



Choose Your Muse is a series of interviews where Marc Garrett asks emerging and established artists, curators, techies, hacktivists, activists and theorists; practising across the fields of art, technology and social change, how and what has inspired them, personally, artistically and culturally.
Ryota Matsumoto is a principal and founder of an interdisciplinary design office, Ryota Matsumoto Studio, and an artist, designer and urban planner. Born in Tokyo, he was raised in Hong Kong and Japan. After studies at Architectural Association in London and Mackintosh School of Architecture, Glasgow School of Art in early 90’s, he received a Master of Architecture degree from University of Pennsylvania in 2007. Before establishing his office, Matsumoto collaborated with a cofounder of the Metabolist Movement, Kisho Kurokawa, and with Arata Isozaki, Cesar Pelli, the MIT Media Lab and Nihon Sekkei Inc. He is currently an adjunct lecturer at the Transart institute, University of Plymouth.
Marc Garrett: Could you tell us who has inspired you the most in your work and why?
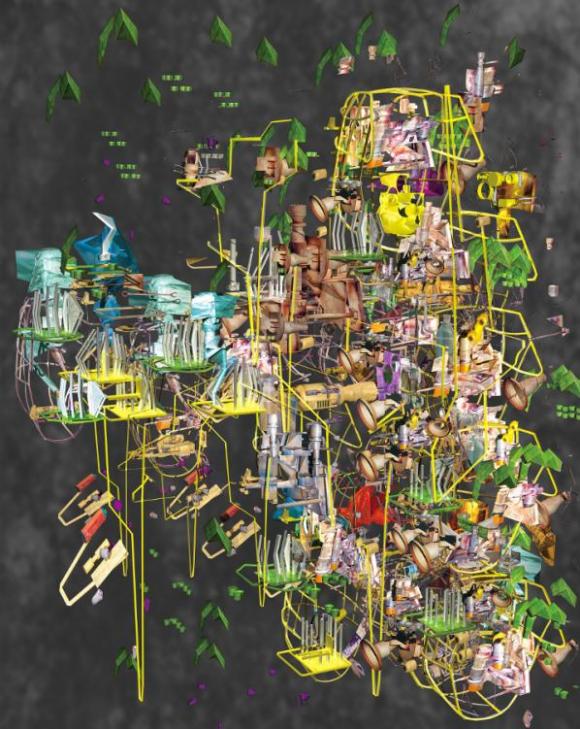
Ryota Matsumoto: As I have collaborated with the founders of the Metabolist movement of the 60s, Kisho Kurokawa and Arata Isozaki, and had the opportunity to meet Cedric Price at Bedford Square, I am keenly aware of the participatory techno-utopian projects by the Situationist International group. Some of the projects by Japanese Metabolism, Yona Friedman, and Andrea Branzi drew inspiration from the concept of unitary urbanism and further developed their own critical perspectives. Their work has helped me to create my own theoretical platform for the status quo urbanism and its built environment.
MG: How have they influenced your own practice and could you share with us some examples?
RM: I identify with the free-spirited and holistic approaches of these theorists on the relationship between language, narrative, and cognition. They embraced a wide range of media for visual communication that simultaneously defied categorization as either art or architecture and denounced the rigid policy-driven urban planning. Who would have thought of using photomontage, computer chips, PVC, or anything else they could get their hands on for architectural visualization in those days? Furthermore, their urban strategy of mobile/adaptable/expandable architecture and the theory of psychogeography dérive resonate with my own creative thinking. I interpret urbanization as the outcome of self-generating, spontaneous and collective intelligence design process and believe that the strategic use of hybrid media with incorporation of multi-agent computing provides an alternative approach for both art and design practice.
MG: How is your work different from your influences and what are the reasons for this?
RM: The utopian aspirations of the groups in the 60s were very much the product of the counter-cultural movement of the time: they were politically engaged and had optimistic outlooks for technology-driven progress of cities. In contrast, while I tend to address the current socio-cultural agendas of urban and ecological milieus, my work doesn’t necessarily evoke or represent the utopian or dystopian visions of spatial cities.


MG: Is there something you’d like to change in the art world, or in fields of art, technology and social change; if so, what would it be?
RM: I explore and question both sustainable and ethical issues of the urban environment that have been influenced by the socio-political realities of the Anthropocene, using visual/cognitive semantics, analogical reasoning, and narrative metaphors. As human population and energy use have grown exponentially with great acceleration, the interactive effects of the planet transforming processes on the environment are impending issues that we have to come to terms with. Thus, my projects hinge on how trans-humanism, the emergence of synthetic biotechnology, and nano-technological innovations can help us respond to the current ecological crisis.
“The themes of my work hinge on how the scientific tenets of trans-humanism, the emergence of synthetic biotechnology and Nano technological innovations might respond to the Anthropocene epoch, and, eventually foster critical thinking in relation to the underlying agendas of the increasing dominance of human-centric biophysical processes and the subsequent environmental crisis.” [1] (Matsumoto 2017)
With my recent work, the symbiotic interplay of the advanced biosynthetic technologies and the preexisting obsolete infrastructures has been explored to search for an alternative trajectory of future environmental possibilities. In short, new technologies can complement old ones instead of completely replacing them, to avoid starting over from a blank slate or facing further ecological catastrophes.


MG: Describe a real-life situation that inspired you and then describe a current idea or art work that has inspired you?
RM: I was fortunate enough to experience firsthand Hong Kong’s rapid urbanization driven by the staggering economic growth throughout 70s and early 80s. In hindsight, it could be called the beginning of rising prosperity in the Pearl River Delta region. I was fascinated by the fact that both the unregulated Kowloon Walled City and the newly-built Shanghai Bank Tower stood only a few miles apart from each other around the same period. They could be seen as two sides of the same coin, as they both represented the rapid and chaotic economic growth of Hong Kong at that time. It suddenly dawned on me that the juxtaposition and coexistence of polar-opposite elements connoted both visual tension and harmony in a somewhat intriguing way, regardless of their nature, function, and field. That contradiction nurtured and defined my own aesthetic perceptions in both visual art and urban design.
MG: What’s the best piece of advice you can give to anyone thinking of starting up in the fields of art, technology and social change?
Although it might sound like a career detour at first, it is always helpful to go off the beaten path before starting out as an artist. In my case, my experience as an architectural designer and urban planner certainly helped me to break the creative mold and approach my work with a broader perspective. Even now, I still firmly believe that it is always helpful to learn and acquire the wider knowledge and skills from other fields, and that opening up your mind to new ideas will allow you to discover your own unique path in your life.


RM: Finally, could you recommend any reading materials or exhibitions past or present that you think would be great for the readers to view, and if so why?
The retrospective of Le Corbusier’s work is the last exhibition I’ve seen and it was very fascinating. He is a great innovator, who had managed to continually reinvent himself to stay ahead of the curve over the course of his life. If you are interested in 20th century architecture encompassing early modernism and the Brutalist movement, it is definitely worth visiting.
Featured image: “Binoculars” at CHB in Berlin (2013)
Varvara Guljajeva & Mar Canet have been working together as an artist duo since 2009. They have exhibited their art pieces in a number of international shows and festivals. As an artist duo they locate thermselves in the fields of art and technology, and are interested in new forms of art and innovation, which includes the application of knitting digital fabrication. They use and challenge technology in order to explore novel concepts in art and design. Hence, research is an integral part of their creative practice. In addition to kinetic and interactive installations, the artists have also experience with working in public spaces and with urban media.
Varvara is originally from Estonia, and gained her bachelor degree in IT from Estonian IT College, and a masters degree in digital media from ISNM in Germany and currently is a PhD candidate at the Estonian Art Academy in the department of Art and Design. Mar (born in Barcelona) has two degrees: in art and design from ESDI in Barcelona and in computer game development from University Central Lancashire in UK. He is also a co-founder of Derivart and Lummo.

Filippo Lorenzin: Open culture is one of the main points of your research and activity. Could you describe how this influences your art practice?
Varvara & Mar: We are living in very exciting times. Open source has introduced democratization of production and creation. Now you can build your own 3D printer, laser cutter, knitting machine, make a light dimmer circuit or develop a body tracking system. Some years ago we couldn’t even imagine this and now we have access to this knowledge. People share their creations and these process, which is incredibly inspiring for us and many more people. Thus, knowledge is built on top of knowledge. We make use of open source marterial in our work and we try also to contribute back. This is the whole point of open source in our mind. And if one looks in the perspective of art to open source projects, then really many open source projects have artists on board, for example, OpenFrameworks, Processing, and more.
Open source also has an educational aspec. We do many workshops with people and teach what we know and how we work. We think open source culture is largely based on the spirit being open to sharing knowledge with many others.
FL: I’m really fascinated by your interest in textile fabrication. it reminds me the early industrial developments that were deeply connected to in the textiles industry. How and why would knitting be integrated these days as part of a makers’ culture?

V&M: The process of integration is well under way. There has been a good number of makerspaces who have dedicated areas for textile production, like WeMake in Milan and STPLN in Malmö. And believe it or not this simple thing helps to introduce gender balance in these kind of places. We’re not just talking about innovation, which can boost gender equality when you introduce knitting to hacking. We’re also talking about the democratisation of production, when thinking about clothing too. This area is quite vital and commonly understood. 3D printing toys is a cool activity for a weekend, but then it becomes boring. Knitting a sweater or a scarf has real value and the quality is always higher than a typical mass produced factory product.
For 3D printing we cannot say the same. Don’t get us wrong, we are not against the 3D printing. We love it and have six printers in our studio. Our point is that the areas of concern for digital fabrication are not complete, and the founders of FabLab have overlooked the whole area of textiles.
FL: You’ve run many workshops taking in account various topics such as 3D printing, solar energy and knitting, of course. How do these activities connect with your research?

V&M: First of all, we like to teach and interact with our students. Second, preparing a workshop, allows us to research more about the field, and organise and share our accumulated knowledge and experience.
And finally, workshops are one part of our income. We don’t have any other jobs on the side, and exhibitions and commissions are not regular and do not always pay well, and yet the bills keep coming in. Hence, workshops help us to pay our bills.
FL: One of your works which most fascinate me is “Sonima” (2010). It’s a project that takes in account questions that have become quite recurrent in last months, mostly linked to Anthropocene discussions. The soft coexistence of technology and nature which is organic and artifical. Which is one of the main topics of your research: why are you so interested in this question? It looks like you’re trying to develop experiments for an utopistic future in which humans and nature live in symbiosis. Am I wrong?

V&M: Yes, many of our works express our futuristic thoughts or imagination where the digital age will lead us and our planet to. It is nice that you have noticed this. I would say this kind of concept in 2010 was quite subconscious. I (Varvara) was very interested in organic form but with mutational origins but still adapted by nature.
More conscious approach towards anthropocene epoch can be seen and felt in “Tree of Hands” (2015), which is one of our recent works. However, it looks like we have touched quite a taboo topic. For instance, “Tree of Hands” was rejected by jury of PAD London fair because of its depressive concept.

FL: “Shopping in 1 Minute” (2011) is another project I would like to ask you about. This work is about consumerism at its finest (or worst), turning one of the most typical capitalistic places (supermarkets) into ludic spaces. It’s a piece of social art that presents itself without informing the public what is right and what is wrong, but it rather suggests in a more subtle way the perversion at the base of that system. What do you think?
V&M: Yes. What we are doing is the absurd exaggeration of the same action (buying) to a maximum with one but: not buying and playing instead. There is a saying that shopping is 5 min happiness. The artwork tries to create a synthetic feeling of satisfaction of the ability to buy. The shopping centers are doing everything to stimulate our consumption needs, and our artwork manages to get inside their ecosystem and playfully releases that artificial desire to buy.
FL: With at least a couple of projects, you’ve also worked to the redefine hurban landscapes by looking at the invisble while at the same time taking on rather specific forces such as mass use of Wi-Fi networks becoming part of the everyday. I can’t help thinking that this is somehow related to privacy questions, probably because one of the most notorious scandals some years ago was Google’s secret recording of Wi-Fi networks with their Street View cars. Am I wrong?
V&M: Not really. But definitely Google has played a role in feeing our concerns about being watched, spied, hacked, scanned, etc. For example, the last scan for WiFi router names we did last summer in Tallinn some people were quite freaked out seeing a person on a bike with a camera on its head and tablet in front. I was even once asked if I worked for Google. 🙂 Anyways, the project was great fun for us, and we got to explore the city and discover the whole invisible communications networks and the self expressive layers of it all. After the Tallinn scan we even changed our minds about the 32-character local Twitter that the WiFi router SSID could be used for. The Tallinn experience showed us the new tendency: where people would use radio waves for semi-anonymous graffiti, communicating sometimes silly, protective, racist or political messages.

Talking about inspiration for this project, we got our interest for WiFi names from one article talking about the ability to track down pro- and contra-Obama communities by just looking at WiFi names in the neighborhood. This was before the US president election. Then we started to thinking of an art project on this topic.
FL: “The Rythm of City” (2011) is another project which is also ‘subtly’ related to control issues. The idea that someone can depict the state of a city by looking at data deducted from social media and web platforms. This type of thing is real now isn’t it – what do you think?

V&M: Definitely it is. However, the work’s main intention is not to talk about control issues rather about big data and its applications. Perhaps the main intention of this work is to offer to the viewer(s) a birds eye view on different cities in real time. In other words, The Rhythm of City allows you to zoom out and witness the larger picture on the current situation. And this larger picture is formed by everybody’s activity on social media, which is tracked down every minute. We call this action ‘unaware participation’ by digital inhabitants. The urban studies of Bornstein & Bornstein from early 1970s served as an inspiration for this artwork. They had discovered a positive correlation between the walking speed of pedestrians and the size of a city. Simply put: the bigger a city, the faster people move. The artwork demonstrates our interpretation of a city’s tempo through in its digital form or life. Hence, The artwork talks about pace of life in different cities at the same moment when the piece is viewed.
FL: What have you been working on these last few months and what plans do you have for 2016?
V&M: We are working on a series of new works talking about money. When we have completed “Wishing Wall” in London in 2014, since then we have noticed that the majority of people, especially a younger audience, wish for money. This really caught our attention. The ongoing hard economical situation in Europe pushes forward the need for money and also introduces a growing gap between the economical classes. So we’re investigating people’s desire for money and its connection with happiness. Making use of interactive technology we are aiming to approach playfully and magically the desire for becoming rich. At the same time, we cannot let go of knitting. At present, we are working on an open source flat knitting machine, which will be able to knit patterns also. Besides the new productions, we are showing our existing works in various exhibitions. For the confirmed ones, “The Rhythm of City” will be part of “REAL-TIME” a group show curated by Pau Waelder in Santa Monica museum in Barcelona from the 28th January. In February “Digital Revolution” (the touring exhibition by Barbican), which “Wishing Wall” is part of, moves from Onassis Cultural Center in Athens to Zorlu Center in Istanbul. And hopefully we get couple of other shows and new productions that are in the air at the moment and still to be confirmed soon.
Trans-gender theorist Jami Weinstein has compared the flocking behaviour of academics and artists around the concept of The Anthropocene, to the adoption by the Hipster of a given locale or fashion appendage. The creative flock, she suggests, can perform a gentrification of concept through uncritical adoption and ‘hyper-consumption’, just as it does of neighbourhoods or workwear. The Anthropocene is indeed the place to be seen, or the guise in which to dress the body of your work, this season. The term is proposed as a way of describing the explicit ‘age’ in which human kind, post-1945 (although possibly since the Industrial Revolution, or stretching right back to the advent of tool use), has come to define the geophysics of the entire earth.

The Anthropocene, combining geology with sociology through a few slights of hand, therefore collapses the distinction of human and nature which is core to basic understandings of our being in the world. If this wasn’t enough, an immanent vote affirming the accuracy of the term The Anthropocene by the scientific community worldwide has also been touted as a gesture which will provide the rhetorical turning point by which the Western powers will acknowledge, and begin reparations for, the ecological sins of the past, potentially saving the human race from mass extinction. Fertile ground then, for readings, interpretations and responses – but as Weinstein suggests, there is a deeply complex responsibility implied when we approach and engage with something as ontologically vulnerable as a concept.
It is this responsibility Sonic Acts assumes when it takes The Anthropocene as its central theme. The four day music festival and conference takes a collection of essays titled The Geologic Imagination as a gathering point for a strong line-up of some of the most influential men working across philosophy, music and the arts today. I attended the first day of the festival, which included a talks and a round-table by Object Oriented Ontologists maverick Graham Harman and his icemanTim Morton, geologist Mark Williams, and art theorist Douglas Kahn, followed by a performance/installation by Florian Hecker featuring work by Reza Negarestani, and a night-time programme of music by M.E.S.H and TCF, Vessel, and finally, as if from outer space, the sole female agent of the programme, Karen Gwyer.
I use the term agent, to distinguish from ‘appearance’ or ‘voice’, because there were several female bodily appearances and women’s voices in evidence onstage during the conference and club. The problem was that they were routinely either denied the right to articulate their own words, for example when The Geologic Imagination editor Mirna Belina was reduced to acting as an interlocutor for Lukas Marxt during a poorly thought out artists presentation section; or worse, used as sound/image material to be cut into, destroyed, and literally degraded for surface affect by male artists. Example of this included the snippet Kurt Hentschläger showed of his work Modell5, during an inexplicable tour of his online portfolio – and the violent envelope-ing of Charlotte Rampling’s vocal performance in Hecker’s audaciously dense new materialist sound opera Script for Machine Synthesis. Certainly none of these phenomena may have stood out as malicious in themselves, but in the context of a festival whose line-up consists of 75 men and only 7 women, and whose female curators are entirely absent from the staged elements of the show, a motif in which women’s bodies and voices are a pretty fabric to be torn and disabused begins to gain the qualities of something else entirely. The ‘glitch’ too must take into account its gender dimension.
This unfortunate gender play reached its misogynistic anticlimax during the closing stages of the club event as the trashy, industrial techno of Vessel was backed by a huge split-screen visual (film created by Pedro Maia) of a woman crying in a bathroom, lying in a corridor naked, kissing another woman in a body bag, and finally being pulled limb from limb in an ambiguous mix of sex-scene and analogue-digital disintegration. What does the complicity and collectivism of a rave space do with images/sound combinations like this when they are conducted by men?

Early in his presentation, delivered with Tedtalk panache, Tim Morton used the fact that literary theory reads gender into texts even when they do not ostensibly mention gender, as an analogy for the way OOO recognizes that objects often ‘withdraw’ from us some core aspect of their being. As Morton affirmed, the Anthropocene is itself a “subcendent” object, being ‘much less than the sum of its parts’ – its parts being of a scale and complexity which must necessarily withdraw from us in order that the concept-as-object here can be revealed. This is explicitly not to infer that the concept-as-object can be emptied of its cultural and social identity and worn with Nikes like a naval overcoat, but rather that it requires a subtle and supple mode of thinking which is capable of excavating ‘that which withdraws’. The gender comment then, was prescient – directly illustrating that the curators, Lucas van der Velden and Annette Wolfsberger undermine the moral agenda of their project by failing to consider, or dismissing, the gender dimension. It might have been a calculated risk, that by not paying attention to gender during their deliberations they might elide that concept altogether from the consideration of the festival, but I think that when a risk backfires like this, the result should be called out for what it is – misguided and arrogant. At times, it felt like rather than proposing ways in which we might retreat from rampant, destructive territorialisation of the Earth, the festival projected a future in which the masculine regime of ownership and domination as ruinous could be helpfully extended and repeated onto womanhood as well – with all the faulty binarism and barbarism that implies.
The one audience question of the day, delivered from under a spotlight and with the barely subdued fury which gave him the air of Rasputin. His question, directed at Harman and Morton, I think picked up on some of the air of hypocracy of the event, but concerned the application of OOO specifically, and its relationship to Accelerationism. As my friend put it, “OOO qua Accelerationist gateway drug”. Needless to say, the question was expertly fielded and evaporated almost without trace.
Despite the regularly fascinating philosophical and cross-disciplinary gestures being made across the discourse/music strands, then, Sonic Acts was articulate through the voices it chose to exclude.
Not that the work itself, or the conversations happening across the theoretical and art strands was insubstantial. For example the way in which electronic artist TCF’s sound work performed the ontological flattening of objects as diverse as a helicopter, a computer circuit, and a Euro-house drop reflected brilliantly on the ideas proposed by Harman, Kahn and Morton, and gave a very tangible way of understanding the new materialist connotations of all. Another highlight included the Reza Negarestani double-bill, in which his notion of the incompatibility of given systems and the resulting philosophical imperative for ‘mixed-level reconfiguration’ through analyzing as both ‘that we can perceive’, and ‘that which we know’, for example, was first purposed as philosophical libereto, and then delivered as an almost equally dizzying Skype lecture.
During the deeply cerebral and attention-demanding ‘Script…’ performance, in which the audience were all seated on the floor, someone tall in mirrored sunglasses did a Jameroqui type dance while people filmed him on their mobile phones.

In Script for Machine Synthesis, (and previous works, such as Chimerisation) Florian Hecker has found in Negarestani’s philosophy a fantastic foil for his ‘dramatization of auditory synthesis’. Script used the motif (and the ‘occasion’) of a melting pink ice cube to enact a simultaneous synthesis and dematerialisation, bringing audio and scent (a specially commissioned perfume by Editions De Perfumes ‘materialised into a rubber trophy presented to each audience member in a foil envelope which made me think of space rations) into play as operators in the field of deconstructing the object-as-concept.
As an audience member completely new (but predisposed) to Negarestani’s work, following this hour-long performance with a lecture via Skype in which he laid out a the chiasmic twisting across neurological-phenomenological and mathematical-physical poles of experience and knowledge, led to a dizzying sense of having been teleported and improperly put back together.
But, despite of these admirable folds in the art/thought continuum, it was impossible to shift the unnerving sense of hypocracy and lack of critical rigour at play in Sonic Acts programming. To return to the central unspoken chimera: The Anthropocene is gendered. In its simple form, it refers to a catastrophic situation resulting from the actions of a patriarchal Western society, and the effects of masculine dominance and aggression on a global scale. This was this subject in withdrawal which dominated my experience – meaning that a curatorial oversight not to include women, presumably in order to include more ‘famous’ names from these male-dominated spheres, was allowed to resonate and mutate into an experience of pervasive, almost hedonistic, misogyny I experienced during the Vessel performance.
The notoriously affluent European festival circuit benefits from a dense network of national and EU funding schemes, coupled with the neoliberal ease of intra-continental transport, cheap flights etc., and leverages this in an arms-race of fees for a mostly-male mostly-white cohort of mostly-electronic music artists. This context, plus that of the ‘lavishly illustrated’ book of essays which sets the scene for this year’s Sonic Acts, and the mode of staging in which the expert-community of the audience was silenced from contributing, in favour of a series of pronouncements from master-rhetoriticians, seems to me in direct opposition to the kind of ‘challenge to the status quo’ and subsquent reversal of the Earth’s fortunes which was frequently advocated for. The blurb for The Geologic Imagination does in retrospect seem to revel in the kind an uncritical adoption of concept Weinstein critiques, making of ecological disaster mere concept for further consumption:
“This new publication by Sonic Acts is inspired by geosciences and zooms in on planet Earth. Fundamental to The Geologic Imagination is the idea that we live in a new geological epoch, the Anthropocene. (!) Human activity has irreversibly changed the composition of the atmosphere, the oceans, and even the Earth’s crust. (!) Humanity has become a geological force. (Huzzah!)” [Exclamations mine.]

Finally, Karen Gwyer’s techno set – devoid from any descernable link with the festival themes, and so in a way also silenced somehow. But nonetheless, experienced like finally being able to breathe. The bass subdued among a mesh of pulsating synth and crystalline threads. Tim Morton’s frenetic big-box-little-box dance moves notable in the throng, somehow saying something indiscernible but very real, about the opportunities missed by this most-preeminent of European festivals. As Gwyer herself notes, in an interview not at all about the Anthropocene: “those forces have testicles.”
[imgs Jon Davies]
Lately, I have noticed in myself a tendency to sign up for events which reveal little of what to expect beforehand. This leads to a heady mix of anticipation and mild terror. Dark Days, the brainchild of Ellie Harrison fitted that description, although I felt that at 16hrs long, it was a mere blip on my riskometer, compared to week-long excursions I’ve previously taken into the unknown. In short, I would be spending the night in Glasgow’s Gallery of Modern Art (GoMA), in a pop-up community of 99 strangers, contemplating how we might manage to live together (put up with each other) in a future where buildings might need to be used in ways which serve the needs of the population better…Count me in!

The camp manual gave thorough and due attention to health & safety issues like pyjamas and woollen blankets, but scant reassurance on how the experiment would avoid a rapid descent into anarchy. In the absence of concrete information, my mind ran amok. I therefore decided, that on arrival we would be immersed in an imagined scenario where all manner of crises has befallen our village, that it would be up to us to work out how we would rebuild society. This would be a tense, high adrenaline experience involving sleep deprivation, maybe starvation, and intractable social issues, to be debated until we all came to a common vision. We might never make it out of there.
As it turned out, Dark Days was none of those things; it was a whole lot more. On arrival in Glasgow, I succumbed to mild panic and bought myself a sleeping pad, twinpack of nougat caramel chocolate, and a bottle of fizzy pop (in direct contravention of the bring a bottle of water mandate), to supplement the food I already had in my rucksack. Provisions bolstered, I relaxed & enjoyed my pilgrimage to GoMA; I felt carefree, adventurous and rebellious; none of the strangers walking beside me had a clue what I was about to do. I felt dangerous and daring.

I joined the short queue outside GoMA, exchanging nervous banter with fellow participants (“Is this where the over-excited and slightly nervous should queue for the coming apocalypse?”). We eyed each other up, I began to relax. We all looked pretty ‘normal and balanced’ individuals. Who could predict what would surface once the pressure was on, though? A child walking past was overheard saying “you’re the worst Mum ever”. He was joking of course, or was he? Was society breaking down already? When the doors opened, we edged inside, one and two at a time. We were subjected to challenging initiative tests – first to register with the clipboard on the right if your surname is A-L. I was standing on the left, I dithered. My surname begins with a ‘G’. My faculties were already leaving me. Through the archway to the welcome desk, I shuffled forward and joined the queue on the right. More nervous exchanges. The queue on the left was faster, we silently wondered whether it would be impolite to skip over to the other line. No one moved. A couple of minutes later, I spotted a notice ‘A-L’ taped to the left side of the desk. A dastardly ploy! Somewhere, a hidden camera would be watching me, a witness to my ineptitude. This was before the evening had even begun. My nerves jangled. Beyond the mysterious white cube that had blocked our view of the great hall (was that where the mind games would take place?), we placed our belongings around the edges and sat in the large circle of chairs which awaited. More nervous chatter, it was clear that no one had the faintest notion what the night would hold. I was reassured. Speakers, microphones and video cameras (with red light already flashing) were dotted around the space, we did our best to ignore them. There will be screenings in March in Glasgow, and the film will be made available online #ohdear. Someone noticed that there were not enough chairs for all members of the community to have a seat. 20ish people stood, or sat on the floor. Was this a lack of resources on GoMA’s part, or was it intentional? Time would tell.
An entertaining and enlightening journey followed, into the challenges of consensus decision making, based around the formation of ‘affinity groups’. The groups were determined by allowing anyone who felt brave enough to make suggestions of how we might spend our time together, members of the community chose which group they wanted to join. The options were many and varied; building a Tower of Awesome; a general knowledge quiz; game playing; climate change discussion group; music & dance; a group with no plan; a manifesto writing group; a skills sharing group and a community focused ‘hub’ group. This was the fascinating moment for me, as my intended plan for the evening was abandoned. Along with my keen interest in community building, I was at GoMA to write poetry, to create a distillation of the night’s happenings for future posterity. Logic would dictate that I should go where the most words would be; but I was filled with an irresistible urge to play games. I had already co-dreamed an impressive list of sleeping bag related games with the person sitting to my left (slug, husky races, who can wear the most sleeping bags, sack races to name a few).
We gathered in our groups to discuss what we would do, what we would need, what format the evening should take and (as it turns out, crucially) what time we would like the lights to go out. A spokesperson was selected to represent each group on a ‘spokescouncil’, where the representatives would reach a consensus on the issues of how the evening would go, any conflicts over resources and at what time the lights should go out. The facilitators did a magnificently heroic job of keeping the discussions focused; ‘brief’ overviews spiralled out of control, the facilitator gently herded the kittens. “I’ll say again: Each spokesperson is to give a brief outline of what their group will do tonight” quickly became “Each person has 30 seconds to tell us”. Those not on the spokescouncil chortled and tried to stifle the mounting hysteria. The only spokesperson not tempted to flout the guidance was from the ‘no plan’ group, because well, they had ‘no plan’. It became clear that with the proposed ‘Tower of Awesome’ and sub-idea of sleeping bag fort, that chairs were the key resource to be negotiated. Turning out the lights also became a decision to be much wrangled over; there were lots of needs, ranging from ‘pretty much now’ to ‘what the hell, let’s stay up all night’.
Negotiations were funny, tense, agonising and did I mention funny? At one point, I was weeping with laughter; we were tantalisingly close to reaching consensus when out of leftfield came a demand for an opening ceremony. Fine we all said, have your opening ceremony, let’s just get this done. The sage advice of the facilitators was beginning to hit home – only use consensus decision making for important decisions and ask yourself ‘do I want to spend all night making decisions, or do I want to have some fun?’. By now it was heading towards 11pm, and there were games waiting to be played. We were close. We were restless. The facilitator then fulfilled the most crucial obligation of consensus decision making, and asked the spokescouncil whether there were any objections. We held our breath, pleading inwardly for no one to speak up. Come on spokescouncil, you could do it! Hands went up. Sigh. 15mins of jaw-clenching tension followed, as the universal ‘need to be heard’ surfaced in a few last desperate arm waves; “Well, this isn’t exactly an objection, but I’d just like to say…”. “Any final objections?” our facilitator said, possibly through gritted teeth. Silence. We breathed a collective sigh of relief. “I think we have a consensus”. We cheered. Let the games begin.
The opening ceremony was a resounding success, as we all ‘became the chairs’ in a self-supporting and poignant human chair circle. Next, we lined up in small groups, ran the length of the gallery, and then turned and felt the breeze on our faces. It was magical. We smiled broad smiles, laughed, and revelled in a joyful camaraderie for the rest of the night. How could anyone think of going to sleep when there was crowdsurfing to be done, wink murder to be played (epic) and thigh drumming to be learned? It was a fascinating experience. I observed an interesting phenomenon; each time an activity gained a certain number of people, others noticed and ran to join. The wink murder circle doubled in size while the detective was behind a column and the silent disco grew within minutes, without a word being spoken. We generally didn’t stay segregated in our own groups, we welcomed others in unreservedly, and joined other groups when the mood took us. We were a model society, just for one night. We self-organised, and ensured that there were enough chairs to meet the needs of towers, forts, hubs and deep discussions. It was beautiful and inspiring. It was epic and poetic. We had survived. No, we had flourished.
Extract from my #DarkDays poem:
Dissent can be difficult,
blocks disrupt.
Build a safe environment
for breaking power,
freefall into your position,
annex yourself from your ideas;
interrupt silence,
with or without permission,
be the instigator of your rebellion.
Move the chairs
Wind-down at 2am came all too soon, and we made ourselves cosy for the night. My mind was skipping and crowdsurfing, and reliving dramatic wink murder deaths; how on earth was I going to sleep?? I didn’t. Well, maybe an hour or so. I lay under my blanket (not woollen) and listened to the rise and fall of contented breathing, with the occasional soft, acoustically augmented, echo-y snoring (cautionary note; snorers should choose their sleeping spot carefully). I contemplated how different the experience might have been in the ‘real world’, where people wouldn’t be so accommodating, wouldn’t be on their best behaviour. I suspect there might have been less laughter and fewer games, certainly no Tower of Awesome or sleeping bag fort. Time will tell.

There is a distinct buzz that goes with embracing the opportunity to stay in a public building overnight, I encourage everyone reading this to add such an experience to their bucket list. You might have to go to some lengths, might have to personally orchestrate an event, in order to create your opportunity. Whatever it takes, it will be worth it. I promise. Think ‘Night in the Museum’, meets giant slumber party, with midnight feast thrown in, but with no adults to tell you what you can and can’t do. We were the adults, we made our own rules. Even when a camper was scaling internal walls in the importance of building the most spectacular sleeping bag fort ever seen, no one came to tell us to stop. We all learned something valuable from that endeavour; the fort was unbearably hot inside, so could only be tolerated for short periods of time. Next time – ventilation. One participant put our limited imaginations to shame, by bringing a hammock to sleep in. We all wanted to be that guy. We ate chocolate and muffins for breakfast.
All of your dreams for a different world, made real in one spectacular night in a museum, art gallery, library, school or conference room (the possibilities are endless). Life will never be the same again, you will be changed, and you will want to do it again and again.
Note from reviewer: Names have been omitted in order to protect the subversive, the wall-scaling, the almost-pyjama-wearing, the non-sleeping campers.
Featured image: Image from Joel Bakan: The Panopticon Power of the new media. Adbusters Jan 2012.
Marc Garrett and Ruth Catlow interview McKenzie Wark ahead of his keynote speech for Transmediale 2015 in Berlin this year.
It’s ten years since McKenzie Wark published his influential book, A Hacker Manifesto. Divided into 17 chapters, each offers a series of short, numbered paragraphs that mimic the epigrammatic style of Guy Debord’s The Society of the Spectacle. Wark then published, amongst others, a series of critically engaging books such as Gamer Theory and the Spectacle of Disintegration. Ruth Catlow and Marc Garrett from Furtherfield ask Wark how things have changed since these publications, focusing on how our everyday lives have been infiltrated by competitive game-like mechanisms that he described more than a decade ago.
Furtherfield: You published the experimental writing project Gamer Theory first as a book in 2006 and then in 2007 with a specially revised 2.0 version online.

Mckenzie Wark: Yes, although I think the network book version is mostly broken now. Good thing there’s a dead-tree format back-up!
F: In it you argue that we’re living in a world that is increasingly game-like and competitive. Also that computer games develop a utopian version of the world that realizes the principles of the level playing field and reward based on merit; whereas in the world, this is promised, but rarely realized.
MW: Yes, I think one way of thinking about certain games is that they are a fully realized neo-liberal utopia, which actually gives them some critical leverage of everyday life, which is a sort of less-real, only partially realized version of this, where the playing field is not level, where the 1% get to ‘cheat’ and get away with it.
F: You also talk of the “enclosure of the world” within the “gamespace” where the logics of the game are applied as the general patterns of organization in the world. And this happens as we adapt to the allegorical forms of contemporary games media.
How do you think this situation has changed since you wrote Gamer Theory?
MW: Well, to me it looks like the tendency analyzed in Gamer Theory became even more the case. GamerGate looks among other things like a reactive movement among people who really want the neoliberal utopia in all its actual neofascist and misogynist glory to not be exposed as different to everyday life. When women gamers or game journalists stick their hands up and say, “hey, wait a minute”1, they just want to mow them down with their pixelated weapons. So the paradox is that as gamespace becomes more and more ubiquitous, the tension between promise and execution becomes ever more obvious.


F: Do you see the term Gamification that many theorists use currently as an elaboration of the ideas you developed in Gamer Theory? Or are there significant new ideas being explored?
MW: Ha! Well no, gamification was about celebrating the becoming game-like of everyday life. So I always saw that as a kind of regression from thinking about the phenomena to sort of cheerleading for it.
F: The software developer and software freedom activist Richard Stallman, when visiting Korea in June 2000 illustrated the meaning of the word ‘Hacker’ in a fun way. During a lunch with GNU fans a waitress placed 6 chopsticks in front of him. Of course he knew they were meant for three people but he found it amusing to find another way to use them. Stallman managed to use three in his right hand and then successfully pick up a piece of food placing it into in his mouth. Stallman’s story is a playful illustration of “hack value,” about changing the purpose of something and making it do something different to what it was originally designed to do, or changing the default.2
Stallman was highlighting fun and the mischievous imagination as part of the spirit of what he sees as hack value.
Where do you see lies the hack value in games culture? What has happened to the fun in games? Who’s having it and where is it happening?
MW: Stallman is one of the greats. Sometimes, people have this experience of scientific or technical culture as one of free collaboration, where there’s a real play of rivalry and recognition but based on producing and sharing knowledge as a kind of gift. JD Bernal had that experience in physics in the 30s and Stallman had, I think, a similar experience in computing. I think it’s important for those of us from the arts or humanities to honor that utopian and activist impulse coming out of more technical fields.

There’s a lively, critical and even avant-garde movement in games right now. That’s part of why it has provoked such a fierce reaction from a certain conservative corner. The culture wars are being fought out via games, which is as it should be, as it’s one of the dominant media forms of our times. So there’s certainly some sophisticated fun to be had alongside the more visceral pleasure of clearing levels.
F: “Our species’ whole recorded history has taken place in the geological period called the Holocene – the brief interval stretching back 10,000 years. But our collective actions have brought us into uncharted territory. A growing number of scientists think we’ve entered a new geological epoch.”3 And, this new geological epoch has been proposed as – the Anthropocene.
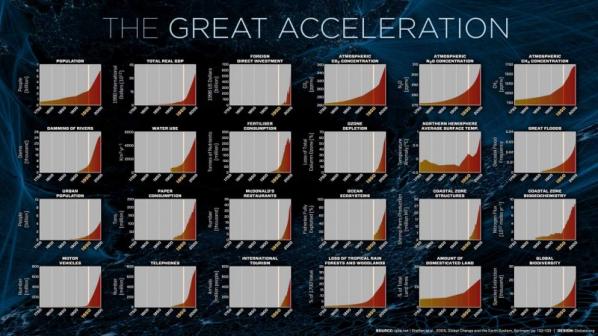
In your essay ‘Critical Theory After the Anthropocene’4 you say “At a minimum, the Anthropocene calls on critical theory to entirely rethink its received ideas, its habituated traditions, its claims to authority. It needs to look back in its own archive for more useful critical tools.”
What are these ‘useful critical tools’ and how might theorists, new media artists, game designers and society at large put these to work?
MW: The ‘cene’ part of Anthropocene (from the Greek kainos) means a qualitative break in time. If time is in a sense always different, then kainos is the differently-different – a new kind of time. Those like Paul Crutzen who have advocated the use of the term Anthropocene to designate a new geological time have issued a major challenge as to how to interpret such a possibility. I leave it to the scientists to figure out if such a claim is scientifically valid. As someone trained in the humanities, I think the generous, comradely, cooperative thing to do is to try to interpret what our friends and colleagues in the sciences are telling us about the times. So in Molecular Red that was what I set out to do. Let’s take seriously the claim that these times are not ‘like’ other times. That I think calls for a rethinking of what from the cultural past might be useful now. I think we need new ancestors. Which is why, in Molecular Red, I went looking for them, based on the question: to which past comrades would the Anthropocene come as no surprise? I think Alexander Bogdanov, who understood a bit about the biosphere and the carbon cycle, would not be surprised. I think Andrey Platonov, who wrote about the attempts and failures to build a new kind of infrastructure for the Soviet experiment in a new mode of production would not be surprised. There are others, but those I thought were particularly helpful, not least because their Marxism remained in dialog with the sciences and technical arts. I don’t think the more romantic anti-science side of Western Marxism and continental thought is all that helpful at the moment, not least because it rules out of court exactly the kinds of scientific knowledges through which we know about the Anthropocene in the first place. The anti-science critique has been captured by the right, so we need new tactics.
F: Who’d be empowered by an encounter with your ideas and where do you see the potential for agency in the current economic and environmental contexts?
MW: Not for me to say really. Writers are usually the last people to have any clues as to what their writing says. There’s a sort of idiot quality to banging away on a keyboard. We’re word processors. Its always surprising to me the range of people who find something in what I write.
My hunch is that the future is in the hands of an alliance between those who make the forms and those who make the content: a hacker and worker alliance. It is clear that this civilization has already become unreal. Everyone knows it. We have to experiment now with what new forms might be.
F: And, where in the world do you see examples of individuals, groups and organizations, and or companies – who are putting into action some of the critical questions that you’re exploring in your writing?
MW: Besides Furtherfield? I never like to give examples. Everyone should be their own example. To détourn an old slogan of the 60s: be impossible, do the realistic!
F: In your later essay ‘The Drone of Minerva’5 you continue to write about the Anthropocene. But, you also bring to the table the subject of the Proletkult.6 The Proletkult aspired to radically modify existing artistic forms of revolutionary working class aesthetic which drew its inspiration from the construction of modern industrial society in Russia. At its peak in 1920, Proletkult had 84,000 members actively enrolled in about 300 local studios, clubs, and factory groups, with an additional 500,000 members participating in its activities on a more casual basis.
You are writing about the Proletkult in your latest book. Could you tell us a little something about this and how it will connect to contemporary lives?
MW: Proletkult was influential in Britain too, during the syndicalist phase of the British labor movement, up until the defeat of the 1926 general strike. After that the dominant forms were, on the one hand, the ethical-socialism and parliamentary path of the Labour Party, or the revolutionary Leninist party. Well, those paths have been defeated now too. I think we have to look at all of the past successes and failures all over again and cobble together new organizational and cultural forms, including a 21st century Proletkult.7 What that might mean is trying to self-organize in a comradely way to try and gain some collective charge of our everyday lives. It does not mean just celebrating actually existing working class cultures. Rather it’s more about starting there and developing culture and organization not as something reactive and marginalized but as something with organizational consistency and breadth. Since the ruling class clearly doesn’t give a fuck about us, let’s take charge of our own lives – together.
Thank you McKenzie Wark – Ruth Catlow & Marc Garrett 😉
Ruth Catlow will be at Transmediale 2015 CAPTURE ALL, moderating the keynote Capture All_Play with McKenzie Wark, on Sat, 31 Jan at 18:00.
Ruth is also participating in two other events, Play as a Commons: Practical Utopias & P2P Futures and The Post-Digital Review: Cultural Commons – http://www.transmediale.de/content/ruth-catlow