



Part of Furtherfield Open Spots programme.
being being read being reading being read and reading beings
A twisted archive of the mind, language and technology project: Torque – presented via the lens of its current research: *reading*
Try:
Animated speed-reading software.
‘Code Karaoke’ with live-coding artist Yaxu (11th April).
The new ‘Outlier’ app that sonifies reading using algorithmic sentiment analysis, by Wesley Goatley.
Record a super-slo-mo reading and broadcast it across the park.
Pick-up for free and read:
A newspaper on privacy, surveillance and ‘being read’ in the age of big data and online lives.
Receipt artworks by James Wilkes (Wellcome Collection resident artist).
Or just soak up the rampant textuality of:
Live readings from performance artist Tim Etchells and remote performance by Yaxu (11th April) and artist writer Claire Potter, with virtual appearance by Mez Breeze (18th April).
Sound work entitled ‘Mind Twist’ by Dennis Oppenheim on the exterior of the gallery.
Experimental text works from Anna Barham, Tim Etchells and Imogen Stidworthy.
A new text-based cgi video artwork by Chris Boyd.
Sound work of Karl Heinz Jeron’s opera singing robot Sim Gishel.
Video and text works by Torque producers Nathan Jones and Sam Skinner, including commissioned score by musician Oliver Coates.
The launch of a new book entitled ‘The Act of Reading’, comprising new essays and artworks on the subject, including a new text by reader/author extraordinaire Katherine Hayles, entitled, ‘Nonconscious Cognition and Jess Stoner’s I have Blinded Myself Writing This’ and further contributions from: Garrett Stewart, Soenke Zehle, Erica Scourti, Stephen Fortune, Esther Leslie, Nina Power, Charles Bernstein, Claire Potter, James Wilkes, Eleanor Rees, Anna Barham and others.
What does it all mean?… well come on down, bury your head in the book, pdf, audio, sentiment analysed and sonified, or speed reading versions… and find out!
It may all sound a bit strange, but that’s the world we live in now and how we read today! 😉
Live Reading #1 – Tim Etchells and Yaxu, 3pm, Saturday 11th April. (Free)
Live Reading #2 – Claire Potter and Mez Breeze, 3pm Saturday 18th April. (Free)
(Yaxu and Mez Breeze remote/online performance)
Furtherfield Gallery
McKenzie Pavilion, Finsbury Park
London N4 2NQ
T: +44 (0)20 8802 2827
E: info@furtherfield.org
Furtherfield Gallery is supported by Haringey Council and Arts Council England
Torque is a transdisciplinary project by artists Nathan Jones and Sam Skinner, that explores the twisting of mind, language and technology, through publications, symposia, performance, workshops and installation.
At Furtherfield, each of the three gallery spaces will be transformed into a three-dimensional manifestation and archive of the three publications and public research Torque have produced to date. The gallery will become a hypermedia reading room and examination of both reading and the Torque project itself, giving members of the public a deep and varying view of the pressures impacting our relationship to language, and in particular – reading – as it occurs today.
Room 1 will be dedicated to the Torque #1 publication.
Room 2 will present The Opticon newspaper – produced over two days at Tate Liverpool, focusing on themes of privacy and surveillance, in particular machinic reading, big data and the phenomenology of ‘being read’. Comprising contributions from over 100 gallery visitors, poets, artist Erica Scourti and professor of social media Christian Fuchs.
Room 3 will launch a new transdisciplinary digital and print publication exploring reading today, and the impact of technology upon it, following The Act of Reading symposium at FACT, Liverpool and a performance event at Static Gallery. This room will also feature new video works by Jones and Skinner synthesizing and investigating reading-related pathologies and pedagogical systems.
Jones and Skinner will be in the gallery throughout the exhibition presenting and speaking about their work, and developing new works informed by their experiences and conversations.
Torque project tumblr here
Free download of Torque #1 book and printed edition available here.
Digital version of The Opticon newspaper here
Torque is supported by an Arts Council England Grants for the Arts, Tate Liverpool and FACT.
“Human Readable Messages_[Mezangelle 2003-2011]” is a book published by Traumawien containing almost a decade of Mez Breeze’s “Mezangelle” writings. Mezangelle is hand-crafted text with the aesthetics of computer code or protocols. What marks Mezangelle out is how deep its use of those aesthetics go and how effectively it uses them.
Computer programming languages have their own logic, and it is not captured by holding down the shift key and bashing the top line of the keyboard to add what looks like a cartoon character swearing or random line noise to text. It’s true that programming languages can look incomprehensible to the uninitiated. This Perl code:
y/A-Za-z/a-zA-Z/
will swap the case of lower and upper case English letters. But the conciseness of this notation hides a clear informational structure only in the same way that mathematical or musical notation do.
Likewise the markup language HTML that this article is written in:
<p>looks “<em>gnarly</em>”</p>
and a computer protocol such as email transmission via SMTP:
220 smtp.example.net ESMTP Postfix EHLO someone.example.org 250-smtp.example.net Hello someone.example.org [192.0.2.201] 250-SIZE 14680064 250-PIPELINING
is incomprehensible without reference to detailed technical documents. But all express clear semantic structures and instructions to the computer systems that have been programmed to understand them.
These notations have been created to express data and concepts in structured ways that are possible for computers to work with. They may look typographically arbitrary but they do involve aesthetic choices and historical precedent. They have associations, they have resonances.
We do not usually see the codes involved in our use of computers and the Internet when they function effectively, but they are always there. When they successfully empower or coerce us they become invisible. In the age of social networking, ecommerce, and mobile devices they are pervasive.
What, then, are we to make of Mezangelle? Human written, but intentionally structured in the style of computer code, it recreates the expressive, communicative underpinnings of software syntax rather than simply its surface aesthetics.
To read Mezangelle is to parse it. Parsing in computer software is the process whereby a computer breaks down textual input into smaller and smaller but more and more closely related chunks of meaningful information. Parsing Mezangelle requires the human reader to group and regroup word fragments into shifting webs of meaning. It takes time to do this, and different textual characters and formatting take different amounts of time, adding rhythm and pacing to the meaning of the text.
The history of literary typography, of mathematical notation, and of programming language design has lent a rich range of often contradictory precedents both to software and to writing that draws on its aesthetics. A dot can mean a fraction or a part of an object. A square bracket can instruct a computer to construct a list in memory, to access an element of an array, or to send a message to an object. As can a colon or two, or various arrows. Hashes can indicate comments, identifier numbers, or other entities.
The raw typographic aesthetics of character glyphs spring from their visual form (smooth, straight, long, slanted), size, and relative visual complexity. A full stop or a vertical bar is simpler than a hash or an ampersand. These factors affect how long it takes to perceive them and the effect they have on the eye as we look across them. The glyph-level and code level visual arrangement of code affects the pacing of our reading, building pace and meter. The more semantic aesthetics of the way these glyphs are used to structure code build on and interact with this. And it affects the relations and meanings that we build as we read the text.
Like computer program code, Mezangelle structures its content in order to communicate to and invoke the resources of its parser. Crucially this is a human parser rather than a software one so those resources are aesthetic and cultural. As well as pacing the experience of the text as spoken performance would, these destabilize and expand its meaning as the attention of critical writing does.
The intrusion of quoted plain English text such as an Alan Sondheim piece or an email from a mailing list that have been the inspiration for an answering piece of Mezangelle serves both to show how different Mezangelle is from written English and how effectively it can be part of a conversation.
Here is a line of Mezangelle (broken by the format of this page):
.. my.time: my time: it _c(wh)or(e)por(ous+h)ate_ _experience____he(u)rtz___.] [end]
Read as code, the underscores mean private data and variables, the square brackets mean list construction, message passing, references to individual elements of data structures. The full stops are decimal fractions or references to data or functions that are parts of larger objects. They do not decorate (in the sense of being frivolous), they evoke.
They also semantically structure and pace, allowing reading and re-reading as poetry. Underscores creates distance, brackets group and shift the meaning of words and fragments of words. Addition signs and colons combine concepts and further disrupt the parsing of language as a flat, linear, structure.
Mezangelle is distinct from much historical code poetry in its structural and semantic mastery of the aesthetics of code. It is distinct from concrete poetry in its semantic, destabilizing, temporal rather than merely structural use of typography.
Mezangelle is net art, it is produced and encountered in the environment of the Internet. Mezangelle lives in blogs and on mailing lists. But it does not die on the printed page, far from it. “Human Readable Messages” is typeset in Donald Knuth’s Computer Modern font, a beautifully spindly artifact of the early days of computer typesetting, with the occasional intrusion of Courier-style monospaced teletype/typewriter fonts. This gives the printed text a digital, online feel retaining a genetic link to the environment it originated in.
Mezangelle surfaces and integrates the hidden aesthetics of computer mediated human activity, setting computing and human language in tension and synthesizing them. It expands the expressive possibilities of text and is a form of realism about the conditions in which human reading is currently flourishing. “Human Readable Messages” provides an ideal opportunity to familiarize ourselves with Mezangelle in the depth that it deserves and rewards.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
This article is co-published by Furtherfield and The Hyperliterature Exchange.
Millie Niss, the writer and new media artist, died of swine flu with complications at 5 a.m. on 29th November 2009. Her mother and longtime collaborator, Martha Deed, was with her then. She had been in hospital for four weeks, mostly in intensive care, after picking up the virus, which quickly became serious in her case, probably because she already had respiratory difficulties due to a rare condition known as Behcet’s Disease. She was 36 years old.
The news would have been sad to hear about anyone, but it was especially sad in Millie’s case because she was one of the people in the new media community with whom I felt particularly close. I met her at the trAce “Incubation” conference in Nottingham in 2004. When I first arrived at the conference, I was directed to the part of the room where Michael Szpakowski was because he and I had already struck up an e-mail friendship, and he’d left a message for me at the door. I found him talking to Millie. Michael was only there for that first evening because he had to go and see his father, but Millie was there for the rest of the conference, and I sat next to her at many events. She was dark-haired, overweight and funny: very easy to talk to. Later in the conference, she gave a presentation about how to attach behaviours to objects in Flash, which I attended along with Jim Andrews and others. She kept saying beforehand that she was feeling pretty nervous about it, but she seemed very natural and nerveless when it came to the event. In the beginning, she asked for suggestions from the audience – I think for an initial idea on which to base her Flash piece – and at first, nobody said anything. She suddenly became acerbic – “Oh come on – don’t make me pick on someone like you were a bunch of school kids!” Immediately you could see her as a teacher and imagine how she would have controlled a classroom. I suggested spiders, which set the ball rolling, and from that point onwards, everything went very rapidly. She quickly and expertly demonstrated how to set up a drawing of a spider as a symbol, and attach a behaviour to it so that when the mouse pointed to it, a sound file played. Another thing I remember was that she was very critical of certain aspects of Flash – how you had to import things into your library and then drag them from the library to the stage before you could do anything with them. You could feel her personality’s force, her opinions’ sharpness, and her sense of humour and fun.
From that time onwards, she and I regularly exchanged e-mails. She knew that I worked in the National Health Service, and because she was very much in the mill of health care herself, we had some lengthy correspondence about how the UK system worked, compared with how things worked in the USA. She also sent me two glass unicorns through the post – occasionally, she would run little competitions on her “Sporkworld” website and offer glass unicorns to participants as prizes. The first of these unicorns went to my daughter Rachel, and the second is still sitting on my study window-ledge in a white cardboard box. He used to stand out on his own four feet, but unfortunately, he had an accident with the curtain, and one of his legs got knocked off. I stuck it back on with Superglue, but it fell off again. Millie knew all about this, and I sent her a photograph of the unicorn on my window-ledge – I think I even sent her a second photograph, showing how he looked after his accident and temporary repair. She was always very interested in Rachel and liked to hear my stories about her. Perhaps they reminded her of her childhood, or perhaps she just liked kids.
One thing which came across from Millie’s correspondence, as well as from her work and her occasional online commentaries, was her sense of perspective on new media art. She was grateful to it because it provided an outlet for her creativity which she had never managed to find through traditional print; but all the same, she remained aware that it was a small and specialised field and that a good deal of new media work might seem incomprehensible to “ordinary” people. Her comments about other new media artists reflected this grounded attitude. She preferred work which didn’t reach for the hi-tech solution that a lo-tech one would do – work, in other words, which didn’t employ technology for its own sake, and where the form was dictated by content rather than the other way round. Likewise, she wasn’t particularly bothered whether her output complied with the dictates of new media theory – whether it was interactive, non-linear, coded or networked. The pieces on her website exhibit a cheerful mixture of genres and media: Flash, video, poetry, prose, photography, sound files and plain old HTML rub shoulders in much the same way that political commentary, literary criticism, observations of places and people, food appreciation, nature notes, raucous humour and occasional obscenity rub shoulders in her blog. The groundedness of her art, and her sense of responsibility towards her audience, is demonstrated by the way in which she habitually presented videos on her site in different sizes and resolutions – for example, “Warhol’s Campbell’s Brodo” is available 8.85mb, 6.23 MB and 2.43 MB – so that people with slower connections could sacrifice a bit of quality to save a long wait if they so desired. Similarly, her introduction to “Warhol’s Campbell’s Brodo” explains that “brodo is the Italian word for soup and the restaurant’s name”. Without talking down to her audience or limiting what she wanted to say, she was always at pains to be as clear and user-friendly as she could – and this insistence on clarity and user-friendliness, her desire to reach out to an audience of “ordinary” people whenever possible, was one of the things which made her voice such a distinctive and refreshing one in the new media world.
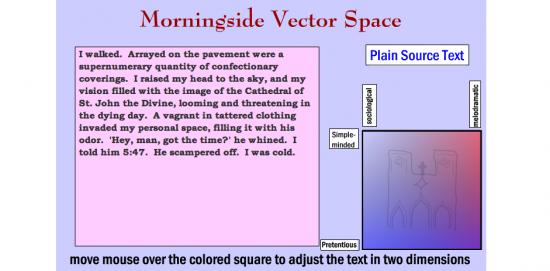
However, this is not to say that she was any Luddite or uninterested in the theory of any description. One of her best-known pieces of work – a collection of six pieces – is the Oulipoems, reproduced in Volume One of the Electronic Literature Collection in 2006. As Millie explains in her introduction, “Oulipoems is a series of six interactive poetry Flash works… loosely based on the Oulipo movement in French literature, which focused on texts based on constraints… and also on mixtures of literature and mathematics.” One of the Oulipoems is “Morningside Vector Space”, which rewrites a description of a simple incident in various ways, depending on how we move the mouse cursor over a coloured square. The source text reads:
Yesterday, I was walking on Amsterdam Avenue. There were cracks in the sidewalk. I looked up and saw the tall and unfinished Cathedral of St. John the Divine. A man approached me. ‘Excuse me, do you have the time,’ he said. I told him at 5:47. He walked (sic) away. It was windy. The coloured square is marked to indicate the inflexions this text will be given if we hover over different areas – from “Simple-minded” to “Pretentious” on the x-axis and from “Sociological” to “Melodramatic” on the y-axis. If we point to the “Simple-minded” corner, we get this:
I walked. On the sidewalk. By the big church. There was a man. He wanted the time. I gave him my watch. He left. I was cold.
The intersection of “Pretentious” with “Melodramatic” yields this:
A vagrant in tattered clothing invaded my personal space, filling it with his odor. ‘Hey, man, got the time?’ he whined…
The intersection of “Pretentious” with “Sociological” produces:
The sidewalk, unmaintained by the municipality, contained evidence of substance abuse…
– and so forth.
A number of observations come to mind about this piece. First of all, although it isn’t tremendously technically sophisticated, it does reveal a very competent grasp of Flash and object-oriented coding. This grasp is also displayed in many of Millie’s other pieces. Secondly, it demonstrates the “mixture of literature and mathematics” to which Millie refers in her Introduction to the Oulipoems – the idea that different styles of writing can be mapped onto a graph and summoned by pointing at different vectors – and in doing so, it demonstrates a willingness to experiment with text, and an openness to the idea that text in digital literature may sometimes be manipulable by the audience, rather than fixed into a single unquestionable form by the author. Thirdly, “Morningside Vector Space” is funny and accessible. The labels with which Millie marks out her vectored space are humorous, and the texts with which she illustrates these different writing styles are exaggerated for comic effect. At the same time, there is an undercurrent of social observation, with a suggestion of political edge: “I was observing a mixed-income neighborhood on the borders of a low socioeconomic enclave… Lacking funds for a watch, he had to rely on others in the community to be on time for his appointment with the social services…”
Lastly, perhaps least obvious is a powerful sense of place. The piece’s title refers to Morningside Heights, an area of Manhattan in New York. The texts allude to Amsterdam Avenue, a street in Morningside, and the Cathedral of St John the Divine, which stands there. St John the Divine is also known as St John the Unfinished because although it was begun in 1892, it remains incomplete to this day – hence the description of the cathedral as “tall and unfinished”. The coloured vector space in Millie’s piece contains another reference to the cathedral, in the shape of a wobbly but recognisable line drawing of its facade. This sense of place is an important aspect of Millie’s output – not only in videos about places such as “Jewel of the Erie Canal” or “A Hecatomb in Cheektowaga” but also in new media works such as “The Talking Escalator at Penn Station”and “Unscenic Postcards” – and like her interest in politics, it demonstrates her commitment to the “real” world, as well as her talent for observation and comment.
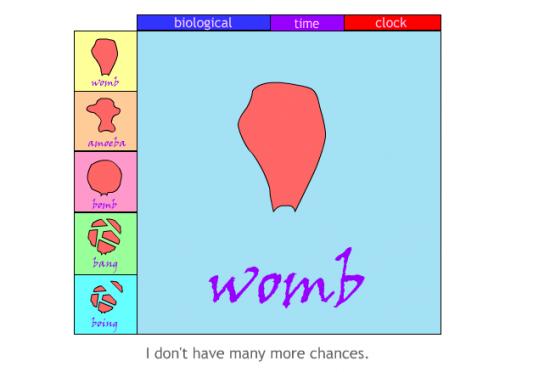
Another of Millie’s Flash pieces, and one of her most personal artworks, is “Biological Time Clock”. In a central pane, the words “womb”, “amoeba”, “bomb”, “bang”, and “boing” appear, accompanied firstly by Millie’s voice intoning the same words, and secondly by drawings of a womb, an amoeba, a womb inflated to the point of bursting, a womb breaking into pieces, and another slightly different drawing of a womb in bits. Underneath this pane appears a randomised sequence of phrases, arguing both for and against getting pregnant and giving birth: “It’s not for me”, “I’d be nurturing”, “I’m more than a womb”, “I’m not together enough”, “maybe I should do it while I can”, and so forth. There are also buttons that allow you to add extra sound effects, such as Millie saying “tick-tock” or chanting “biological”.
There are feminist aspects to the piece – one of the anti-pregnancy phrases is “I don’t want to be a breeding cow”, and another is “I’m more than a womb” – mixed with what seem to be more autobiographical notes, such as “why am I alone?” and “I don’t want to lose my creativity”. However, a question that seems to go to the heart of the piece is what is the word “boing” doing in there? The drawing which accompanies this word is enigmatic. Still, it may be meant to suggest that the womb, which broke apart at “bomb”, is now somehow bouncing back together again – and by implication, that no matter how many times the author talks herself out of childbirth, her consciousness of her womb keeps coming back to bother her afresh. But the word “boing” serves another purpose by introducing into the piece the quirky, unpretentious, comical note essential to Millie’s art. If the word sequence at the heart of the poem were simply “womb, amoeba, bomb, bang,” then both the message and the tone would seem much starker. With “boing” on board, there is a playful and funny element to the piece, a release from serious description into exaggeration, which seems to suggest that Millie herself isn’t taking it completely seriously, and we don’t have to take it completely seriously either.
In some ways, this insistence on the quirky and the wacky might be considered a weakness or a limitation in Millie’s art, flinching away from completely direct and honest engagement with her subject matter, symptomatic of a tendency to let both herself and her audience off the hook, especially if her subject-matter happens to be personal. But it should be borne in mind that Millie had more personal subject matter to deal with than most of us, and her insistence on humour was an essential part of her strategy for dealing with it. One of the anti-pregnancy arguments on “Biological Time Clock” is “I’m not well…” and it is impossible to write about Millie’s art without taking her mental and physical ill health into account, if only because so much of her art deals with it. For many years she was considered – and considered herself – to be mentally ill with Bipolar Disorder. Millie’s experiences of mental illness and the health and social care professionals with whom it brought her in contact are memorialised in “The Adventures of Spork, the Schizophrenic Skua”. As described on Millie’s site:
Millie Niss created Spork… to be a sympathetic and intelligent character who was also an indigent client of the mental health system. The cartoons began to express frustrations about how mentally ill people and welfare recipients are treated, but later on, other issues and pure silliness were added to the Spork series.
Eventually, after years of treatment for mental illness, Millie was diagnosed with Behcet’s disease, a severe disorder of the immune system which can cause depression along with ulcers, skin lesions, stomach problems and inflammation of the lungs. Before this diagnosis, however, she suffered attacks of dangerously acute depression, and one part of her website is devoted to suicide (http://www.sporkworld.org/suicide). The way in which she tackles this subject makes it clear how her sense of humour, far from demonstrating an unwillingness to confront her inner demons, was really evidence of her mental toughness and self-discipline in dealing with them – a refusal to give in to self-pity:
I was often, very often ready to kill myself, but I hate guns and wouldn’t want to use one. And lying on a gun license application was out of the question: I would not sign my name to a paper which said I was not intending to kill myself or was not mentally ill… Hanging was reputed to be painless and so we thought getting sentenced to death was the perfect out: that way you could have the benefit of dying without the guilt of doing it to yourself. It was unfortunate that you had to do something awful to get sentenced to death, though… A big question was the suicide note. Should you leave one or not, and if so what should you say in it? The argument for not leaving a note was a strong one: someone might find the note and stop you from doing it… The desire to write a suicide note that was a literary masterpiece kept me alive at times. I couldn’t kill myself until I thought of something good enough.
In these passages, Millie combines a sharp, satirical, almost gleeful insight into the ironies and self-contradictions of the suicidal mindset with an understated – but nevertheless essential and genuinely tough – conviction of her individuality and status as an artist. As she insists in “Biological Time Clock”: “I have a brain”, “I’m more than a womb”, and “I don’t want to lose my creativity”. In “Suicide”, the idea that she doesn’t want to kill herself until she can devise a sufficiently well-written suicide note is a good joke at her own expense. Still, it also points to something deeper: her writing is her way of dealing with depression and her reason for not succumbing. It gives her a sense of self-worth, and the discipline of art allows her to detach herself from her feelings and sublimate them, thereby gaining some form of control over them.
In an article entitled “Suicide, Art, and Humor”, which she published on Michael Szpakowski’s website “, Some Dancers and Musicians”, Millie wrote that “The artist has a duty, some might say, to produce art. But with that comes the more fundamental duty to stay alive.” This is a typically grounded remark: the artist’s duty to life is “more fundamental” than her duty to art. Referring to her own “Suicide” piece, she goes on: “I was at least trying to be funny… Art is a force that tends towards life… While you are writing a despairing poem, you are, in the act of writing, temporarily suspended from the act of despairing.” The effort to be funny and thereby entertain an audience, art as an affirmation of life, and art/humour as a defence against despair – all of these ideas were essential to Millie’s work.
The same values are apparent on the Sporkworld Microblog, which Millie shared with her mother, Martha Deed. They are present even in the very last days of her final illness. Here is an entry from 16th November: “We like to keep a chipper tone here, and we do not intend this to be a place to list complaints. We also insist that any personal events must be… transformed from raw anecdote into something with literary intent.” Martha actually wrote this, but Millie approved it, and it reflects a shared philosophy that runs right through the site’s contents. “Raw anecdote” is inadmissible, not only because it may lack the “chipper tone” that the Microblog seeks to maintain, but because it also lacks the discipline and detachment of real art. The word “raw” suggests something of the harshness of unfiltered experience. The artist’s job is not to pass on this harshness to the audience direct and unmediated, but to control it through an effort of will, to fit it into a composition, to comment on it, reason about it, make jokes about it and turn it into an element in discourse; and thus to humanise it.
After Millie’s death, Martha published a poem on the Microblog entitled “Travelling with H1N1”, which contains the following lines:
even if it is difficult to be funny
while intubated, you will fight and fight and fight…
you will be sending email on your way to the fluoroscope
with subject lines like
I never thought I would write email while intubated”…
The sense of humour, the refusal to give in, and the determination to fight back against her difficulties by finding something to say about them were all there until the very end. Martha relates that in the intensive care Unit (ICU), although she couldn’t speak because she was on a ventilator, she kept her lines of communication open by writing things down. She struck up a friendship with a nurse supervisor, Tom, who “was astonished at her ability to tolerate the ventilator and keep up a running conversation in her notebooks… He continued to visit her in the ICU and received her candid evaluations of her care there – both good and bad – and he found her to be very funny and brave.”

Mentioning the Sporkworld Microblog, and the fact that it was shared with Martha Deed, brings us to Millie’s frequent and long-term collaborations with her mother. Millie is known as “Spork Major” on the Microblog, while Martha is “Spork Minor”. Apart from the blog, they collaborated on many other works – Martha co-wrote the “Oulipoems” texts, for example, and “Jewel of the Erie Canal” is credited to them both. But one of the largest, most ambitious and most formally developed of their collaborations is News from Erewhon, a series of parallel surreal fictions created by the process of “guided free association”.
News from Erewhon is by no means a perfect work of art. Firstly, the title makes a rather distracting reference to Samuel Butler’s satirical, pseudo-Utopian novel “Erewhon”, which doesn’t really seem to have much to do with the rest of the book. Secondly, each chapter is accompanied by a number of images which zoom up in front of the words and then quickly fade away to allow us to read on. The Introduction argues that these add “another level” to work and that the pictures “appear only briefly to affect the viewer in an almost subliminal manner”. In fact, their main effect is to make you lose your place. Luckily, Millie provides a button which allows us to switch the images off.
Nevertheless, the texts themselves are fascinating. They were written in an almost Oulipo-like manner. Several words were picked randomly from chosen books; then, using these words as “seeds” and incorporating them into their writing as they went along, both Millie and Martha produced a series of eight “miniature fictions, situated halfway between poetry and prose”. As the Introduction says, these fictions suggest “a bizarre alternate universe, whose characters and settings evoke themes such as war and peace, the workplace, and religion. These themes… weave in and out of the texts like strands in a braid. The two authors can also be seen as separate, interacting strands.” The image of strands in a braid suggests both the closeness with which Martha and Millie were able to work together and the fact that they always retained their distinct identities and styles, and News from Erewhon is a good demonstration of this. Millie’s sections are generally longer than Martha’s and more narrative in style, whereas Martha’s tend to be more surreal and poetic. Both, however, display a constant flow of inventive wit. One of the funniest of the lot is Millie’s fourth:
The mice lived in a cream-colored bungalow under Mrs Johnson’s sink. Or so at least it seemed to them. Others less culturally attuned might have seen only some half-eaten Triscuits and the remains of a sesame bagel… “God save all the creatures who crawl under the moon, and all of their offspring,” murmured Chuck in a non-denominational invocation of the Divine. He would feel differently in the morning when he blistered his toe in the empty mousetrap from which the clever mice had stolen the cheese. “God Fuck!” he would swear into the mirror, cursing his fate as he brushed the All Bran from his teeth.
Seed-words for the passage are shown in bold. Here is an extract from Martha’s equivalent passage:
A cream-colored bungalow? How could you? It will curdle in the sun, and this is July, she said… Your invocation of natural disasters has blistered the mirror of my mind, he moaned.
Both writers, it will be noted, start by cheating: instead of introducing the “cream-colored bungalow” into their stories in a literal-minded way, they bring it in obliquely. Martha imagines a bungalow, not the colour of cream, but actually painted with cream on the outside – hence the objection that “it will curdle in the sun” – while in Millie’s story, the bungalow only exists at all in the collective imagination of a family of mice. Martha sticks more closely to an underlying structure suggested by the seed words, producing a more densely written text and poetic texture. This is particularly evident in the alliteration – “colored”, “could”, and “curdle” or “mirror”, “mind”, and “moaned”; but also in the lilting rhythm – “Your invocation of natural disasters has blistered the mirror of my mind, he moaned”. Millie, on the other hand, shows something of the novelist’s delight in incidental detail – “Triscuits”, “sesame bagel”, “under Mrs Johnson’s sink”, and “he brushed the All Bran from his teeth”. Her passage seems to take a serious turn with the phrase “God save all the creatures who crawl under the moon” – simultaneously poetic, literary and religious – yet this moment of gravity is almost immediately reversed by an explosion of comical blasphemy – “God Fuck!”
It would be too simplistic to suggest that Martha was always the more focused and disciplined partner in collaborative work. It should be remembered that Millie was the techno-savvy one, and therefore the design and construction of the Sporkworld site, the Microblog and News from Erewhon were all carried out by her. Her work in this area is always individualistic rather than textbook. Still, at the same time, it exhibits both a powerful emphasis on user-friendly functionality and a considerable visual flair. She may have presented herself as the mercurial, comical, slightly wacky half of the partnership, but there was always a sharpness, toughness, self-discipline and a determination to succeed just under the surface.

On the other hand, Millie’s work undoubtedly has an impulsive element, and in the collaborations, this makes a compelling contrast with Martha’s more studied approach. “God Fuck!” is one example; another is “Voting”, a video made in November 2008 showing Millie’s difficulties, as a disabled individual, in trying to deal with her postal vote form. Her ballot paper combines a list of presidential, senatorial, and Congress options and several constitutional issues specific to North Tonawanda, the town in which Millie and Martha live. As a result, it’s a huge sheet about the size of a tablecloth, with as many creases as an Ordnance Survey map, and just as difficult to flatten or re-fold. Step by step, Martha takes Millie through the different options on offer, with Millie keeping up a gunfire of questions and acerbic commentary, interspersed by short periods of silence during which she gasps for breath. Both Martha and Millie are represented on-screen mainly by their hands – first Martha’s, as she manipulates the ballot paper and fills it out in accordance with Millie’s instructions; then Millie’s, towards the end of the process, as she signs the outside of the envelope to authorise her vote. Apart from this, they are represented by their voices: Martha’s calm and methodical, Millie’s staccato and satirical, but both become increasingly impatient as the difficulties of dealing with the ballot paper become increasingly apparent. Ultimately, Martha can’t get it folded to fit the official envelope. Then Millie has to rehearse her signature because her hands are so afflicted with arthritis that she struggles to hold a pen. Then the envelope is difficult to sign because it’s so fat and unshapely with the ballot paper inside it. Then it turns out that the envelope will have to be taken to the Post Office and weighed because it isn’t pre-franked or freepost; at which point –
MILLIE: Okay, so we’re gonna have to pay postage on top of this… and it has to be weighed because it’s so fucking heavy!
(Slightly shocked pause.)
MARTHA (elaborately self-restrained): Did you mean to put the word “effing” in?
MILLIE (immediately): I did! I absolutely did! I mean, it’s a matter of free speech. The Supreme Court would have upheld my right to say fucking on my own blog. There have been efforts to make it impossible to say that.
MARTHA (holding up the envelope, with a noticeable change of subject): Okay, I think we actually have it done.
It’s a wonderful piece of film-making. Whether or not you agree with what Millie seems to be hinting, that there is a deliberate attempt on the part of the establishment in the USA to discourage people at the margins of society from taking part in the democratic process, or whether you prefer the view that bureaucrats have no conception of the difficulties faced by the people on the receiving end of their bureaucracy; the point that the postal ballot, which is supposed to make it easier for disabled people to vote, actually makes it almost intolerably difficult, has been well and truly established by the end. But the real strength of the video lies partly in the interplay between the two main characters and partly in the underlying theme of Millie’s disability and how they handle it. As with Millie’s work, her illness is central to the meaning of the piece, yet it isn’t about the experience of being ill. It’s about how illness changes your relationship with the rest of society – one of her most powerful themes. But it’s also about coping with that situation through the help of others – in this case, Martha – and through a supreme effort of will.
Much of the poignancy of the piece lies in the soundtrack: Millie gasping for breath on the one hand and Millie rattling off her machine-gun-like commentary on the other. You can’t ignore how ill she is and doesn’t ignore it herself, but she won’t let it shut her up. The video is a gradual crescendo of comedic impatience, culminating in the obscenities at the end. Her outspokenness is a refusal to be silenced by society and the universe, which has trapped her spirit inside such an inappropriate body. She overcomes her difficulties by externalising them. She makes them the subject of her art, and by doing so, she finds her voice.
No doubt Millie would have become an artist of some description, whatever body, circumstances and state of health she was born into. She was sufficiently remarkable for that. But without her ill health, the work she left behind would have been very different: less spiky, poignant, funny and perhaps less urgent. Her output is not defined or limited by her health, but her health gave her her most important themes and powerful moments. The supreme irony of her art is that, like the knotty grain of a piece of burr elm, the things that made her imperfect were the same things that made her unique and beautiful.
©Edward Picot, December 2009
“Postmodernism is dead” declares Nicolas Bourriaud in the opening line of his manifesto for our new global cultural era – the ‘altermodern’. As a preface to the latest Tate Triennial exhibition of the same name, the French curator and theorist sets about defining what he sees as the parameters of our contemporary society and offering paradigms for artistic approaches to navigating and negotiating them.
This essay aims to identify what the birth of this new era tells us about our culture’s relationship to time. It will explore how we choose to define the periods in which we live and how our relationships with the past, present and future seem to constantly evolve. As a central focus, it brings together two examples of cultural events from 2009 which have both, in semi-revolutionary ways, attempted to define our current age. The Altermodern exhibition and its accompanying Manifesto (Bourriaud 2009b) launched at the Tate Britain on 4th February provides the first, and the second is provided by The Age of Stupid – a feature film and accompanying environmental campaign launched in UK cinemas on 20th March.
Set in the year 2055, The Age of Stupid focuses on a man living alone in a world which has all but been destroyed by climate change. In an attempt to understand exactly how such a tragedy could have befallen his species and the society and culture which they created over the course of several millennia, he begins to review a series of ‘archive’ documentary clips from 2008. His aim is to discover how his ancestors – the one generation of people who had the power to prevent the impending disaster – could have demonstrated such disregard or contempt for the future.
By focusing on two central texts – Bourriaud’s Altermodern Manifesto and a faux encyclopedia entry from the future which retrospectively defines ‘the Age of Stupid’ released as promotional material for the film (Appendix One) – the essay aims to explore the disturbing continuities between these two perceptions of our current times and the drastic consequences these could have, if left unchecked, for the future of humanity and indeed the future of art.
Defining the eras in which we live through phrases such as ‘modernity’, ‘postmodernity’ and now ‘altermodernity’, allows us a tangible way of assessing our place within the far less tangible, metaphysical concept of ‘time’. In fact, it could be argued that ‘history’ itself has been invented, documented and perpetuated as a way of helping human beings to get a purchase on their own existence and to define how they should approach their relationships to their past, present and future.
In this sense, the ‘modern’ era could be characterised as encouraging a forward-thinking outlook. According to Jurgen Habermas, its last living prophet:
“modernity expresses the conviction that the future has already begun: it is the epoch that lives for the future, that opens itself up to the novelty of the future.” (Habermas 2004, p.5)
At the very start of the Enlightenment in the mid-17th century the French philosopher and scientist Blaise Pascal portrayed an inspiring vision of humanity as progressing throughout time, by likening the development of human innovation over the course of history to the learning of one immortal man (Stangroom 2005). Scientific knowledge could be advanced by new generations building on what had been discovered before them. The humanist belief held by philosophers, and others alike, was that ‘man’ was the centre of everything; that man could control nature and could master his own destiny.
This optimistic idea was so new, compelling and widespread that it assisted in propelling the project of modernity as it ploughed relentlessly through the centuries – the French Revolution, American Independence, the Industrial Revolution, the rapid expansion of capitalism and the birth of bourgeois society. It was rational, logical and, as though guided by an ‘invisible hand’, was the way things were meant to happen. At the start of the 19th century, Hegel was still convinced; we were getting somewhere, history was progressing through a dialectical process towards its logical conclusion – towards perfection. People’s relationship with the future was one of hope; as though things could only get better.
Reason, however, appeared to have its downsides and catastrophic human developments of the 20th century, such as the holocaust and the atomic bomb, led to a loss of faith in the humanist approach. Towards the end of the twentieth century, a general consensus developed among cultural theorists (Habermas aside) that modernity was no longer working. Its ‘metanarratives’ had resulted in authoritarianism, totalitarianism and terror; minorities had been victimised or marginalised; the ‘differends’ of society smoothed over (Malpas 2003). And so, ‘postmodernism’ was born and with it began a systematic deconstruction and disownment of what were now considered the somewhat embarrassing ideals of its predecessor. The reaction was severe; inciting a series of symbolic revenge killings: the ‘death of man’ (Foucault 1994), the ‘end of humanism’ the ‘end of history’ (Fukuyama 1992), the ‘death of painting’ and even the ‘end of art’ (Danto 1998). It was as though catharsis could be gained by the ridding of a past which had failed to live up to promise. In the wake of all this destruction, however, came a deep uncertainty of what would come to fill the gaps.
Just as modernism had done before, postmodernism “alluded to something that had not let itself be made present” (Lyotard 1993, p.13), only this time that ‘something’ felt more menacing. The decentralisation of ‘man’ from the story of history may have unearthed a hidden fear of the future. If we were no longer in control of nature or masters of our own destinies, then we could be less optimistic about what the future had in store and far more uncertain of the potential consequences of 350 years of rampant ‘progress’ that we may have to face.
The rejection of the past coupled with this uncertainty about the future gave the postmodern era a feeling of limbo within which time itself was “cancelled” (Jameson 1998, p.xii). In his critique of the historical momentum of the 1980s, Jan Verwoert refers to the “suspension of historical continuity” which resulted from the overbearing stalemate politics of the Cold War. Only when it finally ended could “history spring to life again” (Verwoert 2007) and begin accelerating away from postmodernism and into the new cultural era.
In terms of assessing the birth of altermodernism, this specific point in history appears pivotal. Firstly, the end of the Cold War meant that:
“the rigid bipolar order that had held history in a deadlock dissolved to release a multitude of subjects with visa to travel across formerly closed borders and unheard histories to tell.” (Verwoert 2007)
And, according to CERN (the European Organisation for Nuclear Research), not only did 1990 see the reunification of Germany, but it also witnessed “a revolution that changed the way we live today” – the birth of the World Wide Web (info.cern.ch). These were the nascent beginnings of an a priori globalised society in which, as Bourriaud describes, “increased communication, travel and migration affect the way we live.”
What is most interesting about this point in time, however, are discoveries referred to in the definition of ‘the Age of Stupid’. As argued in the final paragraph of the encyclopædic entry, 1988 also marked the point at which humanity had amassed sufficient scientific evidence to “become aware of the likely consequences of continuing to increase greenhouse gas emissions”. The uncertainty about the future which had characterised the postmodern era was suddenly replaced by a real-life certainty, but it was not one which we were prepared to face up to.
Rather than taking heed of these warnings when we still had plenty of time – slowing down and reassessing our lives; curbing our consumption and production – throughout the 1990s we actually did the opposite. As Verwoert suggests, the pace quickened – the population grew, we travelled more, consumed more and wanted more. Life in the new globalised world was more chaotic and less controllable. Before we knew it twenty years had passed and we had still failed to accept the facts and to act in order to avert the course of history and “prevent the deaths of hundreds of millions of people” (Armstrong 2009a) in the future.
As we stand, in the present day, we are still firmly on course to see the devastation envisaged in the film The Age of Stupid, become a reality. At the end of March 2009, a conference on ‘sustainable populations’ organised by the Optimum Population Trust took place in London. In its coverage of the issues raised, The Observer described the future which the overwhelming scientific evidence claims awaits us:
“by then (2050) life on the planet will already have become dangerously unpleasant. Temperature rises will have started to have devastating impacts on farmland, water supplies and sea levels. Humans – increasing both in numbers and dependence on food from devastated landscapes – will then come under increased pressure. The end result will be apocalyptic, said Lovelock. By the end of the century, the world’s population will suffer calamitous declines until numbers are reduced to around 1 billion or less. “By 2100, pestilence, war and famine will have dealt with the majority of humans,” he said.” (McKie 2009, p.9)
As depressing as it sounds, the message of the film The Age of Stupid is one of hope – that it is not quite too late. According to their predictions, we still have until 2015 to make the changes required in order to prevent us reaching the tipping point which would trigger ‘runaway’, irreversible climate change. These corrective measures are huge, they are global and they need to start being implemented now.
What is most terrifying about Bourriaud’s Manifesto therefore, is its absolute lack of acknowledgement of the real and dangerous future that we face. Rather than speaking out and demanding the dramatic changes that are necessary, it seems to support a continuation of the status quo of the last twenty years. In his video interview on the Tate website, Bourriaud describes the purpose of the altermodern as the “cultural answer to alterglobalisation” (Bourriaud 2009a). However, rather than questioning the carbon-heavy lifestyles that a globalised world promotes he seems to complicitly buy into them, insisting that “our daily lives consist of journeys in a chaotic and teeming universe”.
In the film The Age of Stupid ‘archive’ footage from 2007 presents the Indian entrepreneur Jeh Wadia as the ignorant villain, as he goes about launching India’s first low-cost airline GoAir. His mission is to get India’s 1 billion plus population airborne. Although an extreme example, Bourriaud’s fervent support of internationalism is not dissimilar to Wadia’s in its level of denial. He continues to encourage the movement of artists and curators around the world (clocking up substantial air miles bringing in speakers for his four Altermodern ‘prologue’ conference events alone).
What makes Bourriaud’s case worse however is his apparent betrayal of the purpose of cultural theory in providing counter-hegemonic ideas and alternatives. The theorists of postmodernism overthrew the project of modernity in an attempt to save humanity from further nuclear extermination or genocide which had proved the ultimate conclusions of reason. Their cultural vision for postmodernism was also to provide an alternative or an antidote to the new ways of life dictated by post-industrial society. Not only does the vision for altermodernism fail to provide an alternative to the devastating path to future down which ‘alterglobalisation’ is dragging us, but it also remarkably promotes the idea that we turn our backs on and ignore this future altogether. One of the paradigms for artistic approaches Bourriaud suggests is that artists look back in time rather than forward claiming that “history is the last uncharted continent” and therefore should be the focus of artistic attention.
Jeh Wadia’s excuse is easy to fathom – he is in it for the money, but Bourriaud’s seems harder to discern. He is driven by a burgeoning ego no doubt, but alongside this there seems to be a wider problem. A nostalgia for the good times and a refusal to give up privileges and luxuries appear to be endemic in the art world’s attitude to facing up to the realities of climate change. At Frieze Art Fair last year, cultural theorist Judith Williamson delivered a keynote lecture on what she called ‘the Culture of Denial‘. She outlined a view of the world not dissimilar to the definition of ‘the Age of Stupid’ (and indeed altermodernism) that this essay has been discussing, in which a denial of the impending future or perhaps an impossibility to comprehend its severity, prevents us from acting.
What was most interesting about her introduction, however, was the discussion of her deliberate decision not to mention ‘climate change’ in the material promoting the talk, but instead to refer to it more ambiguously as an exploration of “the skewed relationship between what we know and what we do” (Williamson 2008). She identifies the persistent ‘stigma’ attached to directly addressing this issue, describing the common perception of it being “annoying, gauche or over the top to bang on about climate change”. So she was forced to revert to covert tactics in order to sneak this pressing discussion onto the Frieze agenda – in the hope of inciting the beginning of a widespread realisation that the art world is walking the path towards its own destruction.
There seems no doubt that Bourriaud’s altermodernism is the cultural side-kick of ‘the Age of Stupid’. To write a Manifesto of our times at such a crucial make-or-break point in the history of humanity and not to mention the possibility of an impending disaster or offer any suggestions as to what artists and society in general can do to combat it, is not just denial – it’s stupidity.
The truth is that all the ‘ends’ and ‘deaths’ that postmodernism faced on hypothetical grounds are now fast approaching our generation as a reality. Foucault’s famous conclusion to the seminal postmodern text ‘The Order of Things’, now seems all the more poignant:
“If those arrangements were to disappear as they appeared, if some event of which we can at the moment do no more than sense the possibility… were to cause them to crumble… then one can certainly wager that man would be erased, like a face drawn in sand at the edge of the sea.” (Foucault 1994, p.422)
The main character in the The Age of Stupid is an archivist. In 2055, he sits alone in an expansive tower known as the ‘the World Archive’, which houses all the works of art, books, images, film etc ever produced by the human race. It is at this point that you realise this preservation is futile. Art is, after all, a human creation – it relies on humanity to provide its meaning. Without this crucial element it may as well cease to exist. Should it not, therefore, be art and culture that lead the way for the rest of society? To be the first to snap out of this ‘culture of denial’; to overcome the ‘stigma’; to do everything in its power to save humanity, and itself in the process.
Future Encyclopedia Entry: The Age of Stupid
The Age of Stupid constitutes the period between the ascent of the internal combustion engine in the late-19th century and the crossing of the 2c threshold to runaway global warming in the mid-21st.
This era was characterised by near-total dependence on energy from fossil hydrocarbons, together with exponentially increasing consumption based on the destruction of finite natural resources.
The institutionalised lack of foresight regarding future human welfare that held sway during this time earned the period its popular name, but scientists know this era as the Anthropocene: the period during which human activities came to be the dominant influence on the Earth’s biosphere and climate. The end of the Age of Stupid is marked by the sixth major mass extinction event, with the fifth being the K-T asteroid impact which ended the Age of the Dinosaurs. The abrupt loss of the majority of plant and animal species between 2020 and 2090 was followed by a crash in the human population, to just 7.4% of the 9 billion people alive at its peak.
Some historians argue that the Age of Stupid more properly refers to the narrower period between 1988 and 2015, during which humanity had become aware of the likely consequences of continuing to increase greenhouse gas emissions and still had time to avert catastrophe, but largely chose to ignore the warnings.
This article can also be found at:
Original text at Ellie Harrison’s web site – http://www.ellieharrison.com/index.php?pagecolor=7&pageId=press-summerreading
Edited version at The Nottingham Visual Arts web site – http://www.nottinghamvisualarts.net/writing/jun-09/altermodernism-age-stupid