures on a screen; that some artworks work well in pictures but many need to be experiences. We want to stress the value of networking and of giving prominence to your network rather than to your individual identity; but if the project would work as a reminder that reality is still different from media representation, it would be successful anyway.

Daniel Rourke: There is something of Hakim Bey’s Temporary Autonomous Zones in your proposal. The idea that geographic, economic and/or political boundaries need no longer define the limits of social collective action. We can criticise Bey’s 1991 text now, because in retrospect the Internet and its constitutive protocols have themselves become a breeding ground for corporate and political concerns, even as technology has allowed ever more distributed methods of connectivity. You foreground network identity over individual identity in the 6PM YLT vision, yet the distinction between the individuals that create a network and the corporate hierarchies that make that networking possible are less clear. I am of course gesturing towards the use of Twitter as the principal platform of the project, a question that Ruth Catlow brought up at the launch. Do you still believe that TAZs are possible in our hyper-connected, hyper-corporate world?
Domenico Quaranta: In its first, raw conceptualization, 6PM YLT had to come with its own smartphone app, that had to be used both to participate in the project and to access the gallery. The decision to aggregate content published on different social platforms came from the realization that people already had the production and distribution tools required to participate in the action, and were already familiar with some gestures: take a photo, apply a filter, add an hashtag, etc. Of course, we could invite participants and audiences to use some specific, open source social network of our choice, but we prefer to tell them: just use the fucking platform of your choice. We want to facilitate and expand participation, not to reduce it; and we are not interested in adding another layer to the project. 6PM YLT is not a TAZ, it’s just a social game that wants to raise some awareness about the importance of documentation, the power of networks, the public availability of what we do with our phones. And it’s a parasitic tool that, as anything else happening online, implies an entire set of corporate frameworks in order to exist: social networks, browsers, operative systems, internet providers, server farms etc.
That said, yes, I think TAZs are still possible. The model of TAZ has been designed for an hyper-connected, hyper-corporate world; they are temporary and nomadic; they exist in interstices for a short time. But I agree that believing in them is mostly an act of faith.
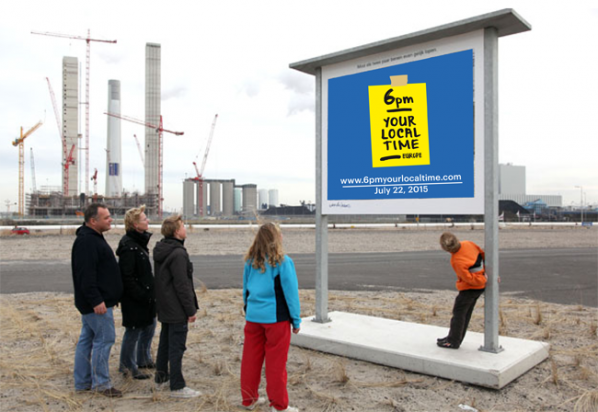

Daniel Rourke: The beta-tested, final iteration of 6pm YLT will be launched in the summer of 2015. How will you be rolling out the project in the forthcoming months? How can people get involved?
Domenico Quaranta: 6PM Your Local Time has been conceived as an opportunity, for the organizing subject, to bring to visibility its network of relationships and to improve it. It’s not an exhibition with a topic, but a social network turned visible. To put it simply: our identity is defined not just by what we do, but also by the people we hang out with. After organizing 6PM Your Local Time Europe, the Link Art Center would like to take a step back and to offer the platform to other organizing subjects, to allow them to show off their network as well.
So, what we are doing now is preparing a long list of institutions, galleries and artists we made love with in the past or we’d like to make love with in the future, and inviting them to participate in the project. We won’t launch an open call, but we already made the event public saying that if anyone is interested to participate, they are allowed to submit a proposal. We won’t accept anybody, but we would be happy to get in touch with people we didn’t know.
After finalizing the list of participants, we will work on all the organizational stuff, basically informing them about the basic rules of the game, gathering information about the events, answering questions, etc.
On the other hand, we have of course to work on the presentation. While every participant presents an event of her choice, the organizer of a 6PM Your Local Time event has to present to its local audience the platform event, as an ongoing installation / performance. We are from Brescia, Italy, and that’s where we will make our presentation. We made an agreement with MusicalZOO, a local festival of art and electronic music, in order to co-produce the presentation and have access to their audience. This is what determined the date of the event in the first place. Since the festival takes place outdoor during the summer, we are working with them on designing a temporary office where we can coordinate the event, stay in touch with the participants, discuss with the audience, and a video installation in which the live stream of pics and videos will be displayed. Since we are expecting participants from Portugal to the Russian Federation, the event will start around 5 PM, and will follow the various opening events up to late night.
One potential reference for this kind of presentation may be those (amazing) telecommunication projects that took place in the Eighties: Robert Adrian’s The World in 24 Hours, organized at Ars Electronica in 1982; the Planetary Network set up in 1986 at the Venice Biennale; and even Nam June Paik’s satellite communication project Good Morning Mr Orwell (1984).

Daniel Rourke: Your exhibition Unoriginal Genius, featuring the work of 17 leading net and new media artists, was the last project to be hosted in the Carroll/Fletcher Project Space (closing November 22nd, 2014). Could you tell us more about the role you consider ‘genius’ plays in framing contemporary art practice?
Domenico Quaranta: The idea of genius still plays an important role in Western culture, and not just in the field of art. Whether we are talking about the Macintosh, Infinite Jest, a space trip or Nymphomaniac, we are always celebrating an individual genius, even if we perfectly know that there is a team and a concerted action behind each of these things. Every art world is grounded in the idea that there are gifted people who, provided specific conditions, can produce special things that are potentially relevant for anybody. This is not a problem in itself – what’s problematic are some corollaries to our traditional idea of genius – namely “originality” and “intellectual property”. The first claims that a good work of creation is new and doesn’t depend on previous work by others; the second claims that an original work belongs to the author.
In my opinion, creation never worked this way, and I’m totally unoriginal in saying this: hundreds of people, before and along to me, say that creating consists in taking chunks of available material and assembling them in ways that, in the best situation, allow us to take a small step forward from what came before. But in the meantime, entire legal systems have been built upon such bad beliefs; and what’s happening now is that, while on the one hand the digitalization of the means of production and dissemination allow us to look at this process with unprecedented clarity; on the other hand these regulations have evolved in such a way that they may eventually slow down or stop the regular evolution of culture, which is based on the exchange of ideas.
We – and creators in particular – have to fight against this situation. But Unoriginal Genius shouldn’t be read in such an activist way. It is just a small attempt to show how the process of creation works today, in the shared environment of a networked computer, and to bring this in front of a gallery audience.

Daniel Rourke: So much online material ‘created’ today is free-flowing and impossible to trace back to an original author, yet the tendency to attribute images, ideas or ‘works’ to an individual still persists – as it does in Unoriginal Genius. I wonder whether you consider some of the works in the show as more liberated from authorial constraints than others? That is, what are the works that appear to make themselves; floating and mutating regardless of particular human (artist) intentions?
Domenico Quaranta: Probably Museum of the Internet is the one that fits best to your description. Everybody can contribute anonymously to it by just dropping images on the webpage; the authors’ names are not available on the website, and there’s no link to their homepage. It’s so simple, so necessary and so pure that one may think that it always existed out there in some way or another. And in a way it did, because the history of the internet is full of projects that invite people to do more or less the same.

Daniel Rourke: 2014 was an exciting year for the recognition of digital art cultures, with the appointment of Dragan Espenschied as lead Digital Conservator at Rhizome, the second Paddles On! auction of digital works in London, with names like Hito Steyerl and Ryan Trecartin moving up ArtReview’s power list, and projects like Kenneth Goldsmith’s ‘Printing out the Internet’ highlighting the increasing ubiquity – and therefore arguable fragility – of web-based cultural aggregation. I wondered what you were looking forward to in 2015 – apart from 6PM YLT of course. Where would you like to see the digital/net/new media arts 12 months from now?
Domenico Quaranta: On the moon, of course!
Out of joke: I agree that 2014 has been a good year for the media arts community, as part of a general positive trend along the last few years. Other highlighs may include, in various order: the September 2013 issue of Artforum, on “Art and Media”, and the discussion sparked by Claire Bishop’s essay; Cory Arcangel discovering and restoring lost Andy Warhol’s digital files from floppy disks; Ben Fino-Radin becoming digital conservator at MoMA, New York; JODI winning the Prix Net Art; the Barbican doing a show on the Digital Revolution with Google. Memes like post internet, post digital and the New Aesthetic had negative side effects, but they helped establishing digital culture in the mainstream contemporary art discourse, and bringing to prominence some artists formerly known as net artists. In 2015, the New Museum Triennial will be curated by Lauren Cornell and Ryan Trecartin, and DIS has been announced to be curator of the 9th Berlin Biennial in 2016.
All this looks promising, but one thing that I learned from the past is to be careful with optimistic judgements. The XXI century started with a show called 010101. Art in Technological Times, organized by SFMoMA. The same year, net art entered the Venice Biennale, the Whitney organized Bitstreams and Data Dynamics, the Tate Art and Money Online. Later on, the internet was announced dead, and it took years for the media art community to get some prominence in the art discourse again. The situation now is very different, a lot has been done at all levels (art market, institutions, criticism), and the interest in digital culture and technologies is not (only) the result of the hype and of big money flushed by corporations unto museums. But still, where we really are? The first Paddles On! Auction belongs to history because it helped selling the first website ever on auction; the second one mainly sold digital and analogue paintings. Digital Revolution was welcomed by sentences like: “No one could fault the advances in technology on display, but the art that has emerged out of that technology? Well, on this showing, too much of it seems gimmicky, weak and overly concerned with spectacle rather than meaning, or making a comment on our culture.” (The Telegraph) The upcoming New Museum Triennial will include artists like Ed Atkins, Aleksandra Domanovic, Oliver Laric, K-HOLE, Steve Roggenbuck, but Lauren and Ryan did their best to avoid partisanship. There’s no criticism in this statement, actually I would have done exactly the same, and I’m sure it will be an amazing show that I can’t wait to see. Just, we don’t have to expect too much from this show in terms of “digital art recognition”. So, to put it short: I’m sure digital art and culture is slowly changing the arts, and that this revolution will be dramatic; but it won’t take place in 2015 🙂
“Tweets in Space beams Twitter discussions from participants worldwide towards GJ667Cc – an exoplanet 22 light years away that might support extraterrestrial life. By engaging the millions of voices in the Twitterverse and dispatching them into the larger Universe, Tweets in Space activates a potent conversation about communication and life that traverses beyond our borders or understanding.”
Marc Garrett: Could you explain to our readers what ‘Tweets In Space’ is?
Scott Kildall and Nathaniel Stern: Tweets in Space is an art project — a networked performance event — which beams your Twitter messages to a nearby exoplanet that might support human-like, biological life. Anyone with an Internet connection can Tweet with the hashtag #tweetsinspace during the performance time, and their messages will be included in our shotgun blast to the stars. The performance is on September 21st, 20:30 – 21:00 Mountain Time (3:30 AM BST / London time).
MG: What was the motivation behind your current collaboration?
SK and NS: We found inspiration from various sources. First, in NASA’s Kepler mission, whose purpose is to discover planets in the “habitable” or “Goldilocks” zone. The project has found over 2000 exoplanets thus far, all of which are “not too hot, not too cold, but just right” for life as we know it. Scientists now estimate that there are at least 500 million planets like this in the Milky Way alone. Our conclusion: extraterrestrial life is almost certainly out there.
![The newly discovered planet is depicted in this artist's conception, showing the host star as part of a triple-star system. Image credit: Carnegie Institution / UCSC. [1]](http://www.furtherfield.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/planet_gj667cc.jpg)
“The latest discovery is at least 4.5 times bigger in size than Earth. Reportedly, the planet exists 22 lightyears away from Earth and it orbits its star every 28 days. The planet is known to lie, in what is being referred to as the star’s habitable zone. A habitable zone is a place where the existing conditions are just perfect for life sustenance. Astronomers, according to this report also suspect that the GJ667Cc may have been made out of earth-like rock, instead of gas.” [ibid]
Another source of great inspiration is how we use social media here on Earth. This is our second, large-scale, Internet-initiated collaboration. In 2009, we amplified the power structures and personalities on Wikipedia, and questioned how knowledge is formed on the world’s most-often used encyclopedia – and thus the web and world at large. Now, we are turning to the zeitgeist of information and ideas, feelings and facts, news and tidbits, on Twitter. The project focuses on and magnifies the supposed shallowness of 140-character messages, alongside the potential depth of all of them – what we say in online conversation, as a people.
We are directing our gaze, or rather tweets, via a high-powered radio telescope, towards GJ667Cc – one of the top candidates for alien life. It is part of a triple-star system, has a mass that is about 4 times that of Earth, and orbits a dwarf star at close range. GJ667Cc most certainly has liquid water, an essential component for the kind of life found on our own planet.
MG: Right from its early years when Jagadish Chandra Bose [2], pioneered the investigation of radio and microwave optics – science, technology and art have had strong crossovers. And it might be worth mentioning here that Bose was not only well versed as a physicist, biologist, botanist and archaeologist, he was also an early writer of science fiction. [3] Which, brings us back to ‘Tweets In Space’, wherein lies themes relating to science fiction, radio broadcasting (commercial, independent and pirate), wireless technology of the everyday via our computers, and ‘of course’ the Internet.
![J.C. Bose at the Royal Institution, London, 1897.[3]](http://www.furtherfield.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/JC-Bose-at-the-Royal-Institution-London-with-his-radio-equipment-The-date-is-1897.png)
But, what I want to pin down here is, where do you feel you fit in historically and artistically with other past and contemporary artists, whose creative art works also involved explorations through electromagnetic waves?
Scot Kildall: The work of JC Bose is incredible and what strikes me is that he eschewed the single-inventor capitalist lifestyle in favor of his own experiments. Isn’t this the narrative that artists (often) take and linked back in many ways to the open-source/sharing movement, rather than the litigious patent-based corporation? And it mirrors in many ways the reception of electromagnetic radiation as well. You can’t really “own” the airwaves. Anyone who is listening can pick up the signal. This comes back, as you point out, to the internet. Twitter is now, one of the vehicles, and, ironically entirely owned by a benevolent* corporation.
Nathaniel Stern: (Agreeing with Scott) and we can’t forget of course Nam June Paik, who played with naturally occurring and non-signal based electromagnetic fields to interfere with analogical signals (as well as the actual hardware) of tube televisions, and more. And of course, there have been other transmission artists, explored in depth by free103point9, among others. I think, like them and others, we are messing with the media, amplifying (figuratively and metaphorically) and intervening, pushing the boundaries of DIY and cultural ethico-aesthetic questions…

MG: What is especially interesting is that all the tweets submitted by the public are unfiltered. How important is it to you that people’s own messages are not censored when going into space?
SK and NS: Absolutely. Tweets in Space is by no means the first project to transmit cosmic messages with METI technologies (Messaging to Extraterrestrial Intelligence). Our fellow earthlings have sent songs by the Beatles, photos of ourselves shopping at supermarkets, images of national flags, and even a gold record inscribed with human forms – controversially, where the man has genitals and the woman doesn’t. These slices of hand-picked content exhibit what a select few believe to be important, but ignore, or willfully exclude, our varied and collective modes of thinking and being.
Tweets in Space is “one small step” with alien communications, in that it is open to anyone with an Internet connection. It thus represents millions of voices rather than a self-selected few. More than that, our project is a dialog. There have been, very recently, a small number of projects that similarly “democratize the universe” but none are like ours: uncurated, unmediated thoughts and responses from a cooperative public. We can speak, rebut, and conclude, and nothing is left out. Our transmission will contain the good, the bad, and the provocative, the proclamations, the responses, and the commentary, together, a “giant leap” for all of humankind – as well as our soon-to-be friends.
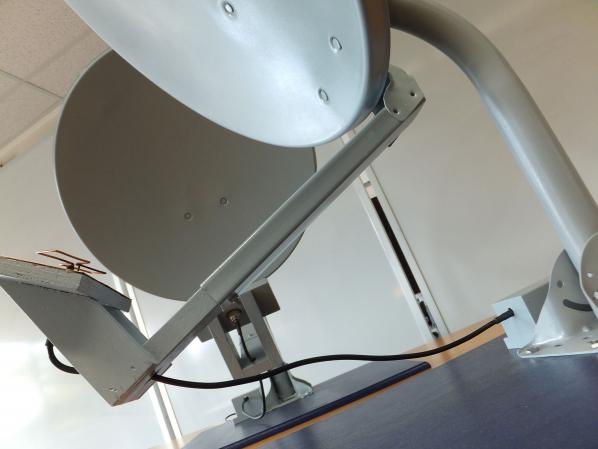
Furthermore, by limiting the event to a small window of only 30 minutes, we are encouraging all our participants to speak then respond, conversing with one another in real-time, through networked space. We are not just sending lone tweets, but beaming a part of the entire dialogical Twitterverse, as it creates and amplifies meaning. Tweets in Space is more than a “public performance” – it “performs a public.”
MG: Now, you will be transmitting real-time tweets toward the exoplanet GJ667Cc, which is 22 light-years away. How long will it all take to get there?
SK and NS: Well, first off, we’re collecting all of the tweets in real time, but only sending them out later in October. The main reason for this is that we have to wait for the planets to align – literally. We want line of sight with GJ667Cc from where our dish is. The added bonus of time, however, is that this will allow us to really flesh out how we send the messages in a bundle. We want to include a kind of Rosetta Stone, where we will not only send binary ASCII codes of text in our signal, but also analog images of the text itself. We additionally intend to choose the most frequently used nouns in all the tweets from our database, then give a kind of “key” for each. If “dog” is common, for example, we can transmit: 1. an analog image of a dog, like a composite signal from a VCR; 2. a text image of the word “dog” in the same format; and 3. the binary ASCII code for the word dog.
In terms of time/distance, when speaking in light years, these are the same thing. A light year is the distance light can travel in one year of Earth time (about 9.4605284 × 10 to the 15 meters). Since radio travels at the speed of light, a big dish on GJ667Cc will pick up the signal in 22 years. We should start listening for a response in 44 – though it may take them a while to get back to us…
MG: Will the code used for the project be open source, and if so, when and where can people expect to use it?
SK and NS: Yes it is! The most useful part of our code is the #collector, which saves real-time tweets to a database, that can then be used for live projections or web sites, or accessed and sorted later via all kinds of info. The problem is that it’s not really user friendly or out of the box – folks need a suped up server (VPN), and to plug into a few other open source wares. The main portion of the backend we used is actually already available at 140dev.com, and then we plugged that into Drupal, among other things. For now, we’re telling interested parties to contact our coder, Chris Butzen, if they want to use our implementation. And we hope to do public distribution on tweetsinspace.org if we are able to package it in a more usable format in the next 6 months.
MG: Are there any messages collected so far, grabbing your attention?
We’ve had thousands of tweets so far – even while just testing the ware in preparation for the performance. We’re anticipating a lot of participation! The tweets we’ve seen have ranged from variations on “hello [other] world” and “don’t eat us,” to political activism and negative commentary, to a whole surreal narrative of about 30 tweets per day over the last 3 months.
go to tweet aliens to add your own words…
Some of our favorite tweets have been those that question how to make our own world better. These speak to both the hope of space age-ike technology, as well as the hope in collective dialog – both of which our project tries to amplify. Such tweeters ask about the alien planet’s renewable energy sources, tax structures, education, art, and more.
We imagine the 30-minute performance will see a much more potent discussion about such things, and hope your readers will participate. The final transmission will be archived permanently on our site once we’ve prepared it for launch.
As part of the International Symposium on Electronic Art in New Mexico (ISEA2012). We will collect your tweets and transmit them into deep space via a high-powered radio messaging system. Our soon-to-be alien friends might receive unmediated thoughts and responses about politics, philosophy, pop culture, dinner, dancing cats and everything in between. By engaging the millions of voices in the Twitterverse and dispatching them into the larger Universe, Tweets in Space activates a potent conversation about communication and life that traverses beyond our borders or understanding. http://tweetsinspace.org/
AND THEY WILL BE SENT INTO DEEP SPACE!!!
Watch the stream LIVE here – http://tweetaliens.org/tweets/tweets.php