



Featured Image: Black Shoals: Dark Matter’, Joshua Portway, Lise Autogena, Big Bang Data.
Big Bang Data is a major travelling exhibition currently set within London’s Somerset House. That a large institution is presenting a journey via data capture through ‘selfies, surveillance and infographics’ is in itself an interesting patchwork of intent and realisation. The aim of the exhibition is to ‘demystify data’. This is a grand, summative and in actuality slightly awkward claim which, in my view, encapsulates the character of an interesting, textured exhibition in an unintentionally astute way.
As Big Bang Data is dedicated to revealing data comprehensively through its various architectures and iterations, it makes sense for the underrepresented materiality of information to have prominence early on. This materiality, perhaps inevitably, was compromised in the gallery space. Entering the first room brings you face to face with Timo Arnall’s Internet Machine, which takes the form of multiscreen video documentation of not just the machines, but also the architecture, which supports mobile telephony.

I would have loved to have experienced the spaces shown more intimately and walked around one of these structures; the installation was illuminating but I was still most certainly watching at a remove. This initial interplay of removal and involvement is central to the way we experience data. How can people begin to understand something which exists as multiple codes and flows, on a scale and at a speed which is not concerned with making itself understood by humans? What form could an understanding of data possibly take? When learning about something this far from our grasp, it seems that ‘understanding’ must be replaced by ‘awareness’. Rather than seeking one answer via one route the visitor to Big Bang Data has to build an impression, obviously subjective and subject to change.
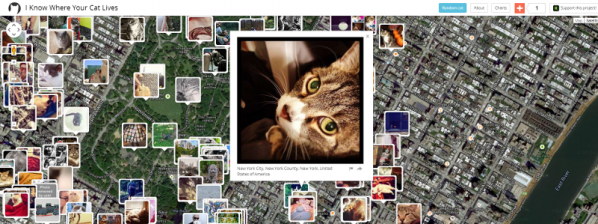
In its quest to expose and explain data’s social and cultural uses, it presents a fairly overwhelming amount of information. It is interesting to walk through the space thinking about how this information has been channeled by each specific project. Some representations, such as Owen Mundy’s ‘I Know Where Your Cat Lives’, link distant people and spaces via connected points, while others such as Phillip Adrian’s ‘One Second’ capture in great detail one specific point in time and space.

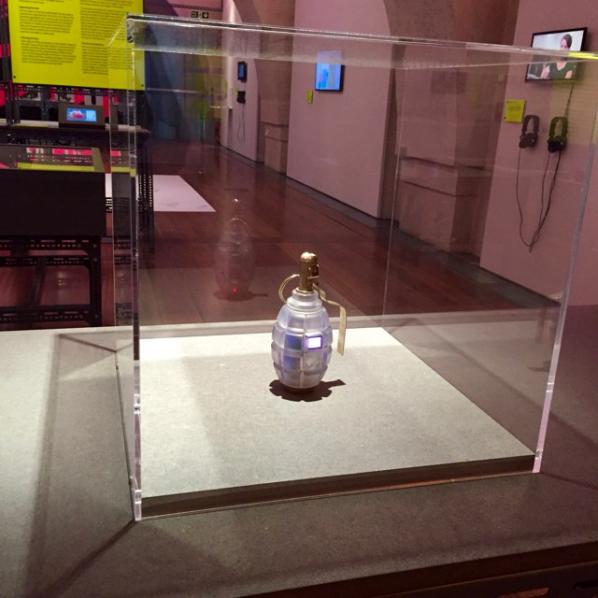
Julian Oliver’s ‘Transparency Grenade’ brings together graphical, console and physical representations of data to offer a transportable means of leaking information as a response to impenetrable governing systems. Each of the works on display demonstrates a negotiation between temporality, materiality and spatiality, and often one is sidelined in favour of the other. Again, considering the exhibition in this way is also to consider the world of data in all its contrariness.

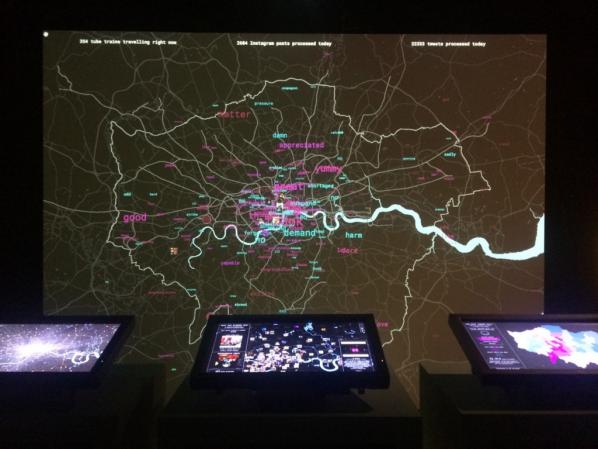
Data manifests itself at the same time locally and globally. As well as addressing specificity, the projects shown in Big Bang Data dwell repeatedly on scale. Works such as Tejka’s ‘London Data Streams’ and Nicholas Felton’s ‘Annual Reports’ pit scales against each other to cast light on the filters through which data is processed.

Ingo Günther’s ‘World Processor’ and Forensic Architecture’s ‘Liquid Traces: The Left-To-Die Boat Case’ are examples of resonant, atypical data visualisations which mutate familiar imagery and present alternative summaries of events. The section entitled ‘Data For The Common Good’ shows some of the ways data is being actively used in society to empower citizens with works such as Safecast’s ‘bGeigie Nano’ and IF’s ‘Data Licenses’, while a series of video interviews with journalists and other professionals working with data illuminate the processes through which information becomes communication.

The previously mentioned tension between object and their presentation recurs at various points throughout the exhibition, a great example being the array of undersea telephone cables, presented in cases of wood and glass which could have been magpied from a display of historical artifacts (each cable segment has a number next to it which corresponds to a factual description). It felt strange not being able to touch them. A work which I felt fully occupied, and knowingly played with, its surroundings was Ellie Harrison’s vending machine, which sits unassumingly in the gift shop; its secret is that when search terms connected to the recession make the headlines, free snacks are dispensed. Its presence in a exhibition on data in a gallery space felt appropriate.

Big Bang Data, which runs alongside a programme of events and has previously been exhibited at CCCB in Barcelona, comes at a moment where large organisations are more frequently bringing concepts such as surveillance, open source and free software into public spaces. There is a great need to bring the concepts and processes surrounding data more wholly into the public eye, and this exhibition strikes me as, overall, a big step in a good direction. It makes real and challenging efforts to bring together world-spanning processes, complex concepts and extremely diverse content into an exhibition space. The task of the exhibition’s curatorial and production teams must have been difficult.
Of course the challenges they faced have been dealt with before many times in many ways, and of course the practical decision-making involved in producing an exhibition invariably creates tension points. The reason I’ve dwelt on the problems of the organisers here is that the tensions evidenced within the space at Somerset House say much not just about the response of the publicly funded arts to data but also about the nature of data itself. The exhibition turns into at times a museum, a bedroom, a classroom, an information point, a scruffy new gallery space and a state of the art new media space. In bringing together the story of data the exhibition also brings together the story of representation in space more generally.
In writing about Big Bang Data I have had to choose to highlight certain works and not others. Your interpretation will be entirely different from mine, which is as it should be where data and cultural inclusion is concerned. What’s important is that the exhibition’s prominence and texture opens up conversation and critique. The exhibition is detailed, procedural and expansive. It is also alive with contrariness, generality and awkwardness. Perhaps one of the great things about the show is that these qualities are left to jostle for space. For me, reading this exhibition as a performative event was useful; others may leave Somerset House with an entirely different view having taken an entirely different route. This is inevitable where data is concerned – learning is incremental and procedural, but not traditionally linear.