



Featured image: Fundamental Forces by Robert Henke and Tarik Barri
In its current state “Fundamental Forces” is a pre-rendered high definition multiple screen projection with surround sound. The visual component is based on Tarik Barri’s ‘Versum’ – a self-programmed computer animation engine. And the auditive component comes from Robert Henke, using MaxMSP, Max4Live and Ableton Live, a software he co-developed. It has been initially commissioned for the RML Cinechamber system which consists of 10 1080p projections and 8 channels of sound (FF00 – FF01). A later version was adapted to work with 5-6 screens and a 5.2 soundsystem. This was used during the sound:frame Festival in Vienna, and it had a highly immersive presence.
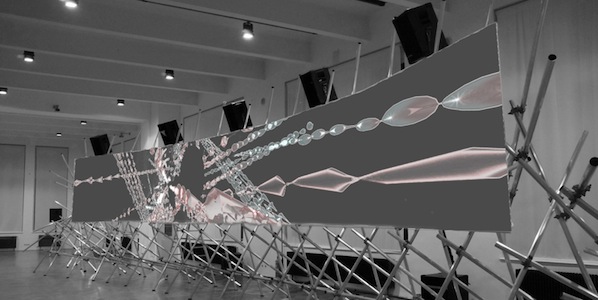
When experiencing the work I enjoyed the absence of narrative. Although I noticed some references alluding to concepts based on physics, and basic foundations of the universe. This led me to ask some questions to both artists about their “audiovisual research project”.
Robert Henke is active as composer, AV artist and professor in sound design at the University of Arts in Berlin. As founder and main member of his solo-project “Monolake”, he gained international reputation as one of the leading artists in the field of electronic club music culture. Henke has released more than twenty albums. His performances and installations have been shown and others at the Tate Modern in London, the Centre Pompidou in Paris, the PS1 in New York and the Experimental Media and Performing Arts Center (EMPAC) in Troy. His work “Layering Buddha” received an honorary mention at Ars Electronica in 2007.
Natascha Fuchs: “Fundamental Forces” is presented at sound:frame Festival this year and you worked on it together with Tarik Barri. How your collaboration has started?
Robert Henke: I was looking for Max programmer a few years ago. Tarik replied, but told me that he had no time for that, even if he would like to. However, later he sent me some video stuff he did and I thought that his work could be integrated into Monolake Live. That’s how it all came together.
NF: You call Fundamental Forces ‘an audiovisual research project’. What exactly do you call research? And how much of research involved into your life?
RH: The research part of it is simply the experimentation with the format: what kind of sound can be combined with which of Tarik’s visual ideas and vice versa. We try to find a common language. And since his work does not suggest a common narrative, we also need to come up with our own large scale structures. Where do we start, where do we stop? What kind of timeframes make sense? How can we shape transitions? Questions like this…
NF: You are involved into many different activities.. Is there anything what you like most of all? Music production, performing, visual ideas development, teaching students maybe? What gives you the feeling of ‘life is great and I am satisfied with everything’?
RH: This always changes, but I am most satisfied in moments when my own sense of achievement finds its counterpart in the perception of what I do in public. If I for myself gave a lecture which I felt was really good, and afterwards students come to me and share that notion, – I am happy. If I had a great day in the studio and afterwards play the music to some friends and they like it too, – I am happy. And if things simply do not work out the way I want to, if I have an idea, but every attempt to turn in into sound or visuals does not satisfy me, then I am most frustrated.
NF: You live in Berlin. How does the city and different generations grown up there change together with technology changes? You see many students probably for whom technology is something ready to use now, and it was different at a time when Ableton Live was not yet created..
RH: The biggest transition in general is from a situation that is characterized by a lack of tool in the early 1990s to the total abundance of tools in 2012. The question today is not: how do I do something, but rather: what am I really interested in? All is possible with current technology. Finding your personal language is the biggest challenge these days.
NF: Currently in the interview to Bleep you said that you have so many ideas to explore yourself in the next future. Could you share one of them, what is Robert Henke’s the next?
RH: The biggest project I am working on is a large scale laser and sound installation called ‘Fragile Territories’. It is a challenge in many ways; technically and artistically. I want it to be very good, it is an important work for me, and I still need to do a lot of research. Laser is a very limited media, and in order to create something that is more than a technology demo one needs to invest a lot of time thinking about what exactly to do with it and also find out how to make the best out of the limitations.

Tarik Barri is a Dutch audiovisual composer and software developer. He started programming at the age of seven and has been making electronic music since he was a teenager. After his first official musical releases at the age of twenty one, he quit his studies in biological psychology to pursue the study of music and technology at the Utrecht School of Music and Technology. During this studies he saw how the methods he used to create music could be adapted for the moving image. He programmed his own software to develop new tools for audio-visual performance, composition and data representation.
Natascha Fuchs: You live in the Netherlands, which is famous for successful promoting of media and digital arts/sound. Which Dutch institutions, festivals do you support?
Tarik Barri: I’ve been living in Berlin for a little while now, but definitely living in The Netherlands has been very very good for me to develop my work and my working methods. After I finished school, there was the WWIK, which is a government funding to help new artists develop their work. Also the Netherlands Foundation for Visual Arts, Design and Architecture helped me a lot by giving me a stipend to develop my work. Then there were organisations and festivals like TodaysArt, Sonic Acts and V2 that helped me introduce my work to the general public. Unfortunately many programs are getting cut these days in a new political climate where art in general seems to be regarded a left wing hobby for elitist snobs. Very sad, especially since I don’t agree that ‘art’ in general would be class related or have any specific political color.
NF: You were graduated from Utrecht School of Arts. What exactly did you study there?
TB: Within the Utrecht School of Arts I studied at their School of Music and Technology. And within thát school I graduated in Audio Design. It was the most technical study they had, where I learned about music programming, sound synthesis, acoustics, etc. Especially the programming courses in Max/MSP given by my teacher Marcel Wierckx inspired me to combine music, realtime visuals and programming into one discipline.
NF: What is your participation in collaboration with Monolake?
TB: Within Monolake the roles of Robert Henke and myself are clearly defined: he does the music, I do the visuals. But of course we discuss the visuals and music intensively together and there’s a constant dialog going on between both ourselves as individuals and the works that we produce. This continuous dialog has been of great value for my development in the last couple of years, both artistically and technically.
NF: The artwork which will be presented at sound:frame called ‘audiovisual research project’. What is this continuous research in your life, your aim in it?
TB: Both Robert and I constantly develop our own methods for the creation of music and visuals, and we research the aesthetical results that can be achieved through these methods. Through the combination of sound and visuals, I aim to create a sense of reality. To achieve this I’ve developed software that establishes 3d virtual audiovisual worlds. I then populate these realities with a multitude of objects of various shapes, sizes and other properties. Those objects behave according to laws taken from the real reality. While thus creating a completely new world, with its own sets of objects, elements of what we know can still be recognized within this virtual space. For me this contrast between the new and the known highlights the sense of wonder and possibility that emerges from the space between strict rules and the imagination that tries to defy and transform them. Through a window of strict and rigid laws we enter into infinite, colorful, playful, imaginary worlds.

May / June 2012: Fundamental Forces in Canada, Montreal @ MUTEK Festival
Robert Henke aka Monolake: www.monolake.de
Tarik Barri: www.tarikbarri.nl
sound:frame Festival: www.soundframe.at
(c) Natascha Fuchs is independent expert in cultural projects management and international public relations, graduate of the University of Manchester (Cultural Management) in 2008. She has been living in Vienna, Austria, studying History of Media Arts at the Donau-Universität and collaborating with sound:frame Festival for audio:visual expressions, since her move from Moscow, Russia in 2011. In Russia she was related to MediaArtLab and Media Forum — the special program of the Moscow International Film festival dedicated to media arts, experimental films and digital context with more than 10 years history. As a researcher and practitioner, she works in a variety of topics and participates different international projects focused on media arts, cinema and sound. Columnist and writer for several online magazines.
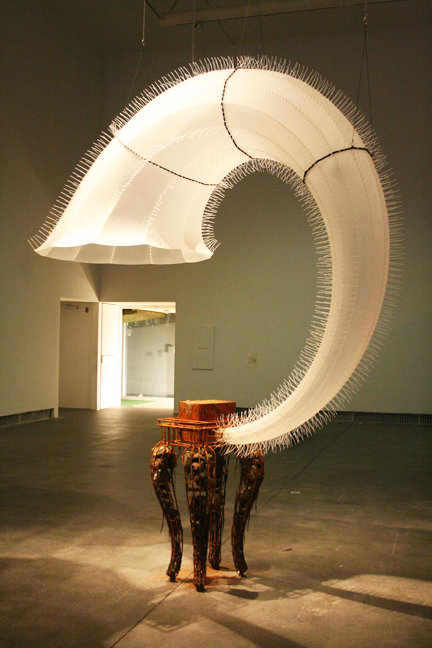
Featured image: Healing Station. mixed media, interactive installation, size variable. Christy Matson and Jon Brumit, 2009.
The New Materiality: Digital Dialogues at the Boundaries of Contemporary Craft.
March 10–June 12, 2011
Decorative Arts Gallery
http://www.mam.org/exhibitions/details/new-materiality.php
For the first half of the 20th century, curator Fo Wilson reminds us, the practice of craft was heralded as a “remedy” to how human values were changed by the Industrial Age. Here the hand-made was given privileged status over the machine-made, and thus craft forms gifted new value through the artisan. In the latter part of the last century, as the world moved from apprenticeship and artisanship to a more intellectual and theoretical-based framework for valuing contemporary art, so too have craft practices and discourses been challenged. This rethinking of craft has accelerated in the last several years, with books like Glenn Adamson’s Thinking Through Craft and Howard Risatti’s A New Theory of Craft (both 2007), both arguing for conceptual rigor and provocative possibilities within craft as a discipline.
The New Materiality: Digital Dialogues at the Boundaries of Contemporary Craft, an exhibition that began at the Fuller Craft Museum and is currently up at the Milwaukee Art Museum (MAM) until June 12, follows on and extends current trends in contemporary craft. It engages not only with craft’s reinvigoration as a creative practice and discourse, but with how these have been shaped by, and also transformed, new technologies, new designs, new materials and new ideas. Wilson’s exhibition and events make discussions around Art or Craft, Art or Design, Digital or Hand-made, and Conceptual or not seem, in a word, quaint; she engages with a broad set of materialized ideas that divide and relate across the artistry of craft, the ephemera of technology, and the theoretical frames of post-conceptual art.
The exhibition can perhaps best be summarized through the work of the four exhibiting artists/artist teams that spoke at the “Dialogues on Innovation” panel at the Milwaukee Art Museum on April 16th. Collaborative artists Donald Fortescue and Lawrence LaBianca, for example, spoke to Milwaukee activist and printmaker Nicholas Lampert about their piece, Sounding. This work consists of a huge, custom built cabriole-legged table, which was initially filled with beach rocks and sunk to the bottom of the ocean. There it lay, for two months, with a hydrophone to record the ambient sounds of the sea, including the overwhelming swish of waves, the low hum of slow-moving current, and the activity of sea life – the most prominent being the continuous clicks of what must be shrimp in its vicinity. When the artists’ creation reemerged, it brought the bottom of the ocean with it: all the messiness and stink and poetry of the sea – barnacles, rusty parts, plant life, fish scents, mystery and more. It is exhibited with an over sized hornlike funnel, a huge phonograph tied together with zip ties, to amplify the recorded sound.

Sounding, avowedly inspired by Captain Ahab’s hunt for an un-killable whale, acts as a kind of parallel to the ongoing hunt for singular disciplinary focus in craft. The piece dives into the sea, hits “rock bottom,” and looks as if it barely survived; and on its return, we see that Sounding is far from a singular entity. Yes, it is trashed and torn, but it’s also imbued with literal life, entwined with technical innovation, and rich with stories of its journeys. Like the theories and practices behind the current craft movements, it came back more beautiful, more visceral, more sensory, and more technological than it ever was: a new materiality.
You can listen to or download Sounding file here:
http://www.furtherfield.org/audio/Soundings-1.mp3
My discussion with artist Christy Matson revealed an exploratory practice that shifts between digital and hand-made, generative and interactive, and always with an eye towards the implications of each. Soundw(e)ave, her piece on show, is a self-referential textile, where the actual sounds of computerized Jacquard looms were used to create woven compositions. Her noisy sound waves were turned into three patterned pieces of fabric, made by hand-operated, computer-assisted and fully automated (Jacquard) looms, respectively – each weave growing progressively denser with the more advanced technologies used in their production. The piece, says Matson, was a huge turning point in her practice; it pointed her towards a kind of digital craftsmanship, where she was better able to place value on the ideas, materials and skillfulness needed to be an artisan across contemporary digital, craft and art domains.

Soundw(e)ave, generative weaves, triptych (each 34″ x 54″). Christy Matson, 2004.
For example, Matson then began weaving copper wire directly into her fabrics, and, using the magnetic waves our interactions generate and alter, engendered new aural compositions. In other words, her sonic sculpture turns cloth into a Theremin, where movement and hand-waving at the gallery are transformed into the kinds of musical gestures often associated with science-fiction films of the seventies. While Matson’s earlier, sound-generated works were generative and performative on some level, here she moves into real-time interaction, invoking our embodied relations to textiles, craft, technology and language, all in one fell swoop.
healing station, a collaboration with Jon Brumit and quite possibly the most complex of Matson’s installations thus far, sees piezo sensors placed inside of swaths of fabric to pick up the ambient sounds of the room – including gallery-goers, passersby, street sounds, and the minute vibrations in the fabric itself. This lovely noise is then fed back into the space with bass shakers: speakers optimized for sending waves into solid media rather than air. Viewers can literally feel the low hum of presence, absence and movement as the textile, bodies and room speak at and to one another in a perpetual feedback loop of embodied music. The small crowd at the MAM laughed along with Matson when she relayed a story in which her wired-up piece, and its feedback, caused a small fire at one of its showings – quite a performance, indeed.
Tim Tate artfully explained to Milwaukee staple Tom Bamberger that nowadays “craft” is a starting point rather than an end point. I’m paraphrasing here, but he treats craft as an approach, a space of understanding materials, what they’re good at, perhaps their “habits,” and most certainly their implications. Here, narrative, function and the conceptual are always already implicated across technique – whether new or old – and value is derived from a contextual corpus.
Tate’s work is itself a beautifully resolved hodgepodge of hand-blown glass, hi-tech LCD screens, and visceral videos of typewriters and books, all literally tied together with plastic (zip ties again – don’t knock it ‘til you try it!) around a printed circuit board. In Virtual Novelist, for example, miniature monitors display the aforementioned “dead media” tools from behind artefactual casings of glass. Atop are beguiling sculptural homages to each of the gone-but-not-forgotten analog recording devices of yesteryear.
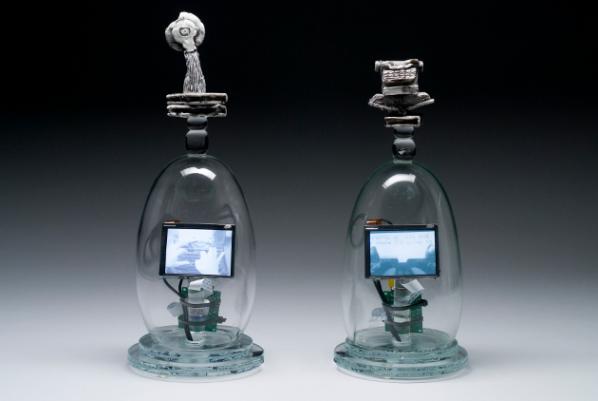

Bamberger is a smart artist with a quick wit, and Tate is similarly not one to spar with unless you have a good grasp of the discourses at hand. In this lively thirty-minute discussion, the two managed to disarm the Art vs Craft debate as both unproductive and long-since over, and open up possibilities for “ornamental aesthetics” in time-based media. Here the implication was that, following Tate’s lead, video objects and installations could place more emphasis on the object and installation – rather than the video – and use each as an equal material that informs and plays off of the other; the video and screen need not be the central focus.
Sonya Clark then told us how she views her practice as a fiber artist as similar to how author Toni Morrison views her own writing practices. In one of her essays (found in several publications, including a collection entitled What Moves at the Margin), the latter tells a story of the Mississippi River, which was laboriously straightened for travel and transport by boat. Every so often, the river floods; but, Morrison goes on, it’s not really flooding. It is remembering. The water is trying to get to where it belongs, to re-member, to embody again. Morrison says writers do the same with their texts; and Clark claims that she remembers through her materials. Originally trained as a fiber artist and now working across found objects, digital art and more, Clark’s practice sees her reclaiming forgotten histories, and giving them greater potency through her processes and media.
Clark discussed this approach with longtime friend and former colleague, UW-Madison Professor Henry J. Drewal – one of the foremost thinkers surrounding African Art. Clark’s brilliant work on the exhibition, a portrait of Madam CJ Walker, is constructed entirely out of small, acrylic and thin toothed, black hair combs. She overlays the combs and removes some of their teeth to make a huge, grayscale, and literally bit-mapped image.
Madam Walker, the first ever female millionaire in America (and African American to boot), made her fortune selling beauty products to black women hoping to straighten their hair – as was the fashion of the time. And so Clark utilizes her combs, with their own memory, narrative and political weight, to construct a lo-resolution digital image. This exceptional work manages to explicitly straddle issues of race, gender, class, memory and materiality on its very tactile surface, and implicitly engage with the contemporary conceptual frames of digital art and data, in its transcoding of the image from one form to another, and craft, in the final material and hand-made form it takes.

Clark finished with the generous idea that, at present, all art work is collaborative in that it fits into broad social and cultural contexts, builds on extant technologies, and is produced, received, and engaged with outside of the individual’s studio. And Drewal concluded by declaring that technology has always been at center of the arts in the form of new techniques. When something comes into the world, he went on, whether technical or formal or as an image, artists take it someplace else. They “turn common objects… into uncommon things, stretching our imagination and the world” along with them.

These are just a handful of the works in The New Materiality, by four of the artists represented in our discussions – not even all the works they contributed, much less those of the other artists, which include Brian Boldon, Shaun Bullens, Lia Cook, E.G. Crichton, Maaike Evers, Wendy Maruyama, Cat Mazza, Nathalie Miebach, Mike Simonian, Susan Working, and Mark Zirpel.
It is a show that, in its entirety, succeeds in stretching our imagination, through its expansion of craft, art and digital forms, and what they individually and collectively mean today.
Nathaniel Stern (USA / South Africa) is an experimental installation and video artist, net.artist, printmaker and writer. He has produced and collaborated on projects ranging from interactive and immersive environments, mixed reality art and multimedia physical theatre performances, to digital and traditional printmaking, concrete sculpture and slam poetry http://nathanielstern.com.
‘Made Real’, an exhibition by Scott Kildall and Nathaniel Stern, the founders of Wikipedia Art. Can be seen at Furtherfield’s Gallery from 27th May 2011 http://www.furtherfield.org/exhibition/made-real