



The insights of American anarchist ecologist Murray Bookchin, into environmental crisis, hinge on a social conception of ecology that problematises the role of domination in culture. His ideas become increasingly relevant to those working with digital technologies in the post-industrial information age, as big business daily develops new tools and techniques to exploit our sociality across high-speed networks (digital and physical). According to Bookchin our fragile ecological state is bound up with a social pathology. Hierarchical systems and class relationships so thoroughly permeate contemporary human society that the idea of dominating the environment (in order to extract natural resources or to minimise disruption to our daily schedules of work and leisure) seems perfectly natural in spite of the catastrophic consequences for future life on earth (Bookchin 1991). Strategies for economic, technical and social innovation that fixate on establishing ever more efficient and productive systems of control and growth, deployed by fewer, more centralised agents have been shown conclusively to be both unjust and environmentally unsustainable (Jackson 2009). Humanity needs new strategies for social and material renewal and to develop more diverse and lively ecologies of ideas, occupations and values.
In critical media art culture, where artistic and technical cultures intersect, alternative perspectives are emerging in the context of the collapsing natural environment and financial markets; alternatives to those produced (on the one hand) by established ‘high’ art-world markets and institutions and (on the other) the network of ubiquitous user owned devices and corporate social media. The dominating effects of centralised systems are disturbed by more distributed, collaborative forms of creativity. Artists play within and across contemporary networks (digital, social and physical) disrupting business as usual and embedded habits and attitudes of techno-consumerism. Contemporary cultural infrastructures (institutional and technical), their systems and protocols are taken as the materials and context for artistic and social production in the form of critical play, investigation and manipulation.
This essay presents We Won’t Fly for Art, a media art project initiated by artists Marc Garrett and I in April 2009 in which we used online social networks to activate the rhetoric of Gustav Metzger’s earlier protest work Reduce Art Flights (from 2007) in order to reduce art-world-generated carbon emissions... Download full text (pdf- 88Kb) >
Published in PAYING ATTENTION: Towards a Critique of the Attention Economy
Special Issue of CULTURE MACHINE VOL 13 2012 by Patrick Crogan and Samuel Kinsley.
“It is not accidental that at a point in history when hierarchical power and manipulation have reached their most threatening proportions, the very concepts of hierarchy, power and manipulation come into question. The challenge to these concepts comes from a redsicovery of the importance of spontaneity – a rediscovery nourished by ecology, by a heightened conception of self-development, and by a new understanding of the revolutionary process in society.” Murray Bookchin. Post-scarcity and Anarchism (1968).
The rise of neo-liberalism as a hegemonic mode of discourse, infiltrates every aspect of our social lives. Its exponential growth has been helped by gate-keepers of top-down orientated alliances; holding key positions of power and considerable wealth and influence. Educational, collective and social institutions have been dismantled, especially community groups and organisations sharing values associated with social needs in the public realm. [1] Bourdieu.
In this networked society, there are controversies and battles taking place all of the time. Battles between corporations, nation states and those who wish to preserve and expand their individual and collective freedoms. Hacktivist Artists work with technology to explore how to develop their critical and imaginative practice in ways that exist beyond traditional frameworks of art establishment and its traditions. This article highlights a small selection of artists and collaborative groups, whose work is linked by an imaginative use of technology in order to critique and intervene into the opressive effects of political and social borders.
In June 2000, Richard Stallman [2] when visiting Korea, illustrated the meaning of the word ‘Hacker’ in a fun way. When at lunch with some GNU [3] fans a waitress placed 6 chopsticks in front of him. Of course he knew they were meant for three people but he found it amusing to find another way to use them. Stallman managed to use three in his right hand and then successfully pick up a piece of food placing it into in his mouth.
“It didn’t become easy—for practical purposes, using two chopsticks is completely superior. But precisely because using three in one hand is hard and ordinarily never thought of, it has “hack value”, as my lunch companions immediately recognized. Playfully doing something difficult, whether useful or not, that is hacking.” [4] Stallman
The word ‘hacker’ has been loosely appropriated and compressed for the sound-bite language of film, tv and newspapers. These commercial outlets hungry for sensational stories have misrepresented hacker culture creating mythic heroes and anti-heroes in order to amaze and shock an unaware, mediated public. Yet, at the same time hackers or ‘crackers’ have exploited this mythology to get their own agendas across. Before these more confusing times, hacking was considered a less dramatic activity. In the 60s and 70s the hacker realm was dominated by computer nerds, professional programmers and hobbyists.
In contrast to what was considered as negative stereotypes of hackers in the media. Steven Levy [5], in 1984 published Hackers: Heroes of the Computer Revolution [6]. In three parts, he writes about the canonical AI hackers of MIT, the hardware hackers who invented the personal computer industry in Silicon Valley, and the third-generation game hackers in the early 1980s. Yet, in this publication, what has had the most impact on hacker culture and is still used widely as a guideline by many is the ‘hacker ethic’. He identified this Hacker Ethic to be a code of practice consisting of key points such as that “all information is free”, and that this information should be used to “change life for the better”.
1. Access to computers—and anything which might teach you something about the way the world works—should be unlimited and total. Always yield to the Hands-on Imperative!
2. All information should be free.
3. Mistrust authority—promote decentralization.
4. Hackers should be judged by their hacking, not bogus criteria such as degrees, age, race or position.
5. You can create art and beauty on a computer.
6. Computers can change your life for the better.
Levy’s hacker ethic promotes the idea of performing a duty for the common good, an analogy to a modern day ‘Robin Hood'[ibid]. Proposing the concept that hackers are self-reliant whilst embracing a ‘healthy’ anti-authoritarian stance, combined with free and critical thinking. Proposing that hackers should be judged by their ability to hack, and presenting hacking as an art-form. Levy also says that the Free and open source software (FOSS) movement is the descendant of the hacker ethic. However, Levy’s hacker ethic has often been quoted out of context and misunderstood as to refer to hacking as ‘breaking’ into computers. This specifically prescribed role, denies the wider and creative context of what hacking is and could be. It does not have to be just about computer security.
This leads us to ‘crackers’. All crackers hack and all hackers hack. But, crackers are seen as second rate wannabe hackers by the older generation of hackers. The Black Hat Hacker or cracker designs and releases malicious code, gathers dangerous information and brings down sensative systems. The White Hat Hacker hunts down and destroys malicious code, and the casual hacker who hacks in order to learn information for his or her own curiosity; both generally dislike ‘Black Hats’ and ‘Crackers’, and tend to view them as computer criminals and dysfunctional juveniles. Lately, crackers have also been labeled as ‘script kiddies’. As a kind of snobbish insult, it refers to those who are not capable of building or programming their own tools, but tend to use scripts and programs written by others to perform their intrusions. To add to the confusion we also have the term ‘Grey hat’. Which refers to a hacker acting between black hat and white hat. Indeed, this could demonstrate where art hacktivists reside, challenging the trappings of the traditional concept of goody and baddy.
“There is another group of people who loudly call themselves hackers, but aren’t. These are people (mainly adolescent males) who get a kick out of breaking into computers and phreaking the phone system. Real hackers call these people ‘crackers’ and want nothing to do with them.” [7] Raymond.
“The basic difference is this: hackers build things, crackers break them.” [ibid] Raymond.
But before we judge,
let’s view a snippet of the \/\The Conscience of a Hacker/\/ by +++The Mentor+++
Written on January 8, 1986.[8]
“This is our world now… the world of the electron and the switch, the
beauty of the baud. We make use of a service already existing without paying
for what could be dirt-cheap if it wasn’t run by profiteering gluttons, and
you call us criminals. We explore… and you call us criminals. We seek
after knowledge… and you call us criminals. We exist without skin color,
without nationality, without religious bias… and you call us criminals.
You build atomic bombs, you wage wars, you murder, cheat, and lie to us
and try to make us believe it’s for our own good, yet we’re the criminals.”
The term ‘Hacktivism’ was officially coined by techno-culture writer Jason Sack in a piece about media artist Shu Lea Cheang published in InfoNation in 1995. Yet, the Cult of the Dead Cow [9] are also acknowledged as defining the term. The Cult of the Dead Cow are a group of hackers and artists. They say the Hacktivism phrase was originally intended to refer to the development and use of technology to foster human rights and the open exchange of information.
Hacktivism techniques include DoS attacks, website defacement, information theft, and virtual sabotage. Famous examples of hacktivism include the recent knocking out of the PlayStation Network, various assistances to countries participating in the Arab Spring, such as attacks on Tunisian and Egyptian government websites, and attacks on Mastercard and Visa after they ceased to process payments to WikiLeaks.
Hacktivism: a policy of hacking, phreaking or creating technology to achieve a political or social goal.
“Hacktivism is a continually evolving and open process; its tactics and methodology are not static. In this sense no one owns hacktivism – it has no prophet, no gospel and no canonized literature. Hacktivism is a rhizomic, open-source phenomenon.” [10] metac0m.
The practice or behaviour of Hacktivism is at least as old as Oct 89 when DOE, HEPNET and SPAN (NASA) connected to (virtual) networked machines world wide. They were penetrated by the anti-nuclear group WANK worm.
WANK penetrated these machines and had their login screens altered to…
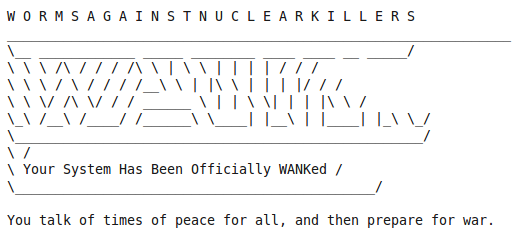
HACKING BORDERS: Examples of Art Hacktivism & Cultural Hacking…

“Radical groups are discovering what hackers have always known: Traditional social institutions are more vulnerable in cyberspace than they are in the physical world. And some members of the famously sophomoric hacker underground are becoming motivated by causes other than ego gratification.” [11] Harmon.
Hacktivism, exploits technology and the Internet, experimenting with the immediacy of distributable networks as a playful medium for independent, creative and free expression. There has been a gradual and natural shift from net art (and net.art) into Hacktivism. Net Art in spirit, has never really been just about art being viewed on a web browser alone. Some of the very same artists whose artwork involved being shown in browsers and making code behind the browser as part of the art, have also expanded their practice outside of the browser. One such artist is Danja Vasiliev, “Fifteen years ago WWW was something very new in Russia and besides the new dial-up aesthetics and world-wide means it brought a complete new layer of existence – “netosphere”, which made my youth.” Vasiliev very soon moved on from playing with browsers into a whole new territory. [12]
Danja co-founded media-lab moddr_ in 2007, a joint project at Piet Zwart Institute alumni and WORM Foundation. Based in Rotterdam moddr_ is a place for artists and hackers, engaging with critical forms of media-art practice. He collaborated with Gordan Savicic and Walter Langelaar from the moddr.net lab on the project Web 2.0 Suicide Machine, which lets you delete your social networking profiles and kill your virtual friends, and it also deletes your own profile leaving your profile image replaced by a noose.”The idea of the “Web 2.0 Suicide Machine” is to abandon your virtual life — so you can get your actual life back, Gordan Savicic tells NPR’s Mary Louise Kelly. Savicic is the CEO — which he says stands for “chief euthanasia officer” — of SuicideMachine.org.” [13]

Just like another project called ‘Face to facebook’ that stole 1 million facebook profiles and re-contextualized them on a custom made dating website (lovely-faces.com), set up by Italian artists Paolo Cirio and Alessandro Ludovico, whom also just so happens to be editor in chief of Neural magazine. Web 2.0 Suicide Machine, had to close its connections down regarding its Facebook activities after receiving a cease and decease letter from Facebook. [14]
Julian Oliver and Danja Vasiliev teamed up and formed the mysterious group Men in Grey. The Men In Grey explore our online vulnerabilities by tapping into, intervening into wireless network traffic. Observing, tracing and copying what we do. This hack then redisplays our activities back to us, showing the data of our online interactions.
At first no one (except myself & a few others) knew who they were. When they first arrived on the scene I started an interview with them and then suddenly, I was asked to hold back due to their antics on the Internet and interventions in public environments receiving much coverage. They were not sure how it would pan out for them. Partly due to the anonymous nature of their project, and also because of the sudden impact of the larger hacktivist group Anonymous getting much press in commercial media themselves.
“Men In Grey emerge as a manifestation of Network Anxiety, a fearful apparition in a time of government wiretaps, Facebook spies, Google caches, Internet filters and mandatory ISP logging.” M.I.G
“Spooks are listening into calls, just like they always have,” said Eric King of London’s Privacy International, in an e-mail. “With A5/1 being broken—you can decrypt and listen into 60 calls at once with a box smaller than a laptop.” [15]
Later they won the Golden Nica (1st prize) Interactive Arts category, Prix Ars Electronica in 2011. In a show called Project Space — M.I.G. — Display of unknown, quarantined equipment hosted at the Aksioma Project Space Komenskega, Ljubljana 2011. The statement read:
“The particularly threatening quality of the Men In Grey equipment is its apparently invasive nature; it seems able to penetrate – and even hack into – virtually any electronic device in its reach. While we are all aware of the wire-tapping and data retention done by the government (along with the spying carried out by corporations like Facebook and Google), Men In Grey seem to operate with a range of tools and techniques well beyond those that are currently known to be in use.”

Hacktivism involves many different levels of social intervention and engagement. Whether it is to do with direct action, self-referential geekiness, obscure networked antics, crtical gaming, or peer 2 peer and collective change. Hacktivists challenge defaults put in place by other people, usually the systems imposed upon them and the rest of us by authority. Even though the subjects themselves may be concerning serious matters, humour and playfulness are both essential ingredients.
“A promising tactic for the early Situationists was the unpredictable yet forceful potential of play — what anthropologist Victor Turner termed the “liminoid,” or the freeing and transformational, moments of play when the normal roles and rules of a community or society are relaxed.” [16] Dovey & Kennedy.
One group crossing over from the digital into physical and social realms, is Tiltfactor. [17] Their form of intervention is not necessarily about causing political controversy, but is engaged in reaching people through games of play. Experimenting with social everyday contexts, making games that tackle less traditional topics, such as public health, layoffs, GMO crops. One of the many games creating awareness on these subjects, is POX “Our game actually helps a player understand how a disease can spread from one place to another and how an outbreak might happen” says Mary Flanagan. [18]
A local public health group called Mascoma Valley Health in the New Hampshire region of the US approached Tiltfactor with the problem of the lack of immunization. “At first, a game about getting people immunized seemed like one of the most “un-fun” concepts imaginable. But that sinking feeling of impossibility almost always leads to good ideas later.” [19] Flanagan.

“Geopolitical space has always been a conflicted and fragile topic. Borders and frontiers are changing so fast, that sometimes it seems that our sociopolitical status can change from “citizen” to “immigrant” from one moment to another, or simply live under the “immigrant” status all your life. We’re getting used to words like refugees, enclaves, war, borders, limits –and the list has no end.” Ethel Baraona Pohl & César Reyes

Ricardo Dominguez collaborated with Brett Stalbaum, Micha Cardenas, Amy Sara Carroll & Elle Mehrmand, on (TBT) (and others), on a hand-held mobile phone device that aids crossers of the Mexico-US border. An inexpensive tool to support the finding of water caches left in the Southern California desert by NGO’s for those crossing the border.
“The entire group of artists who are part of Electronic Disturbance Theater 2.0/b.a.n.g. lab working on the Transborder Immigrant Tool (TBT) was being investigated by UCSD and 3 Republican Congressmen starting on January 11, 2010. Then I came under investigation for the virtual sit-in performance (which joined communities statewide against the rising students fees in the UC system and the dismantling of educational support for K–12 across California) against the UC Office of the President (UCOP) on March 4, 2010. This was then followed by an investigation by the FBI Office of Cybercrimes.” [20] Ricardo Dominguez.

In an interview with Lawrence Bird Dominguez discusses that the TBT is still developing as a gps tool, but infers that it is not just a tool but also ‘border disturbance art’, consisting of different nuances existing as part of a whole with other factors at play. Such as a hybrid mix of things, objects and expressions “artivism, tactical poetries, hacktivism(s), new media theater, border disturbance art/technologies, augmented realities, speculative cartographies, queer technologies, transnational feminisms and code, digital Zapatismo, dislocative gps, intergalactic performances, [add your own______].” [ibid]
“Borders are there to be crossed. Their significance becomes obvious only when they are violated – and it says quite a lot about a society’s political and social climate when one sees what kind of border crossing a government tries to prevent.” [21] Florian Schneider
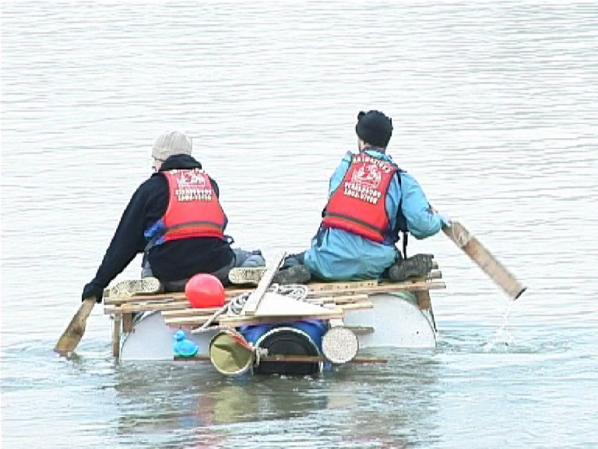

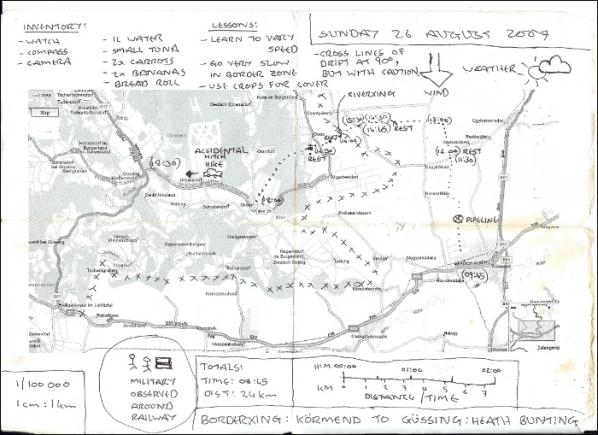
National borders are front-lines of political and social friction. The exerience of asylum-seekers and political migrants reflect some of the most significant issues of our time. Immigration is a toxic issue and unpopular with voters. Bunting’s BorderXing Guide, plays on the fear of invisible alien hordes of people crossing our borders illegally.
The context of this work fits well with issues about borders, whether it is about creating borders online or physical environments. Only those needing to cross a border are allowed access to the site, it is limited to ‘social clients’ who have a static IP (Internet Protocol) address and who, most notably, have gained the artist’s confidence. Such as peer activists and immigrants using libraries, colleges, cultural centres. The site allows those who would other wise end up crossing borders in harmful ways, such as in containers, on the backs of (and underneath) lorries and planes.
Heath Bunting’s BorderXing Guide website primarily consists of documentation of walks that traverse national boundaries, without interruption from customs, immigration, or border police. The work comments on the way in which movement between borders is restricted by governments and associated bureaucracies. It is a manual written not at distance like a google map, but by foot. A physical investigation, involving actually going to these places; trying these discovered routes out and then sharing them with others. A carefully calculated politics of public relations.
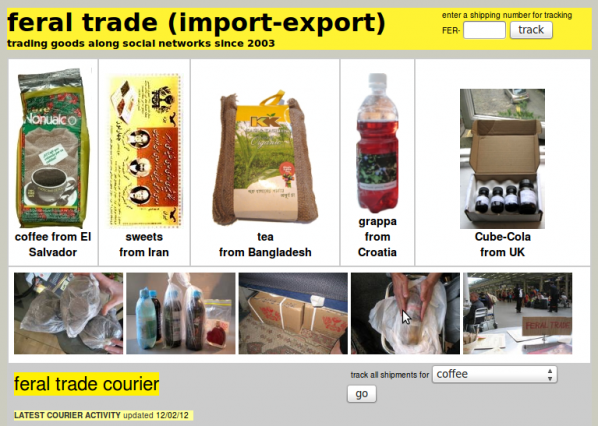
“The Feral Trade Café is more than just an art space that’s a working café, it’s about provoking people to question the way big food corporations operate by looking at the journey of the food we end up scraping into our pampered bins.” [22] Gastrogeek
Feral Trade uses social and cultural hand baggage to transport food based items between cities, often using other artists and curators as mules. Feral Trade products (2003-present), alongside ingredient route maps, bespoke food packaging, video and other artefacts from the Feral Trade network. The goods rangefrom coffee from El Salvador, hot chocolate from Mexico and sweets from Montenegro, as well as locally sourced bread, vegetables and herbs.
Kate Rich uses the word ‘feral’ as a process refering to being deliberately wild, as in pigeon, as opposed to romantic nature wild as the wolf. It is an unruly wild, shitting everywhere, disruption and annoyance in contrast to ‘official’ human structures and connected infrastructures. Feral Trade freight operates largely outside commercial channels, using the surplus potential of social, cultural and data networks for the distribution of goods. Working with co-operatives, small growers and food producers.
The Feral Trade Courier is a live shipping database for a freight network running outside commercial systems. The database offers dedicated tracking of feral trade products in circulation, archives every shipment and generates freight documents on the fly.

Every shipment is different and has its own story of how and where it was delivered from. Also included is information on who the carriers are with details about producers and their local culture as contextual information. The product packaging itself is also a carrier of information about social, political context and discussions with producers and carriers.
![Feral Trade at Furtherfield's Gallery (2009) [23] Link to exhibition](http://www.furtherfield.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/3657297700_42b1c26014_b.jpg)
Since the rise of the Internet individual and collective actions are symbiotically connected to the every day. In a world transformed, common people have access to tools that can change ‘our’ cultures independently; sharing information, motivating actions and changing situations. We know of the Arab Spring, the Occupy movement, Anonymous and Wikileaks and how successful they have been in exploiting technology and social networks. Technology just like any other medium is a flexible material. By tweaking, breaking and remaking ‘something’ you can re-root it’s function, change its purpose.
The links between these mass social movements and the artists here are not just relating to technology’s use but, a shared critique at the same enemy, neo-liberalism.
“”Neo-liberalism” is a set of economic policies that have become widespread during the last 25 years or so. Although the word is rarely heard in the United States, you can clearly see the effects of neo-liberalism here as the rich grow richer and the poor grow poorer.” [24] Martinez & Garcia.
At the same time as highlighting the continual privatization of human society. This form of art practice shows us the cracks of where a social divide of gate-keeping has maintained power within the Western World’s, traditional art structures. We now realize that the art canons we have been taught to rely on as reference are more based around privelage, centralization and market dominance rather than democratic representation or even just pure talent. Hacktivist artists adapt and recontextualize with a critical approach, towards a larger and more inclusive context beyond their own immediate selves. Demonstrating a respect and use of autonomy, and an awareness of social contexts and political nuances, freeing up dialogue for new discussions which include a recognition of social contexts, as a vital ingredient and valued resource in art. Re-aligning, reconfiguring the defaults of what art is today.