



Body Drift: Butler, Hayles, Haraway (Posthumanities)
Author Arthur Kroker. University of Minnesota Press (22 Oct. 2012).
Body Drift by Arthur Kroker, takes the work of three leading women thinkers as its main focus. It therefore would feel strange, before venturing on to the review, not to mention Marilouise Kroker, his wife and collaborator who he credits with shaping the critical direction of his thought “on bodies and power.” [1] Together Marilouise and Arthur Kroker have created an abundance of work in the fields of technology and contemporary culture. They both edit the peer publishing electronic journal CTheory founded in 1996. They co-authored the influential Hacking the Future (1996), and Marilouise Kroker has co-edited and introduced numerous anthologies including Digital Delirium (1997), Body Invaders (1987), and Last Sex (1993) and Critical Digital Studies: A Reader. Marilouise Kroker is Senior Research Scholar at the University of Victoria. A recent bio written about them says “Arthur and Marilouise Kroker are the hipsters of Canadian media theory.” [2]
Arthur Kroker is Canada Research Chair in Technology, Culture and Theory, Professor of Political Science, and the Director of the Pacific Centre for Technology and Culture (PACTAC) at the University of Victoria. His recent publications include The Will to Technology and the Culture of Nihilism: Heidegger, Nietzsche, and Marx (University of Toronto Press) and Born Again Ideology: Religion, Technology and Terrorism. Dr. Kroker’s current research focuses on the new area of critical digital studies and the politics of the body in contemporary techno-culture. http://web.uvic.ca/~akroker/

This review is written three years after the publication of the book but it feels even more relevant now than ever for reasons that will, I hope become plain…
Body Drift focuses on three major feminist theorists, Judith Butler, Katherine Hayles and Donna Haraway. They have had a deep influence on my own work and of course on media art culture through the years. They have profoundly altered our views on technology, feminism, queer theory, postmodernism, marxism, hacking, hacktivism, cybernetics, the Internet, network culture, politics and posthumaniism. Re-examining their critical perspectives and creative processes – assemblages, remixing and cyborgs- Kroker terms the emerging technological spectre body drift. He examines the connections between what he sees as Judith Butler’s postmodernism, Katherine Hayles’s posthumanism, and Donna Haraway’s companionism.
Through the spectrum of Body Drift he attempts to find a clearer understanding of the contemporary material body and its societal complexities. He views two opposing forces at work in body drift. One is, the continual disappearance of human things and values, alongside excluded ethnicities and outlawed sexualities. He connects this with an entrapment by social crisis in which actual democratic aspiration is dwindling. In parallel to this mass loss of our freedoms other factors are at work. He sees it as overall, and an eventual series and states of resistances. These are evolutionary forms of hybridity and as such are key paths for what he argues is the function of our posthuman condition. [3]
There are numerous techno-visions expounding how technology will change our lives and futures. What for me, separates a classic posthumanist and a critically aware posthumanist is that the latter is not only aware of the necessity of grass roots culture and inclusion of female voices, but is also critical of domination over others as key when engaging in the processes of innovation. Thus moving beyond existing frameworks that perpetuate patriarchal language, methods of centralization and colonial habits.
In his book You Are Not A Gadget: A Manifesto, Jaron Lanier described Ray Kurzweil’s excitement about The Singularity as apocalyptic. Lanier says “The coming Singularity is a popular belief in the society of technologists. Singularity books are as common in a computer science department as Rapture images are in an evangelical bookstore.” [4] Kurzweil’s digestible techno-bites fit well alongside big business and with Peter Diamandis a wealthy entrepreneur. Dr. Peter H. Diamandis and Dr. Ray Kurzweil co-founded the Singularity University. In To Save Everything, Click Here: Technology, Solutionism, and the Urge to Fix Problems that Don’t Exist, Evgeny Morozov writes that Diamandis “promises us a world of abundance that will essentially require no sacrifice from anyone – and since no one’s interests will be hurt, politics itself will be unnecessary.” [5]

In The Joy of Revolution Ken Knabb wrote, “Marx considered it presumptuous to attempt to predict how people would live in a liberated society. “It will be up to those people to decide if, when and what they want to do about it, and what means to employ.”” [6] Kroker says, “In my estimation, while Marx, Nietzsche and Heidegger may have provided premonitory signs of the charred landscape of the technological blast, it is the specific contribution of Butler, Hayles and Haraway to provide a deeply compelling account of the fate of the body in contemporary society.” [7] This includes how we evolve our Internet freedoms, surveillance, and cyber attacks in a post-Snowden world. While we’re, either reshaping or being reshaped through the constant production of new technologies and political re-invention, it is crucial that there exists regular critique reflecting on these influences and changes on people, animals, society, the planet, and the universe. Thankfully, Butler, Hayles and Haraway disrupt the normalization and dangerously hegemonic acceptance of ‘the male overlord and his machine’ over the rest of us.
How our bodies and the idea of our bodies relate to this complex world is Kroker’s primary interest. In the introduction Kroker says that we no longer inhabit a body in any meaningful sense of the term but rather occupy a multiplicity of bodies – imaginary, sexualized, disciplined, gendered, laboring technologically augmented bodies. [8] Hayles has not only bridged the gap between science and literature, but also media art. In 2000, Hayles wrote an insightful piece on Patchwork Girl, an artwork made by Shelley Jackson in 1995, a hypertext fiction and remix of Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein. When discussing Jackson’s piece Hayles said, “As the unified subject is thus broken apart and reassembled as a multiplicity, the work also highlights the technologies that make the textual body itself a multiplicity.” [9]
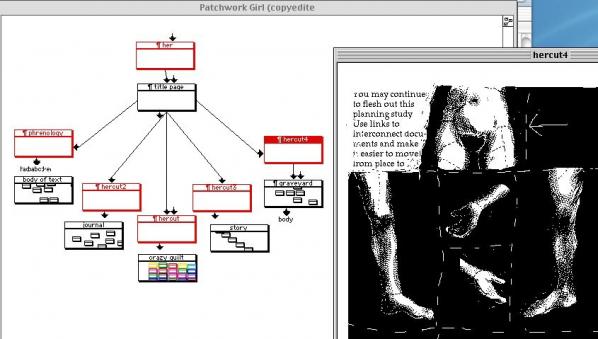
Kroker says, “”Like Heidegger before her, Hayles refuses to privilege either interpretation to the exclusion of its opposite, preferring a form of thought similar to “pendurance,” that moment when, in the folded twists of complexity theory, “one comes over the other, one arrives in the other.”” [10] In an interview with Josephine Bosma on the Nettime email list, in Nov 1998, Hayles said “There may be other ways to think about the subject that don’t find themselves first and foremost on this notion of ownership. New technologies open up possibilities for rethinking other ways to begin to construct the subject.” [11] Krokers sees Hayles as providing us with the digital alphabet to explore the complexity and connections of technopoesis. “To read Hayles is, in fact, to begin to experience the fractures, bifurcations, and liminality that stretches across the skin of posthuman culture.” [12]
Donna Haraway in her introduction to A Cyborg Manifesto: Science, Technology, and Socialist-Feminism in the Late Twentieth Century, in 1985 she said, “Though both are bound in the spiral dance. I would rather be a cyborg than a goddess.” This unsettled many feminists at the time. Haraway was not interested in reclaiming what she saw as a lost ideal based on matriarchal values. Instead, she wanted women to re-invent and create their own versions of what a female could be or not be, by playfully exploiting the cyborg myth and concept in the here and now. [13] This reconstruction of the woman, Kroker says, poses particular twists and knots, and contradictions. He emphasises that we’re not discussing a traditional form of feminism but a hybrid vision of feminism. [14]
“Not waiting passively for the capricious experience of biotechnology to produce spliced bodies, Haraway has made of her own mind a biopolitics on creative hyperdrive. Deeply immersed in the (bio)scientific disciplines, always distancing herself from seductions of technological representationality by feminist difference, continuously provoking boundary breakdowns in her own thought by refusing to assent to an anthropomorphic species-heirarchy, Haraway is a theorist of the splice.” [15] Kroker (2012)
Kroker moves on from Haraway’s concepts on the cyborg to her later inter-species theory. He tries to untangle the complexity of her personal, political and theoretical relations in respect to where her critical strength is best engaged. He’s drawn to what he sees as ““Haraway’s profound conceptualization of “companion species.”” Haraway challenges the established role and hierarchical control by us humans over animals, plants, objects, and humans. [16] In her publication The Companion Manifesto: Dogs, People, And Significant Otherness, Haraway says, “I believe that all ethical relating, within or between species, is knit from the silk-strong thread of ongoing alertness to otherness-in-relation.” [17]
Haraway’s text in The Companion Manifesto conveys a shocking sense of freedom as if written by someone who longer gives a damn about her academic reputation. Perhaps, what I mean here is that the thinking reaches further than academia and builds alliances with others who may not have read her other works. In the chapter A Category of One’s own, Haraway says, “Anyone who has done historical research knows that the undocumented often have more to say about how the world is put together than do the well pedigreed.” [18] As with her concept for Situated knowledges her intention is to connect beyond officially accepted canons and norms, and established hegemonies. In his chapter HYBRIDITIES Kroker says “Haraway’s writings reveal the apocalypse that is possibly the end condition of hundreds of years of (Western) scientific experimentalism.” [19] This does not mean the West is doomed. However, Haraway has always been on the side of otherness, whether for humans or nonhuman entities. In her eyes our futures or the world as it actually is may not necessarily be as reliant on technology as we like to think.
“Perhaps most importantly, we must recognise that ethics requires us to risk ourselves precisely at moments of unknowingness, when what forms us diverges from what lies before us, when our willingness to become undone in relation to others constitutes our chance of becoming human.” [20] Judith Butler.
Of this quote from Butler’s Giving an Account of Oneself, 2005 [21], which opens the second chapter in Body Drift, Kroker says, “Could there be any text more appropriate to both understanding and perhaps, if the winds of fate are favorable, transforming contemporary politics than Judith Butler’s eloquent study of moral philosophy..?” [21] In Giving an Account of Oneself, Butler presents us with an outline for a different type of ethical practice and proposes that, before you even ask what ought I to do? Ask yourself the question who is this ‘I’? Butler, proposes that it is “a matter of necessity” that every person should “become a social theorist.” [22] Indeed, in the City Lights interview with Peter Maravelis, Kroker says Butler is speaking in terms of people breaking their silence, such as “the repetition chorus of OCCUPY during the Wall Street insurrection”. [23] And then he says, “In many ways, all of Butler’s thought is “standing as witness.” [24] Butler stands witness to what we now know in the 21st century as a violent regime of heterosexual masculinity spreading its domination over history, technology and life itself.
Butler, Hayles and Haraway are major players in feminist and queer academia and media art culture. They have all been active in breaking away from the traditional behaviours that have kept us caught within loops in various ways. Their fluid and progressive approaches to feminism are not only of value to women alone but it can also help others think beyond restrictive behaviours. Kroker’s book manages to reflect the fluidity of networked and contemporary aspects of body drift well, especially from a critically aware, posthumanist perspective. However, no matter how you slice it, it’s about personal and collective freedoms, how we can somehow reclaim our states of being, and how we can own our subjectivities and our psyches in whatever forms these may take. As artists, as humans and or as posthumans – we need Butler, Hayles and Haraway to guide us through this ever-changing, twisting, everyday, posthuman terrain.
“None but those who have experienced them can conceive of the enticements of science.” Mary Shelley, Frankenstein.
Rachel Falconer writes about the cyberfeminist art collective subRosa, a group using science, technology, and social activism to explore and critique the political traction of information and bio technologies on women’s bodies, lives and work.
Following a recent interview with the founding members of the collective, Hyla Willis and Faith Wilding, this article presents subRosa’s trans-disciplinary, performative practice and questions what it means to claim a feminist position in the mutating economies of biotechnology and techno-science.

The technological redesigning and reconfiguration of bodies and environments, enacted through the economies of the biotech industry, is an emerging feature of contemporary life. As these new ‘bits of life’ enter the biotech network, there is a slippage in our mental model of what constitutes the body, and more specifically, ‘life’ itself. As radically new biological entities are generated through the processes of molecular genetic engineering, stem cell cultivation, cloning, and transgenics, bio-artists and bio-hackers co-opt the laboratory as a site of critical cultural practice and knowledge exchange. Human embryos, trans-species and plants are constructed, commodified, and distributed across the biotech industry, forming the raw materials for bio-art, DIY biologists and open science culture.[1] These corporeal products and practices exist within new and alien categories, transgressing the physical and cognitive boundaries set by biopunk science fiction and edging towards the possibility of a destiny driven by genetics and life sciences. With the eternal rhetoric of a high-tech humanity, and the threat of Michel Foucault’s[2] biopolitics constantly on the horizon, today Harraway’s[3] myth of the cyborg exists in the form of corporeal commodities travelling through the global biotech industry. Scientific research centres stock, farm, and redistribute biological resources, (often harvested from the female scientists themselves). Cells, seeds, sperm, eggs, organs and tissues float on the biotech market like pork belly and gold. Seeds are patented, and other agro-industrial elements are remediated and distributed as bits of operational data across the biotech network. We/cyborgs[4], are manifested as a set of technologies and scientific protocols, and, as a result, the female body in particular, is reconfigured into a global mash-up of cultural, political and ethical codes.
The increasingly pragmatic realisation of the biotech revolution has provoked a ‘cultural turn’ in science and technology studies in general, and feminist science studies in particular. Carolyn Christov-Bakargiev’s dOCUMENTA (13) proposed an interdisciplinary approach to the role of science for ‘culture at large’. Certainly, by foregrounding the heavy hitters in the field such as Donna Haraway and Vandana Shiva, dOCUMENTA (13) laid claim to addressing the global conflicts of biotechnology. However, the feminist agenda was not specifically addressed, and the key issues of the impact of biotechnologies on feminist subjectivities were only paid minimal lip service. With the exception of Shiva[5], the tone of dOCUMENTA (13) hinted at a positivist, emancipatory take on biotechnology and technoscience without assuming a critical position. There was very little public debate or critical analysis engaging the philosophical, ethical, and political issues of feminism and female subjectivities within the realm of biotechnology.
Notably absent from last year’s dOCUMENTA (13), the activist feminist collective subRosa’s performative, interdisciplinary projects are channelled towards embodying feminist content, practices, and agency, and laying bare the impact of new technologies on women’s sexuality and subjectivities – with a particular emphasis on the conditions of production and reproduction. Through their research-led practice and pedagogical mission, the collective analyse the implications and conditions of the constantly surveyed female body, whilst mapping new possibilities for feminist praxis. subRosa interrogate the conditions of surveillance, private property rights, and other control mechanisms the female body is subjected to by ART(Assisted Reproductive Technologies). The collective’s hybrid, interdisciplinary practice navigates the multiple identities the female body has taken on through techno-scientific development, including: the distributed body, the socially networked body, the cyborg body, the medical body, the citizen body, the soldier body and the gestating body. In contrast to the overarching and pervasive illustration of the technoscientific cultural landscape painted by dOCUMENTA(13), the current members and founders of the collective, Hyla Willis and Faith Wilding, are very clear in their critical intent. The collective choreograph and place themselves within globalized bio-scenarios in order to question the potential for resistance and activism within these constructs.
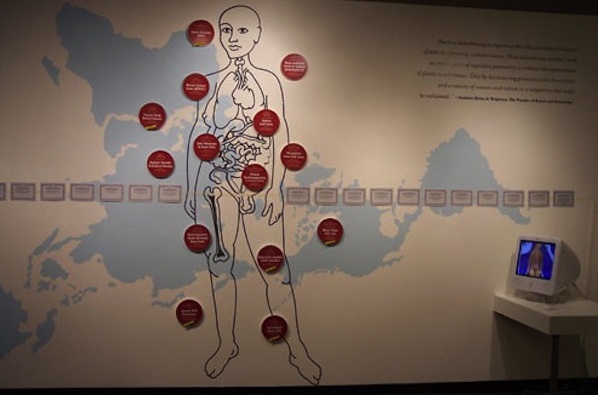
subRosa’s overarching vision to create discursive frameworks where feminist interdisciplinary conversations and experiments can take place, is research-led and takes its cue from the canon of radical feminist art practices. Cell Track: Mapping the Appropriation of Life Materials has featured in a number of exhibitions, most recently in Soft Power. Art and Technologies in the Biopolitical Age, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain. This project consists of an installation and website examining the privatization and patenting of human, animal and plant genomes in the context of the history of eugenics. Cell Track highlights the disparity between the bodies that produce stem cells and the corporations that control the products generated from them. Bringing together scientists, cultural practitioners and wider publics in the construct of the gallery space, subRosa generate discourse around the patenting and licensing of DNA sequences, engineered genes, stem cell lines and transgenic organisms. The project’s participatory aim is to set up an activist, feminist embryonic stem cell research lab in order to produce non-patented stem cell lines for distribution to citizen scientists, artists and independent biotechnologists. This environment of shared knowledge production and speculative, alternative, research activity is at the heart of subRosa’s social practice.

Due to the pedagogical nature of subRosa’s activities, the collective’s critical stance towards IVF and ART has proven to be particularly provocative, and their scepticism towards the emancipatory language of ‘choice’ co-opted by ART, has been met with some resistance by other feminist practitioners. However, it is in this very agonism[6] that subRosa wish to become more visible, and they welcome criticism and debate in the public discursive spaces that they create. In a recent interview, Faith Wilding and Hyla Willis both expressed their desire to generate an expanded, and deeper discussion about the wider issues involved in ART in particular and biotechnology’s effect on female identity in general. subRosa’s potential to reach wider publics and audiences is partially determined by the socio-political context of the communities in which they operate. Perhaps in reaction to this, subRosa’s focus is now shifting towards embracing the aforementioned ‘cultural turn’ in science as they address the position of feminist scientists themselves.
The imperative to reclaim feminist discourses and narratives in science is of growing concern to subRosa, as they believe that feminist agency lies in the practice of science itself. By relocating lab-work from the dominant scientific institutions to the public environment of the gallery, subRosa provide the critical space in which new feminist scientific praxis can operate,[7] and new dialogues and discourses can be created. Their conviction that political and critical traction lies in practice as discourse, and the potential of face to face encounters, is demonstrated in their recent project for the Pittsburgh Bienal: Feminist Matter(s): Propositions and Undoings (2011). In this installation, SubRosa take Virginia Woolf’s[8] assertion that ‘tea-table thinking’ provides an effective antidote to the male-driven ‘war-mentality brewed in boardrooms and command centers’ as their main conceit. Redeploying Woolf’s idea toward the rethinking of the traditionally male-dominated discipline of science, Wilding and Willis’ installation brings traces of the science laboratory to the intimacy and hospitality of the kitchen table, and in turn, also situates what is normally a private, feminized space in a more public domain.

These tables stage a dialogue between one or two visitors in response to the presentation of female figures in science, both the popularly acknowledged and the underexposed. subRosa foreground women scientists past and present and reimagine an alternative, feminized history of science and technology. The installation explores feminism and participatory practices as modes of scientific research, with the aim of generating dialogue and discourse around the questioning of the dominant historical narrative of science. Specially tailored installations reside on each table, evoking lab work while celebrating the history of the women protagonists they play host to – from anarchist painter Remedios Varo to geneticist Barbara McClintock.

subRosa’s pedagogical imperative is at once inclusive and provocative, and their role as facilitators of a discursive space outside the traditional institutions and control structures of science, is where their radical aspirations lie. Pedagogical art practices often teeter on the brink of propaganda, and subRosa are quite comfortable with the propagandistic label. Considering the economic and cultural climate in the USA with regard to the politics of reproduction, their work has been particularly well received in the context of European cultural institutions, whereas in the USA there is greater interest for the work in academic institutional settings. Perhaps this could be symptomatic of the general privileging of discourses around intersex, transgender and queer subjectivities. The dominant bias of the gatekeepers of the artworld to showcase queer practices is evident in the promotion of artists such as Ryan Trecartin and Carlos Motta on the international circuit. Curators have tended to position artists addressing the gendered ‘Other’ within a contemporary queer framework, whilst keeping feminist art practices on the peripheries of 1960s/1970s retrospective nostalgia. This tendency presents a muddying of the waters for contemporary feminist art practices such as subRosa.
This may also be part of a more general tendency to demonize and move away from feminist identities and discourses in wider society. The academic shape shifting from ‘women’s studies’ to ‘gender studies’ to ‘queer studies’ has diminished the feminist conversation and, therefore, the impact and receivership of feminist art practices. This has rendered the popular conception of ‘Queer’ as acceptable and non-aggressive. Furthermore, the term ‘Queer’ and the subsequent morphing into the verb ‘queering’, has been co-opted by transdisciplinary academic discourse, and is now an expansive, all embracing cultural term – a phenomenon that has met with a certain amount of scepticism from the queer community.
This privileging of the expansive ‘othering’ of queer rhetoric has often resulted in feminism being rejected as a radical and out-dated political identity by art practitioners themselves. This ambivalent attitude is perhaps also indicative of the wider feminist debate, in which post-feminism has splintered into fragmented, diluted groups, each policing their own identity politics with little sense of a bigger struggle. However, the collaborative, interdisciplinary environments orchestrated by subRosa signal a return to the indisputably material actuality of the female body. Through their insistence on the possibilities of feminist bench-side practices, and the forensic unpicking of the power/control structures inherent in biotechnology, subRosa expands the feminist lexicon through the empirically re-appropriated organic materiality of the body.
Charlie Gere is a Media Theory and History professor in the Lancaster Institute for Contemporary Arts, Lancaster University. Co-curator of FutureEverybody, the 2012 FutureEverything exhibition in Manchester. In 2007 he co-curated Feedback, a major exhibition on art responsive to instructions, input, or its environment, in Gijon, Northern Spain. He has given talks at many major arts institutions, including the Centre de Cultura Contemporània de Barcelona, the Architectural League in New York, Tate Britain, and Tate Modern. Gere’s new book, Community without Community in Digital Culture (Palgrave MacMillan, 2012), is out now.
Previous titles include: Digital Culture (Reaktion Books, 2002), Art, Time and Technology (Berg, 2006), Non-relational Aesthetics, with Michael Corris (Artwords, 2009). Gere was co-editor of White Heat Cold Logic (MIT Press, 2009), and Art Practice in a Digital Culture (Ashgate, 2010), as well as writing many papers on questions of technology, media and art. He is also co-editing with Robin Boast an anthology entitled Allegories of the Information Age (forthcoming).
Marc Garrett: Digital Culture was originally published in 2002, which happens to be the version I’ve had all these years. In 2008 it was republished, revised and expanded. Now the book has an extra chapter ‘Digital Culture in the Twenty-first Century’. Of course, we already know that digital technology and society has changed dramatically since 2002. So, what themes and historical contexts did you choose, as necessary to include in this new and last chapter?

Charlie Gere: What happened after the first edition’s publication was of course, the rise of so-called Web 2:0, which was simply the greater exploitation of the reciprocal possibilities of the Web. I tried to reflect on how this reciprocity was visible beyond the Web itself and was becoming part of a more general culture of engagement and exchange, not that I share some of the more utopian visions of this phenomenon. Indeed, in my new book Community without Community in Digital Culture, I try to counter the, for me, more naive visions of community in relation to digital technology. I advocate a more ‘non-relational’ approach that does not deny the transformative effects of new media in terms of community but thinks of it more in terms of hospitality to the other.
MG: Many of the artists we have worked with are using new media to explore and critique the utopian assumptions you discuss: YOHA, IOCOSE, Liz Sterry, M.I.G (Men In Grey, Julian Oliver and Danja Vasiliev), Heath Bunting, Face to facebook (Paolo Cirio and Alessandro Ludovico), Annie Abrahams and more. Each of them work in a deeply relational way to intervene in the mythologies projected about digital technology; and, with a knowingly crtical eye of the technical limitations and the social controls at work when using networked technology. At different levels, all are producing work that ‘consciously’ incoporate relational contexts, in some way or another, this includes ideas and approaches with autonomy as part of their art, but not necessarily advocating technology as a singular, saving grace.
How do you view the role of this practice in the context of the wider corporate and state impact on the way technical cultures are evolving. How do you see the notion of hospitality working between the arts and these other more mainstream cultures?
CG: I greatly admire and like the work of the artists you mention and others doing similar things. For me they exemplify the complexity of the idea of hospitality. In general the Web is about exchange, whether that of money for goods, social links and relational exchanges in social networks, or the exchange of speech and dialogue in on-line fora. The work of these artists refuses this demand for exchange and profit within a restricted economy. Thus they are in a sense parasitical on the Web. The word ‘parasite’ comes from ‘para sitos’, meaning ‘beside the grain’, and refers to those animals that take advantage of grain stores to feed. They are the creatures to who must be offered hospitality, as a gift, without expectation of return, which means that while they are bound up with the technological systems that comprise the Web, they are not part of the restricted economy of exchange, profit, and return that is at the heart of capitalism, and to which everything else ends up being subordinated and subsumed. Thus they find an enclave away from total subsumption not outside of the market, but at its technical core.


MG: Many are aware that technology and digital culture have changed the world we live in and appreciate their immediate effects on our everyday behaviours and situations. But there is a bigger story to tell, and history can offer us insightful glimpses, important clues and ways into this story about our relationship with technology and digital culture. One of the arguments outlined in your book ‘Digital Culture’ is that digital culture is neither radical, new nor technologically driven. With this in mind, which past developments do we need to acknowledge and be reminded of and why?
CG: For me the emergence of digital technology is part of a much longer story of abstraction, codification, quantification and mathematisation that can be traced back to numerous points in the history of the West, from Ancient Greece, to early Modernity to the rise of industrial capitalism. Here one might think of Heidegger’s use of ‘cybernetics’, a word we normally associate with post-war computing culture, to describe the technology and calculative enframing of modern society which he traces back to the Ancient Greeks and especially to Plato. I am not a particular advocate of digital technology, and while I appreciate its uses, I also think we must try to be aware of how it determines the way in which we think, and in which we conceive of the world. Above all we should not regard it as merely a conduit to an uncomplicated world simply out there, but rather the means by which a particular world comes to be for us. That said, this is very hard, given that in my view, and to adapt a well-known phrase from Derrida, il n’y a pas de hors-media, there’s no Archimedean point outside of our medial condition, from which we can understand it as from a god’s eye view. ‘Media determine our situation’ as Friedrich Kittler put it.
MG: In Digital Culture, you write about the composer John Cage and how he “has had the most profound influence on our digital culture”, and how his influence has opened up various different avenues of creative engagement. And, many of his ideas on interactivity and multi-media not only “have repercussions in the art world”, but also a strong influence on how computers are used as a medium. Which art movements in particular did he influence and what kind of legacy did he leave for others in relation to computers?
CG: Actually Cage’s influence on those using computers in the arts is probably less to do with what he himself did with such technology and more to do with his use of aleatory methods in many his different projects across many artforms. Also there is something about Cage’s own refusal of a normative Western subjectivity that is also consonant with aspects of our hyper-technologised existence with its emphasis on decentering the individual. Both the refusal of such subjectivity and the aleatory work together to produce a new model of the artist as conduit of contingent social forces rather than protean demi-urge or genius.
MG: Your new book ‘Community without Community in Digital Culture’, has come out at the same time as Geert Lovink’s ‘Networks Without A Cause: A critique of Social Media’. Lovink asks “How do we overcome this paradoxical era of hyped-up individualization that results precisely in the algorithmic outsourcing of the self? How do we determine significance outside of the celebrity paradigm and instead use intelligence to identify what’s at stake?” [1]
Where are your thoughts in regard to Lovink’s question, and does it relate to what you propose in terms of “hospitality to the other?”
CG: I haven’t read Geert’s book, yet at least… But I am highly sympathetic to what I take to be his position. My view is that the Web is part of a broader set of developments that apparently concern relationally, but actually emphasize the sovereign individual and autonomous subject of modernity, as well as promoting spectacular and image-bound forms of presentation and relation. The problem is that one alternative to this individualization is a kind of fascistic identification with the mass, in the form of fusion that negates the individual. A solution maybe to engage with the idea of the other in terms of difference, as both relational and separate, and yet also that which we depend on for our identity in a process of differentiation; thus the idea of hospitality as a reception of the other in difference.
MG: Community without Community in Digital Culture, is a curious title. It proposes contradictory meanings and these contradictions are clearly explained in the introduction. Although, the last sentence says “In this such technologies are part of the history of the death of God, the loss of an overarching metaphysical framework which would bind us together in some form of relation or communion. This can be understood in terms of contingency, which has the same root as contact.”
Could you unpack this last sentence for us, I’m especially interested in what contingency means to you?
CG: I owe my understanding of contingency to the work of philosopher Quentin Meillassoux, whose book After Finitude is causing a stir. Meillassoux is one of a small number of young philosophers sometimes grouped together under the name ‘speculative realism’, mostly because of their shared hostility to what they call ‘Kantian correlationism’, the idea that there can be no subject-independent knowledge of objects. Meillassoux follows the work of David Hume, who questioned the whole notion of causation; how one can demonstrate that, all things being equal, one thing will also cause another. For Hume causation is a question of inductive reasoning, in that we can posit causation on the grounds of previous experience. Meillassoux pushes the implications of Hume’s critique of causation to a point beyond Hume’s own solution, to propose the only necessity is that of contingency, and that everything could be otherwise, or what Meillassoux calls ‘hyperchaos’.
![Community without Community in Digital Culture [Hardcover]. Dr Charlie Gere. Palgrave Macmillan (2012) http://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/community-without-community-in-digital-culture-charlie-gere/1110025572 See on Amazon.](http://www.furtherfield.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/179510500.jpg)
I use his ideas to think through the implications of the ‘digital’. According to the Oxford English Dictionary ‘digital’ has a number of meanings, including ‘[O]f, pertaining to, using or being a digit’, meaning one of the ‘ten Arabic numerals from 0 to 9, especially when part of a number’, and also ‘designating a computer which operates on date in the form of digits or similar discrete data… Designating or pertaining to a recording in which the original signal is represented by the spacing between pulses rather than by a wave, to make it less susceptible to degradation’ (the word for data in the form of a wave being ‘analog’).
As well as referring to discrete data the dictionary also defines ‘digital’ as ‘[O]f or pertaining to a finger or fingers’ and [R]esembling a finger or the hollow impression made by one’, thus by extension the hand, grasping, touching and so on. Much of the book concerns deconstructing the ‘haptocentric’ implications of contact, and communication, especially in relation to the claims made for social networks, and to engage with what I understand as the relation between ‘contact’ and contingency’. ‘Contingency’ is derived from the Latin con + tangere, to touch. ‘Contingency’ enables us think through the implications of the term digital, by acknowledging both its relation to the hand and touch and also to the openness and blindness to the future that is a concomitant part of our digital culture after the death of God.
MG: What other subjects can we expect to read about in the publication?
CG: Touch in Aristotle and medieval theology, cave painting, mail art, Darwin and Dawkins, Luther Blissett, On Kawara, Frank Stella, Bartleby the Scrivener, Christianity – among other things… oh, and a lot of Derrida.
MG: If there is a message you’d like to send to the world, as it carries on regardless with its “permanent exposure of life, of all lives, to ‘all-out’ control […] thanks to computer technology” [2] (Virilio 2000), and it was printed on a banner, or on a billboard in the streets, what would it be?
I am reading Blanchot at the moment, so perhaps something like ‘the disaster has already happened’ (it’s suitably enigmatic to annoy people).
<———————————- The End (for now) ——————————>
Featured image: Sculptured relief of Roman soldiers fighting the barbarians.
Lies, Lawlessness and Disbelief 1. Thinking Art and Capital: Unknown Unknowns, is the second of five essays by Canadian artist & critical thinker, Katie McCain. McCain discusses how capitalism has become on the one hand all encompassing and on the other utterly unreal. Arguing that we need to be prepared to think the impossible so that resistance is able to grow.
DOWNLOAD the full text (including all 5 parts) here, or read part two below:
In 1942 the Ministry of Defense labeled Gruinard Island as X Base. It was an isolated island that had been deemed acceptable for testing the viability of an anthrax weapon, as it was unknown if the spores be able to survive the blast. An anthrax bomb was dropped on a herd of sheep kept in individual crates, their heads in hoods so they could not lick the spores. Of 15 sheep, only 2 survived. The test was repeated with less success as a change in wind direction caused the bomb to land in a peat bog where it sank. The test was moved to Wales. In 1981 operation dark harvest – led by a team of microbiologists – collected soil samples from Gruinard Island, which had since been quarantined. Their demand was for the government to decontaminate the island or the samples would be weaponized and distributed. Two samples were found outside a research facility in Porton Down, and in Blackpool, where the ruling conservative party were meeting.[1]
Unknown unknowns are intrinsic to this conceptual, contemporary capitalism, and operate as the risk that can eventually cause a system to fail. Failure emerges from the unprecedented, from the unthinkable, from the things you do not know you do not know.[2] Instead of attempting to predict these events for market gains, what would it mean to merely acknowledge the paradoxical nature of thinking the unthinkable? Unthinkable operates as the other to any thought capacity, and in an attempt to access this impossible, it would be possible to access a non-knowledge, something on the edge of logic, of research, of ideas.
Non-knowledge is not the same as ignorance, but rather references the other of the knowledge system itself, an indeterminate zone between knowledge and ignorance.[3] Huberman addresses this topic in the exhibition catalogue: For the Blind Man in the Dark Room Searching for the Black Cat that Isn’t There. The phrase was initially attributed to Charles Darwin’s description of a mathematician, but here is used to underscore the type of knowledge, the type of logic, that art explores. A work of art that isn’t. As a method of generating new forms of thinking and unknown circuits of consciousness, visual art often verges on logic.[4]
Quantum physics is constantly pushing the boundaries of the unknown. If these formulations, these theories, constitute the boundary of the known, imagine the possibilities contained in unknown unknowns. This of course is impossible, but in the impossible lays unimaginable possibilities. The acceptance of the fact that there are unknown unknowns and, like dark matter, they are invisible, but make up the majority, could operate as a placeholder for limitless possibilities.[5] The things we do not know are impossible, contradictory and badly behaved; the things, then, that we do not know we do not know could be more radical still in terms of reality and the perception of it –an impossibility for thought, but this is the heart of it, the possibilities contained in the impossible. It is fundamentally possible for anything to be true (or conversely false), to be known (or to be unknown)[6]. The more this point is exhumed the more amazing and simultaneously frustrating it can become.
Quantum reality proves that we can alter reality just by looking at it. Photons behave differently under scrutiny than when left to their own devices, which leaves us incapable of describing their behaviour.[7] Einstein asked physicist Niels Bohr if he really believed that the moon disappears when no one is looking at it, to which the retort was “can you prove otherwise?”[8] The answer is of course no, we are incapable of removing ourselves, of removing our relation to the thing-in-itself, of removing the impact of thought from suppositions of reality.
‘Quantum physics is an exciting theory because it is extremely precise, it is mathematically beautiful, it describes everything. It just doesn’t make sense.’[9]
Perhaps the language of mathematics is not a language invented in order to describe reality, but rather is the basis on which the physical world manifests, and slowly consciousness grasps more and more of this structure. If the theory is wrong, fundamental physics will hit a roadblock beyond which is it impossible to tread; if the theory is right everything is potentially understandable, dependant on thought’s capacity to understand.[10] These fundamentally opposite poles of reality offer, to us, the same plain of comprehension – the capacity of thought, the very limit of which we cannot pass.
Dreamwork, specters, illogic, the impossible – it is where thought begins to break down in terms of accuracy or coherent narrative that it begins to get interesting. On the fringes of thought lie truth, radicalism, subversion and change. And on the fringes of reality are lies, paradox and the imaginary. Does this mean that truth can be found in lies, paradox and the unreal?
The market depends on our belief in it, and our lack of faith can have catastrophic results. So bolstering collective belief in markets is the main strategy for their stabilization. But consciousness is not so simple; the market begins to rely not only on our belief in it, but in our belief in our belief in it[11], and so on ad infinitum. An infinite regress of belief created in order to prop up that self-same belief. How can consciousness continue to reconcile itself with this infinite regress? In quantum physics, observing photons can change how they behave. In the market, disbelief can cause it to collapse. A ping pong ball, by the time it’s bounced nine times factors the gravitational pull of a body standing next to the table into it’s bounce, by the 56th bounce ever single elementary particle of the universe has to be present in your assumptions [12]. In reality, many things are affected by human existence, but thought, or existence itself is not one of them.
It is not true that in order to live one has to believe in one’s own existence. There is no necessity to that. No matter what, our consciousness is never the echo of our own reality, of an existence set in “real time.” But rather it is its echo in “delayed time,” the screen of the dispersion of the subject and of its identity – only in our sleep, our unconscious, and our death are we identical to ourselves. Consciousness, which is totally different from belief, is more spontaneously the result of a challenge to reality, the result of accepting objective illusion rather than objective reality. This challenge is more vital to our survival and to that of the human species than the belief in reality and in existence, which always refers to spiritual consolations pertaining to another world. Our world is such as it is, but that does not make it more real in any respect. “The most powerful instinct of man is to be in conflict with truth, and with the real.”[13]
Asleep, unconscious or dead. These are the three options in which one is identical to oneself. But what does that mean? Harman discusses sleep as a lack of relations. We still exist as pieces that make a physical whole, but the thing we lack in sleep is relations. ‘Sleep is our closest approach to the freedom from relations in which we are most ourselves’[14]
An object, too, can be dormant. It is capable of existing apart from a specific situation, and therefore is capable of existing apart from any situation at all; therefore, it is relationless, or has the possibility to be relationless. Unlike objects, however, this dormancy is not so much a freedom from the world, as a dormancy to the world, withdrawn, incapable of anything else.
Yet, in a sense we are always inside the world through the fact that we are made up of pieces – and only therefore are we free, with our components doing the work of liberty on our behalf. For there is an excess in our pieces beyond what is needed to create us, and this excess allows new and unexpected things to happen.[15]
So perhaps seeking freedom in individuation, in isolation, as the linking of subject to object, in the perpetual delay of satisfaction that capitalism offers is the achievement of the exact opposite of the freedom sought. Perhaps the individual freedom presented by capital and democracy is in fact a relationless sleep that removes the other, the alternative, removes the opportunity for change, and ultimately time itself.
sl
sle
slee
sleep
Freudian kettle logic is an example, a joke employed by Freud to explore the mind’s capacity for self-deception. It is this logic, or rather this illogic that some manages to access the impossible. Kettle logic refers to the thought process of a mind on the defensive. It shows the impossibility of thought or rather it’s circular nature, that manages to disregard laws of non-contradiction. It goes as follows:
A neighbour is accused of borrowing a kettle and returning it with a hole. He answers simultaneously that 1) he did not borrow the kettle; 2) it was unbroken when he returned it, and 3) that it was broken when he borrowed it.[16]
Freud uses this to unpack dream logic, during which time mutually exclusive answers or states can easily co-exist. “Wendy Brown says that dreamwork provides the best model for understanding contemporary forms of power. It produces a confabulated consistency that covers over anomalies and contradictions”[17]. Žižek uses Freudian kettle logic to explain the U.S.’s right to wage war on Iraq, and the notion of the pre-emptive strike, which renders events of the future to a fictional or probabilistic past.[18]
Žižek also argues:
If we postpone our action until we have full knowledge of the catastrophe, we will have acquired that knowledge only when it is too late. The certainty on which to act is never a matter of knowledge, but a matter of belief. If, accidentally, an event takes place, it creates a preceding chain which makes it appear inevitable – Hegelian dialectic of contingency and necessity. In order to confront a disaster – we should accept it as fate, as unavoidable, and then retroactively insert into the past of the future possibilities on which to act in the present.[19]
This is frighteningly similar to the rhetoric of war used by the right, but employed by the left with regard to environmental disaster. Both the right, and the quite radical left in this instance, are using the same logic of prediction to validate an action. The difference, it seems, is Žižek’s disbelief, or awareness of the impossibility of a situation that requires action despite the fact that the specifics of the situation itself are still largely unknown.
Link to first article
https://www.furtherfield.org/lies-lawlessness-and-disbelief-1/
Adorno, Theodor.W. Negative Dialectics. Translated by E.B. Ashton. New York: Continuum, 2005. First Published 1966 by Suhrkamp Verlag.
Associated Press. “Romanian Witches Curse Latest Government Clampdown,” The Guardian, February 9, 2011, main section, 20.
Bartlett, Monica Y., Aida Cajdric, Nilanjana Dasgupta and David DeSteno, “Prejudice from Thin Air: The Effect of Emotion on Automatic Intergroup Attitudes.” Psychological Science 15, no. 5 (May, 2004): 319-324.
Baudrillard, Jean. Global Debt and Parallel Universe. Translated by Francois Debrix. http://www.egs.edu/faculty/jean-baudrillard/articles/global-debt-and-parallel-universe/ (accessed April 4, 2011).
Baudrillard, Jean. Radical Thought. Translated by Francois Debrix. Edited by Sens & Tonka. Paris: Collection Morsure, 1994.
Bey, Hakim. T.A.Z.: Temporary Autonomous Zone, Ontological Anarchy, Poetic Terrorism. New York: Autonomedia, 2003. First Published 1985.
Bradley, Will. “Guarana Power.” in Self-Organization/Counter-Economic-Strategies, edited by Bradley, Hannula, Ricupero and Superflex, 311 – 333. New York: Steinberg Press, 2006.
Brassier, Ray. “I Am a Nihilist because I Still Believe in Truth” Interview with Marcin Rychter. Kronos: March 4, 2011 http://kronos.org.pl/index.php?23151,896 – accessed: march 23rd, 2011.
Brassier, Ray. Nihil Unbound: Enlightenment and Extinction. Basingstoke: Palgrave McMillan, 2007.
Critical Art Ensemble. Marching Plague: Germ Warfare and Global Public Health. New York: Autonomedia, 2006.
Declercq, Frédéric. Lacan on the Capitalist Discourse: Its Consequences for Libidinal Enjoyment and Social Bonds. Psychoanalysis, Culture & Society 2006, 11, (74-83).
Fisher, Mark. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative? Winchester: Zero Books, 2009.
Foucault, Michel. Power/Knowledge: Selected Interviews & Other Writings: 1972-1977. New York: Pantheon Books, 1980.
Fromm, Erich. The Fear of Freedom. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd., 1966.
Groys, Boris “Art and Money,” E-Flux 24 (2011), http://www.e-flux.com/journal/view/226.
Harman, Graham. Circus Philosophicus. Winchester: Zero Books, 2010.
Hofstadter, Douglas R. Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid. London: Penguin Books Ltd., 1979.
Holt, Jim. “The Way We Live Now: Against Happiness,” New York Times, June 20, 2004.
Horizon: What is Reality? Documentary. Directed by Helen Shariatmadari. BBC: ep. 9, 2011.
Huberman, Anthony, ed. For the Blind Man in the Dark Room Looking for the Black Cat that Isn’t There. St. Louis: Contemporary Art Museum St. Louis, 2009.
Huxley, Aldous. Brave New World. London: Vintage Books, 2007. First published 1932 by Chatto & Windus.
K-Punk Blog. http://k-punk.abstractdynamics.org/archives/004421.html
Kafka, Franz. The Castle. Middlesex: Penguin Books Ltd., 1964. First published 1926 by Das Schloss.
Kurant, Agnieszka and Nassim Nicholas Taleb. “Unknown Unknowns: A Conversation between Agnieska Kurant & Nassim Nicholas Taleb about the Benefits of Uncertainty.” Frieze, September 2010, 127 -135.
Lacan, Jacques. “Seminar on the Purloined Letter.” Yale French Studies 48 (1972): 39-72.
Lacan, Jacques. The seminars of Jacques Lacan: Book II: The Ego in Freud’s Theory and in the Technique of Psychoanalysis 1954-1955. Ed: Jacques-Alain Miller. New York: W. W. Norton and Co., 1991.
MacKinnon, Catharine A. “Feminism, Marxism, Method and the State.” Chicago Journals 8, no. 4 (1983), 635-658.
Meillassoux, Quentin. After Finitude: An Essay on the Necessity of Contingency. London: Continuum, 2008.
Mouffe, Chantal. The Democratic Paradox. London: Verso, 2000.
Noys, Ben. Persistence of the Negative: A Critique of Contemporary Continental Theory. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2010.
Place, Vanessa and Robert Fitterman. Notes on Conceptualisms. New York: The Ugly Duckling Presse, 2009.
Stephen, Kylie. “Sexualized Bodies.” in Real Bodies: A Sociological Introduction, edited by Evans and Lee, 29-45. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan. 2002.
Taleb, Nassim Nicholas. The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable. London: Penguin Books Ltd., 2007.
Thacker, Eugene. “Nihil Unbound” review of Nihil Unbound: Enlightenment and Extinction, by Ray Brassier, Leonardo 42: no.5, (2009): 459-460, http://muse.jhu.edu/journals/leonardo/v042/42.5.thacker.html (Accessed April 2, 2011).
The Trap: What Happened to Our Dream of Freedom? Documentary. Directed by Adam Curtis. BBC Two: March 2007.
Trotta, Roberto. “Dark Matter: Probing the Arche Fossil.” Interview with Robin Mackay. Collapse: Philosophical Research and Development 2 (2007): 83-169.
Vidal, John. “Bolivia Enshrines Natural World’s Rights with Equal Status for Mother Earth.” The Guardian. April 11, 2011. Main section, 15.
Weaver, Matthew. “Romanian Witches to Cast Anti-Government Spell.” The Guardian. January 7, 2011. Main section, 23.
Wilson, Eric G. Against Happiness. New York: Sarah Critchton Books, 2008.
Žižek, Slavoj. First as Tragedy, Then as Farce. London: Verso, 2009.
Žižek , Slavoj. The Iraqi Borrowed Kettle. http://www.lacan.com/zizekkettle.htm (accessed April 4, 2011).
Žižek, Slavoj. What Rumsfeld Doesn’t Know that He Knows About Abu Ghraib. (2004) http://www.lacan.com/zizekrumsfeld.htm (accessed April 4, 2011).
Since the turn of the millennium, there have been shifts toward new forms of sociopolitical dissent. These include strategies such as cellular forms or resistance including asymmetrical warfare like global insurgencies, the use of social media. Examples would be Twitter and Facebook in their ability to lens dissent for actions in Syria, Egypt and Tunisia, Wikileaks and its ability to mirror, and politics that use anarchistic forms of collective action such as the Occupy Movement. Although my focus is more concerned with the Occupy Movement, what is evident is what I call an amorphous politics of dissent. Amorphous is defined as “without shape”, and can be applied to most of the mise en scenes listed above.
The dissonance of power in regards to conventional politics can be seen in its structure. For example, the nation-state has a tiered, hierarchical structure of power relations. There is a President or Prime Minister, a legislative organ of MPs or Representatives, Parliaments, Houses, and the like, a Judicial organ, and a Military organ that includes any number of militia and police. Although I am referring mostly Western forms of government, we can also argue for the hierarchical form in terms of the Corporation, with its CEO, Board, Shareholders, Managers, and Workers. This can be expanded historically to Feudal lords with their retinue of Vassals, Nobles and Warlords with their coteries of Warriors and support personnel. The point is that conventional power typically operates in a pyramidal command and control hierarchy with a centralized Leader at the “capstone”. One can argue that the pyramid may have different shapes, or angles of distribution of power, but in the end, there is usually a terminal figure of authority. To put it in terms of stereotypical Science Fiction terminology, when the alien comes to Earth, the standard story is that it pops out of the spacecraft and says, “Take me to your leader.” This signifies the hegemonic paradigm of Leadership as the central gestalt of First world power. Leadership, then, is the conventional paradigm of power in Western culture, and dominates the industrialized world.

Territorialization refers to the exertion of power along perimeters, or borders. Functionaries expressing the constriction of territory include customs agents, and border patrols; but are terminally expressed by the military wing of the nation state. This military is also generally pyramidally constructed in terms of Generals, Colonels, and other officers leading Battalions, Regiments and Divisions, which are organized as defenders of a nation’s sovereignty. These military organs are conversely best optimized to exert their power against either parallel or subordinate structures. Parallel structures include the armies of other nations, their Officers, et al, and their troops and ordnance that possess a similar organization. Conversely, subordinate structures over which military powers can exert power over are domestic masses that can be overrun with overwhelming power, although these forces are more specialized (such as National Guards or Gendarmeries). In the conventional sense, power is expressed orthogonally, whether it is against equal or subordinate forces.
Another aspect of this conversation relates to the expression of power/force through conflict and violence, but has its inconsistencies The examples I will use from American pop culture I will use in this missive to explain amorphous action may be violent in nature, but the violent nature of these examples do not relate to the paradigmatic jamming of conventional power. Their citation is related more to the fact of conventional power’s orthogony, or parallelism of exertion of power to similar structures or dominance of the subordinate, and the panic state it experiences when confronted with non-conventional difference or passive resistance. We could express the power relationships between amorphous politics and conventional power in terms of a tetrad in terms of examples of violent and peaceful exertion of amorphous dissent as well as orthogonal conflict. We could cite the Occupy movement as a site of passive, and the Tunisian uprising as violent exemplars of amorphous conflict or dissent. Conversely, the Gandhi/King is a non-violent model of as orthogonal/hierarchical/led action, and World War Two as conventional orthogonal conflict. What is important here is the inability of the conventional politics and power to cope with leaderless, non-hierarchical, non-orthogonal discourse that refuses to talk in like terms such as centralization, leadership and conventional negotiations that include concepts such as “demands”. This is where the site of cognitive dissonance erupts, often resulting in a panic state or in the “figureheading” of dispersed networks of power.
The need for the traditional power structure to focus identity on the antagonist in terms of figureheads is evident in the Middle East and Eurasia in the personification of terrorist and insurgent networks, but is more simply illustrated in the films Alien and Aliens, and Star Trek: The Next Generation. Both of these feature their respective antagonists, the “alien” as archetypal Other, and the Borg, symbol of autonomous, collective community. In Alien, the crew of the Nostromo encounters an alien derelict ship that has been mysteriously disabled to find a hive of eggs of alien creatures whose sole role is the creation of egg factories for further reproduction. At the onset of the franchise, pilot Ellen Ripley is positioned as the “everywoman” placed in the center of cataclysmic events. In the Alan Dean Foster book adaptation, and an extended edit of the Scott film, Ripley finds during her escape from the ship that Captain Dallas has been captured and organically transformed into a half-human egg-layer whom she immolates with a flamethrower. However, in the Aliens sequel, the amorphous society of the self-replicating aliens has been replaced by a centralized hive, dominated by a gigantic Queen that threatens to impregnate the daughter-surrogate Newt. This transformation from a faceless to centralized threat creates a figurehead for the threat and establishes a clear protagonist/antagonist relationship, and establishes traditional orthogony.
This simplification of dialectic of asymmetrical politics is also evidenced in Star Trek: The Next Generation by the coming of the Borg, a collective race of cybernetic individuals. Although representations of the Borg vary as to fictional timeline, in televised media they began as a faceless hive-mind, which abducted Captain Jean-Luc Picard as a mouthpiece, not as a leader. It was inferred that if one sliced off or destroyed a percentage of a Borg ship, you did not disable it; you merely had the percentage left coming at you just as fast. However, by the movie First Contact, the Borg now possesses a hierarchical command structure to their network and, more importantly, a queen. With the assimilated and reclaimed android Lieutenant Data, the crew of the Enterprise infiltrates higher level functions of the Borg Collective, effectively shutting down the subordinate elements of the Hive. In addition, the Queen/Leader is defeated, assuring traditional figurehead/hierarchy power relations rather than having to deal with the problems of the amorphous, autonomous mass. There are other “amorphous” metaphors in cinema that address the issue of amorphousness. These include the 1958 movie, The Blob, in which a giant amoeba attacks a small town and grows as it engulfs everything. Another is The Thing, about a parasitic alien that doppelgangs its victims, creating another form of faceless threat. Lastly, we have the classic Invasion of the Body Snatchers where alien plant “pods” would bear fruit of duplicates of living people, giving a metaphor for the Communist threat of the Red Scare originating during the Cold War. Perhaps these are historical references to mediated expressions of anxiety in regard to autonomy’s threats to regimented/striated hegemony, stating that this sort of anxiety and terror are not new.

One of the most asymmetric cultural Western interventions in relation to constructs of traditional power is the involvement of Anonymous as part of the Occupy Movement. Anonymous, which has been called a “hacker group” in the mass media, is a taxonomy created on the online image sharing community 4chan.org, arising from the practice of posting “anonymously” unless one wants to use a name, or handle. Although the idea of Anonymous is at best an ad hoc grouping, the use of the “group” name has been ascribed to various factions. According to The State News, “Anonymous has no leader or controlling party and relies on the collective power of its individual participants acting in such a way that the net effect benefits the group.“ The idea of Anonymous fits with the “faceless collectives” mentioned above, and certainly presents an asymmetric, if not non-orthogonal, exercise of power. Anonymous first rose as a voice of dissent that emerged against the Church of Scientology (see Project Chanology), where flash mobs of individuals in Guy Fawkes masks and suits arrived to protest at sites around the world, with boom boxes playing “The Fresh Prince of BelAir”, a popular agitational or “trolling” anthem. It has engaged in other activities, including hacking credit card infrastructures opposed to handling donations to Wikileaks and creating media around Occupy Wall Street. However, without a clear infrastructure and only transient figureheads, Anonymous functions as an organizing frame for a cloud of individuals interested in various collective actions, and represents an indefinite politics based on networked culture. In an expected exercise of force, during the actions against elements opposed to Wikileaks, conventional power struck back wherever it could against members of Anonymous, by arresting over 21, some violently, in July during the actions against credit providers boycotting Wikileaks. This exercise of power was repeated in September, with admonitions about the arrests appearing on YouTube thereafter. Anonymous has also posted videos in support of the Occupy movement. Such a response is not surprising, but is the exact response to non-orthogonal dissent under our model. The problem is that in arresting any number of Anonymous members, traditional power is confronted with the first, distributed model of the Borg that merely exists minus two or twenty members.

Another dissonance between the Occupy Movement and conventional politics is the perceived lack of agenda. This is due to its dispersion of discourse in giving its constituents collective importance in voice. What is the agenda of the disempowered 99% of Americans, or world citizens marginalized by global concentration of wealth? Simply put, the agenda is for the disempowered to be heard. What does that mean? It means anything from forgiveness of student loans to jobs to redistribution of wealth to affordable health care, and so on. It isn’t a list; it is a call to systemic change of the means of production, distribution of wealth and empowerment in political discourse. It isn’t as simple as “We want a 5% cut in taxes for those making under $30,000.” It’s more akin to “We’re tired that there are so many sick, hungry, poor and uneducated, and we want it to end. Let’s figure it out.” It is the invitation to the beginning of a conversation that has no simple answers other than the very alteration of a paradigm of disparity that has arisen over the past 40 years through American capitalism.
The last challenge to the traditional power discourse is that of passive resistance. This is not a new strategy, especially under the aegis of Gandhi and King’s movements. However, it is traditional power’s mere tolerance of nonviolent resistance that does not result in violence. As we can see from the UC Davis assaults and the dispersions after the second month anniversary, conventional power exerts its force against, as Brian Holmes put it, “anomalies” so that the system can be restored and the commodifiable classes are reintegrated into the system to reproduce its agendas. As long as resistance does not present undue inconvenience for the circulation of power and capital, it is allowed. Once it loses its patience with non-orthogonal forces, or if materially sacralized spaces, like Wall Street are threatened, the hegemonic order is reified. The irony of the technical loophole of Zucotti Park being privately owned and having few rules allowed the Occupy movement also highlights the tenuousness of public discourse in Millennial America. However, even with this oddity, on the two-month anniversary of Occupy Wall Street, force has begun to be used against the occupiers as traditional power’s patience grows thin with amorphous politics. In the streets, the marches are split up, and rules about occupation begin to be enforced with cupidity. As said before, hegemonic patience has worn thin, with assaults/dispersions taking place in Oakland, Davis, Philadelphia, and New York, among others. However, the movement moves forward for the moment.
Amorphous politics is based on plurality, collectivism, dispersion and ideas. The hierarchical nation-state has no idea what to do with the amorphous blob as it grows except to try to contain it, but as with Anonymous, it is a whack-a-mole game. If one smacks down one protest, two pop up across town, or five websites pop up on the Net. Shut down Wikileaks, and a thousand mirror sites show up. People in the streets swarm New York and other cities throughout the US, and the world, and conflict arises. Asymmetry and amorphousness are dissonances to traditional power. Ideas in themselves are not hierarchical.
Desires sometimes have no agendas.
Sometimes people want what is right, and all of it.
Between July 27th and August 29th, 2010, the eleventh edition of the FILE festival is taking place in Sao Paulo (Brazil), at several locations along the popular Paulista Avenue. After a decade of existence, this veteran festival, which spreads over several cities in Brazil (including Rio de Janeiro and Porto Alegre) as well as other international locations, has introduced for the first time its own award: the FILE PRIX LUX. With a total amount of approximately 120,000 euros, distributed in three categories, the prize is unprecedented in the continent and has received, on this first edition, 1,235 registrations from 44 countries.
Yet this award is not the only remarkable aspect of this year’s festival, which stands out for being particularly accessible to the general public. On the one hand, the exhibitions, performances and workshops as well as the symposium have no entrance fees, and therefore there have been many visitors, most of all young people who line up every day to experience the interactive installations at the FIESP-Ruth Cardoso Cultural Centre. On the other hand, the festival organizers, Ricardo Barreto and Paula Perissinotto, have developed this year a project that takes digital art to the Paulista Avenue by placing several interactive artworks at different locations in the public space. Finally, even the FILE PRIX LUX has been open to the interaction with the public by introducing a popular vote category and an online voting system which was accessible between May and June. This openness sets a good example of how media art festivals can engage the general public to approach this somewhat ignored form of art.
In general terms, the award categories at media art festivals have been subject to change as the creative uses of technology evolved during the last decades. The FILE PRIX LUX has the advantage of being created at a time in which it can be relatively safe to set up a few broad categories that cover most of the forms of combining art and technology. Only three categories have been established: Interactive Art (which usually refers to objects and installations that respond to inputs from the viewer/s), Digital Language (related to the festival’s title and which embraces any artwork that deals with language, narrative, code or text in a generative or interactive manner) and Electronic Sonority (the category assigned to any artwork in which the production or manipulation of sound is a key element). These three categories prove to be comprehensive, as shown by the diversity of the projects distinguished with a prize or an honorary mention: immersive interactive installations, musical performances, urban interventions, bioart pieces, a collectively created machinima movie and even an iPhone app are among this year’s FILE PRIX LUX awardees.

In the Interactive Art category, the winners are Ernesto Klar for Relational Lights (1st prize) and Kurt Henschläger for Zee (2nd prize). Both present immersive environments in which light and space are key elements, although the interaction is totally different. Klar’s work invites the viewer to interact with two projected geometric drawings inspired by the work of Lygia Clark. In a hazy dark room, the viewer sees two T-shaped projections of white light on the ground, which form a three-dimensional space which reacts to the visitor’s presence. The interaction is playful and really beautiful in its simplicity, whilst also limited in time: after a few minutes, the projections suddenly stop reacting to the user’s movements and reconfigure themselves in a new shape. This abrupt interruption is consciously introduced by the artist in order to remind the viewer that the artwork has a life of its own. In contrast, Henschläger’s Zee takes place mostly in the mind of an audience exposed to an overdose of audiovisual stimuli in a foggy room. Continuing the experience of his acclaimed performance FEED, this time the artist allows the viewer to walk around the space and have a more meditative sensory experience.

The Electronic Sonority category has brought together several outstanding works, among which Jaime E. Oliver’s Silent Percussion Project and TERMINALBEACH’s Heartchamber Orchestra have been distinguished with the 1st and 2nd prize, respectively. In both projects the human body is incorporated in a novel form in the creation of music, the sound being produced, moreover, not simply by direct inputs but by complex interactions in a constant flow of data. Oliver’s instruments convert the shapes created by the performer’s hands into streams of data that generate, in turn, different sounds. These sounds are not always the same, as could be the case in a traditional instrument, but are changed by the variables established in previous interactions. Thus, Oliver does not simply create a new form of interacting with an instrument but rather a new form of creating music. In a similar way, the [i]Heartchamber Orchestra[/i] project developed by TERMINALBEACH (Erich Berger and Peter Votava) explores a form of creating music based on a feedback loop in which the performers are writing and following the score at the same time. As the artists state, in their project “the music literally comes from the heart”: a network of 12 independent sensors record the heartbeats of the musicians in an orchestra and sends the data to a software that generates a musical score in real time. The musicians play the score as it is displayed on the laptops in front of them, while their heartbeats set the notes in a continuous cycle in which music and performer constantly influence each other.

Digital Language is certainly the broadest category of this FILE PRIX LUX, its awardees being quite dissimilar in the formats they use and the objectives of their respective projects. The organizers define this category as including “all research and experiments in the ambit of the multiple disciplines that use digital media”, and the winners exemplify how diverse these disciplines can be. The 1st prize winner, Tardigotchi by the artists collective SWAMP (Douglas Easterly, Matt Kenyon and Tiago Rorke) is a bioart project that sets a critical comparison between artificial and real life. A nicely designed, steam punk-inspired device hosts, on the one hand, a tardigrade, a microorganism measuring half a millimeter in length, along with a robot arm that injects a substance that feeds the creature and a heating lamp that provides warmth. On the other hand, a digital display shows the virtual avatar of this tardigrade, with which the user can interact. Humorously referencing the popular Tamagotchi toy, the artists create a link between the avatar and the real creature: when the user presses the button to feed the avatar, the device inserts real food in the environment of the tardigrade; when an email is sent to the digital creature, a heating lamp gives warmth to the microorganism. Thus, interacting with the virtual pet has consequences in a real living being. This brings our attention into what we can consider alive and how we emotionally attach to artificial creatures while at the same time we undervalue the existence of other living beings. On a different approach, the 2nd prize winner, Hi! A Real Human Interface, by the collective Multitouch Barcelona (Dani Armengol, Roger Pujol, Xavier Vilar and Pol Pla), proposes a more human relationship with technology. A video presents the concept developed by this interaction design group of a different GUI in which a real person is displayed as impersonating the computer. Common interface elements are replaced by handmade physical objects which remind the aesthetics of a video by Michel Gondry. The result is a playful form of interaction in which simple operations such as checking email or upgrading the operating system are shown as actions carried on with real objects by a person inside a box. The proposal is engaging and certainly sets a departure from the old desktop concept, yet it remains unsure to what extend this type of interaction can be applied in a real operating system.
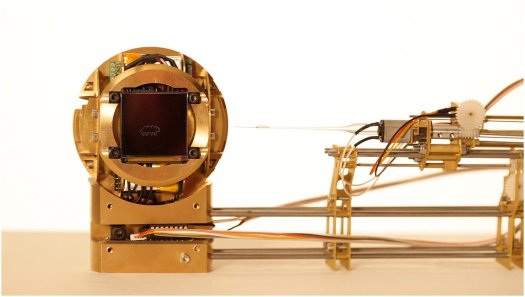
The works that obtained a Vesper statuette (symbol of the FILE PRIX LUX award) along with the also outstanding Honorary Mentions are exhibited at the FIESP-Ruth Cardoso Cultural Centre in a group show that also includes FILE Media Art, a selection of more than 70 works that can be accessed on several computers, as well as a selection of videogames and machinima films. The exhibition is thus richer in content than it would seem at first sight, as the space is divided in numerous sections that conceal several installations which demand (as usual) almost total obscurity. The artworks are well presented, although at times the sound from one installation invades the others, and there are no wall labels that inform the viewer about the concept of the piece or the way to interact with it. The latter, much-discussed issue is quite important, since the info-trainers cannot explain the artworks to every visitor, and quite often this entails that some people may not interact with the pieces or worse, start smashing buttons or interfering projections blindly in the hope of modifying them. Despite this fact, the exhibition has proven to be very successful during the first week of the festival, with a steady flow of visitors who showed a profound interest in the artworks.

A part of the exhibition is devoted to the FILE MACHINIMA section, curated by Fernanda Alburquerque, who selected over 40 works. Among these is the award winner in the Popular Vote category, War of Internet Addiction, by Corndog and the Oil Tiger Machinima Team from China, a 64-minute movie collectively created by players in the MMORPG War of Warcraft. More than mere entertainment, this film has been created as a form of protest against the Chinese authorities’ attempt to control the access and commercial benefits derived from the WoW game, which is extremely popular in the country. The film has had 10 million views since January 2010 and despite being available only in Chinese, it has been the favorite work of those who participated in the online voting system of the FILE PRIX LUX. Besides this feature film, other short films explore the possibilities of building narratives in virtual environments such as Second Life and videogames such as Half Life 2, Eve Online or Shadow of the Colossus.
In addition to the main exhibition, the FIESP Cultural Centre hosts a series of performances and screenings. Under the title Hypersonica, the festival presented a series of digital music performances, among which where the two winners of the FILE PRIX LUX in the Electronic Sonority category. FILE DOCUMENTA, curated by Eric Marke, offers in its 5th edition a selection of “rare and new” documentary films, among which Andreas Johnsen’s Good Copy Bad Copy, an interesting exploration of the conflicts between remix artists and copyright owners, or Robert Baca’s Welcome to Macintosh, which records the first years of the history of Apple Computers.

The symposium, hosted by the Instituto Cervantes in Sao Paulo, gathered several experts and artists who presented their explorations in the theory and practice of media art. Among the most interesting contributions were the presentation of Prof. Espen Aarseth on the aesthetics of ludo-narrative software, and the colloquy of South American digital art, in which Raquel Renno (Brazil), Jorge Hernandez, Ricardo Vega (Chile) and Vicky Messi (Argentina) discussed the current developments in the media art scene in the South Cone.
Alongside the FILE PRIX LUX, the most outstanding feature of the present edition of the festival is FILE PAI (Paulista Avenida Interactiva), which takes several interactive artworks to the public spaces in the Paulista Avenue. Interactive art offers the possibility of bringing art to the public space in a more efficient and dynamic form than what is usually known as “public art”. As Ricardo Barreto states: “the public environment is not something empty, aseptic and dead, as is the old white cube; on the contrary, it is an environment teeming with life, with multiple interests and multiple behaviors”. Interactive art integrates itself into this environment and is much more apt to relate to a public that is now willing to take an active role. The organizers of the FILE festival have distributed twelve interactive artworks along the Paulista Avenue, at subway stations, inside shopping malls, and even in a bus. The selected artworks include, among others, videogames such as Patrick Smith’s Windosill or the celebrated games of That Game Company, Flower and Flow; VR/Urban’s SMSlingshot, an urban intervention project that allows users to write a message in a custom-made slingshot that incorporates a screen and a keyboard and then send the message to a wall, where it is displayed as a virtual graffiti; Karolina Sobecka’s Sniff, an interactive projection in which a virtual dog reacts to the presence of passersby; the installations of Rejane Cantoni and Leonardo Crescenti Piso and Infinito ao Cubo, which attracted a large number of people, and the sound piece Omnibusonia Paulista by Vanderlei Lucentini, which is played in a bus as it moves along the avenue, interacting with several points in the itinerary and thus generating a new set of sounds in every trip. These works reveal the possibilities of integrating interactive art in the public space, to the point that, as Ricardo Barreto indicates, “the new paradigm of public art will be the interactive city”. The busy Paulista Avenue is certainly a good location for the creation of an emerging, interactive city.

In this 11th edition, the FILE festival has achieved a state of maturity. The FILE PRIX LUX, FILE PAI and an estimated 25,000 visitors to date support its claim of being the largest festival of its kind in Latin America, and a steady event that places Brazil in the map of the international digital art scene. In a tightly interconnected world, each region is a node: there isn’t a center and a periphery anymore, there are no colonies. FILE exemplifies how a region can become a powerful node in this network by promoting the most recent developments in art and technology, avoiding obsolete distinctions between North and South and becoming a point of development for the future stages of our digital culture.
‘Living’ is the result of a six month residency at the V&A by Christian Kerrigan – from January to June 2010 – and it is part of The 200 Year Continuum. The 200 Year Continuum is the title of a project by the same artist that explores the relationship between nature and technology. Interestingly ‘Living’ was exhibited in the same space where it was created: in the digital studio of the V&A. This was a small room with dim light and crowded with rarities. It felt like one was penetrating the secretive and magical space of experimentation of some sort of mad professor.

Once in the space my gaze wandered around a series of oddities. On the right, a table full of raw materials; in the middle of the room, a fish tank with algae floating in high pH waters; on a wall, a real time video projection showing the evolution of the algae; on a different wall, a slide projection showing some drawings; in some shelves, notebooks with notes by the artist; above the sink, chemical products piled up on a shelf; and on each and every window a semi-transparent drawing. No explanations, no titles, nothing. It’s you and the objects. Luckily Christian Kerrigan was always about, meeting visitors and discussing the work. We started looking at the materials on the table. Christian told us those were unprocessed rocks and crystals that he used as the starting point for his drawings. He scanned pieces of amber, moss, fiber glass, volcanic rock or resin and produced a model using 3D software. Then he manipulated that model to create his drawings and printed them on semitransparent paper. He eventually placed them on the windows of the space. This routine allowed him to explore the different stages of a process that makes real matter and virtual space intermingled. It is a practice that explores where the process of creation begins, and what it does to reality. ”The drawings, he tells us, become extensions of the physical material which I started with.” Although we have become accustomed to discuss the hybridity of our nature-culture, the way Christian carefully interwove materialities and virtualities was very evocative. The fact that the drawings were placed on the windows gave yet another layer of complexity to the mixture. The colours of the printings morphed natural light into a hybrid light turning the atmosphere of the room into a creative and ongoing process.

Next I wondered about that mysterious fish tank in the middle of the room where algae lived (and died) in high pH waters: Encased Nature. Apparently the algae reacted to the elevated pH creating a protective coat that eventually killed them. At the bottom of the tank: a graveyard of coated dead algae showed the consequences. I instantly loved the idea. Again an experiment about the hybridity of natural and controlled habitats. I thought it was a particularly dystopic illustration of the environment we inhabit where control works on the conditions of the environment, dictating the way reality unfolds. This is an emerging tendency in our most-discussed societies of control, what has come to be called soft control. And we could take it even further, and see it as a great illustration of today’s climate of fear. In such a habitat, the threat has become virtual and all-pervasive, it has become poisonous in itself, just like high pH. The nightmare of security measures that this artificially produced environment justifies links quite well to the ‘lethal-protective’ coat. What this allegory leaves out, though, is the power of imagination! The capacity of conditions to be turned around, the potential for intervention and deviation from the pre-programmed chain of (re)actions. The idea of projecting a live video recording on the wall was to intensify the experience and highlight the importance of mediation. As Christian argued, we are now more used to experience nature through a lens than to experience its presence. However, the quality of the footage seemed to work against the intentions of the artist and rather than intensifying the experience of that enclosed nature, it tended to obscure it. The particular texture that the webcam gave to the recordings turned that hybrid habitat almost into an abstract movie. On a different corner there was another video projection made out of a series of drawings. Interestingly they had been created using a ‘living technology’ and recorded at a nano-scale. For Living Drawing, the artist had collaborated with Martin Hanczyc from the Department of Physics and Chemistry at the University of Southern Denmark. They had manipulated some protocells that inhabited chemical gradients and reacted to ultraviolet light. When UV light was applied to the fiberglass where these protocells ‘lived’ their motion left traces of colour that were recorded. This technique, although still in its early stages, allowed the artist to ”explore the spontaneous event of drawing by using organic systems”, he told us. Kerrigan’s rather cryptic exhibition proved to be an inspiring and very personal exploration of the blurring between nature and culture in its absolute physicality. Paying particular attention to the materiality of the creative process, from the composition of the materials used, to the chemistry of the drawing process or to the laws of electromagnetism that inform light in its interaction with his work, his methodologies show a passion for unfolding reality in its many scales. His work is that of someone who’s starting to explore rather than someone who’s making an assertion; it is tentative rather than conclusive, it is interesting for its questions rather than its answers. However, even if sometimes vague, it is at points pleasingly dark and sometimes inspiringly intense.
From September 2008 – June 2010, Ellie Harrison undertook a Leverhulme Scholarship on the Master of Fine Art programme at Glasgow School of Art. The thesis published below forms one of the major outcomes of her research during this period. This is part one of four.
The thesis published below forms one of the major outcomes of her research during this period and builds on two earlier essays How Can We Continue Making Art? – which questions whether there is a place for art in a world which is fast approaching environmental catastrophe, and Altermoderism: The Age of Stupid – which uses Nicolas Bourriaud’s Altermodern exhibition at Tate Britain in 2009 as a paradigm for exploring the art world institution’s lack of acknowledgement and action over climate change.
Trajectories: How to Reconcile the Careerist Mentality with Our Impending Doom addresses the ethical implications of continuing to choose the career of artist in the twenty-first century. It is a manifesto of sorts, written from the personal perspective of a young UK-based artist looking to identify worthwhile reasons for continuing down this ‘self-interested’ path, given that the future we are likely to face as a result of climate change, is so different from how we dreamt our careers might pan out whilst growing up under Thatcher and New Labour. It explores how we should aim to evolve our roles as artists, in light of this, and what form a new ‘reconciled practice’ might take.
The graph below shows the projected average global temperature increase over the forthcoming century if we remain on our current trajectory of economic growth and population increase (peaking at 9 billion in 2050), but also incorporate new efficient technologies, a convergent world income and a balanced emphasis on energy sources. This is known as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s ‘scenario A1B’ (IPCC 2001).
The graph is extracted from the official AVOID response to the United Nations Climate Change Summit in Copenhagen in December 2009 published on 26 March 2010. AVOID is a United Kingdom governmental research programme led by the Met Office with the aim of averting dangerous climate change (AVOID 2010).

Looking back, 1979 now emerges as a pivotal year in the recent history of our species. On 6 October this year the US central bank, the Federal Reserve, increased interest rates by 20 points (Fisher 2009, p.33). This act, which on paper appears of little significance, opened the gates to a whole new breed of free-market capitalism which, as a result of reduced regulation, would spread its way all over the globe. It signified the switch between Fordism and post-Fordism as the predominant economic system of production; from the ‘disciplinary societies’ of late modernism characterised by Foucault, to the ‘control societies’ which constitute our present reality (Deleuze 1990). It was the beginning of a carefully choreographed and intricately planned neoliberal project, which would serve the “restoration or reconstitution of naked class power” (Harvey 2007, p.119) to an economic elite; radically transforming the way in which all our lives would operate in its wake. Our attitudes towards work, politics, society; our relationships to one another, even the internal structuring of our own minds, would never be the same again.
It is no coincidence that it was on 4 May 1979 that Margaret Thatcher came to power in the United Kingdom; she was, of course, instrumental in overseeing this ‘revolution’. What is coincidental however is that it was also in 1979, on 11 March to be precise, that my own life began its trajectory. The rapidly changing society into which I was born would not only prove fundamental in shaping the artist I would become, but it would also prove key in determining the ‘mentality’ with which I would come to visualise my future: to plan my career.
‘Thatcher’s children’ as my generation are known, were indoctrinated to believe that the world owed us a living (Blackburn 2009). “Success”, she said, was “a mixture of having a flair for the thing that you are doing; knowing that it is not enough, that you have got to have hard work and a certain sense of purpose”. It was simply a question of making the right career choice. If we aimed for the top, we had just as much chance of getting there as anyone else. All we had to do was look out for number one. The secret, she taught us, was to have a strategy – to “plan your work for today and every day, then work your plan” (M. Thatcher n.d.); to think about what we wanted our lives to be like in the future and then to work flat-out towards that ‘goal’.
In hindsight, it now seems inevitable that my life took the course it did. Entering art school for the first time in 1997 – the year the seminal Sensation exhibition at the Royal Academy of Arts took place – we could see ‘success’ being played out before our very eyes. A group of Young British Artists (YBAs), just one generation older, were now ‘living the dream’. As 18-year-old students, we were now able to visualise the paths we wanted our own lives to take and to see exactly where we aimed to find our fortune. Like most of my art school peers, I was from an “above average social background” – raised in suburbia by a middle class family of teachers. And, as Hans Abbing notes, this added “social capital” gave me the “flair, self-assurance, and… sense of audacity” (Abbing 2002, p.95) which now seemed so essential to commodify and sell myself – to keep going, regardless of failure and rejection, with eyes firmly fixed on the prize.
My career trajectory led me blinkered along a familiar path – a BA (Hons) degree in Fine Art from Nottingham Trent University; a Postgraduate Diploma in Fine Art from Goldsmiths College (where nearly all my YBA role models had been before me). It was as though every incremental step took me ever closer towards my ‘goal’: towards ‘success’. Finally, I won a scholarship to study on the Master of Fine Art (MFA) programme at The Glasgow School of Art; yet another prestigious art school to add to my expanding curriculum vitae. What I hadn’t banked on, however, was that on the very same day I was heading north up the M1 to Glasgow to begin this new stage in my life, the global economic order was fast collapsing around us into its own new distinct epoch, taking with it the belief systems which had been carefully constructed around it over the past 29 years.
On 15 September 2008 the investment bank Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. filed for the biggest bankruptcy in US history with more than $600 billion of debt (Mamudi 2008). Over the course of the next year a slew of bailouts took place all over the world to prevent other banks going under. The neoliberal project had, “in every sense, been discredited” (Fisher 2009, p.78). The ideology on which, knowingly or not, my own life’s trajectory had been modelled was now on the ‘scrapheap’. And, as Mark Fisher suggests, a bleak, empty and relentless state known as ‘capitalist realism’ – in which nobody could believe, but equally nobody could stop – crept in from every corner to fill the void.
Society, it seemed, had reached a hiatus; a ground zero amid a sea of “ideological rubble” (Fisher 2009, p.78). Lots of suggestions emerged about what had gone wrong, lots of questions about where we should go next. From the privilege of my funded MFA place, I was able to enter into my own period of self-reflection about the path I had so blindly been following. Was the vision I upheld of my life in the future essentially a delusion, based on a now defunct model of ‘success’ from the past? Was I suffering from the “self-deceit” (Abbing 2002, p.114) Hans Abbing diagnoses to be prevalent in young artists, coupled with the complete “disavowal” (Fisher 2009, p.13) of the negative side-effects of my complicity in the system of capital? With a sudden and overwhelming urgency it felt essential that I question how I could begin to reconcile my career choice and the entrepreneurial methodology (Abbing 2002, p.96) with which I was pursuing it, with the harsh realities that both science, and now science fiction, are predicting the future actually holds in store…
Films such as The Road (Hillcoat 2009) offer us a very different picture of the forthcoming century. In this barely hospitable, yet eerily recognisable version of our present world there is no Turner Prize, no Frieze magazine to be reviewed in; no canon to become part of. In fact, there is no scope for the non-essential; no room for aesthetics; no space for art at all. Whereas it now appears clear that the trajectory I had planned for my life since art school is constituted by fantasy, the trajectory which befalls the lives of the protagonists of this particular post-apocalyptic vision is in part based on what the current overwhelming scientific evidence points towards.

The United Nations Climate Change Summit which took place in Copenhagen in December 2009 offered what many scientists and campaigners referred to as our ‘last chance’ of averting global catastrophe within the coming century. Prior to the talks the 10:10 Campaign’s ‘call to arms’ statement outlined what sort of trans-governmental worldwide commitment it would be necessary to achieve:
“The best deal currently on the table is that from the EU, which calls for a 30% reduction [in greenhouse gas emissions] by 2020 (compared to 1990 levels). If this deal were to be accepted (which is a very big if, given that Japan argues for 8%, Australia for 5% and America for between 0%-6%) and if the emission cuts were then carried out (which is an even bigger if), this would give us about a 50/50 chance of not hitting the dreaded two degrees. Two degrees is where we trigger runaway climate change [emphasis added]: two leads to three, three to four, four to five, five to six… by which time it’s about over for life on Earth.” (Armstrong 2009b)
Given that Copenhagen was by all accounts a complete failure and that, in fact, not even the least significant of the ‘deals’ presented was agreed upon and signed off, the balance now appears to be swaying decisively towards the latter of these two potential trajectories. We find ourselves “trapped inside a runaway narrative, headed for the worst kind of encounter with reality” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.11). Unless it is fully acknowledged and hastily acted upon in consensus across the globe, climate change “threatens to render all human projects irrelevant” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.6). It appears that it is not just the future of our careers we should be worried about but now, more likely, the fundamental ability of our species to survive on the planet.
The concern of this essay is to uncover exactly how we could have arrived at a situation where these two distinct visions of our future can so wildly diverge – to explore the factors which have allowed our careerism to persist, in light of advice to the contrary. The aim is to illuminate the significance of this ‘now or never’ moment in the history of our species as an opportunity for radical change, and to develop a ‘plan of action’ and a ‘new moral code’ which may help us, as artists, determine what role we can and should play in the reality of the twenty-first century.
To read Part 2 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-24
——-
References:
Armstrong, F., 2009b. What is 10:10? 10:10 Campaign website. Available at: www.1010uk.org/1010/what_is_1010/arms [Accessed April 10, 2010].
Abbing, H., 2002. Why Are Artists Poor?: The Exceptional Economy of the Arts, Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
AVOID, 2010. Will the Copenhagen Accord avoid more than 2°C of global warming? AVOID website. Available at: ensembles-eu.metoffice.com/avoid [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Blackburn, S., 2009. Do we need a new morality for the 21st century? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/nov/02/cambridge-festival-of-ideas.
Deleuze, G., 1990. Society of Control. L’Autre Journal, (1). Available at: www.nadir.org/nadir/archiv/netzkritik/societyofcontrol.html.
Fisher, M., 2009. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative?, Ropley, Hampshire: 0 Books.
Harvey, D., 2007. A Brief History of Neoliberalism, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Hillcoat, J., 2009. The Road, Dimension Films.
IPCC, 2001. Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. GRID-Arendal website. Available at: www.grida.no/publications/other/ipcc%5Fsr/?src=/climate/ipcc/emission [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Kingsnorth, P. & Hine, D., 2009. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. Available at: www.dark-mountain.net/about-2/the-manifesto.
Mamudi, S., 2008. Lehman folds with record $613 billion debt. MarketWatch website. Available at: www.marketwatch.com/story/lehman-folds-with-record-613-billion-debt?siteid=rss [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Thatcher, M., Margaret Thatcher Quotes. About.com website. Available at: womenshistory.about.com/od/quotes/a/m_thatcher.htm [Accessed May 2, 2010].
To read Part 1 of this article visit this link:
http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-14
To read Part 2 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-24
Drawing together the diagnoses which recur throughout the literature of the moment, such as Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative? (Fisher 2009), First as Tragedy, Then as Farce (Zizek 2009a) and The Coming Insurrection (The Invisible Committee 2009) alongside the key suggestions, ideas and solutions from these two manifestos, our ‘plan of action’ begins to materialise.
In the spirit of Pascal’s famous ‘wager’ (Hajek 2008) the plan aims to cover all bases: our active and / or passive responses to the situation. Encouraging the belief that we might still be able to use our roles as artists to incite the radical change to our societal structure (in the art world and globally) needed to avert climate catastrophe, whilst simultaneously developing philosophies for coping with our lives – finding meaning and happiness – should our active response fail.
The seven points below offer a set of guidelines for rethinking our lives, which should act as the starting points for redefining our roles as artists and thinking about how it might be possible to reconcile ‘the careerist mentality’ into which we have been inculcated with the possibility of ‘our impending doom’:
1. stand back and view the world objectively
The main focus of Uncivilisation and our greatest existential priority is to enable ourselves to grasp perspective, not only of the relative insignificance of our individual career plans within the wider world, but more pertinently of the fragility of our entire species within the greater timescales of the universe. Once this mind shift is achieved it becomes easier to distil what is actually important in our lives – happiness and our two unending desires for survival and meaning (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.2). Only then will the remaining six points become easier to implement.
2. offer an external critique of the system
In our new ‘state of mind’ it becomes easier to see the systems in which we have been blindly functioning. From beyond the grasp of the dominant hegemony we can offer a vital ‘external critique’. As Chantal Mouffe suggests, our duty as artists then becomes to challenge the “given symbolic order” and the “existing consensus” (Mouffe 2007) – to revivify the belief that ‘an alternative’ is possible.
3. develop ways or working outside institutions
Our criticisms should extend to the hegemony of the art world, severing our dependence on “legitimisation” (Araeen & Appignanesi 2009, p.500). We must have the courage of conviction in our ideas to find ways of operating outside of art world institutions, especially the marketplace. We require what Mark Fisher describes as a “positive disengagement” – a protest of sorts – which should take the form of “collective activity” (Fisher 2006) to help us break out of our entrepreneurial solitude…
4. escape solipsism; work with and not against peers
As individual artists, working alone, we typify the global trend towards what Adam Curtis calls the “empire of the self” (Curtis 2002), in which anxiety and paranoia are rife. For Araeen, it is this “extreme self-centred individualism of art today” which is “a disturbing symptom of its detachment from our collective humanity” (Araeen 2009, p.679). And so, we must prioritise “collective activity” (Fisher 2006), learning to work in co-operation rather than competition with our friends. Peer support will relieve our paranoia and allow our capacities for empathy to be resuscitated.
5. reject ego and embrace anonymity
Collaboration will enable us to surrender our egos to the collective force; liberating our ideas from their “containment” (Araeen & Appignanesi 2009, p.500). We should “flee visibility” and embrace the new powerful, but faceless forms of resistance being pioneered by The Invisible Committee – encouraging us to turn our “anonymity… to our advantage” (The Invisible Committee 2009, pp.112-3).
6. create free ideas, not objects for sale
Our role as artists should be to focus on the creation of ideas, not the production of objects. The rejection of commodity is an important part of our ‘disengagement’ from the marketplace. Our ideas should not remain private property and should be gifted to the ‘creative commons’ for the ‘public good’ (Blackburn 2009). As Hakim Bey suggests in his book Immediatism, “The more imagination is liberated and shared, the more useful the medium” (Bey 1994, p.36).
7. abandon the trajectory; find motivation in immediacy, not legacy
We must cease to think of our art as a means to an end; a way of getting somewhere – into a book, a magazine, an exhibition etc, as it is pointless to base our motivations on a future which will, very likely, not be able to function as the present does. We should abandon the very notion of a career trajectory and learn to focus our attentions on the reality of now. Without an overpowering emphasis on the future our anxieties will begin to dissolve and we will be able to unearth the absolute state of happiness that exists in the “continuous present” (Crisp 1996, p.54). We must remain alert and not complacent, notice and appreciate the things which are actually good and, as Kurt Vonnegut suggests, continually remind ourselves “if this isn’t nice, I don’t know what is” (Vonnegut 2003).

The ‘plan of action’ forms the basis of a new ideology, which acts as a counterpoint to neoliberalism – advocating our extrication from the system of capital that is the “ultimate cause” (Fisher 2009, p.70) of our environmental crisis. Heavy on words such as ‘abandon’, ‘reject’, ‘stand back’ and ‘disengage’ it calls us to make radical changes. It demands that we overcome our “path dependency” (Abbing 2002, p.96) by shifting our goals away from the fantasy status of the ‘successful’ artist. It all makes our new role seem far less glamorous than our dreams may have envisaged – insisting that we renounce our vanity, abandon our egos, move towards collectivism and anonymity; in short, commit “career suicide” (Sharp 2010, p.52).
But would it really be so beneficial to scrap everything and start again – to admit that our lives up until this point had been “lost causes” (Zizek 2009b)? The emphasis of this essay is on the possibility of reconciliation. Therefore, it aims to explore what positive characteristics of ‘the careerist mentality’ that has driven us to take this individualistic path, we might be able to “salvage” (Williams 2009) and, in doing so, reconfigure to become a positive force that can help us put the plan into action all the more effectively: to take the necessary risks and make a stand for the ‘right’ ethical choice.
Counter to Kant’s belief that the fields of ethical decision making (part of ‘practical reason’) and aesthetic decision making (part of ‘judgement’) be kept separate (Guyer 2004), it appears that the gravity of the situation we face means that these two spheres must begin to coincide. Indeed, in his final book Chaosmosis: An Ethico Aesthetic Paradigm, Felix Guattari argues for the culminating phase of art to be one in which it has an integral relationship with ethics (Guattari 2006). And so, the ethical implications of the ‘plan of action’ become difficult to ignore. Its focus on ‘tugging our attention away’ from our obsession with our own lives to reconnect with our “collective humanity” (Araeen 2009, p.679) is clearly a moral proposition, soliciting a shift from prudent self-interest towards more altruistic behaviour.
The conflict that emerges between the self-interest of ‘the careerist mentality’ and the apparently selfless altruism called for by several points of the ‘plan of action’ has long been the concern of moral philosophy. The recurring question being whether they can ever coexist or be reconciled. In her essay Altruism Versus Self-Interest: Sometimes a False Dichotomy, Neera Kapur Badhwar argues that in certain cases, where individuals display particular characteristics, reconciliation of these traditional polarities is possible (Badhwar 1993).
Badhwar’s essay is based on the analysis of extreme instances of altruism (in this case the behaviour of those who rescued / harboured Jews from the Nazis in the Second World War). What is interesting, and indeed relevant, is the way in which she demonstrates how these definitive acts of altruism are able to coexist with self-interested motivations. Her argument is based on an extension of the categories of self-interested motivation from “feeling virtuous, becoming famous, gaining wealth” (Badhwar 1993, p.101) – equate these to the artist’s extrinsic motivations “money, recognition, fame” (Abbing 2002, p.82) – to include “integrity and self-affirmation” (Badhwar 1993, p.101) – read the artist’s intrinsic motivations of “inner gratification or private satisfaction” (Abbing 2002, p.82). Even though she acknowledges that these altruistic acts were carried out with an “awareness of the risk, in the absence of expectations of material, social, or psychological rewards [and with] the spontaneity of their choice to help” (Badhwar 1993, p.96), she demonstrates that it was precisely because these individuals took the risk that they were able to satisfy the:
“fundamental human interest, the interest in shaping the world in light of one’s own values and affirming one’s identity.” (Badhwar 1993, p.107)
Furthermore, she unearths another peculiarity at the heart of the dichotomy of individualism / collectivism (Triandis 1995) which also becomes key to the possibility of reconciliation. The individuals that she studied were compelled to carry out these altruistic acts because they were able to perceive of themselves as part of the “collective humanity” (which Araeen demands we reconnect with) and so had a more developed capacity for empathy. But, moreover, that it was something inherent in their individualism that gave them the “confidence in the value of their mission, and their own capacities for carrying it out” (Badhwar 1993, p.100): to stand away from the crowd and to stand up for what they believed to be right.
Following Badhwar’s argument, it becomes possible to identify the first of the characteristics of ‘the careerist mentality’ we should aim to salvage. For it is our “flair, self-assurance, and… sense of audacity” (Abbing 2002, p.95) which we shall have to depend on in order to take the risk necessary to make a stand against the mainstream.
What might it look like if we took the risk? What might we end up with if we followed the points in the ‘plan of action’ to the word? It is possible that rather than resulting in a radical new type of art practice, what would actually take place is a shift away from art and into the field of activism.

The Clandestine Insurgent Rebel Clown Army (CIRCA) was formed in 2003, to mark the official state visit of George W Bush to London at the onset of the Iraq war. It aimed to bring together “the ancient practice of clowning and the more recent practice of nonviolent direct action” (CIRCA 2003) – staging a series of strategic protests as part of an ongoing offensive against the evils of ‘war’ and ‘capitalism’. Before the protests at the G8 Summit at Gleneagles in 2005, the Rebel Clown Army embarked on a national recruitment tour of the United Kingdom. Anyone and everyone was invited to join, the only stipulation being that Basic Rebel Clown Training (BRCT) was first undertaken.
Much like the ‘plan of action’, the BRCT process focuses on the individual’s emancipation – on “transformation” and “personal liberation” from the dominant hegemony (CIRCA 2003). This internal reprogramming enables clownbatants, as they are known, to shut off their previous assumptions about hierarchical power structures and to step back and see the world with fresh eyes. From this new perspective the absurdity of a situation in which a line of protesters face-up against a line of police, becomes apparent. Beyond the signifiers of each others’ uniforms, Ranciere’s notion of the omnipresence of equality becomes evident (Ranciere 2007) and play and humour then perhaps do seem the natural human responses. Against the forward planning tactics of a traditional army (and indeed the career-minded artist) CIRCA’s emphasis is on spontaneity: “because the key to insurgency is brilliant improvisation, not perfect blueprints” (CIRCA 2003).
In a uniform which combines camo and greasepaint, clownbatants (as Point 5. suggests) ‘reject ego and embrace anonymity’ and so their inhibitions and embarrassment become irrelevant. So much more becomes possible without the worry of how they are perceived, of how others will judge them. Their individual subjectivities come together as a collective force of resistance. Their creativity exists in a space beyond the system of capital and they are utilising it to actively fight back.
The founders of the Rebel Clown Army were so aware of the importance of creativity in the process of resistance and of the potential for an evolution between art and activism, that they later set up the Laboratory of Insurrectionary Imagination (Lab of ii) as “a space to bring artists and activists together” (Harvie et al. 2005, p.249). The idea was to enable situations where they could work together and transfer skills – cultivating confidence in their “creative capacity as [a] fundamental tool for social change” (Lab of ii 2005). Functioning across the public realm, art world institutions and sites of traditional protest, the Lab of ii manages to successfully infiltrate and subvert different aspects of the hegemony. Most recently at Tate Modern in London, where under the banner of Disobedience Makes History – a two-day workshop on “art-activism” – they deliberately disobeyed the curator’s orders, encouraging participants to aim public attacks relating to the climate crises directly at the museum’s sponsors BP (Jordan 2010, p.35).
To read Part 4 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-44
————
References:
Araeen, R., 2009. Ecoaesthetics: A Manifesto for the Twenty-First Century. Third Text, 23(5), 679-84.
Araeen, R. & Appignanesi, R., 2009. Art: A Vision of the Future. Third Text, 23(5), 499-502.
Badhwar, N.K., 1993. Altruism Versus Self-Interest: Sometimes a False Dichotomy. In Altruism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 90-117.
Bey, H., 1994. Immediatism, Oakland, California: AK Press.
Blackburn, S., 2009. Do we need a new morality for the 21st century? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/nov/02/cambridge-festival-of-ideas.
CIRCA, 2003. About the Army. Clandestine Insurgent Rebel Clown Army website. Available at: www.clownarmy.org/about/about.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Curtis, A., 2002. The Century of the Self, BBC 4.
Crisp, Q., 1996. The Naked Civil Servant, London: Flamingo.
Fisher, M., 2006. Reflexive Impotence. k-punk blog. Available at: k-punk.abstractdynamics.org/archives/007656.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Fisher, M., 2009. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative?, Ropley, Hampshire: 0 Books.
Guattari, F., 2006. Chaosmosis: An Ethico Aesthetic Paradigm. In Participation. London / Cambridge, Mass.: Whitechapel / MIT Press.
Guyer, P., 2004. Immanuel Kant. In E. Craig, ed. Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. London: Routledge.
Hajek, A., 2008. Pascal’s Wager. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Available at: plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2008/entries/pascal-wager [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Harvie, D. et al. eds., 2005. Shut Them Down!, Leeds / New York: Dissent! / Autonomedia.
Jordan, J., 2010. On refusing to pretend to do politics in a museum. Art Monthly, (334), 35.
Kingsnorth, P. & Hine, D., 2009. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. Available at: www.dark-mountain.net/about-2/the-manifesto.
Lab of ii, 2005. About Us. The Laboratory of Insurrectionary Imagination website. Available at: www.labofii.net/about [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Mouffe, C., 2007. Artistic Activism and Agonistic Spaces. Art & Research, 1(2). Available at: www.artandresearch.org.uk/v1n2/mouffe.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Ranciere, J., 2007. Hatred of Democracy, London: Verso.
Sharp, C., 2010. Career Suicide. Art Review, (40), 52-4.
The Invisible Committee, 2009. The Coming Insurrection, Los Angeles / Cambridge, Mass.: Semiotext(e).
Triandis, H., 1995. Individualism and Collectivism, Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press.
Vonnegut, K., 2003. Knowing What’s Nice. In These Times. Available at: www.inthesetimes.com/article/knowing_whats_nice [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Williams, E.C., 2009. Putting the punk back in salvage (where it was not to begin with). Socialism and/or Barbarism blog. Available at: socialismandorbarbarism.blogspot.com/2009/08/putting-punk-back-in-salvage-where-it.html [Accessed May 4, 2010].
Zizek, S., 2009a. First As Tragedy, Then As Farce, London: Verso.
Zizek, S., 2009b. In Defense of Lost Causes, London: Verso.
To read Part 1 of this article visit this link:
http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-14
To read Part 2 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-24
To read Part 3 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-34
Returning to Badhwar’s essay, it is important to note the impulsive and/or compulsive nature of the acts of altruism that she studied – “the spontaneity of their choice to help” (Badhwar 1993, p.96). She observes that:
“Those who acted spontaneously, then, acted with a sense that they had no alternative but to help, and that, under the circumstances, helping was nothing special… [Their actions were] a spontaneous manifestation of “deep-seated dispositions which form one’s central identity” or character.” (Badhwar 1993, p.97)
Of course, impulsion and / or compulsion are not the sorts of qualities which can be taught or learnt. As is suggested, you really have to believe in what you are doing in order to act instinctively – in a way which is not premeditated or over-deterministic. In this sense you cannot simply follow a ‘plan’ to be altruistic as this is in its essence self-defeating. It is, however, possible to develop one’s “character” or “identity”, so that we do begin to notice when things are wrong or unjust and we really do feel compelled to act to change them. This is done through periods of self-reflection but also, more importantly, by acquiring knowledge.

Oliver Ressler uses his research-based practice as a way of not only acquiring knowledge for himself, but of disseminating it to others – via video, installation and public realm contexts. His 2008 film What Would It Mean To Win? in collaboration with Zanny Begg focuses on the counter-globalisation protests at the G8 Summit in Heiligendamm in Germany in 2007. The documentary sections of which probe members of resistance movements to consider just what form society might take if they were to ‘win’ what they have been fighting for. His creation of a bank of knowledge about social alternatives is extended in Alternative Economics, Alternative Societies – a documentary, installation and billboard project which presents ideas and proposals for alternative economic and societal models, which all use the rejection of the system of capital as a starting point (Ressler 2007). The research from this project was published as a book in 2007.
Ressler’s book can be seen as a companion to that of art collective Superflex who in 2006 initiated and published Self-organisation / Counter-economic Strategies. As a “toolbox of ideas”, the book puts forward a series of proposals for self-organised models of social and economic systems that also aim to offer an alternative to capitalism (Bradley et al. 2006). Both books aim to spark debate about the negative effects of our current social order and (as Point 2. suggests) ‘to revivify the belief that ‘an alternative’ is possible’.

What is interesting is that the more we learn about the connections between capitalism and environmental catastrophe – the more self-reflection we undertake – the more ‘responsibility’ we inherit. In his famous essay exploring the moral differences between active and passive action Killing and Starving to Death, James Rachels illuminates this notion:
“There is a curious sense, then, in which moral reflection can transform decent people into indecent ones: for if a person thinks things through and realises that he is, morally speaking [in the wrong]… his continued indifference is more blameworthy than before.” (Rachels 2006, p.73)
And so the self-reflexive artist enters into a spiral. The more knowledge that they research and acquire – the more their conscience is likely to compel them to act. The question then becomes whether art is the most efficient way of effecting real change.
According to Artur Zmijewski, his recent work Democracies – a series of documentary clips depicting different protest movements from around the world – is not art. “Art”, according to Zmijewski, “is too weak to present political demand” (Prince 2009, p.6). Artists have in the past reached a similar conclusion – turning to existing political systems as a more direct means of effecting change. In 1980 Joseph Beuys was instrumental in setting up the Green Party in Germany, running as its candidate for the European Parliament, and, in 1988 Maria Thereza Alves co-founded the Green Party in Brazil. In a recent lecture Alves points out that it becomes the role of the artist to “judge in each situation whether art or politics provides a better solution” (Alves 2010).

As well as proposing theoretical solutions in book form, Superflex have also attempted to find practical solutions to real life problems in Africa. Although falling under the umbrella of their artistic practice, these projects seem more akin to the sort of thing you might expect to see being pioneered by a charity or a development agency. In 1996-7 they worked with engineers to develop the Supergas system, which is capable of turning compostable waste in the form of human / animal dung into “sufficient gas for the cooking and lighting needs of an African family”, thereby allowing them to “achieve self-sufficiency in energy” (Superflex 1997). The realisation of the Supergas system seems to epitomise the marriage between creative thinking and functionality which Araeen calls for by presenting the example of the desalination plant. What is interesting about this project, and indeed Beuys’ and Alves’ involvement in Green politics, is how it shifts our perception of the role of the artist when viewed as an important component part of a wider practice…
It has been suggested that the most successful campaigning bodies, such as Greenpeace, function “through multi-pronged channels of official, semi-official and illicit activity to negotiate specific ends” (Perry 2010, p.8). They operate under several different ‘hats’ – as a registered charity for raising funds (sometimes even stooping so low as to employ the cynical marketing strategies of the ‘charity-mugger’ on the street) and, at once, as a band of renegade activists aboard the Rainbow Warrior causing real disruption to cruel and exploitative practices and playing tactical media games. They demonstrate a “positive disengagement” (Fisher 2006) from the mainstream, coupled with a savvy co-option of the system, where it clearly presents itself as a more productive solution.
It is possible that the new model for a ‘reconciled artistic practice’ could take a similar form, where the artist (or preferably the collective of artists) balances a variety of activities across different fields. Described as “a group of freelance artist-designer-activists committed to social and economic change” (Myers 2007), Superflex do not ‘abandon’ the art world altogether and, in addition to the projects described above, they continue to work on commissions for its major institutions. For example, in 2009 they made a series of short films The Financial Crisis (Session I-V) for the art market’s number one annual trade fair – Frieze. Like the Lab of ii and following in a long lineage of institutional critique, Superflex appear to understand the benefits of being able to use the system by infiltrating it, criticising and beginning to change it from within.
In now seems evident that our success at adapting to this multi-pronged mode of operation, which straddles real political action, activism and art world insider jobs, depends on our flexibility in approaching different tasks – our ability to wear these different ‘hats’ with conviction and our adeptness at switching between roles. So here it becomes possible to identify the second of the characteristics of neoliberalism which we might aim to salvage. For it is “the very hallmarks of management in a post-Fordist, Control society” – our ‘flexibility’, ‘nomadism’ and ‘spontaneity'” (Fisher 2009, p.28) which we must now begin utilise, as well as our ability to cope with and adapt to change. Both very useful skills to have as the temperatures begin to rise and the food stocks begin to run low.
The final characteristic particular to the career-minded artist, which we must aim to reconfigure as central to our new roles in the twenty-first century, is our work-ethic, which results from our comparatively high levels of intrinsic motivation (Abbing 2002, p.82). The acceleration of work rates is something which has developed across the board under neoliberalism to the extent that we are now “bound” to our work in an “anxious embrace”…
“Managers, scientists, lobbyists, researchers, programmers, developers, consultants and engineers, literally never stop working. Even their sex lives serve to augment productivity.” (The Invisible Committee 2009, p.47)
However, it is the artist’s ability and willingness to work twenty-four-seven often in situations completely removed from wage-labour relations, that makes us ‘exceptional’ (Abbing 2002) and offers the potential, even, to act as a paradigm for a general approach to work in a world beyond capital. For it is this position of “radical autonomy” which presents the opportunity for “real education of our socialised senses and human potentials that releases development in all directions” (Ray 2009, p.546). We continue, over the course of our lives, to relentlessly acquire knowledge, self-reflect and develop, adapt, evolve and act – not for money, but because something inside us – something inherent in our ‘character’ – compels us to. If we could only succeed in “freeing” a small fraction of this exceptional motivation “from the self-destructive narcissist ego” (Araeen 2009, p.683) and releasing it in a more selfless and functional direction, it could still be a hugely positive force for change.
Following Aristotle’s classic assertion that moral excellence is found in a person’s rational capacity to choose the mean between extremes (Mautner 2005, p.43), the introduction to the Cambridge reader on Altruism, in which Badhwar’s essay is published, suggests that:
“The most challenging task of a moral theory is to strike a balance between the weight we give to our own interest and the weight we give to those of others. A theory that directs us to give too much to others is as deficient as one that directs us to give too little.” (Paul et al. 1993, p.ix)
And, so it seems that ‘a reconciled practice’ will also, to a certain extent, be about compromise. It will be about attempting to ‘strike a balance’ between the time we invest in each of the various facets of our activity – direct political action or more conventional art world activity – and about how we best use our judgement as to when to focus on one thing over another. If we can achieve this equilibrium in our ‘multi-pronged approach’ to practice, and indeed in our lives in general, then this is perhaps also where we will find our “private satisfaction” (Abbing 2002, p.82): our happiness.
In a recent interview Ranciere reminds us “that there are certain situations where only reality can be taken into account – there is no room for fiction” (Charlesworth 2010, p.75). What this suggests is that perhaps the balance between the ‘selfish’ and ‘selfless’ activity which artists undertake will only really begin to shift when we are directly confronted with the realities of climate change. As James Lovelock suggests it may well take until the point of real global disaster – such as an event on the scale of the Pine Island glacier breaking off into the ocean causing tsunamis and an immediate and permanent sea rise of two metres (Hickman 2010, p.12) – until we are, through absolute necessity, able to totally reconfigure our motivations. Perhaps only when we do come face-to-face with this “worst kind of encounter with reality” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.11) will we, as artists, be able to assume our fully functional role in society.
When Franny Armstrong, founder of the 10:10 Campaign, says “if you’re not fighting climate change or improving the world, then you’re wasting your life” (Armstrong 2009a, p.8), she is essentially reinforcing the ‘wager’ set out in our ‘plan of action’. However the future pans out, do you really want to look back on this pivotal moment in the history of our species and say ‘I did nothing’, ‘I did not make a stand’, or do you want to be able to say the opposite and to retain what should be our most commanding of all human motivations – our integrity.
——-
Abbing, H., 2002. Why Are Artists Poor?: The Exceptional Economy of the Arts, Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
Alves, M.T., 2010. The Friday Event. The Glasgow School of Art. Available at: www.gsaevents.com/fridayevent/alves [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Araeen, R., 2009. Ecoaesthetics: A Manifesto for the Twenty-First Century. Third Text, 23(5), 679-84.
Araeen, R. & Appignanesi, R., 2009. Art: A Vision of the Future. Third Text, 23(5), 499-502.
Armstrong, F., 2009a. Franny Armstrong: If you’re not fighting climate change or improving the world, then you’re wasting your life. The Guardian, 8.
Armstrong, F., 2009b. What is 10:10? 10:10 Campaign website. Available at: www.1010uk.org/1010/what_is_1010/arms [Accessed April 10, 2010].
AVOID, 2010. Will the Copenhagen Accord avoid more than 2C of global warming? AVOID website. Available at: ensembles-eu.metoffice.com/avoid [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Badhwar, N.K., 1993. Altruism Versus Self-Interest: Sometimes a False Dichotomy. In Altruism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 90-117.
Bey, H., 1994. Immediatism, Oakland, California: AK Press.
Blackburn, S., 2009. Do we need a new morality for the 21st century? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/nov/02/cambridge-festival-of-ideas.
Bradley, W. et al. eds., 2006. Self-organisation / Counter-economic Strategies, New York: Sternberg Press.
Brown, W., 2009. What will be the legacy of recession? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/oct/26/culture-cambridge-festival-ideas.
Cameron, D., 2009. The Age of Austerity. The Conservative Party website. Available at: www.conservatives.com/News/Speeches/2009/04/The_age_of_austerity_speech_to_the_
2009_Spring_Forum.aspx [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Charlesworth, J.J., 2010. Jacques Rancière Interview. Art Review, (40), 72-5.
CIRCA, 2003. About the Army. Clandestine Insurgent Rebel Clown Army website. Available at: www.clownarmy.org/about/about.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Crisp, Q., 1996. The Naked Civil Servant, London: Flamingo.
Curtis, A., 2002. The Century of the Self, BBC 4.
Deleuze, G., 1990. Society of Control. L’Autre Journal, (1). Available at: www.nadir.org/nadir/archiv/netzkritik/societyofcontrol.html.
Fisher, M., 2009. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative?, Ropley, Hampshire: 0 Books.
Fisher, M., 2006. Reflexive Impotence. k-punk blog. Available at: k-punk.abstractdynamics.org/archives/007656.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Fowkes, M. & Fowkes, R., 2009. Planetary Forecast: The Roots of Sustainability in the Radical Art of the 1970s. Third Text, 23(5), 669-674.
Guattari, F., 2006. Chaosmosis: An Ethico Aesthetic Paradigm. In Participation. London / Cambridge, Mass.: Whitechapel / MIT Press.
Guyer, P., 2004. Immanuel Kant. In E. Craig, ed. Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. London: Routledge.
Hajek, A., 2008. Pascal’s Wager. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Available at: plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2008/entries/pascal-wager [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Harvey, D., 2007. A Brief History of Neoliberalism, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Harvie, D. et al. eds., 2005. Shut Them Down!, Leeds / New York: Dissent! / Autonomedia.
Hickman, L., 2010. James Lovelock: Fudging data is a sin against science. The Guardian, 10-12.
Hillcoat, J., 2009. The Road, Dimension Films.
IPCC, 2001. Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. GRID-Arendal website. Available at: www.grida.no/publications/other/ipcc%5Fsr/?src=/climate/ipcc/emission [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Jordan, J., 2010. On refusing to pretend to do politics in a museum. Art Monthly, (334), 35.
Kerr, A., 2010. Goldsmiths: But is it Art?, BBC 4.
Kingsnorth, P. & Hine, D., 2009. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. Available at: www.dark-mountain.net/about-2/the-manifesto.
Lab of ii, 2005. About Us. The Laboratory of Insurrectionary Imagination website. Available at: www.labofii.net/about [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Mamudi, S., 2008. Lehman folds with record $613 billion debt. MarketWatch website. Available at: www.marketwatch.com/story/lehman-folds-with-record-613-billion-debt?siteid=rss [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Mautner, T., 2005. Aristotle. In The Penguin Dictionary of Philosophy. London / New York: Penguin, pp. 40-4.
Mouffe, C., 2007. Artistic Activism and Agonistic Spaces. Art & Research, 1(2). Available at: www.artandresearch.org.uk/v1n2/mouffe.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Myers, J., 2007. Superflex. Frieze Magazine, (106). Available at: www.frieze.com/issue/review/superflex [Accessed May 9, 2010].
Paul, E.F., Miller, F.D. & Paul, J. eds., 1993. Altruism, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Perry, C., 2010. Art v the Law. Art Monthly, (333), 5-8.
Priddle, A., 2009. School of Saatchi, BBC 2.
Prince, M., 2009. Art & Politics. Art Monthly, (330), 5-8.
Prince, M., 2010. Remakes. Art Monthly, (335), 9-12.
Rachels, J., 2006. Killing and Starving to Death. In The Legacy of Socrates: Essays in Moral Philosophy. New York: Columbia University Press, pp. 60-82.
Ranciere, J., 2007. Hatred of Democracy, London: Verso.
Ray, G., 2009. Antinomies of Autonomism: On Art, Instrumentality and Radical Struggle. Third Text, 23(5), 537-46.
Ressler, O., 2007. Alternative Economics, Alternative Societies. Oliver Ressler website. Available at: www.ressler.at/alternative_economics [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Sharp, C., 2010. Career Suicide. Art Review, (40), 52-4.
Strawson, P.F., 2008. Social Morality and Individual Ideal. In Freedom and Resentment and Other Essays. London / New York: Routledge, pp. 29-49.
Superflex, 1997. Supergas. Superflex website. Available at: superflex.net/tools/supergas [Accessed May 5, 2010].
Thatcher, J., 2009. Crunch Time. Art Monthly, (332), 5-8.
Thatcher, M., Margaret Thatcher Quotes. About.com website. Available at: womenshistory.about.com/od/quotes/a/m_thatcher.htm [Accessed May 2, 2010].
The Invisible Committee, 2009. The Coming Insurrection, Los Angeles / Cambridge, Mass.: Semiotext(e).
Triandis, H., 1995. Individualism and Collectivism, Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press.
Vonnegut, K., 2003. Knowing What’s Nice. In These Times. Available at: www.inthesetimes.com/article/knowing_whats_nice [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Walker, J., 2002. Left Shift: Radical Art in 1970s Britain, London / New York: I.B. Tauris.
Williams, E.C., 2009. Putting the punk back in salvage (where it was not to begin with). Socialism and/or Barbarism blog. Available at: socialismandorbarbarism.blogspot.com/2009/08/putting-punk-back-in-salvage-where-it.html [Accessed May 4, 2010].
Zizek, S., 2009a. First As Tragedy, Then As Farce, London: Verso.
Zizek, S., 2009b. In Defense of Lost Causes, London: Verso.
Image by Alice Alexandrescu.
This year’s edition of Artivistic brings the fields of art, politics and academia together under the theme of TURN*ON.
Eventually, the investigation about systems of representation – be they semiotic, informational or political – might slip into the one psychoanalysis considers the most elementary and surreptitious of them all: sex. That’s precisely where the Artivistic gathering got into in its fourth edition, which happened in Montreal from 15th to 17th October. To be exact, the theme under which the event tied the fields of art, politics and academia together was TURN*ON – according to its curatorial statement, ‘a fragile bridge extending, over a valley of which the depth you cannot see, to a life centered on pleasure, consciousness, togetherness, understanding, and joy’.
Formulated this way, the concept seems to be a response to the well-worn verses by journalist Eduardo Galeano, in which he states that utopia ’causes us to advance’ only because it ‘lies in the horizon’. With turn on, Artivistic proposes that the forces that move people forward and bring worlds into existence are not far away: in a scenario emptied of grand narratives, the desire (of the self?) should gain preponderance over any masterplans (of the party?).
So, if libido is the why, could we say that art is the how? As crude as it can be, this comparison makes clear that aesthetics, just as politics, mainly operate in the level of methods. They are more concerned with the way desire is manipulated (often repressed or enhanced) than with its ontological truth. Language cannot explain affect, and it shouldn’t pretend to – the best it can do is create spaces for its continuous exercise.

In that sense, what really stood out during the event were the workshops. I wouldn’t go as far as to agree with the idea that such activities are a distinct genre within the contemporary art circuit. Workshops indeed revitalize the exhibition space – however, they do so not by occupying it with new forms, but by proposing new forms of occupying it. In Artivistic, these interfaces ranged from diy electronics and card game design to pornographic filmmaking and even a kind of un-workshop on workshops! Among those, there was a remarkable amount of projects concerning the performative of one’s own identity.
In fact, the workshops punctuated Artivistic in a not much different way than the everyday activities of cooking and eating in group (or translating things to French or English – it was a true bilingual event). One thing led to another, keeping the gathering together in spite of the healthy excess of participant autonomy allowed by the organization crew. Of course, the concentration of (almost) all activities in the same place helped building this integration. This was a strategic option, very coherent with the intimate theme of this edition; the former Artivistic, about un.occupied spaces, had been distributed in different venues throughout Montreal.
The integration of the participants was so successful it had the minor side effect of creating an almost self-centred environment. Even though some activities would have been very interesting for people outside regular art-audience, it was hard to see among the public someone besides those that were immersed 24/7 in the event. For instance, it was a pity that the orgasmic birth workshop, which introduced alternative ways of pregnancy and labour, had no pregnant women participating.
This paradoxical isolation was imploded in the last night of the event – most ironically, not by the long-waited closing performance Resist Me Release Me: Turn On Act On, which artist Shu Lea Cheang had been organising with the participants throughout the gathering, but because of its impending cancellation. It seems that the managers of the venue where Artivistic was happening had not understood that the event would contain nudity and explicit sexual acts, and took account of this just in time of the final soiree. Since they had no public license to host this kind of activity, they said it was impossible to have the performance there: either it had to be suspended or transferred elsewhere.

The organizers explained this incident to the participants and called for a collective decision. That immediately ignited a very intense discussion, where it became clear that what was at hand was not mere censorship, but a very subtle negotiation of the different spheres that Artivistic addressed. The autonomy people were requesting was not sexual, but artistic – ‘we do not intend to do an orgy, but performances’, as someone said. Hence, it was not a simple conflict between raw libidinal impulse and oppressive morality; it concerned more complex, structured systems – i.e. art and Montreal society, both already contradictory in themselves.
I dare say that some solutions proposed in this debate – for example, live-streaming the works from another place or ‘censoring’ performances in real-time – were way more interesting than any prescripted show might have been. These proposals were the sign of an art that was alive and kicking, ready to respond emergencies and fight back, instead of just claiming its secular, innocuous freedom (a freedom that critic Julian Stallabrass very cunningly regards as supplementary to that of the market).
The result was that in a couple hours the whole programme for the night was adapted and moved to a venue nearby, in a beautifully orchestrated, self-organized effort. Unfortunately, due to limitations of structure and space, not everything that had been planned before could be presented. Nevertheless, the accident had allowed the necessary hands-on without which a turn on just fades away, and something bigger was engendered in the process – I’d say revolutionary freedom, a kind of autonomy that, as the old leftist maxima states, must always be conquered.
Links:
“Postmodernism is dead” declares Nicolas Bourriaud in the opening line of his manifesto for our new global cultural era – the ‘altermodern’. As a preface to the latest Tate Triennial exhibition of the same name, the French curator and theorist sets about defining what he sees as the parameters of our contemporary society and offering paradigms for artistic approaches to navigating and negotiating them.
This essay aims to identify what the birth of this new era tells us about our culture’s relationship to time. It will explore how we choose to define the periods in which we live and how our relationships with the past, present and future seem to constantly evolve. As a central focus, it brings together two examples of cultural events from 2009 which have both, in semi-revolutionary ways, attempted to define our current age. The Altermodern exhibition and its accompanying Manifesto (Bourriaud 2009b) launched at the Tate Britain on 4th February provides the first, and the second is provided by The Age of Stupid – a feature film and accompanying environmental campaign launched in UK cinemas on 20th March.
Set in the year 2055, The Age of Stupid focuses on a man living alone in a world which has all but been destroyed by climate change. In an attempt to understand exactly how such a tragedy could have befallen his species and the society and culture which they created over the course of several millennia, he begins to review a series of ‘archive’ documentary clips from 2008. His aim is to discover how his ancestors – the one generation of people who had the power to prevent the impending disaster – could have demonstrated such disregard or contempt for the future.
By focusing on two central texts – Bourriaud’s Altermodern Manifesto and a faux encyclopedia entry from the future which retrospectively defines ‘the Age of Stupid’ released as promotional material for the film (Appendix One) – the essay aims to explore the disturbing continuities between these two perceptions of our current times and the drastic consequences these could have, if left unchecked, for the future of humanity and indeed the future of art.
Defining the eras in which we live through phrases such as ‘modernity’, ‘postmodernity’ and now ‘altermodernity’, allows us a tangible way of assessing our place within the far less tangible, metaphysical concept of ‘time’. In fact, it could be argued that ‘history’ itself has been invented, documented and perpetuated as a way of helping human beings to get a purchase on their own existence and to define how they should approach their relationships to their past, present and future.
In this sense, the ‘modern’ era could be characterised as encouraging a forward-thinking outlook. According to Jurgen Habermas, its last living prophet:
“modernity expresses the conviction that the future has already begun: it is the epoch that lives for the future, that opens itself up to the novelty of the future.” (Habermas 2004, p.5)
At the very start of the Enlightenment in the mid-17th century the French philosopher and scientist Blaise Pascal portrayed an inspiring vision of humanity as progressing throughout time, by likening the development of human innovation over the course of history to the learning of one immortal man (Stangroom 2005). Scientific knowledge could be advanced by new generations building on what had been discovered before them. The humanist belief held by philosophers, and others alike, was that ‘man’ was the centre of everything; that man could control nature and could master his own destiny.
This optimistic idea was so new, compelling and widespread that it assisted in propelling the project of modernity as it ploughed relentlessly through the centuries – the French Revolution, American Independence, the Industrial Revolution, the rapid expansion of capitalism and the birth of bourgeois society. It was rational, logical and, as though guided by an ‘invisible hand’, was the way things were meant to happen. At the start of the 19th century, Hegel was still convinced; we were getting somewhere, history was progressing through a dialectical process towards its logical conclusion – towards perfection. People’s relationship with the future was one of hope; as though things could only get better.
Reason, however, appeared to have its downsides and catastrophic human developments of the 20th century, such as the holocaust and the atomic bomb, led to a loss of faith in the humanist approach. Towards the end of the twentieth century, a general consensus developed among cultural theorists (Habermas aside) that modernity was no longer working. Its ‘metanarratives’ had resulted in authoritarianism, totalitarianism and terror; minorities had been victimised or marginalised; the ‘differends’ of society smoothed over (Malpas 2003). And so, ‘postmodernism’ was born and with it began a systematic deconstruction and disownment of what were now considered the somewhat embarrassing ideals of its predecessor. The reaction was severe; inciting a series of symbolic revenge killings: the ‘death of man’ (Foucault 1994), the ‘end of humanism’ the ‘end of history’ (Fukuyama 1992), the ‘death of painting’ and even the ‘end of art’ (Danto 1998). It was as though catharsis could be gained by the ridding of a past which had failed to live up to promise. In the wake of all this destruction, however, came a deep uncertainty of what would come to fill the gaps.
Just as modernism had done before, postmodernism “alluded to something that had not let itself be made present” (Lyotard 1993, p.13), only this time that ‘something’ felt more menacing. The decentralisation of ‘man’ from the story of history may have unearthed a hidden fear of the future. If we were no longer in control of nature or masters of our own destinies, then we could be less optimistic about what the future had in store and far more uncertain of the potential consequences of 350 years of rampant ‘progress’ that we may have to face.
The rejection of the past coupled with this uncertainty about the future gave the postmodern era a feeling of limbo within which time itself was “cancelled” (Jameson 1998, p.xii). In his critique of the historical momentum of the 1980s, Jan Verwoert refers to the “suspension of historical continuity” which resulted from the overbearing stalemate politics of the Cold War. Only when it finally ended could “history spring to life again” (Verwoert 2007) and begin accelerating away from postmodernism and into the new cultural era.
In terms of assessing the birth of altermodernism, this specific point in history appears pivotal. Firstly, the end of the Cold War meant that:
“the rigid bipolar order that had held history in a deadlock dissolved to release a multitude of subjects with visa to travel across formerly closed borders and unheard histories to tell.” (Verwoert 2007)
And, according to CERN (the European Organisation for Nuclear Research), not only did 1990 see the reunification of Germany, but it also witnessed “a revolution that changed the way we live today” – the birth of the World Wide Web (info.cern.ch). These were the nascent beginnings of an a priori globalised society in which, as Bourriaud describes, “increased communication, travel and migration affect the way we live.”
What is most interesting about this point in time, however, are discoveries referred to in the definition of ‘the Age of Stupid’. As argued in the final paragraph of the encyclopædic entry, 1988 also marked the point at which humanity had amassed sufficient scientific evidence to “become aware of the likely consequences of continuing to increase greenhouse gas emissions”. The uncertainty about the future which had characterised the postmodern era was suddenly replaced by a real-life certainty, but it was not one which we were prepared to face up to.
Rather than taking heed of these warnings when we still had plenty of time – slowing down and reassessing our lives; curbing our consumption and production – throughout the 1990s we actually did the opposite. As Verwoert suggests, the pace quickened – the population grew, we travelled more, consumed more and wanted more. Life in the new globalised world was more chaotic and less controllable. Before we knew it twenty years had passed and we had still failed to accept the facts and to act in order to avert the course of history and “prevent the deaths of hundreds of millions of people” (Armstrong 2009a) in the future.
As we stand, in the present day, we are still firmly on course to see the devastation envisaged in the film The Age of Stupid, become a reality. At the end of March 2009, a conference on ‘sustainable populations’ organised by the Optimum Population Trust took place in London. In its coverage of the issues raised, The Observer described the future which the overwhelming scientific evidence claims awaits us:
“by then (2050) life on the planet will already have become dangerously unpleasant. Temperature rises will have started to have devastating impacts on farmland, water supplies and sea levels. Humans – increasing both in numbers and dependence on food from devastated landscapes – will then come under increased pressure. The end result will be apocalyptic, said Lovelock. By the end of the century, the world’s population will suffer calamitous declines until numbers are reduced to around 1 billion or less. “By 2100, pestilence, war and famine will have dealt with the majority of humans,” he said.” (McKie 2009, p.9)
As depressing as it sounds, the message of the film The Age of Stupid is one of hope – that it is not quite too late. According to their predictions, we still have until 2015 to make the changes required in order to prevent us reaching the tipping point which would trigger ‘runaway’, irreversible climate change. These corrective measures are huge, they are global and they need to start being implemented now.
What is most terrifying about Bourriaud’s Manifesto therefore, is its absolute lack of acknowledgement of the real and dangerous future that we face. Rather than speaking out and demanding the dramatic changes that are necessary, it seems to support a continuation of the status quo of the last twenty years. In his video interview on the Tate website, Bourriaud describes the purpose of the altermodern as the “cultural answer to alterglobalisation” (Bourriaud 2009a). However, rather than questioning the carbon-heavy lifestyles that a globalised world promotes he seems to complicitly buy into them, insisting that “our daily lives consist of journeys in a chaotic and teeming universe”.
In the film The Age of Stupid ‘archive’ footage from 2007 presents the Indian entrepreneur Jeh Wadia as the ignorant villain, as he goes about launching India’s first low-cost airline GoAir. His mission is to get India’s 1 billion plus population airborne. Although an extreme example, Bourriaud’s fervent support of internationalism is not dissimilar to Wadia’s in its level of denial. He continues to encourage the movement of artists and curators around the world (clocking up substantial air miles bringing in speakers for his four Altermodern ‘prologue’ conference events alone).
What makes Bourriaud’s case worse however is his apparent betrayal of the purpose of cultural theory in providing counter-hegemonic ideas and alternatives. The theorists of postmodernism overthrew the project of modernity in an attempt to save humanity from further nuclear extermination or genocide which had proved the ultimate conclusions of reason. Their cultural vision for postmodernism was also to provide an alternative or an antidote to the new ways of life dictated by post-industrial society. Not only does the vision for altermodernism fail to provide an alternative to the devastating path to future down which ‘alterglobalisation’ is dragging us, but it also remarkably promotes the idea that we turn our backs on and ignore this future altogether. One of the paradigms for artistic approaches Bourriaud suggests is that artists look back in time rather than forward claiming that “history is the last uncharted continent” and therefore should be the focus of artistic attention.
Jeh Wadia’s excuse is easy to fathom – he is in it for the money, but Bourriaud’s seems harder to discern. He is driven by a burgeoning ego no doubt, but alongside this there seems to be a wider problem. A nostalgia for the good times and a refusal to give up privileges and luxuries appear to be endemic in the art world’s attitude to facing up to the realities of climate change. At Frieze Art Fair last year, cultural theorist Judith Williamson delivered a keynote lecture on what she called ‘the Culture of Denial‘. She outlined a view of the world not dissimilar to the definition of ‘the Age of Stupid’ (and indeed altermodernism) that this essay has been discussing, in which a denial of the impending future or perhaps an impossibility to comprehend its severity, prevents us from acting.
What was most interesting about her introduction, however, was the discussion of her deliberate decision not to mention ‘climate change’ in the material promoting the talk, but instead to refer to it more ambiguously as an exploration of “the skewed relationship between what we know and what we do” (Williamson 2008). She identifies the persistent ‘stigma’ attached to directly addressing this issue, describing the common perception of it being “annoying, gauche or over the top to bang on about climate change”. So she was forced to revert to covert tactics in order to sneak this pressing discussion onto the Frieze agenda – in the hope of inciting the beginning of a widespread realisation that the art world is walking the path towards its own destruction.
There seems no doubt that Bourriaud’s altermodernism is the cultural side-kick of ‘the Age of Stupid’. To write a Manifesto of our times at such a crucial make-or-break point in the history of humanity and not to mention the possibility of an impending disaster or offer any suggestions as to what artists and society in general can do to combat it, is not just denial – it’s stupidity.
The truth is that all the ‘ends’ and ‘deaths’ that postmodernism faced on hypothetical grounds are now fast approaching our generation as a reality. Foucault’s famous conclusion to the seminal postmodern text ‘The Order of Things’, now seems all the more poignant:
“If those arrangements were to disappear as they appeared, if some event of which we can at the moment do no more than sense the possibility… were to cause them to crumble… then one can certainly wager that man would be erased, like a face drawn in sand at the edge of the sea.” (Foucault 1994, p.422)
The main character in the The Age of Stupid is an archivist. In 2055, he sits alone in an expansive tower known as the ‘the World Archive’, which houses all the works of art, books, images, film etc ever produced by the human race. It is at this point that you realise this preservation is futile. Art is, after all, a human creation – it relies on humanity to provide its meaning. Without this crucial element it may as well cease to exist. Should it not, therefore, be art and culture that lead the way for the rest of society? To be the first to snap out of this ‘culture of denial’; to overcome the ‘stigma’; to do everything in its power to save humanity, and itself in the process.
Future Encyclopedia Entry: The Age of Stupid
The Age of Stupid constitutes the period between the ascent of the internal combustion engine in the late-19th century and the crossing of the 2c threshold to runaway global warming in the mid-21st.
This era was characterised by near-total dependence on energy from fossil hydrocarbons, together with exponentially increasing consumption based on the destruction of finite natural resources.
The institutionalised lack of foresight regarding future human welfare that held sway during this time earned the period its popular name, but scientists know this era as the Anthropocene: the period during which human activities came to be the dominant influence on the Earth’s biosphere and climate. The end of the Age of Stupid is marked by the sixth major mass extinction event, with the fifth being the K-T asteroid impact which ended the Age of the Dinosaurs. The abrupt loss of the majority of plant and animal species between 2020 and 2090 was followed by a crash in the human population, to just 7.4% of the 9 billion people alive at its peak.
Some historians argue that the Age of Stupid more properly refers to the narrower period between 1988 and 2015, during which humanity had become aware of the likely consequences of continuing to increase greenhouse gas emissions and still had time to avert catastrophe, but largely chose to ignore the warnings.
This article can also be found at:
Original text at Ellie Harrison’s web site – http://www.ellieharrison.com/index.php?pagecolor=7&pageId=press-summerreading
Edited version at The Nottingham Visual Arts web site – http://www.nottinghamvisualarts.net/writing/jun-09/altermodernism-age-stupid