



“I-love-you: the figure refers not to the declaration of love,
to the avowal,
but to the repeated utterance of the love cry.”
Roland Barthes, The Lover’s Discourse. Fragments, 1977.
Designed and published online on October 14th 2004[1], restored for The Wrong (Again) on November 1st 2015, the website I Love You by French artist Jacques Perconte[2] is not only a wonderful achievement of his research on image files visualization through the Internet, but also a fundamental piece of artwork for three reasons: first, it crystallizes a history of audiovisual technologies in the web age; next, it allows the analysis of his singular inventions on plasticity which are shaped by the offensive processes and techniques Perconte has developed until 2015; finally, it makes explicit the artist’s constant will to put the body to the test of digital technologies (in this case the partner’s body) and to literally inject life (each and every thought, interest, feeling, emotion, excitement, and desire aroused in him by the beloved body).
Two events in 2003 gave birth to this piece: a publication proposal from French publisher Didier Vergnaud of a book with the digital photographs of bodies he had been taking tirelessly; and his romantic encounter with the woman who would become his partner, muse and model, Isabelle Silvagnoli. I Love You merges two stories, two passions. The one with Isabelle blooms in May 2003[3]; at this time, Perconte has already an extensive experience of digital technologies that he had developed since 1995[4].
At the Bordeaux University, when Perconte notices that a computer is connected to the rest of world, he becomes aware of the technical and aesthetic issues of the digital network, issues largely ignored at this time. His quick mastering of how the web operates leads to a decisive work on “the digital bodies”: three image generator websites (ncorps) and four films made by re-filming multiple loops of these animated pictures. This series denotes that Perconte has assimilated four essential dimensions of the digital.
First, he notes the image exists primarily in the state of a compressed digital signal that needs to be displayed; the signal recorded and stored as a file is a model, shaped by algorithms; its visualizations change only according to the codecs and the supports. Next, he distinguishes the human dimension of the web: the bodies of the users surfing the Internet on their computers and interlinking one another.
Then, the material dimension: the computers interconnected by an abundance of servers all around the world which produces a random digital time; indeed Perconte noticed the connection time to the hosting server of his websites was unpredictable since the answering time fluctuated according to the Internet traffic density, the connection’s and the browser’s qualities, and the computer’s performance executing the query.
So he notices the fantastic system failures: “when the first JPEGs popped up on websites, it wasn’t unusual for a picture to be only partially displayed. Sometimes, this happened to produce strange distortions in the image. (…) Every now and then, the image would totally turn into an abstract composition with amazing colors.”[5] Consequently, these fluctuations of display reveal a prodigiously fertile field of investigation: recoding the visualization. Finally, the web can be defined by the coexistence of places, bodies, machines, protocols and programs interacting in complex ways as an evolving ecosystem. Thus, a device aimed at transforming models could be designed (model meaning both the person the artist reproduces with forms and images and the coded reduction), as GIF or JPEG sequences animated on a website. Since the parameters involved in the visualization of these sequences are renewed at each connection, Perconte knows these metamorphosis will be unlimited and give birth to n bodies [corps]). This research allowed Perconte to establish, by 1996, a stable platform aimed at recoding the visualization within the web to ultimately break the limitations of the model’s code into which the digital signal is reduced.

As he undertakes assembling photographs of Isabelle for the book project (38 degrés), this experience of the web will come back to him. The collection of several thousands digital pictures springs from the extensive exploration of the beloved body’s patterns and the obtained signals he looped (he retakes the displayed pictures several times), in an attempt to test the representation of love. The problem is twofold. On the one hand, this collection can only be unlimited since the observation is inexhaustible as he puts it: “when I think about her body, I dream of landscapes so large that one gets lost completely, there is so much to recognize, kilometers of skin where warmth rules, a soft, almost empty desert. Beauty, immensity where every vibration of light pushes the colors to reveal themselves in new ways. The variations (…) are endless.”[6] Furthermore, despite experimental photography techniques, he quickly reaches the limits of how much an image is capable of expressing absolute love. In order to find and visualize this love present within these files, Perconte selects and ranks hundreds of these images in a database and places them in an ecosystem on the web.
Perconte developed a server-side program by writing an open source application in PHP, the love writing program[7], in order to quantify the love present in the source code of these digital images displayed on the web. Love being unquantifiable by definition, the artist must add an arbitrary but rigorous calculation. This quantification is performed by the application triggered when a user clicks on one of the images of the collection: it calculates a specific variable by taking into account all the physical parameters of the connection but also the mathematical constants of proportions and universal harmony – ∏ and F (the golden section); then the application opens the image file, transforms it as a hexadecimal code and substitutes every occurrence of the sought value by the phrase “I Love You,” thus changing the architecture of the code describing the image. The browser requested to visualize the image compiles the modified code, but can only display it partially, at the cost of radical visual transformations, such as reconfigurations pixel structures, the emergence of new colors resulting in the reinterpretation of original motifs or subjects; the greater the amount of pure love, the more intense the abstraction. The motifs of the beloved body can mingle or merge entirely with the figuration of love. The browser is sometimes unable to visualize the image resulting in the appearance of a broken icon with a quote from Roland Barthes: “To try to write love is to confront the muck of language: that region of hysteria where language is both too much and too little, excessive (…) and impoverished (…).”[8]The broken icon evokes a digital iconoclasm, but furthermore signifies the limitations of visualization protocols that have been overtaken by an overflow inexpressible love. This substitution in the image source code of a value by the literal writing of love, raises the Perconte’s program to a “loveware.”[9]
Not only has Perconte given life to this website, but he has been maintaining it for the eleven years he has been sharing his life with his partner. First and foremost, he constantly upgrades it. Indeed, he programmed on February 14th 2005 an “I Love You Collection” of all the “I Love You’s” which will be written in the images’ source code; from this description, the “Love Counter” determines the number of “I Love You’s” and their transposition in bytes: “This is a concrete and scientific way to know as precisely as possible how much love is streamed online, and more importantly how much love is contained in this work. Every time a picture is displayed and the code modified by love messages, the counter is updated. The more time goes by, the more love grows.”[10] Thus, the users themselves, without suspecting it, testify to the history of this Perconte’s love for his partner, write this love, perpetuate and amplify it. Donating his images to the network, leaving it to others to speak for him, the artist is no longer the excessive delirious lover (wonderfully described by Barthes[11]), but one who loves. Then, the artist updates his website on a regular basis.
For each exhibition he replaces the image collection and operates small technical changes in order to avoid falling behind on the developments of the web. Furthermore, he designed a photographic exhibition of this work started in 2003, It’s All About Love, from January 17th to April 17th 2008 in Pessac, where he gives to the public a synthesis and extension of the project, in the form of prints and animations on iPods[12]. Finally, he undertakes a complete restoration of the website in 2015. Indeed, I Love You has suffered from a rapid disruption of the web and the visualized pictures often began to show large gray patches. The invitation from The Wrong gave him the opportunity to get back to this core piece. The solution – consisting in placing the website in its original technological context, that is to say, on a server with the same configurations as in 2004 – was met with refusal from the web hosting providers. This is how he decided to work with one of his students of Chalon-sur-Saône, Garam Choi, a true code virtuoso, in order to rethink the programming of the website according to a large principle which governs web in recent years.
From the beginning of the web until the posting of I Love You, applications were executed by servers. However, with the exponential increase in web traffic, servers quickly became overloaded; moreover, computers have seen their computing power and storage soar while other programming languages, like JavaScript, gained importance. Thus, the logic that governed web-programming moved applications to the client-side. Choi and Perconte have therefore developed identically, from the original program in PHP, an application written in JavaScript so that it could be interpreted on the client-side, while maintaining the database on a server. The issue at stake was to create a dialogue between the server and the client-side application, especially to quantify the number of “I Love You’s” and write it into the database. Indeed, server specifications entail technological obstacles as soon as the instructions are not in compliance with the protocol. But the artist was quickly able to find a way to instruct the program to circumvent the prohibitions. Indeed, not only does he operates the substitution technique to modify the images source codes, but uses it as a trick to fool the server. The idea is to do it as if the client were loading an image from the server to display it; but the called address executes instead a script, in other words, instead of the image URL, the number of “I Love You’s” is shown.

The website restoration therefore takes hold of the website’s programming in the 2010’s, but reinvents it with ingenuity. It also alerts the Internet user on how some multinationals IT companies (Apple, Google) consider the universality of the net: Chrome hinders some images display, while Safari denies their visualization. Also, in the latter case, Perconte and Choi have provided the following message to the attention of the user: “Safari is not ready for love. It’s still blind.” On the contrary, the Firefox browser, developed by a global open-source community, allows optimal operation of I Love You at the exact replica of the first 2004 version. Indeed, Mozilla defends a free Internet that would be “a global public resource that must remain open and accessible” in which “everyone should be able to shape the Internet and their own experiences on the Internet.”[13] That is why the growing love of I Love You does not only symbolize the artist in his couple, but elevates itself to a principle of universal union and intimate communion through the web: a set of values that affirm a convivial conception of society resisting consumerist models imposed by technical industries, and taking the power of the Web back in the hands of all users.
I Love You is therefore crucial for the Internet user, the historian, the media theorist, the film analyst, the archivist and the curator of the twenty-first century. It invents a thought of the program as a plasticity fertilization tool through digital visualization technologies understood as open and unstable. It successfully manages to offer bright and virtuoso processes and techniques of recoding, exciting insights on the operation of some display supports and devices, along with their history and unrelenting criticism, and the refined and infinite visual writing of the story of a man in love through a limitless range of radical visual forms generating a pure aesthetic delight. It is an artwork that lives and grows thanks to the Internet users as a digital lining of a relationship blossoming in the world, and which, since it has adapted and transformed to the changing technological environment, becomes the figurehead of a libertarian conception of the Internet and digital technologies in general.
Warmest thanks to Nicole Brenez, Gaëlle Cintré, Kamilia Kard,
Filippo Lorenzin, Zachary Parris,
Jacques Perconte and Isabelle Silvagnoli.
(In)exactitude in Science : http://inexactitudeinscience.com
and I Love You : http://iloveyou.38degres.net
Text is translated from the first french extended edition : http://www.debordements.fr/spip.php?article431
Structures. Something has been built, grown, stretched. Maybe skin, maybe a web, maybe a protective barrier – it is a plastic protein emitted by an organism in order to increase its survival opportunities, it is a food matrix for its offspring which thrive on glossy resin. You can travel across it and it can easily be mapped, although not by humans.
We can’t say anything about it – we can speculate everything about it. It is something possible or as the author says another reality. The real is replaced by the potential. This is one of a series of works by St. Petersburg-based artist Elena Romenkova. The works are glitches, abstract distortions, alien expressions of what for her is a subconscious realm.
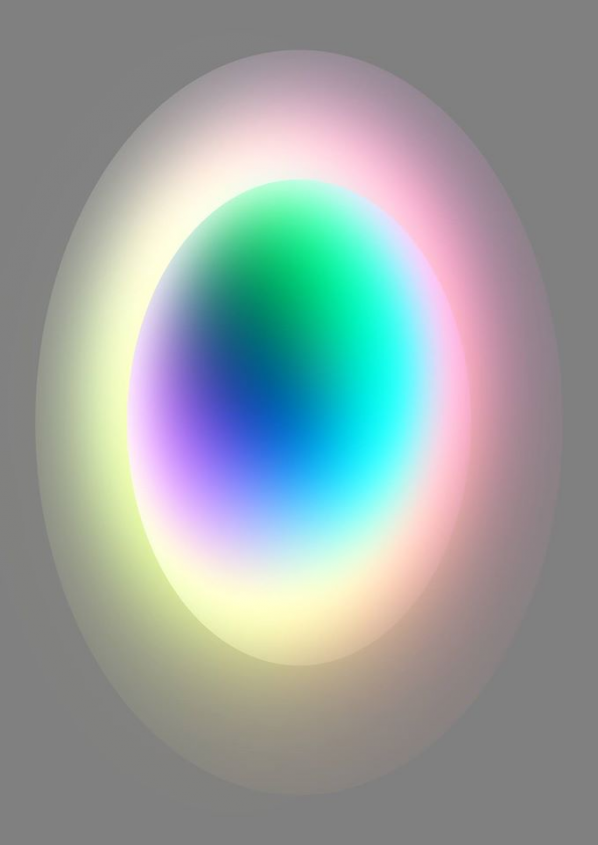

A portal. You are entering the rainbow world contained within two concentric eggs within the grey world. This is light, reflections, haze, indescription. It looks inviting. The colour spectrum is odd, the whites creep up on everything else, the shape of everything is strange. Basic synaesthetic rules are inapplicable at the rainbow/grey world junction.
There is nothing that this image, by French artist Francoise Apter (Ellectra Radikal), has in common with Romenkova’s. They are united only by their adherence to strangeness, a technically created vista that looks like nothing we know. A world not of local cultures, but of computational production. Here anyone can know anything, it doesn’t matter where you’re from.

What is culture when locality is secondary to epistemology? What is knowledge when the portable device takes precedent over your situated environment? Worlds are built around us, sophisticated electrical spaces, they travel where we travel, and only after do we factor in the idiosyncracies of specific geography. If the banal experience is one of nomadic alienation, of search methods based on no place, what does the role of culture and art become? Everyday life is a subject for hypothetical language. The digital commons is a species of posthuman that communicates via speculative misunderstanding.
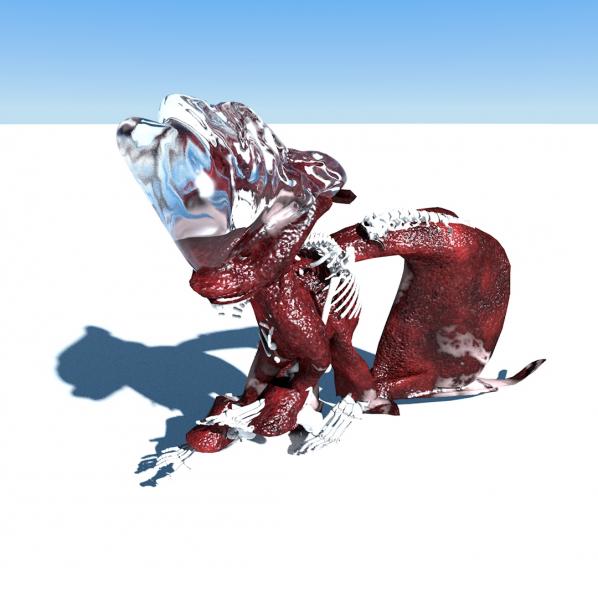
Korean artist Minhyun Cho (mentalcrusher) shows us what the dinosaurs really looked like. When you put the meat and scales back on. He shows us what an ice building being looks like in the shadow of terminal cartoon winter. How rubber can be used to erect sculptures and bones can be taken out of museums and put to good use in civic architecture. No one is around to see this, but still the idea sets a precedent. Crown each ghost with ice mountain prisms.
With visual language, very quickly we get to a stranger and more indeterminate range of science fiction possibilities than narrative tends to map out for us. How much imagination is possible, and how much does our internal experience match anything presented around us. If our environments advance exponentially quicker than any generational or traditional mythology, what sort of language can we have for expression? The maker’s invention precedes the reception of form. Innovation is a matter of banal activity, communicating an experience of the real which is never the same.

And now an eyeball. Triangles. A vessel. To Cho’s blinding world of light, Spanish artist Leticia Sampedro responds with a featureless darkness. All absurdities once on display, now they recede into nothing. It might be a mandala, perhaps an artifact from the ancient future, a portable panopticon that fits conveniently on your desktop. Your feelings are here, your peculiar distances, everything’s reflecting off the glass, the metal, the camera. You are the mirrored fragments of an invention we’ve lost the blueprints to. Foresight the womb of a disembodied politics of community.
Community held together by structures. In German artist Silke Kuhar‘s (ZIL) work, we enter into one of these structures. Inside we find hallways, a nice selection of windows and all kinds of data – scripted, graphed, symbolized. This is the plan for the future. I hope you can read what it says. Her work meshes spaces with collapsing foreign constructs – if we can just read the language we’ll know what to do. But no one reads it, and no one wrote it. This is a building without inhabitants – architecture without people. Democratic ballots are automatically filled out by a predetermined algorithm. Your agency is a speculative proposition for popular media – people collaborate with you, but they can’t be sure where you are, when you wrote, and if you really exist as such.
No people. This is a unifying principle. Cold, silver, streams. Machines in the sky. Silicon waterfalls, diagonal. Civilization distilled into physical patterns, an obtuse object photographed in another dimension. What is the word for reality again. What is the word for scientific investigation? A Venezuelan based in Paris, Maggy Almao’s abstract glitch world is silent – it’s a gradient, it’s some illusion of partial perspective.
What is the language to talk about the world? If we turn to artists’ visualizations, what does that tell us about languages we speak, and ones we read? What does the graphing of incomprehensible mechanisms tell us in turn about art and its history? The machine’s narratives tend to drown out any functional reality. Genre storytelling tropes become repurposed as collective cultural ideas. Conceptual works are followed by pragmatic speculation, medium-centric analysis replaced by experimental failures. You can never get a fictional experiment to work.
Science has indelibly entered the art field, for each of its medial innovations it requires further attention in terms of its technical makeup. Half the work is figuring out what the canvas even is, we are building canvases, none of them look alike, and their stories read like data manuals. An aesthetics of unknown information.

This is the homeland. The homeland is mobile and has many purple bubbles. It’s an airship from the blob version of the Final Fantasy series. It has satellite TV to keep in touch with the world. It has some tall buildings so you know it’s civilized. It is part of Giselle Zatonyl, an Argentine-born Brooklyn-based artist’s opus which deals comprehensively with science fiction ideas and their implications.
The ship travels, where the culture originates is more and more unknown. It is technically divided, access is the key, we can worry about language and culture later. We are still embodied, still located somewhere, but all this has become subject to the trampling of scientific mythologies, where their utilities might go, and where their toys are most needed. Crisis is a genre now, about as popular as time travel. You are now free to dream up whatever future society you wish, and subjugate whatever cyborg proletariat your heart desires. In the realm of speculation, anything is possible, and nothing is fully acceptable.
The themes of internet art production give us some language, some set of visions that tell certain stories – works found throughout the internet, posted in communities, shared online – sometimes part of gallery exhibitions or products, sometimes not. You get a profile, some social media pages, build a website, you begin making, sharing and remixing images. Folk art is a subsidiary of new media art – social sculpture meets internet content management systems. A language for political engagement based on the creative activity of speculation. Scientific dreams for a technological commons.

Dreams where sight is physicalized into complex data graphs. Where Sampedro’s portable gelatin panopticon is cloned into a regularized matrix. Inspired vision is just one aspect of algorithmic predictability. In Taiwanese artist Lidia Pluchinotta‘s visual work, the cloned image is central. Mechanical reproduction, skulls, spirals, symbols, the internet has it all. Civic participation has never been so mathematical, observation never so multiple.
Inside the city, architecture is actually a colour-coded map that helps you find the store you’re looking for. The map is the territory except there’s no info on how to read it. We are here, we are home, but the walls of the buildings were designed by some specialist that we haven’t met yet. Stairs, depths, the complex and layered constructions in Canadian artist Carrie Gates‘ work aren’t quite one of Zatonyl’s buildings. More fragmented, more saturated, more chaotic. It’s speculated that people could live here, although we don’t see them anywhere. Not yet anyway.
The maelstrom of technological progress presents us with the need to adapt our participation and rhetoric accordingly. Science fiction is a folk language for common experience within a technoscientifically oriented world. These images are imaginative products of social and participatory artist communities who, when marrying the personal and contextual, create speculative objects of general strangeness. Their description is nothing less that one of alien entities – alien entities that are everywhere. Earth is the most sophisticated foreign planet we’ve yet to invent, we just need to discover how to populate it.
The video works of A Bill Miller seem to be at once futuristic and something recalled from our childhood (those of us who grew up with computers in some form or other) in what might be considered as a hauntological affectation that seems like a memory of the future from our childhood, with lines and simplicity of many early computer programs, forming complex ghosts of our pasts across the screen. These are a reminder that what computer graphics can do, doesn’t have to be composed of 3D, with million of vectors and a painful, failing attempt at verisimilitude. Just as theatre, with it’s artificial simplified set designs and symbolism. It can sometimes be more real, offering a greater empathy than a well designed and directed film. Often, there can be greater beauty and compulsion when engaged in simple works than those of greater complexity.
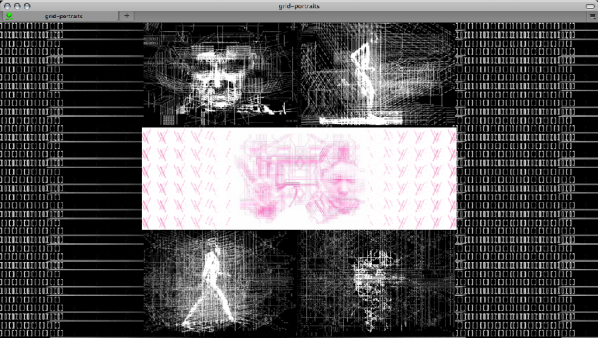
“We exist within a built environment that is constantly mediated by the grid. Grids organize space through coordinate mapping and patterns of development. Grids compress, redisplay, and reorder information. Grids are an enforcement system imposed upon both nature and culture. I respond to this ubiquity by creating gridworks. These forms examine the blurred boundary between the machine and the human – the tool of data collection and the interpretive mind.”
Like a lot of people, my first encounter with the work of A Bill Miller was on the small screen. Despite the numerous festivals and exhibitions that his works have appeared in1, this may be the only chance viewers have to enjoy them. Which is a shame because they really work well when expanded on to a larger screen. Even if you only get to view them on a larger television screen, it’s worth doing. Even some of the work that is small in scale and scope, benefits from being shown on as large a screen as possible. It takes a broader and more encompassing screen to really engage the viewer completely into the work. For some of the black and white work, the overlaying of ASCII letters (reduced to just shapes when not ‘read’ as alphanumeric characters) shows how some works can explore the technical palette of the production software as possible. Which isn’t to say that some of the works aren’t also complex and (literally) multilayered.
There is a psychic landscape explored in Miller’s works. A landscape that feels as though it sits just behind the everyday, observable world we inhabit. Not in a David Lynch, behind the picket fence, kind of way, but inside the mind’s eye, at a point where the brain hasn’t yet coalesced the datastreams of visual stimulation into a recognisable image. It’s that in-between space that seems to at the heart of some of the Gridworks: the spaces between being held in check by the grids. And clean white spaces are beautiful in themselves, but they also divide the elegance of those lines so that the work is about those spaces and the tension of being held in check: stopping them from bleeding into one another. The psychic landscape they map out is the same one that we have to face everyday as we negotiate our way through the ongoing datastream of western life. Work, rest, work, rest, shop, consume. Those days that you feel as though you’ve experienced and understood everything and life begins to blur into one continuous event: all it takes is to step back and really focus on individual moments to remind ourselves that life is actually full of thousands of unique and wonderful moments.
Works like Gridfont 7 suggest that the elegance of a few lines carefully placed can lead to great complexity through simple juxtaposition and rotation of basic forms. Just like so many other things in life, greater complexity begins to emerge from a gradual build up of even the simplest of those elements. Some of the work begins as a few short, hand-drawn lines before they re-adjust themselves and become a hive of geometric shapes: a honeycomb forming from the arrangement and connection of lines. Some works have the colour-bleed of early video work where over-saturated colours refuse to hold their place in the ordered spaces and begin to wander slightly.

gridworks_textanimation2010 is made from pure ASCII text characters, and “transmits an unreadable message that is aesthetic and abstract.” It’s stark black & white play of the non-text elements of written communication gives the impression of loss and emptiness, like lines of communication broken down through digital channels. This could be extracted from a relationship being held together via email or it could be text messages sent between two unreliable narrators each hoping to convince the other of some shared moment. A line of Xs brings to mind censorship but the blank underlines suggest space for the other party to fill in the blanks that we don’t always admit to when trying to maintain the peace in a relationship. Things are constantly being said, but nobody is ever saying anything to each other. Those are the worst accusations of Internet communications but they’re just as guilty of being performed in every other channel. They just become more visual on the Internet and even more so in works like this.
In case these descriptions suggests that the works are dry and overloaded with metaphor and meaning, they can be enjoyed on their purely aesthetic merits. Gridworks2000-anim09 is a work that can only be described as beautiful in its elegance and deceptive simplicity.
Although these works are positioned within media art, they (like many moving image art work) could be considered as cinema (and let’s face it, cinema could do with a fresh burst from a ruptured blood vessel right now). These are part of a cinema of special effects where the use of computer graphics enhances the moving image and steps away from verisimilitude. As mentioned previously, this lack of verisimilitude is part of the reality of these works. An added element of what makes them hauntological ghosts within the screen.
It’s imprinted into the very nature of cinema that it is a ghostly illusion or special effect, either computer generated or produced in the camera that belongs to every moment of cinema’s history. In fact it is even an illusion to believe that we are viewing an actual moving image when we watch a film or video. Either way, cinema is created on-the-fly by our own eye. The trick of creating moving images is to know how the brain responds to them and leverage that response to your own desires. The cross slicing of lines in Miller’s Gridworks feels so much like early computer graphics that at times it’s hard to step beyond thinking about technology’s desire for the new and the increasing momentum of the special effect algorithm and find the beauty in their simplicity. It’s in there and doesn’t take much effort to uncover. Like a good oyster in a restaurant, the reward can be unusual and pleasurable, but you have to get in and expend some energy to extract it.
FILE RIO 2012, Electronic Language International Festival, Art Galery of Oi Futuro, Rio de Janeiro, BR, Mar 12-Apr 8th
Scan2Go, New Media Caucus year long online exhibition, Released at CAA 2012
<terminal> monitors, Austin Peay State University, Clarksville, TN, 2/20-3/2
A/Vworkssssss, One Night Event/Performance, Borg Ward Collective, MIlwaukee, WI Jan 3
Streaming Festival 6th Edition, Het Nutshuis, The Hague, Netherlands, Dec. 1-18 2011
FestivalMulti2011_Especial – Curator David Quiles Guillo, Video Art Program, Rio de Janiero, BR, Nov-Dec 2011
Sheroes, One-Night Interactive Installations (Monthly), Toronto, CA, Nov. 18 and Dec. 23
GLI.TC/H Chicago – Live Video Performance, Chicago, IL Nov. 3-7
GLI.TC/H Program at FLIP Animation Festival, Birmingham, UK, Oct. 29
Punto Y Raya Festival, Museo Reina Sofia Madrid, November 3-6, 2011
BYOB Sao Paulo, Rojo Nova Sao Paulo, Oct. 29
Video On Paper Zine http://videoonpaper.tumblr.com/
3ra Convocatoria Belica, Valencia, Venezuala, September 2011 http://mvs.260mb.com/index2.html
I AM NOT A POET Festival, Edinburgh Aug.8-21 http://tkunst.wordpress.com/
An Interview with Heath Bunting – Part 1
I first met Heath when I moved to Bristol (UK) in 1988. It felt important, even profound. Not in a ‘jump in a bed’ kind of way. Yet our meeting did seem life changing somehow, to the both us. We hit it off and we collided – as equals – our collisions resonated, it shook our imaginations. From then on our paths, our lives connected and clashed regardless. We regularly challenged each other through constant, critical duels of dialogue; about activism, art, technology and ideas surrounding different life approaches and philosophies. From 1988 – 1994 (just before the Internet had properly arrived), in Bristol and London we collaborated on various projects such as pirate radio, street art and the cybercafe BBS – Bulletin Board System. We then went our separate ways exploring our own concerns more deeply, but continued to meet every now and then. Us both meeting in Bristol changed both of our worlds, it built the grounding of where we are now.

Heath founded the Irational.org collective in 1995, a loose grouping of six international net and media artists who came together around the server irational.org. The collective included Daniel Garcia Andujar / Technologies to the People (E), Rachel Baker (GB), Kayle Brandon (GB), Heath Bunting (GB), Minerva Cuevas / Mejor Vida Corporation (MEX) and Marcus Valentine (GB).
Heath Bunting’s work manifests a dry sense of humour, a minimal-raw aesthetic and a hyper-awareness of his own artistic persona and agency whilst engaging with complex political systems, institutions and contexts. Crediting himself as co-founder of both net.art and sport-art movements, he is banned for life from entering the USA for his anti GM work, such as the SuperWeed Kit 1.0 – “a lowtech DIY kit capable of producing a genetically mutant superweed, designed to attack corporate monoculture”. Bunting’s work regularly highlights issues around infringements on privacy or restriction of individual freedom, as well as issues around the mutation of identity; our values and corporate ownership of our cultural/national ‘ID’s’, our DNA and Bio-technologies “He blurs the boundaries between art, everyday life, with an approach that is reminiscent of Allan Kaprow but privileging an activist agenda.”[1]
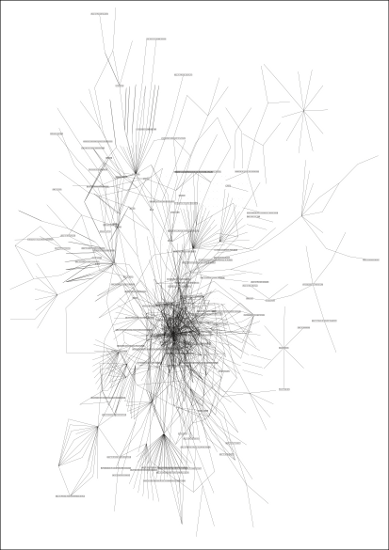
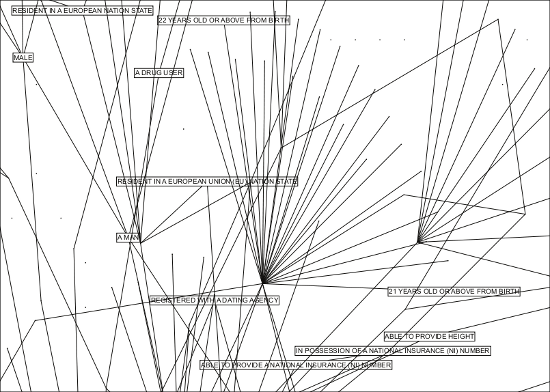
In this two part interview we will discuss his current work within two distinctive areas of digital culture and sport-art starting with The Status Project, which studies the construction of our ‘official identities’ and creates what Bunting describes as “…an expert system for identity mutation”. His research explores how information supplied by the public in their interaction with organisations and institutions is logged. The project draws on his direct encounters with specific database collection processes and the information he was obliged to supply in his life as a public citizen, in order to access specific services; also on data collected from the Internet and from information found on governmental databases. This data is then used to map and illustrate how we behave, relate, choose things, travel and move around in social spaces. The project surveys individuals on a local, national and international level producing maps of influence and personal portraits for both comprehension and social mobility.
Marc Garrett: For many years now, your work has explored the concept of identity, investigating the various issues challenging us in a networked age. The combination of your hacktivist, artistic approach and conceptual processes have brought about a project which I consider is one of the most comprehensive, contemporary art projects of our age. The Status Project, deals with issues around personal identity head-on.
Why did you decide to embark on such a complex project?
Heath Bunting:
Three reasons
1. the network hacker
the network hacker fantasises about unlimited access to all systems made available through possession of treasure maps, keys and navigation skills
2. the Buddhist
the Buddhist intends to destroy the self and become only the summation of environmental factors plus find enlightenment in even the most banal bureaucracy
3. the computer scientist
the computer scientist aims to find comfort and hidden meaning in complex data
I am all three and am attempting to combine the obsessions of each into one project.
So far I have
Created a sketch database of the UK system with over 8000 entries
Created over 50 maps of sub-sections of the system to aid sense of place and potential for social mobility
Created system portraits of existing persons
Created software to generate new identities lawfully (off the shelf persons) and sold these identities
I am currently adding more data to the database. Which is split between the human being (flesh), the natural person (strawman) and the artificial person (corporation). Remaking maps using upgraded spider software, researching how to convert my identity generating software into a bot recognised under UK law as a person; and hence covered by the human rights act i.e. right to life and liberty; freedom of expression; peaceful enjoyment of property. I am very close to achieving this.
Did you know that 75% of the human rights act applies to corporations as well as individuals? If you were afraid of corporations in the 90’s and noughties then be very afraid of the automated voices that speak to you on stations or programs that transact currency exchanges, as they will soon be your legal equals as with all Hollywood propaganda, the reverse is true. The human beings will be the clumsy, half wit robot like creatures serving the new immortal ethereal citizens. If you think I am mad or joking, check back in 10 years time.
MG: Way back in 1995, there were already various groups and individuals (including yourself) who were critiquing human relationships whilst exploiting networked technology. Creative people who were not only hacking technology but also hacking into and around everyday life, expanding their skills by changing the materiality, the physical and immaterial through their practice. It was Critical Art Ensemble (CAE) who in 1995 said “Each one of us has files that rest at the state’s fingertips. Education files, medical files, employment files, financial files, communication files, travel files, and for some, criminal files. Each strand in the trajectory of each person’s life is recorded and maintained. The total collection of records on an individual is his or her data body – a state-and-corporate-controlled doppelganger. What is most unfortunate about this development is that the data body not only claims to have ontological privilege, but actually has it. What your data body says about you is more real than what you say about yourself. The data body is the body by which you are judged in society, and the body which dictates your status in the world. What we are witnessing at this point in time is the triumph of representation over being. The electronic file has conquered self-aware consciousness.”[2]
15 years later, we are dealing with an unstoppable flow of meta-networks, creeping into every area of our livng environments. We have mutated, become part of the larger data-sphere, it’s all around us. As you describe, it seems that we are mutating into fleshy ingredients, nourishing a technologically determined world.
HB: Data body is quite a good way to think about it. I consider each human being to possess one or more natural person(s) and each natural person to control or possess none, one or more artificial person(s) (i.e. corporation). The combined total of natural and artificial persons possessed or controlled by a human being can be thought of as their databody. As human beings, we have quite a lot of control over our persons (natural and artificial). The problem is that we either don’t realise this or it takes the time to manage them. It’s possible to obtain a corporation for less than the price of a train ticket between Bristol and London. Why do so many people live without one? Could anti corporate propaganda have something to do with this ?
“What is most unfortunate about this development is that the data body not only claims to have ontological privilege, but actually has it. What your data body says about you is more real than what you say about yourself.”(CAE).[2]
Only if you remain a passive user of it. The natural person is only linked to the human being through such fine devices as a signature, which we decide to give or withhold, most human being’s natural person is actually owned by the government and borrowed back by the human being. This does not have to be the case as we can create and use our own persons.
“The data body is the body by which you are judged in society, and the body which dictates your status in the world. What we are witnessing at this point in time is the triumph of representation over being. The electronic file has conquered self-aware consciousness.”(CAE).[2]
I would say laziness has triumphed over mindfulness. All information about the functioning of natural persons is easily available, all persons have the same rights unless they choose not to claim them. Instead, people choose to get lost in their own selves and dreams, indulged by those that seek to profit from their labour.
Technology is becoming more advanced and the administration of this technology is becoming more sophisticated and soon, every car in the street will be considered and treated as persons, with human rights. This is not a conspiracy to enslave human beings, it is a result of having to develop usable administration systems for complex relationships. Slaves were not liberated because their owners felt sorry for them, slaves were given more rights as a way to manage them more productively in a more technologically advanced society.
MG: Getting back to the part of your project which incorporates a complex process of compiling and creating ‘off the shelf persons’, as you put it. Are you using some of the collected data as a resource to form these new identities, or is it a set of ‘hybrid’ identities?
HB: Please expand this question further…
MG: Near the beginning of the interview, you mention that you “Created software to generate new identities lawfully (off the shelf persons) and sold these identities.” I am asking whether most of these ‘new identities’ that you have formed and sold are, a mixture of different bits of information. Like data-versions of body parts from a machine or vehicle, reused, recycled to recreate, make new hybrid identities?
HB: The identities I can create are all new and legal, they are a portfolio of new unique legal relationships created with existing artificial persons. For example, registering with Tesco Clubcard either creates or consolidates the new natural person http://status.irational.org/identity_for_sale – for a new natural person to be credible, it must be coherent and rational. This is achieved simply by following the rules of the system, the more interrelating links with other persons, the more real the new person becomes.
Off the shelf natural person.
Comes with supporting physical items:
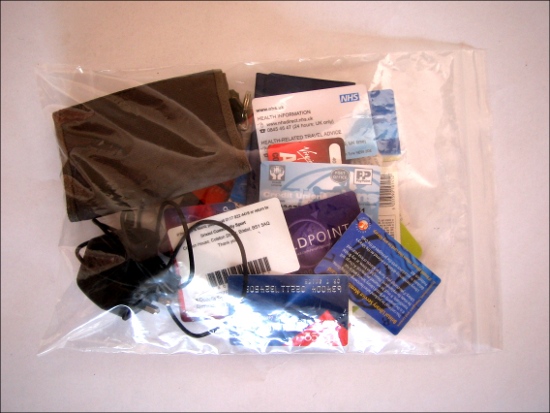

personal business cards, boots advantage card, marriott rewards card, cube cinema membership card, baa world points card, tesco clubcard, vbo membership card, WHSmith clubcard, silverscreen card, airmiles card, somerfield loyalty card, post office saving stamps collector card, virgin addict card, subway sub club card, dashi loyalty card, t-mobile top up card, european health insurance card, waterstone’s card, 20th century flicks card, bristol library card, co-operative membership card, nectar card, oyster card, bristol ferry boat company commuter card, love your body body shop card, co-operative dividend card, bristol credit union card, choices video library card, national rail photocard, bristol credit union account, bristol community sports card, star and garter public house membership card, first class stamp, nhs donor card, winning lottery ticket (2 GBP), t mobile pay as you go mobile and charger…
Upgradable to both corporate and governmental levels.
(500.00 GBP) – SOLD
MG: I can see on the web site, in the section The Status Project – Potentials that there are various ready-mades, ‘Off the shelf natural person – identity kits’. Am I right in presuming that there are individuals out there who have bought and used these kits?
HB: These are mostly existing persons, only one of them was synthetic. I will be setting up a small business soon though to manufacture and sell natural person.
MG: On exploring deeper into the Status Project data-base, there is link to a file called ‘In receipt of income based job seeker’s allowance’. This information is taken from ‘Jobcentre plus’, a UK government run organisation and on-line facility, inviting visitors to search for jobs, training, careers, childcare or voluntary work. How important was this source in compiling data for your database of individuals?
HB: This is only one record of over 8000 in the database, each record refers to one or more other record(s) in the database.
MG: What projects relate to/have influence on The Status Project in some way, and what makes them work?
HB: They Rule[3] – It allows users to browse through these interlocking directories and run searches on the boards and companies. A user can save a map of connections complete with their annotations and email links to these maps to others. They Rule is a starting point for research about these powerful individuals and corporations. A glimpse of some of the relationships of the US ruling class. It takes as its focus the boards of some of the most powerful U.S. companies, which share many of the same directors. Some individuals sit on 5, 6 or 7 of the top 500 companies.
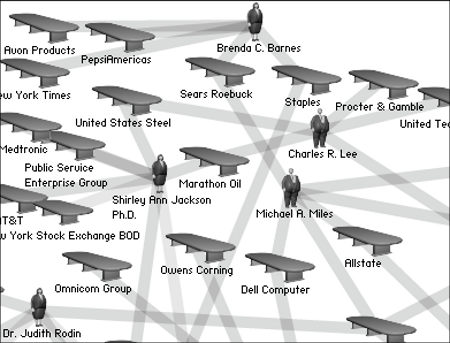
“Go to www.theyrule.net. A white page appears with a deliberately shadowy image of a boardroom table and chairs. Sentences materialize: “They sit on the boards of the largest companies in America.” “Many sit on government committees.” “They make decisions that affect our lives.” Finally, “They rule.” The site allows visitors to trace the connections between individuals who serve on the boards of top corporations, universities, think thanks, foundations and other elite institutions. Created by the presumably pseudonymous Josh On, “They Rule” can be dismissed as classic conspiracy theory. Or it can be viewed, along with David Rothkopf’s Superclass, as a map of how the world really works.”[4]
Bureau d’etudes – distribution.
http://bureaudetudes.org/
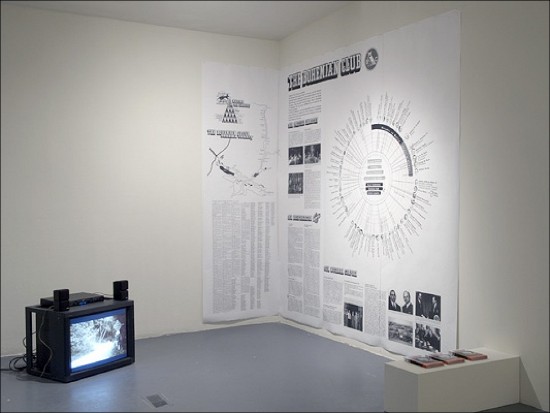

The Paris-based conceptual group, Bureau d’etudes, works intensively in two dimensions. In 2003 for an exhibition called ‘Planet of the Apes’ they created integrated wall charts of the ownership ties between transnational organizations, a synoptic view of the world monetary game. Check the article ‘Cartography of Excess (Bureau Bureau d’etudes, Multiplicity)’ written on Mute by Brian Holmes in 2003.[5]
MG: The sources of data for the Status Project seem to vary in type. Where do you collect them from and how do you collect the different kinds of data?
HB: It ranges from material instruments such as application forms right through to constitutional law and then common sense .
MG: How do you propose the Status Project might be used as a system for ‘identity mutation’?
HB: I want to communicate the fact that people in the UK can create a new identity lawfully without consulting any authority. I intend to illustrate the precise codification of class in the UK system, and there are three clearly defined classes of identity in the UK: human being, person and corporate . I am looking at the borders between these classes and how they touch each other, this can be seen with my status maps. Also, I intend to create aged off-the-shelf persons for sale similar to off-the-shelf corporations.
Taken from the front page of the Status Project:
Lower class human beings possess one severly reduced natural person and no control of an artificial person.
Middle class human beings possess one natural person and perhaps control one artificial person.
Upper class human beings possess multiple natural persons and control numerous artificial persons with skillful separation and interplay.
End of Part 1.
————–
Article by Rosa Menkman
Based on an interview with the Critical Glitch Artware Category organizers and contenders of Blockparty and Notacon 2010: jonCates, James Connolly, Eric Oja Pellegrino, Jon.Satrom, Nick Briz, Jake Elliott, Mark Beasley, Tamas kemenczy and Melissa Barron.
From April 15-18th, the Critical Glitch Artware Category (CGAC) celebrated its fourth edition within the Blockparty demoparty and this time also as part of the art and technology conference Notacon.
The program of the CGAC consisted of a screening curated by Nick Briz, performances by Jon Satrom, James Connolly & Eric Pellegrino, and DJ sets by the BAD NEW FUTURE CREW. There were also a couple of artist presentations and the official presentation of a selection of the (115!) winners within the Blockparty official prize ceremony.

The fact that CGAC was coupled with a demoscene event is somewhat extraordinary. It is true that both the demoscene and CGAC or ‘glitchscene(s)’ focus on pushing boundaries of hardware and software, but that said, I (as an occasional contender within both scenes) could not think about two more parallel, yet conflicting worlds. The demoscene could be described as a ‘polymere’ culture (solid, low entropic and unmixable), whereas CGAC is more like an highly entropic gas-culture, moving fast and chaotically changing from form to form. When the two come together, it is like a cultural representation of a chemical emulsion; due to their different configuration-entropy, they just won’t (easily) mix.
But all substances are affected (oxidized) by the hands of time; there is always (a minimal) consequence at the margin. And this was not the first time these two cultures were exposed to each other either; Criticalartware had been present at Blockparty since 2007. Moreover, a culture can of course not be as strictly delineated as a chemical compound; it was thus clear that this year the two were reacting to each other.
While over the last couple of years the demoscene has been described in books, articles and thesis’, this particular kind of ‘fringe provocation’ is not what these researchers seem to focus on; they (exceptions apart) concentrate on the exclusivity of the scene and its basic or specific characteristics. The ‘assembly’ of these two cultures during Blockparty could therefore not only serve as a very special testing moment, but also widen and (re)contextualize the scope of the normally independent researches of these cultures. So what happened when the compounds of the chemicals were ‘mixed’ and what new insights do we get from this challenging alliance (if there is such a thing)?
The demoscene is often described as a bounded, delimitated and relatively conservative culture. Its artifacts are dispersed within well-defined, rarely challenged categories (for the contenders, there is the ‘wild card’ category). Moreover, the scene is a meritocracy – while the contenders (that refer to themselves with handles or pseudonyms) within the scene have roles and work in groups, the elite is ‘chosen’ by its aptitude.
The demoscene also serves a very specific aesthetics, as enumerated by Antti Silvast and Markku Reunanen this week on Rhizome (synced music and visuals, scrolling texts, 3d objects reflections, shiny materials, effects that move towards the viewer – tunnels and zooming – overlays of images and text, photo realistic drawing and adoption of popular culture are the norm). In the same article Silvast and Reunanen declare that: ‘Interestingly, even though we’re talking about technologically proficient young people, the demosceners are not among the first adopters of new platforms, as illustrated by numerous heated diskmag and online discussions. At first there is usually strong opposition against new platforms. One of the most popular arguments is that better computers make it too easy for anybody to create audiovisually impressive productions. Despite the first reactions, the demoscene eventually follows the mainstream of computing and adopts its ways after a transitional period of years.'[1]
More about this can be read at Rhizome’s week long coverage of the demoscene. Silvast and Reunanen’s statement might be most interesting when we move along to see what happened during the meeting of the two scenes.
Co-founded by jonCates, Blithe Riley, Jon Satrom, Ben Syverson and Christian Ryan in 2002, Criticalartware is a radically inclusive group that started as a media art history research and development lab. Since 2002 the group has shifted and transitioned. Criticalartware’s formation was deeply influenced by the Radical Software platform (publications and projects). Since then it has been an open platform for critical thinking about the use of technology in various cultures. Criticalartware applies media art histories to current technologies via Dirty New Media or digitalPunk approaches. Through tactics of interleaving and hyper threading it permeates into cultural categories of Software Studies, Glitch Art, Noise and New Media Art.
During the first phase of Criticalartware (from 2002 – 2007), the group was a collaborative of artist-programmers/hackers. It also functioned as a media art histories research and development lab. In this form, Criticalartware had become an internationally recognized and reviewed project and platform.
When this phase ended in 2007, jonCates, Tamas Kemenczy and Jake Elliott were the remaining active members of Criticalartware. During this time, Elliott and Kemenczy wanted to take the project in a new direction; into the demoscene. This direction has ultimately defined the second phase of Criticalartware; an artware demo crew, making work for and appearing annually at the Blockparty event and Notacon conference in Cleveland.
2010 marked the next important transition for the Criticalartware crew, when it started using the phrase ‘Critical Glitch Artware’- Category. Criticalartware now not only organizes itself around the demoscene but also around the concept of the glitch. While a glitch (not to be confused with glitch art) appears as an accident or the result of misencoding between different actors, CA’s Glitch-art category exploits this possibility in an metaphorical way. Criticalartware is now foregrounding these glitch art works (with an emphasis on the procedural/software works) that have been on a ‘pivotal axis’ of the crew for a long time.

CGA, just like the demoscene, can be described as an open (plat)form for artistic activity/culture/way of life/counter culture/multimedia hacker culture and (unfortunately a bit of ) a gendered community. CA are about pointing out ideas or concepts within popular culture and incorporating (standardizing) these as machines or programs in a reflexive and critical self-aware manner.
CA can also be described as an investigating of standard structures and systems. They are often amongst early adopters of technology, in which they (politically) challenge and subvert categories, genres, interfaces and expectations. But the CGA – artists do not feel stuck in a particular technology, which makes it aesthetically, at least at first sight hard to pinpoint a common denominator.
There is not a real organization within this scene. The artists and theorists are scattered over the world, connected in fluid/loosely tied networks dispersed over many different platforms (Flickr, Vimeo, Yahoo groups, Youtube, NING, Blogger and Delicious).
Because of its bounded, intricate conservative qualities, the demoscene has been an easy target for outsiders to play ‘popular’ ironic pranks on, to misunderstand or misrepresent. A growing interest for the demoscene by outsiders has compelled jonCates and the Criticalartware crew to articulate their position towards the demoscene more extensively. In an interview with me, jonCates articulates Criticalartware’s points and contrasts these with problematic representations of the demoscene within two works by the BEIGE Collective (that in 2002 existed along side the Criticalartware crew in Chicago).
When the BEIGE collective went to the HOPE (Hackers on Planet Earth) Conference in 2002 they made a project called: TEMP IS #173083.844NUTS ON YOUR NECK or Hacker Fashion: A Photo Essay by Paul B.Davis + Cory Arcangel.
jonCates writes to me that ‘this problematic project characterizes or epitomizes a kind of artists as interlopers positionality that i + Criticalartware as a crew has always attempted to complicate. we do not want or understand ourselves as seeking out an ironic or sarcastically oppositional position in relation to the contexts that we choose to work in. we have not set out to ridicule the demoscene or otherwise make ridiculous our relations to the demoscene. in contrast, we set out to operate within a specific demoscene through multi-valiant forms of criticality, playfullness, enthusiasm, respect, interest, admiration, etc… this has also been in efforts to connect this specific demoscene to our experimental Noise & New Media Art scenes or what you Rosa referred to earlier as glitchscene…’
Another point of contention for jonCates is the Low Level All-Stars project by BEIGE (in this case, Cory Arcangel) + Radical Software Group (Alexander R. Galloway). this work is described as ‘Video Graffiti from the Commodore 64 Computer’ (2003) by Electronic Arts Intermix who sells/distributes this work as a video in the context of Video Art.
Low Level All-Stars has been shown at Deitch Projects in NYC in 2005 and circulated in the contemporary art world. jonCates writes to me saying the work seeks ‘to isolate + thereby establish cultural values for this ‘quasi-anthropological’ view of demos as found object + functioning as a tasteful ‘testament to a lost subculture.’ It is now being offered online as an educational purchase for $35 dollars.
However, as jonCates and Criticalartware work in the demoscene demonstrates, the demoscene subculture is not lost, nor over. jonCates moves on by writing that ‘the demoscene is a vibrant whirld wit a dynamic set of pasts + presents. this is another of which many (art) whirlds are possible. we seek to make those whirlds known to each others + ourselves out of respect, curiosity, investment, inclusiveness, criticality, playfullness, etc…’


The Criticalartware crew has been taking part in Blockparty since 2007, when it won the last place in a demo competition and was disqualified. One year later, in 2008, through a number of efforts (including Jake Elliott’s presentation Dirty New Media: Art, Activism and Computer Counter Cultures at HOPE, the Hackers on Planet Earth conference in NYC in 2008). CA was able to mobilize and manifest the concept of the Artware category at Blockparty, a category which Blockparty itself retroactively recognized CA for winning.
In the same year (2009) CA organized a talk at Blockparty in which they revealed the “secret source codes” of the tool they used to develop the winning artware of the year before.
By 2010 CA wanted to expand the concept of Artware within the demoscene, which lead to the development of the ‘Critical Glitch Artware Category’ event. Within the CGAC Compo there where 115 subcategory winners, which showed some kind of glitch-critique towards systematic categorization of Artware. Jason Scott (the organizer of Blockparty) personally invited CGAC to pick 3 winners and present their wares at the official Blockparty prize ceremony. Besides these three winners, CGACs efforts got extra credits when Jon Satrom’s Velocanim_RBW also won the Wild card category compo.

Therefore, not only did CA intentionally open up the Blockparty event to outsiders of the demoscene, it also provided a place for new media art and the glitchscene within the demoscene and got Blockparty to accept and invite the CA within their program. Thus, the outsiders (CA) moved towards the inside of the event, while the insiders got introduced to what happens outside of the demoscene (event), which led to conversations and insights into for instance bug collecting, curating and coding.
The Critical Glitch Artware Category has been accepted by, at least, the fringe of Blockparty 2010. Even though the category itself is not (yet) visible on the website, Satrom’s winning work Velocanim_RBW is. Moreover, CGAC was part of the official prize ceremony, streamed live on Ustream, the live Blockparty internet television stream. So how does CGAC redefine or reorganize the fringe between them and the demoscene and how does the demoscene redefine and reorganize the structure of CGAC?
For now, I think crystallized research into the aesthetics of the demoscene can also help describe the aesthetics within CGAC. Custom elements like rasters, grids, blocks, points, vectors, discoloration, fragmentation (or linearity), complexity and interlacing are all visually aesthetic results of formal file structures. However, the aesthetics of CGA do not limit themselves, nor should they be demarcated by just these formal characteristics of the exploited media technology.
Reading more about the demoscene aesthetics, I ran into a text written by Viznut, a theorist within the demoscene (who also wrote about ‘thinking outside of the box within the demoscene’). He separates two aesthetic practices within the scene: optimalism (an ‘oldschool’ attitude) which aims at pushing the boundaries in order to fit in ‘as much beauty as possible’ in as little code necessary, and reductivism (or ‘newschool’ attitude), which “idealizes the low complexity itself as a source of beauty.'[2]
He writes that “The reductivist approach does not lead to a similar pushing of boundaries as optimalism, and in many cases, strict boundaries aren’t even introduced. Regardless, a kind of pushing is possible — by exploring ever-simpler structures and their expressive power — but most reductivists don’t seem to be interested in this aspect”.
A slightly similar construction could be used for aesthetics within Glitch Art. Within the realm of glitch art we can separate works that (similar to optimalism) aim at pushing boundaries (not in terms of minimal quantity of code, but as a subversive, political way, or what I call Critical Media Aesthetics; aesthetics that criticize and bring the medium in a critical state) and minimalism (glitch works that just focus on the -low- complexity itself – that use supervisual aesthetics as a source of beauty). The latter approach seems to end in designed imperfections and the (popularized) use of glitch as a commodity or filter.[3]
Of course these two oppositions exist in reality on a more sliding scale. Debatebly and over simplified I would like to propose this scale as the Jodi – Mille Plateaux (old version) – Beflix – Alva Noto – Glitch Mob – Kanye West/Americas Next Top Model Credits continuum; A continuum that moves from procedural/conceptual glitch art following a critical media aesthetics to the aesthetics of designed or filter based imperfections.
This kind of continuum forces us to ask questions about the relationships between various formalisms, conceptual process-based approaches, dematerializations and materialist approaches, Software Studies, Glitch Studies and Criticalartware, that could also be of interest or help to future research into the demoscene. When I ask jonCates what other questions CGAC brings to the surface, he answers:
“when i asked Satrom to participate in the CRITICAL GLITCH ARTWARE CATEGORY event + explained the concept that Jake + i had developed to him he was immediately interested in talking about it as form of hacking a hacker conference, by creating a backdoor into the conference/demoscene/party/event. im also excited about this way of discussion the event + our reasonings + intentions, but i want to underscore that this effort is also undertaken out of respect for everyone involved, those from the demoscene, glitchscenes, hackers, computer enthusiasts, experimental New Media Artists, archivists, those who are working to preserve computer culture, Noise Artists + Musicians, etc… so while this may be a kind cultural hack/crack it is not done maliciously. we are playful in our approach (i.e. the pranksterism that Nick refers) but we are not merely court jesters in the kingdom of BLOCKPARTY. we have now, as of 2010, achieved complete integration into the event without ever asking for permission. perhaps that is digitalPunk. + mayhaps that is a reason for making so many categories +/or so many WINNERS! 🙂
…also, opening the category as we did (with a call for works [although under a very short deadline], an invitational in the form of spam-styled personal/New Media Art whirlds contacts + mass promotional email announcements of WINNERS! (in the style of the largest-scale international New Media Art festivals such as Ars Electronica, transmediale, etc…) opens a set of questions about inclusion.
…whois included? who self-selects? whois in glitchscenes? are Glitch Artists in the demoscene? etc… this opening also renders a view on a possible whirld, which was an important part of my intent in my selection of those who won the invitational aspect of the CRITICAL GLITCH ARTWARE CATEGORY. by drawing together (virtually, online + in person) these ppl, we render a whirld in which an international glitchscene exists, momentarily inside a demoscene, a specific timeplace + context.”
Lately the demoscene seems to get more and more attention from “outsiders”. Not only ‘pranksters’, artists and designers who are interested in an “old skool” aesthetic, but also researchers and developers that genuinely feel a connection or interest to a demoscene culture (I use ‘a’ because I think there still should be a debate about if there might be different demoscene cultures).
This development makes it possible to research a subculture normally described as ‘closed/bounded’ and to see where and how these different cultures are delineated. The tension between Blockparty/Notacon and Critical Glitch Artware Category is one that takes place on a fringe. They do not come together, but while it would be easy to just think that probably the CGAC sceners were just ignored (and maybe flamed) by the demosceners half of the time, some more interesting and important developments and insights also took place.
The CGAC-crew has over the years shown itself to be volatile, critical and unexpected, but it has also shown respect to the traditions of the demoscene and in doing so, earned a place within this culture (at least at Blockparty). This gave the CGAC-democrew not only the opportunity to put a foot in the backdoor of a normally closed system, but also to give some more insights into what they expose best: they confronted the contenders with their (self-imposed) structures and introduced them to (yet to be understood and accepted) new possibilities.
So what happens when a polymere is confronted with entropic gasses? I think the chemical compounds get the opportunity to measure the entropic elasticity of their dogmatic chains.
Also read:
Carlsson, Anders. Passionately fucking the scene: Skrju.
http://chipflip.wordpress.com/2010/05/20/passionately-fucking-the-scene-skrju/ Chipflip. May 20th, 2010.
Curated by Carolyn Kane for Rhizome September, 2009.
#60605 plus #20101 does not equal black, but it looks like it to me. And despite Newton’s insistence, a rainbow is never made from seven colours in neat lines, nor can I see millions of colours on my calibrated monitor. It is more likely that each day I engage with the screen as a greenish-blue glow infused with hits of magenta. Or as it is today: a summer grey of sea fog glimpsed through the rain. Is that a colour? Carolyn Kane curated HTML Color Codes in order to ask these questions of the relationship between colour, code, and subjectivity. Tracing a carefully structured path through twelve artworks Kane seeks to examine whether artists working with the Internet are limited to a ‘ready-made’ colour palette. Asking if digital colours reflect the programming languages that have been adopted, Kane considers whether the Internet adds its own rules for colour through the adoption of the hexadecimal system of colour values. Does the language determine the content?
The answer is, not quite. It all depends on where and how the viewer approaches the screen. Rather than trying to be paintings these works engage with the materiality of digital colour and the manipulation of a different kind of flat predetermined surface – the screen. Chris Ashley gives us rectangles within rectangles, Dlsan manipulates circles within circles, and Michael Atavar offers the blue screen of an empty window with text written as if in the condensation of a cold morning. It is the noise of the digital image embraced by the inadequacy of a gif representation of a treasure heap of digital gold in Jacob Broms Engblom’s “Gold”, or the absence of any controlling frame in Owen Plotkin’s “Firelight” and the flickering spaces nested within and alongside one another in Rafael Rozendaal’s “RGB” that suggest different rules for the digital image. In these latter works the illusion of immediacy raises a spectre of some kind of phenomenological directness.

Twentieth century colour field painting was never a single set of experiments yet it carried within it a set of cultural and formal presuppositions. The digital colour field has its own baggage set. It is inbetween: inbetween code and software, browser and window, network and bandwith. More often than not the experience of the digital colour field is the result of an image within an image or a screen within a screen. Despite its origins in hexadecimal notation digital colour is not a ready-made, but an experience and a process of light and interaction. Anyone who has attempted to capture or translate a colour between screens knows that accidents occur. Noah Venezia’s “The Rainbow Website” suggests that a kind of synaesthesia can be experienced through the screen, that colour exceeds the values assigned to it. Andrew Venell’s “Color Field Television” mimics the flicker of experimental film from the 1970s. Perception becomes a process of seeing the colours inbetween, the work turns back on itself mirrored within a screen. Structural film experiments were about exploring more than perception they too turned back to the medium. Morgan Rush Jones gets even closer with the phased colour space of “Number of ManufacturingIndustriesbyNumberof Product ClassesinanIndustry”. The work is simultaneously overloaded with image and abstracted from it. There is a strange congruence reflected here: in their formality these works do not push new experimental boundaries but reflect older ones.
Michael Demers explicitly engages the materiality of the digital medium by establishing a series of systems within which abstraction can occur. Sampling Morris Louis’s oil painting “Where” from 1960, Demers generates a sequence of flat colour planes (windows) from left to right that disappear as quickly as they appear. The drip and movement of Louis’s work is rendered temporal. Brian Piana’s “Elsworth Kelly Hacked my Twitter” also addresses the temporality of the digital. Real-time data orders the compositional frame in a direct chronological sequence. Each square is a representation of an invisible network. Manipulation of the scale, size and shape of the frame is left to the viewer. For me it is Elna Frederick’s “@ = landscape” that allows an interactive experience of the subjective dimension of colour that is specific to the digital. The click of a mouse becomes the experience of putting a finger into a stream of water and disturbing the flow. It is not necessarily the colour that makes the rain but the movement and the belief instilled in us from Super Mario that onscreen fluffy white blobs potentially contain rain. There is a cool sensuousness to the trickle of pixels as it becomes water and when left alone returns to simply being yet another onscreen blue.

There is a risk of over determination in this show, the kind of visual parity that results from too many works looking at the same thing and becoming somewhat redundant. It is the quiet spaces between the works, the mutable changing structures of the blue screen that resist this limitation. As long as bandwidth remains with us, and the links stay live, these works are infinite and through their repetition we experience an abyss of generated colour and code. These are predominately forms consisting of colour alone, and surprisingly, that is enough. This is how the medium of digital colour should be approached. There is no translucency, but there is an unlimited interplay of substitutions.

Digital Pioneers
Victoria And Albert Museum
7 December 2009 – 25 April 2010
(Illustration – Herbert W. Franke, Squares (Quadrate), screenprint, 1969/70)
Digital Pioneers is a deceptively modest exhibition hidden away in two rooms upstairs at the Victoria and Albert Museum. It contains some of the earliest examples of art produced using electronic devices and computing machinery along with some creative later work.
The bulk of the art in the show was produced between the 1950s and the 1970s. This means that it was produced or recorded as photographs from cathode ray tubes or as print-outs from teletypes and pen plotters. Some of this work will be familiar to students of the history of art computing through reproductions but as with most art reproductions do not tell the whole story.
Seeing the actual work itself is as important for art made using the paraphernalia of early digital computing as it is for art made with linseed oil and cotton duck. What Digital Pioneers drives home is just how deeply and intentionally involved early computer artists were in manipulating the aesthetically limited but socially and ideologically key technology of computing machinery. This leaves both social art historians and code aesthetes with some explaining to do, or at least some catching up.

The show starts in the 1950s with the algorithmic and electronic but non-digital and non-computational photographs of oscilloscope patterns by Ben Laposky and screen-prints of photographs by Herbert W. Franke. Most of the works included in the show are prints of one kind or another, and these are no exception. They record the movement of a beam of light on a cathode ray tube as other prints in the show record the movement of a plotter pen or a laser in a laser printer.
If Constructivism was socially realistic for revolutionary Russia then these works are socially realistic against the backdrop of NATO’s military-industrial-educational complex. They turn the technology of that culture back on itself, using it not to produce weapons or market products but to produce aesthetics. This reclaims a space for perception and contemplation that is not simply militarily or economically exploited. The obsessively quantitative managerial culture of spreadsheets and inventories yields uncomfortably to the qualitative culture of aesthetics, productively so. These strategies continue through the show. Technology is pushed beyond its intended uses to address cultural tasks.
Many of the prints in the show have a similar number of stages of production to Franke’s process of screen, then photograph, then silkscreen prints. His later plotter-drawn work is also screen printed, as are Klee-inspired generative images by Frieder Nake, and Charles Csuri’s random montage of flies. I don’t know what to make of this. It feels like something should have been lost in the move from an original to a print but plotter drawings aren’t particularly originals, being already representations of data structures in the computer’s memory.
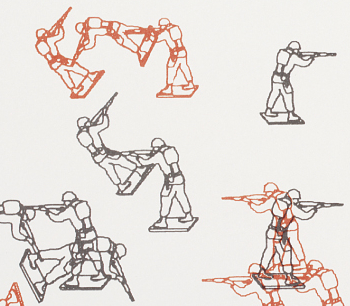
Csuri’s lithograph of randomly placed vector outlines of toy soldiers was produced in 1967 during the Vietnam War, a war that ran as long as it did in no small part due to game theory and computer simulation. There are two armies, one plotted in red and one plotted in black. They meet and presumably battle inevitably but only by chance. There’s more of the outside world in art computing than is often assumed.
William Fetter’s wonderful three dimensional vector images of human figures produced for the aircraft manufacturer Boeing, a lithograph from the Cybernetic Serendipity show of 1968, also deal with the human figure within the military-industrial complex. We should not be confused about the status of such images as art by the use and funding of computer graphics by corporations any more than we should be confused about the status of painting as art by the use and funding of oil painting by the Catholic church.
Ken Knowlton’s cheeky nudes and other typographic images of the 1960s and 1980s are an effective escape or release from the constraints of corporate information culture. I’d seen them many times in reproduction but again they are much richer visually as prints.

More detailed systems-based patterns emerge in the 1970s in the work of artists such as Manfred Mohr, Paul Brown, and Vera Molnar. This era that epitomises the approach of rule based serendipity so beloved of later Generative artists. These images are pleasurable to look at but also contain visual or psychological complexity. They also continues to push the performance of computer systems outside of their intended use cases.
By the late 1980s the technical achievements of computerised mass media were exceeding those of art computing. Pen plotters, where they were still used, were no rival to laser printers. Rendered images had to compete with the earliest rumblings of Pixar and Adobe. The increasing availability of digitally designed fashion and entertainment meant that far from being the exception, digital elements in the lived visual environment were becoming the rule.
The reactions to this that art computing in general have made are the subject of the Decode show that is also running at the V&A. Digital Pioneers instead follows the printmaking thread of art computing into the present day where artists such as Roman Verostko, Mark Wilson and Paul Brown have continued with the systems art all-overness of print-based art computing.
To continue in this way marks such work out as something different from the all-pervasive presence of digital imagery in the visual environment. The work has to look different from graphic design and new media rather than from CAD plots or teletype reports, and it does. These works remind us of the history and of the wiring under the board of digital culture. They successfully resist any attempt to reduce them to digital mass media images comparable to the output of the design software that they exist in the same era as.
This switch away from early adoption is necessary to maintain a figure/ground relationship (or a critical distance, or a constructive difference) between the general level of technology in society and the level of technology in art computing. It is not the only solution to this problem, as the Decode show demonstrates, but it is not a retreat.

As a long time fan of Harold Cohen, I found the show’s inclusion of computer generated works from his very earliest 1960s felt-tip-on-teletype-print experiments with generating figure and ground relationships computationally to a recent large-scale full-colour inkjet abstract was a real treat. Plotter drawings of abstract shapes from the 1970s and of human and plant forms from the 1980s show the progress that Cohen made in using computers to rigorously explore how art and images are created and function. Being able to study this work close-up reveals details such as debugging information in the teletype prints and the operation of the collision-detection algorithm in the 1980s images. And it provides the pleasure of seeing detailed, well-composed drawings.
This is a recurring experience in Digital Pioneers. Despite the uniformly dismissive attitude of both popular and academic criticism towards art computing the fact is that when you actually see the work in the flesh it rewards sustained attention. Not as historical or technical curiosities, but as images with cultural and aesthetic content and resonance. To ignore this and to continue to claim that this art is less than the sum of its parts would ironically be to fall prey to a particularly extreme attitude of technological determinism.
The show also contains displays of ephemera including magazines and books such as back issues of the Computer Arts Society’s “PAGE” and William Gibson’s supposedly self-erasing story on a floppy disk “Agrippa”. I’d not seen an actual copy of “Agrippa” before. PAGE back-issues are available online, but their presence here flags an important point.
The revived Computer Arts Society has been key in promoting and deepening understanding of the history of art computing in the UK. The Digital Pioneers show and its excellent accompanying book are a good example of how CAS’s project has spread out into more traditional cultural institutions, and many of the images and exhibits in the show come from the archives that CAS has donated to the V&A.

The “Digital Pioneers” book (by Honor Beddard and Douglas Dodds, V & A Publishing, 2009) serves as a catalogue for the show . It contains an informative introductory essay and printed images of many of the works on display as well as a CD-ROM with 200dpi scans of them. These scans are high-resolution enough to be able to examine the images in some detail, although they are no substitute for seeing the images in the gallery. A slightly excessive copyright licencing notice is the only indication that the book has in fact been produced as one in a series of pattern books from the V&A. It’s a must-have if you enjoy the show or have any interest in early art computing.
Digital Pioneers is an opportunity to really look at the work of early computer artists and to evaluate that work directly rather than through the medium of poor reproductions or through the fog of received critical opinion. As a slice of artistic history that just so happens to have been produced on computer it contains much to reward both the eye and the mind.
Update: Two recently published books provide more extensive background to the period covered by the show, making the history of this fascinating era available to current practitioners –
White Heat, Cold Logic: British Computer Art 1960-1980‘ edited by Charlie Gere et al covers the history of British computer art and the Computer Arts Society.
A Computer in the Art Room by Catherine Mason describes the relationship between British art schools and computing (which is how I became interested in this area in the first place).
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.