



Featured Image: Black Shoals: Dark Matter’, Joshua Portway, Lise Autogena, Big Bang Data.
Big Bang Data is a major travelling exhibition currently set within London’s Somerset House. That a large institution is presenting a journey via data capture through ‘selfies, surveillance and infographics’ is in itself an interesting patchwork of intent and realisation. The aim of the exhibition is to ‘demystify data’. This is a grand, summative and in actuality slightly awkward claim which, in my view, encapsulates the character of an interesting, textured exhibition in an unintentionally astute way.
As Big Bang Data is dedicated to revealing data comprehensively through its various architectures and iterations, it makes sense for the underrepresented materiality of information to have prominence early on. This materiality, perhaps inevitably, was compromised in the gallery space. Entering the first room brings you face to face with Timo Arnall’s Internet Machine, which takes the form of multiscreen video documentation of not just the machines, but also the architecture, which supports mobile telephony.

I would have loved to have experienced the spaces shown more intimately and walked around one of these structures; the installation was illuminating but I was still most certainly watching at a remove. This initial interplay of removal and involvement is central to the way we experience data. How can people begin to understand something which exists as multiple codes and flows, on a scale and at a speed which is not concerned with making itself understood by humans? What form could an understanding of data possibly take? When learning about something this far from our grasp, it seems that ‘understanding’ must be replaced by ‘awareness’. Rather than seeking one answer via one route the visitor to Big Bang Data has to build an impression, obviously subjective and subject to change.
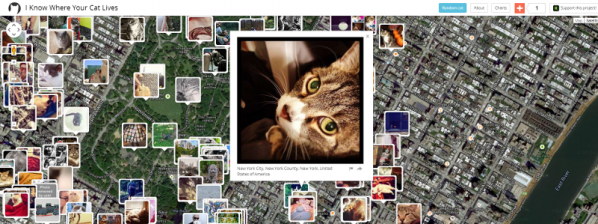
In its quest to expose and explain data’s social and cultural uses, it presents a fairly overwhelming amount of information. It is interesting to walk through the space thinking about how this information has been channeled by each specific project. Some representations, such as Owen Mundy’s ‘I Know Where Your Cat Lives’, link distant people and spaces via connected points, while others such as Phillip Adrian’s ‘One Second’ capture in great detail one specific point in time and space.

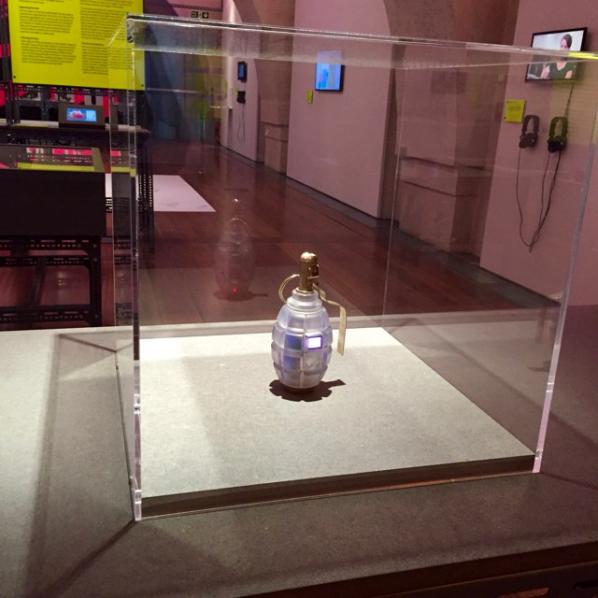
Julian Oliver’s ‘Transparency Grenade’ brings together graphical, console and physical representations of data to offer a transportable means of leaking information as a response to impenetrable governing systems. Each of the works on display demonstrates a negotiation between temporality, materiality and spatiality, and often one is sidelined in favour of the other. Again, considering the exhibition in this way is also to consider the world of data in all its contrariness.

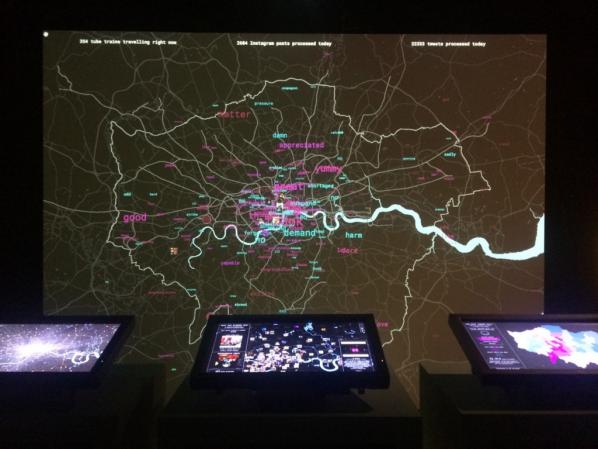
Data manifests itself at the same time locally and globally. As well as addressing specificity, the projects shown in Big Bang Data dwell repeatedly on scale. Works such as Tejka’s ‘London Data Streams’ and Nicholas Felton’s ‘Annual Reports’ pit scales against each other to cast light on the filters through which data is processed.

Ingo Günther’s ‘World Processor’ and Forensic Architecture’s ‘Liquid Traces: The Left-To-Die Boat Case’ are examples of resonant, atypical data visualisations which mutate familiar imagery and present alternative summaries of events. The section entitled ‘Data For The Common Good’ shows some of the ways data is being actively used in society to empower citizens with works such as Safecast’s ‘bGeigie Nano’ and IF’s ‘Data Licenses’, while a series of video interviews with journalists and other professionals working with data illuminate the processes through which information becomes communication.

The previously mentioned tension between object and their presentation recurs at various points throughout the exhibition, a great example being the array of undersea telephone cables, presented in cases of wood and glass which could have been magpied from a display of historical artifacts (each cable segment has a number next to it which corresponds to a factual description). It felt strange not being able to touch them. A work which I felt fully occupied, and knowingly played with, its surroundings was Ellie Harrison’s vending machine, which sits unassumingly in the gift shop; its secret is that when search terms connected to the recession make the headlines, free snacks are dispensed. Its presence in a exhibition on data in a gallery space felt appropriate.

Big Bang Data, which runs alongside a programme of events and has previously been exhibited at CCCB in Barcelona, comes at a moment where large organisations are more frequently bringing concepts such as surveillance, open source and free software into public spaces. There is a great need to bring the concepts and processes surrounding data more wholly into the public eye, and this exhibition strikes me as, overall, a big step in a good direction. It makes real and challenging efforts to bring together world-spanning processes, complex concepts and extremely diverse content into an exhibition space. The task of the exhibition’s curatorial and production teams must have been difficult.
Of course the challenges they faced have been dealt with before many times in many ways, and of course the practical decision-making involved in producing an exhibition invariably creates tension points. The reason I’ve dwelt on the problems of the organisers here is that the tensions evidenced within the space at Somerset House say much not just about the response of the publicly funded arts to data but also about the nature of data itself. The exhibition turns into at times a museum, a bedroom, a classroom, an information point, a scruffy new gallery space and a state of the art new media space. In bringing together the story of data the exhibition also brings together the story of representation in space more generally.
In writing about Big Bang Data I have had to choose to highlight certain works and not others. Your interpretation will be entirely different from mine, which is as it should be where data and cultural inclusion is concerned. What’s important is that the exhibition’s prominence and texture opens up conversation and critique. The exhibition is detailed, procedural and expansive. It is also alive with contrariness, generality and awkwardness. Perhaps one of the great things about the show is that these qualities are left to jostle for space. For me, reading this exhibition as a performative event was useful; others may leave Somerset House with an entirely different view having taken an entirely different route. This is inevitable where data is concerned – learning is incremental and procedural, but not traditionally linear.
Many of both Bitcoin’s most vocal proponents and detractors agree that the way the cryptocurrency operates technologically determines the form of the economy and therefore the society that uses it. That society would be anarcho-capitalist, lacking state institutions (anarcho-) but enforcing commodity property law (capitalist). If this is true then Bitcoin has the potential to achieve a far greater political effect than financial engineering efforts like the Euro or quantitative easing and with far fewer resources. Perhaps variations on this technology can create alternatives to Bitcoin that determine or at least afford different socioeconomic orders.
Bitcoin is already more than half a decade old and “Crypto 2.0” systems that build on its underlying blockchain technology (the blockchain is a network-wide shared database built by consensus, Bitcoin uses it for its ledger) are starting to emerge. The most advanced allow the creation of entire organizations and systems of organization on the blockchain, as Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). We can use them to help create those different socioeconomic orders.
Workers’ Councils are a Liberatarian Socialist system of organization. Rather than implementing Soviet-style centralized command economies, workers councils are decentralized and democratic. Workers in a particular workplace decide what their objectives are then appoint temporary (and instantly revocable) delegates to be responsible for them. Workplaces appoint representatives to local councils, local councils appoint representatives to regional councils, and so on, always temporarily and revocably. It is a system of face to face socialisation and political representation rather than top-down control.
This system emerged at various times in Europe, South America and the Middle East throughout the Twentieth Century. It is a very human method of governance, in stark contrast to the “trustless” code of Bitcoin as well as to the centralized politics of the Soviets. That said, technology can assist organization as easily as it can support material production. In the 1970s the cordones of Chile interfaced with the Allende government’s Project Cybersyn network, and contemporary online workers collectives can use the Internet to co-ordinate.
A DAO is a blockchain-based program that implements an organization’s governance and controls its resources using code rather than law. There can be a fetishistic quality to the idea of cold, hard, unyielding software perfect in its unambiguous transparency and incapable of human failing in its decision making. There can be similar fetishistic qualities to legal and political organizational perfectionism, this doesn’t disqualify any of their subjects as useful ideals however they need to be tempered pragmatically.
Using the public code and records of a DAO can help with the well known problem of structurelessness, and can store information more efficiently and reliably than a human being with a pen and paper. The much vaunted trustlessness of cryptovurrency and smart contract systems can help build trust in communication within and between groups – cryptographically signed minutes are relatively hard to forge although the ambiguity of language is impossible to avoid even in the mathematics of software.
The delegates of a workers’ council can be efficiently and transparently voted on, identified by, and recalled using a DAO. This makes even more sense for distributed groups of workers, groups that share a common cause but lack a geographic centre. Delegates can even be implemented as smart contracts, code written to control resource allocation and evaluate performance in the pursuit of their objective (unless recalled by the council that created them).
Entire councils, and inter-council organisation, can be supported or implemented in their organization as DAOs. Support includes communication and record keeping. Implementation included control of resources, running delegates as code, and even setting objectives for delegates programatically.

The latter finally brings the concept of DAOs into direct conflict with the spirit of the Workers’ Council. Councils exist to allow individual human beings to express and agree on their objectives, not to have them imposed from above. Being controlled by code is no better than political or economic control. It is the nature of this relationship to code, politics or the economy that is positive or negative – writing code to charge someone or something with seeing that a task be undertaken is no different from writing it in the minutes and makes mroe explicit that organization is production as the subject of work in itself. A democratic, recallable DAO that sets objectives is very different from a blob of capital with unchangeable orders to maximise its profits online.
The resources that a DAO controls need not be monetary (or tokenized). A DAO that controls access to property, energy or other resources can contribute to avoiding the pricing problem that conventional economics regarded as a showstopper for the Soviet cybernetic economic planning of “Red Plenty“. DAOs need not even be created to represent human organization – “deodands” can represent environmental commons as economic actors. These can then interact with workers council DAOs, representing environmental factors as social and economic peers and avoiding the neoliberal economic problems both of externalities and privatisation.
Workers Council DAOs – Decentralized Autonomous Workers Councils (DAWCs) are science fiction, but only just. Workers councils have existed and been plugged in to the network, structurelessnes and scalability are problems, DAOs exist and can help with this. Simply tokenizing “sharing economy” (actually rentier economy) forms, for example replacing Uber’s taxi sharing with La’zooz, while maintaining the exploitative logic of disintermediation isn’t enough.

If we are unable or unwilling to accelerate the social and productive forces of technology to take us to the moon, we can at least embrace and extend them in a more human direction.
The text of this article is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 4.0 Licence.
Featured: Toast McFarland
Synthetic bodies, mediated selves. What themes become relevant in a technoprogressive world – as objects proliferate, what do the inundated people talk about?
You are alone, at a computer. You talk to people but they are not around. There is no bar, no village square, no space in which you speak. There is your device and your physical presence. The social location is your body and its interface with the communicative device. What is the language for landscapes which can’t be seen, and yet which predicate subjectivity?
You express yourself. You are certain state statistics, a resume, you are a myspace profile long defunct. We require your legal name. Certain cards, from when you were born, from when you became qualified to drive, define you, make or break you. You are an ok person provided your paperwork is in order – morality is preceded by bureaucracy.
What’s the relationship between a legitimated self and that person’s body? The more modes of documentation we have the greater possibility for fictional aberration. The disparities between someone’s situated life and the records which make up their memory proliferate.
The image above by artist Toast McFarland was taken in a cartoon world. It is a selfie, a socially streamed validation of presence, but it is also a meticulous reframing of that practice. Everything is subtle, deceptively common, and yet the composition is entirely irreal. Flat colours, almost abstractly plain costuming, this is what happens when a vector world invades your computer room. It exists between personal expression and the self as actor within the surreal.
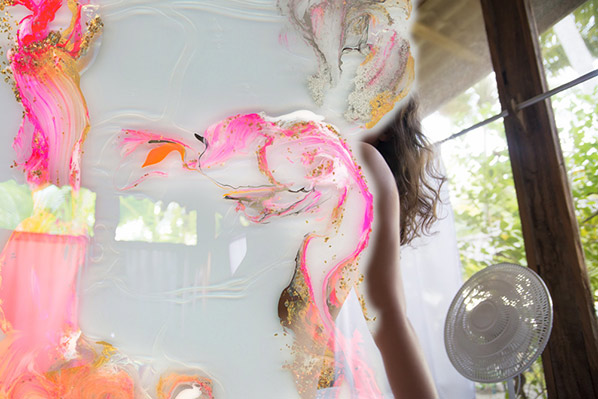
Leah Schrager‘s modelling-inspired self-portraits covered over with bright streams of paint. The model image professionalizes the act of self-representation in image form. In the profession there are industry demands – self-validation may be about confidence and friendship, where industrial success might tend towards epitomization and abstraction. Are you a good model – do you meet the sexual and aesthetic demands of the collective consumer unconscious? Schrager’s work combines a toying with such psychological implications with a background in their material underpinnings – the body in dance, the body in biological study. This combination allows for work and commentary that penetrates the relationship between the vessel you are indelibly given and the psychological relationship it develops mediated for oneself and a public.
Do you view Schrager’s images out of an interest for her or for the type of beauty she represents? Once the image is painted over, is there any interest left? Through different personas, she delivers these in a variety of web contexts, each time asking us to reconsider who we’re looking at, and who we are to look.


Screens, correspondents, professional speakers. We are happy to take your call. These two screenshots are taken from two videos by media artist Aoife Dunne. Both combine a juxtaposition of found broadcast footage, the enveloping commercial TV world, and her own crafted filming sound stages. They are installations, videos, and imagist combinations that take our question of the self directly to the media world. In the second, Dunne acts directly over top found footage, performing as doppelganger of the telemarketer in the projection. Her simultaneously comic, retro and coolly provocative aesthetic places her into an 80s infomercial dream world. She acts her own fiction, the selfie is the superlative thought experiment, and yet the proliferation of doubles buries her subjectivity in an imagined space of marketed image sheen. In the first work we only have a double, and Schrager’s biological world is fleshed out and externalized. This is what you really look like. Dunne’s own medicalized outfit says that this telecommunication is also a biological translation. For your image, we need your face, but for your face, we need organs and cells. Between the public and economic demands of the screen, and the material demands of your body, where are you?

Dafna Ganani‘s work, through a combination of images, code, social internet art and theoretical reflection, gives us an exemplar of how self-representation meets technical distortion. Her own performative presence proliferates in her work, yet always accompanied by animations, entire interactive worlds complicating any personal space. In this image, self-reflection is directly addressed – at first glance it mirrors what is represented but on closer inspection nothing of what that would look like quite match up. Where are the dragon head things located, where is she, before and after mirroring – the almost comical comparison is undermined by a disquieting sincerity. She appears intent on knowing where she is, however much the dragon doesn’t have her best interests in mind. And the right hand, reaching into the animation cloud on the left, nowhere to be seen on the right.

Dunne’s world of media culture screens is made specific and celebratory in Georges Jacotey‘s self-portraiture as Lana del Ray. An internet performance artist whose work explores media culture and self-image, the picture’s combination is both nearly seemless and parodically collaged. We all participate on some level in commercial culture, but we can never admit it. We might genuinely like aspects of it, we might hate aspects – but the popular bent of this culture means that as long as it is pleasing to a common consumer base it will gain a cultural existence. You know so much about iconic entertainers you never asked to know about. Jacotey takes on this conundrum, joins in on it, participates – what if instead of merely liking a celebrity, you seek to emulate and become them? Some people like del Ray’s albums, Jacotey’s the one who sang them. Capitalism asks that you buy, what if you take the role to sell? Human images make for great products, before we make the necessary transactions let’s make sure we know how to transform ourselves into them.
Good self-representation requires good media savvy. Before you think about your online identity simplify the process by becoming a celebrity. They’ve already figured out all the questions of the self in society – the right names, dress, mannerisms, the right look. Everything is acceptable, everything is inspiring, nothing is quite familiar.

Rafia Santana further draws out Jacotey’s comparison of the celebrity image and the selfie. Two different trajectories are taken up here – one is to deconstruct the fictions of the “real celebrity image”. The second is to fictionalize and play with one’s own portrayal. The result is layered, offering multiple points of entry for both observation and critique. If the digital image is just bits and bytes, what happens to ethnic history, to situated lives and experience? Putting herself repeatedly in her own work, Santana asks the basic question at hand – what, in re-representation, am I? And, with Jacotey, she probes the obverse of media celebrity existence and identification. If I like a celebrity, am I participating at all in their imagery or life? If so, in what way – what right to I have to their life, or in turn, what right do they have to be omnipresent in mine?
Subjectivity is the sentence, objects the fetish – be sure to glamour up.


Be sure to dress things up so you can recognize them well. Try not to mix up hair with noses, and composure with distortion. Each act of mediation further twists and reinvents our own images. You thought you knew where your lips were, what your skin looked like, but everything that goes through the machine comes out different, strange. It’s not a human, it’s a landscape. There’s an eye at the top, but you have no idea what it’s for. In the work of Sam Rolfes, the self is almost abstract, technical distortions take over any recognizable vestige of a human. Technique is everything, humanity nothing.
The self is painted, photographed, symbolized. It’s not a live image on the phone. Sometimes people in canvases try to get out. There are a few people here, all the same, that have nothing to do with one another. In Carla Gannis‘ selfie series, we return to a cartoon realism – but this time with a few added mirrors. Is the skull in the background also her? What is that a memento of?
Death in the image, life in its reproduction. You are now invisible, but we know more about what you look like than ever. Technological proliferation upends and eliminates traditional context but can never efface bodies and their identities. Indeed its societal saturation emphasizes these presences, their inevitability and all their embodied ties that digitize incompletely.
These practices work to situate the self, the body. Physiological maps are now more important than ever – they give us the image of the virtual. Mythology says we are in an immaterial age, that humans are obsolete and will be succeeded by machines. Reality says something far more disturbing – that our own materiality is the means of that obsolescence.
Some have proposed Jennifer Chan to be part of what has been termed as the post-internet era. But, this is an inadequate representation of the spirit, criticality and adventure at play in her work. Chan’s awareness and use of the Internet reflects a way of life, that situates its networks as a primary resource. Chan lives amongst various worlds and engages in different shades of being; a self-described ‘amateur cultural critic’, a net artist, a media artist, and academic. Her work exists both online and in physical realms, it is always present and contemporary. This is because her work lives in a world where the scripting of official art definitions loses its power. People have exploited technology to facilitate new behaviours where the artist or art amateur redefine what art is on their own terms. We are now in a post-art context. It reflects a very real, societal shift. Mainstream art culture no longer owns the consciousness of art, Chan and others like her are pulling it apart.
Marc Garrett: In your video Interpassivity a kind of docu-performance made for the exhibition REALCORE, you’re in a park spraying a brown cardboard box, silver. As you go through the process of walking around the box whilst spraying it, you comment on the object’s formal aspects. But, what you mainly discuss are your own personal views about contemporary art. It then becomes apparent that the box is a prop for the performance, enabling the subject to be explored.
Alongside your interpretations of the work my own thoughts on the subject feel as though they are included in the conversation. I know as a viewer, that the artist is not aware of my thoughts on the matter. However, it feels like there is space for me to be a part of the conversation. Not literally through a feedback system or interaction, but as an individual considering your personal questions. The artwork knows I am experiencing it, it knows that a consciousness out there is somehow engaging with its dialogue.
It is clear you are in tune with the feeling of dysfunction. You say, “I need to spit out some creative truth”. On hearing this, I was not sure whether this was a parady, irony or an expression of despair, or all these. You also say “contemporary art is removed from our everyday feelings”. As you express these words I begin the view the box as a symbol of contemporary art as a centralized, institutional monolith? So, before I unwittingly place my own meanings onto the work could you tell us what it means to you?
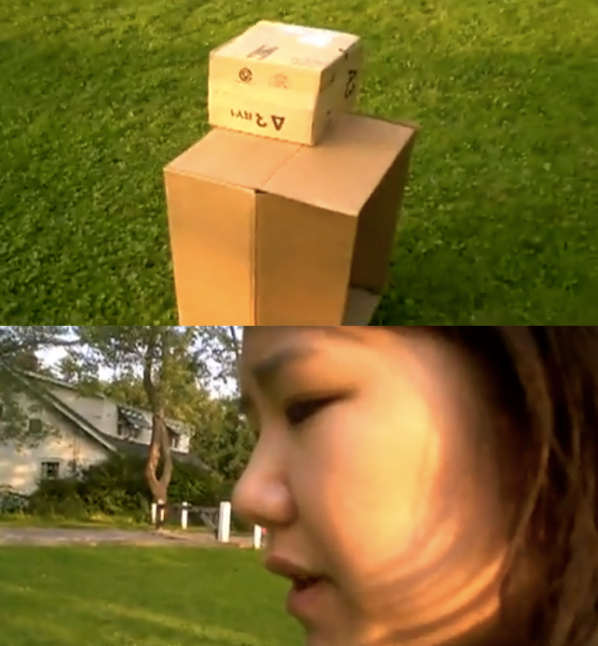

Jennifer Chan: Interpassivity is the instance of something cueing an audience to feel a certain way, such as canned laughter to stand in for humoured social reaction to jokes in a sitcom– even when it’s not funny. I titled it that because I felt like another art student trying to convince herself or the viewer what she made is art. I feel embarrassed about this self-aware but privileged complaining. A few people have found this work online and screened it, but I’m still mortified to watch it with them.
I made that video because I think a lot of contemporary art is sterile, mannered and removed from emotion. I wasn’t thinking of Donald Judd at that point but I could see the box standing in as a poor attempt at work, like his work. What I was working on (or seven years of art education) had little to do with what was happening in my life. (So to answer your question, yes, it is despair) Using my flipcam and talking over it was immediate for recording those ideas. It’s also a big trope of Canadian video art… a breathy voiceover conveys something serious and personal.
re: REALCORE. The title came about as a play on the idea of “real life”, or face-to-face life away from keyboard. Likewise, users would say “irl”(in real life), or “so real~” in Facebook comment threads to joke about the divide between online/offline contexts. The curator David Hanes felt the video was important to contextualize my use of sincerity and clichés, I was not being ironic in my intention. Arielle Gavin and Jaakko Pallasvuo thought it was questionably ironic and an emotive perspective on the Internet as a form of new sincerity.
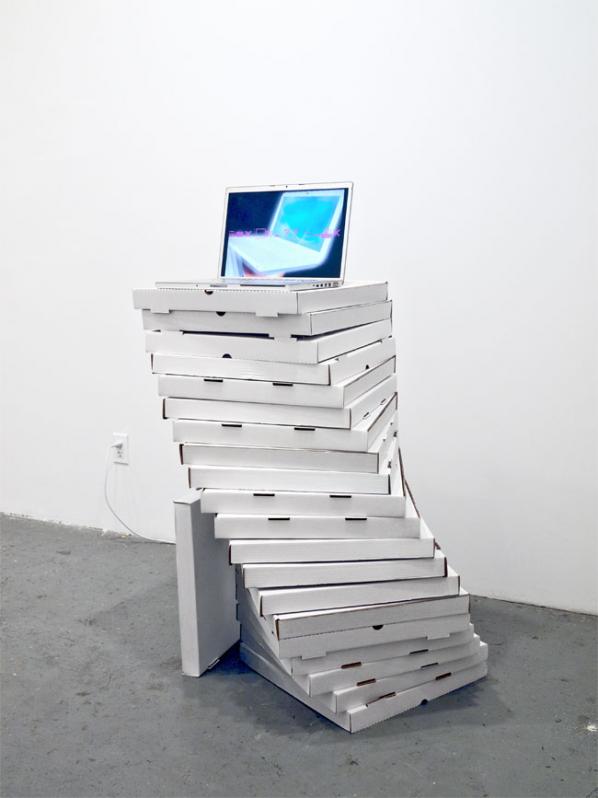
I later found that someone wrote a paper by someone who coined “realcore” as a kind of amateur user-generated porn, which is a cool double-meaning. The “interpassivity” video was used to promote the show online but I showed my kitschy found footage videos on twisted pizza box plinths for the show. This was my fuck-you to geometric minimalism and boring white plinths, but I suppose it resulted in a different take of it…

MG: In one of your recent videos “Grey Matter” when watching it felt like I was immediately pulled into a remixed world of teenage celebrity, products and brands, dripping in an orgasmic noise of techno-capitalism. Most of it is found footage, images, video and sound remixed into an edited compilation. Running through the video in between the high octane fuelled cuts and glitches, are messages to the Internet user who chances upon the video. These messages feel like they are from an individual voice but also of a multitude – caught up in a constant state of mediated folk hedonism.
What intentions lie behind this work as an artistic explorer of the entertainment culture you have remixed?
JC: Grey Matter is a first person account on feeling politically inactive online while having access to a wealth of information. I wanted to use remix in a confessional manner, so I combined obscure nostalgic media with embarrassing statements. The video begins with sped up footage of early 3D simulator ride called “Millennium Bug”. Y2K was the first technological “crisis” I recalled with clarity when I was growing up. The rest of the video includes cynical commentary on online spaces I’ve engaged with in the past year. (shopping on aliexpress.com and lurking people on OkCupid) “Little Prince” is compressed 25 times and sped up by 400%. I included old profile pics and some summary text from my OkCupid profile–I thought it was quite telling about how I wanted to be seen online and irl. I think it’s possible to feel mutually exclusive feelings at the same time, or maybe the experience of being active on different social networks produces a kind of schizophrenia. Collaging Internet pop culture is a way to appreciate it-as artifacts-in a complex light, and to be critical of it by acting out within its language.
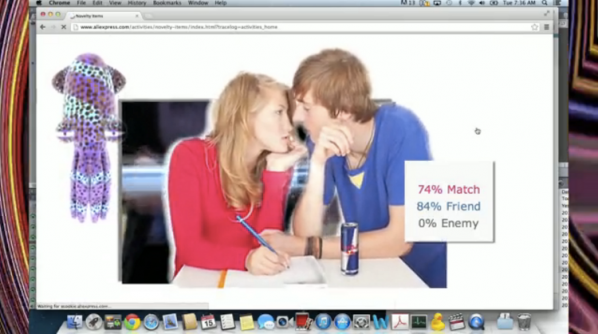
MG: What do you find fascinating about popular culture on the Internet?
JC: Anything minuscule has the potential to be popular amongst disparate users and they form vernaculars to talk about their interest in that. I find that desire relatable. That is what I think of as “community” online. It’s based on human interest and media fandom. Justin Bieber is made into something of a scapegoat for the first world’s shortcomings; people who like his image/music idolize him, and people who hate him are waiting for him to crack. Both are forms of fanaticism (one based on affinity; the other on hate-watching something.) Supercuts of Justin Bieber hairflips, object crushing fetishists, disease forums, long threads debating a detail…etc. I like the solipsism and intensity of all that.
MG: Can you share with us some of your critical insights and personal pleasures on this subject?
JC: Pop culture is paradoxical and audiences selectively enjoy it. (like teens dancing to hip hop with irreverence to its violent or sexist content.) Consuming and sampling pop allows people to indulge into its meanings, and through this there is a reconsideration of what “the masses” find important. Like the use of “users”, “masses” is what cultural studies calls everyone or everyone except-you. But every “user” has a specific relationship with interfaces and platforms, so they aren’t so homogenous.
Pop culture is also political. There was a time when more people voted for American Idol than the US elections, and if 10,000 people showed up to the 2012 cat video festival, entertainment is generally more seductive than current affairs–until there is a gatekeeping emergency (like mainstream media not covering the early days of Occupy). In terms of “internet pop culture”, perhaps traffic with social networking has overtaken porn and gambling online, but social news is also a kind of entertainment.

MG: Olia Lialina and Dragan Espenschied in their book Digital Folklore they celebrate everyday people’s use of personal computers with “glittering star backgrounds, photos of cute kittens and rainbow gradients”. They value the non-professionalism and amateur spirit that has come about from millions of people enjoying the Internet since it started. There is a difference now, the Internet masses have been shifted and prodded into large web 2.0 frameworks such as Facebook, and an abundance of personal web projects have been lost since.
And, like them do you find reassurance or a personal connection with the Internet Amateurs of the world?
JC: In context of new media art, it’s probably more accurate to think of amateurs as people who don’t self-identify as artists or technicians. What non-artists do with software and video appears facile, sincere, and intuitive. I make amateur-looking work to dialogue with that.. I like to say something dumb to say something serious. Something that’s made simplistically and filled with kitschy references can be packaged as critique that also appeals to non-art audiences.
I caught the tail end of the homepage-o-sphere/webring 1.0 period. Non-artists made personal websites out of a genuine interest in something. tumblr and pinterest is used in a same way today–to collect indiscriminately. Like 2.0 frameworks, the early internet also had free webpage hosting that users relied on (Geocities and Lycos). Personal website design isn’t over either; net artists still make them or bind together to create their own sites (like tightartists.com). I think I have an idea of what you mean though; it was less commercial and there weren’t as many distinct “most-visited” places online.
I made a lot of gothy dark art on DeviantArt before I knew about contemporary art, and my sensibility towards Photoshop was more romantic and impulsive without the baggage of art education. Maybe this “revival” cult of amateur-looking digital folklore happened because I/we exoticize that kind of amateur production. Web vernaculars have also become stylized and this aesthetic is shared with seapunks and filmmakers. Artists need to adapt to that.
MG: What do you feel is still alive and open for everyday online expression and play, in respect of what Lialina and Espenschied perceive as Digital Folklore?
JC: I think a lot of emerging artists have a greater awareness of obsolescence and upgrade culture than we give them credit for–while still complacent to the socialization structures on Facebook. Many seem more interested in navigating these networks to question their inner control mechanisms than overthrowing them or innovating new ones. It can be simple things like friending as many users as possible, looping webcam feeds, archiving and re-uploading banned content on different platforms, having an anonymous/alternate personas/using multiple accounts…etc. People like glitchr and Ian Aleksander Adams are always looking for ways to use a system against its intended functions in the same way jodi did all the cheat moves in max payne CHEATS ONLY. I admire glitch practices for that.
There’s also the possibility for re-appropriating anything to rebrand or critique particular communities. I think Angela Washko and Jaakko Pallasvuo are doing this in a compelling way that covers a large territory between art and Internet culture.
MG: So, what are you working on at the moment?
JC: <–for some reason this sounds less perverted than if I were an old guy doing this to teen girls but its really just as perverse–>
I’m observing what young adult/teen boys do on YouTube: bulking up, performing dares, talking about how to pick up a White/Asian girls etc. I’m also making a video about Asian guys (both diasporic, Asian American, and more specifically, Korean and Taiwanese men) and their interpretations of mediated masculinity. There is something disturbingly tantalizing in terms of how they have learned to look at the webcam as if they are boy band stars yet they are not fully grown men. A lot of this is informed by growing up in Hong Kong, and knowing that fashion and romance, is inspired by many “neighbouring” cultural media from Japan, Korea and Taiwan even though American/British influence is also prominent in the club scene.
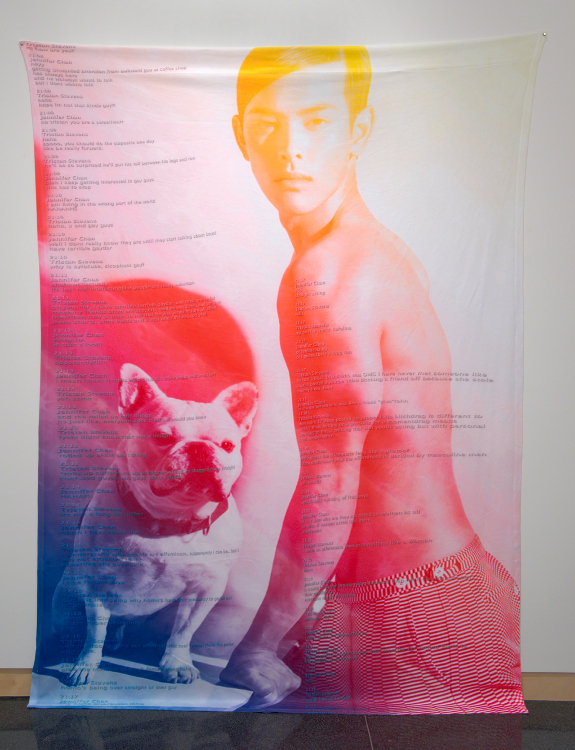

Here are two images from my late installation that will foreshadow this interest. It’s chat text over layered on modified fashion and makeup adverts targeted at Korean and Chinese men, and printed onto micro-fibred bedding. I feel like they’re treated as pleasant freak shows on tumblr but this imagery is a banal, idealized kind of masculinity in Asia. I think western facial features are really common amongst these popular images of Asian-ness, and most would tend to read it as aspiring to western culture, though the hyperfemme “doll” look or metro-masculinity has been a regional style since the 90s.
Chan’s work reflects an emerging condition described by Zizek as “interpassivity” in which our engagement with interactive experience has lost traction and is replaced with “its shadowy and much more uncanny supplement/double “interpassivity””[1], a “Fetish between structure and humanism”[ibid]. We are pulled into a paradox, where ‘interaction and passivity’ are joined together as spectacle of constant mediation. Millions have joined online centralized, megastructures such as Facebook, and this is not a black and white situation. Many are coerced from social and consumer pressures into the state of being seen as interacting. As the futuristic time machine streams onwards at high-speed, agency slouches into a spurious and distant dream. Others and the same are enjoying the flow for the sake of self expression within these scripted frameworks.
Chan’s work critiques, plays with, and exploits this networked, social intervention, as well as her viewers’ desires. Her imaginative palette revivifies questions about agency, passivity, sexuality, privacy, individuality, behaviour, networked consumption and its production. These remixed artworks have much material to work with, as the endless ether of everyday noise is uploaded and distributed through blogs and social networking sites; then returned into the ether as cut-ups where a transforming culture is engaged in its own mutation.
Its noise engages us whether we enjoy it or not, in the medium of “interpassivity”, and we all find ourselves caught within this spectacular enticement driven by the Netopticon. “On a holiday trip, it is quite common to feel a superego compulsion to enjoy, one “must have fun” — one feels guilty if one doesn’t enjoy it.”[ibid]
Jennifer Chan – http://www.jennifer-chan.com/
Heavy MetaVernacular video after the popularization of the internet
http://jennifer-chan.com/index.php?/curatorial/heavy-meta/
SELF-LOVE A non-consensual exhibition of emerging net art
http://jennifer-chan.com/index.php?/curatorial/self-love/
New Insularity Peer backpatting. A screening of works by friends and users whose works I admire.
http://jennifer-chan.com/newinsularity.html
Feeling VideoThe affective appeal of antisocial video
http://jennifer-chan.com/index.php?/curatorial/feeling-video/
Trivial Pursuits Distracting “new media art”
http://jennifer-chan.com/index.php?/curatorial/trivial-pursuits/
It’s a bizarre thing when you stumble upon the “new art movement” filtering through discursive chatter. Is it actually a movement, or is it simply a bunch of like-minded individuals telling me its a movement?
Behold The New Aesthetic then – a new art meme in visual culture whimsically constructed by James Bridle, which manifests itself in a Tumblr blog, a presentation for Web Directions South, Sydney and an original blog post. Recent attention to it has reached feverish proportions coming off the back of a SXSW panel in March and a generally positive endorsement by Bruce Sterling in Wired, plus some group responses on the creators project. More recently, the computational media scholar and philosopher Ian Bogost has posted his own thoughts for The Atlantic.

As a meme should do, “the New Aesthetic” has fulfilled its role – it has a lot of people talking about it. Like any meme which dices visual culture with some sort of research element, it has artists, writers, even media and aesthetic scholars measuring their own opinions on it in rank order without anyone knowing exactly where it’s going, what it really is or who exactly is doing it. In our noisy and crowded “I can’t believe I got 50+ retweets” over-networked epoch, this is quite an achievement even if you don’t take it that seriously.
But here’s the question: can the new aesthetic be more than a meme? More to the point, does it want to be? Is it capable of a direction? Can it be serious?
That said (and as Bridle avers) this isn’t really a prominent “movement” of ideas as such. Neither does it present material which it would deem ‘arty’. Instead, it’s an extremely broad and oblique orientation which seeks to document the subtle (and sometimes explicit) changes within our information saturated existence. It simply contextualises the contingent manifestations of computational activity, and how they are reversing and revising computational and human activities back in on themselves. Bridle’s tumblr simply presents the new aesthetic for what it is, much akin to perusing through pictures in a Facebook profile, a Reddit top ten list or clicking on Stumbleupon – simple snapshots of “stuff” which echo a blurring between the world of networks, machines and everything outside of it (with a particular emphasis on where it goes a bit wrong, hence a certain infatuation with glitchyness). Quoting Bridle’s Tumblr page;

“It is a series of artefacts of the heterogeneous network, which recognises differences, the gaps in our overlapping but distant realities.”
In another video presentation ‘We fell in love in a coded space‘ at Lift12, Bridle terms this ‘network realism’ – instances where the amalgamation of computational networked activity blurs with non-computational activity, to such an extent that it reduces any observer to nothing but a curious, passive node, gleefully whittling through instances of vaguely creative stuff. For Bridle, this occurs not just in industry but also architecture, finance, storage, fashion and now an attempt at aesthetic understanding. It’s an infatuation with the alterity of bots, algorithms, pixels and realised fictions. In this presentation however, Bridle is largely concerned with how one can respond or understand the ‘desires’ of bots, unaware that anthropomorphising the situation may not reap the rewards required. In this interpretation the new aesthetic is charged with the task of asking how we can think and orient ourselves computationally, whether it be designers, thinkers, writers, scholars or artists.
Sterling himself, mostly issues praise with a pinch of amusing impatience, as if the New Aesthetic movement should progress faster than it actually is doing, with more ideas and more focus. Kyle Chayka states that artists are already embracing it as a ‘contextual seedbed, rather than a label’. Jonathan Minard understands it as a new method of reflection concerning cultural tool-making, where the ‘dumb tools’ of machinic interface scream images back at us.

Digital Humanities scholar David Berry has blogged a similar view echoing that the new aesthetic is tapping into what he calls ‘Computationality’, a historical paradigm frame-making of sorts, which constructs specific meaning-making practices. Visualisation revolves around processes and patterns and so the list making exercise of Bridles’s Tumblr blog would seem apt in this regard, as it issues unparalleled amounts of pattern making not just as content, but as form. The archive is a jamboree of other pattern recognising events; security face recognition, retro 8bit encapsulation, satellite visuals and generally messing about with an Xbox 360 Kinect. James George mentions something similar but suggests that the new aesthetic should question the critical distance between artistic activity and technological use. It resembles a massive screen dump from a digital artist’s delicious account. Quoting Bridle again in an interview with The Design Observer Group;
“The New Aesthetic is not criticism, but an exploration; not a plea for change, rather a series of reference points to the change that is occurring. An attempt to understand not only the ways in which technology shapes the things we make, but the way we see and understand them.”
To most of the established readers here, it’s easy to criticise the “newness” of the New Aesthetic, in the same way the 90’s trope “New Media” has been quickly bundled away as if it never existed (Marius Watz makes this point). For those of you who have been studying such issues concerning hacking, play, enumeration, collecting, remixing, glitch-ing, (see Rosa Menkman in particular) in the broader realm of the computational arts, there really isn’t anything novel to gawk at: this is more of a rearrange or a rebadge. Indeed, internet discussion has been rife with such criticism, from the triteness of using Tumblr as the ‘official site’, to quick dismissals concerning the New Aesthetic’s distinct lack of any historically serious ‘substantial practice’ – not that it wanted it in the first place (Indeed it’s a pity that it has contingently replaced an identical term for a movement unrelated to Bridle’s own, coined by arts writer Michael Paraskos and realist artist Clive Head. Moreover, depending on how one looks at it, Paraskos and Head’s own movement has similar views espoused by Bridle’s version, including perhaps a direct opposition to conceptualism and foregrounding art as a material practice).
If Bridle were not so sincere about the whole affair, one would be mistaken that this was a too-cool-for-school strategy straight out of a Nathan Barley episode. But thats an easy misread. As Bogost states, Bridle is just curious about the weirdness of the network we all rely on and revel in. But there is a point where fascination with creativity turns into ADHD. The New Aesthetics tumblr site, already does just that, without any hint of standing still. “What’s going to come next? What can we do next? What are the limitations? What happens if I click that? What is that doing there?”
However both Bogost and Greg Borenstein issue a different view about the new aesthetic. They both discuss it in relation to a recent trend in philosophy called Object Oriented Ontology (OOO), a movement to which I am extremely sympathetic to. Bogost explains OOO succinctly enough;
“If ontology is the philosophical study of existence, then object-oriented ontology puts things at the center of being. We humans are elements, but not the sole elements of philosophical interest. OOO contends that nothing has special status, but that everything exists equally–plumbers, cotton, bonobos, DVD players, and sandstone, for example. OOO steers a path between scientific naturalism and social relativism, drawing attention to things at all scales and pondering their nature and relations with one another as much as ourselves.”
The link to OOO is fairly self-evident. If one of the most prominent aspects of the new aesthetic is an obsession with how a machine “sees” the world, OOO is a commitment to the seeing of things in widest possible sense. But while Borenstein generally aligns OOO to the new aesthetic with exuberant equivalence, Bogost’s view is one of general optimism, but not broad acceptance. For a start, the new aesthetics is based on a continual divide and repair between two opposing realms; the physical and the digital, each coming together and breaking apart endlessly, like throwing a box of magnets.
One of the main stipulations of being an OOO advocate is the realist eruption of what counts as a thing, and how that thing contingently relates to different types of entities. This is why Bogost decenters computation in the new aesthetic, and emphasises the multitude of things that escape the physical/digital divide. Their adventures are always-already strewn across the ontological landscape. One of the other main stipulations involves us lacking secure knowledge in fully understanding discrete units on their own terms – we can never experience their being in the same way we experience our being.
If one has read Bogost’s latest publication, Alien Phenomenology (and if you haven’t, I’d urge you to do so immediately), one would understand Bogost’s view that the new aesthetics misses out not just speculating on the hidden lives of objects other than computers and humans, but it also hovers on the inescapable problem of anthropomorphising machines and objects to within an inch of their lives. The alien aesthetics challenge is provocative.
“[T]his Alien Aesthetics would not try to satisfy our human drive for art and design, but to fashion design fictions that speculate about the aesthetic judgments of objects. If computers write manifestos, if Sun Chips make art for Doritos, if bamboo mocks the bad taste of other grasses–what do these things look like? Or for that matter, when toaster pastries convene conferences or write essays about aesthetics, what do they say, and how do they say it?”
There is an interesting discussion to be had in OOO about the usefulness of anthropomorphising the infinitesimal non-human relationships between the properties of things. Whilst others (including Bogost) see it as an inevitable factor of being one finite human entity amongst a crowd of other finite entities, I see it as a hinderance.
In particular, I’m interested in the way the new aesthetic never manages to access computation ‘just’ as it is. It only takes computation seriously when it functions as a qualitatively intelligent system, which meets or surpasses rational intelligence, or, it directly flips into “dumb tools” of (mis)communicative manipulation for the whims of human mental acts.
But I digress. Last year Bridle released a book called “Where the F**k Was I?”, which accurately sums up the mentality of the movement. The really interesting element of the new aesthetic is that it presents genuinely interesting stuff, but Bridle’s delivery strategy is set to ‘gushing disorientation’. At present, it’s the victim of the compulsive insular network it feeds off from. It presents little engagement with the works themselves instead favouring bombardment and distraction. Under these terms, aesthetics only leads to a banal drudgery, where everything melts together into a depthless disco. Any depth to the works themselves are forgotten.
Memes require instant satisfaction. Art requires depth.