



All Raise This Barn – a group-assembled public building and/or sculpture.
“Artists MTAA are conducting an old-fashioned barn-raising using high-tech techniques. The general public group-decides design, architectural, structural and aesthetic choices using a commercially-available barn-making kit as the starting point.” -MTAA
Eric Dymond: Could you give me a brief history of MTAA?
T.Whid: Mike Sarff (M.River of MTAA) and I met in college at the Columbus College of Art & Design in Columbus, OH. We both separately moved to NYC in 1992 and started collaborating as MTAA in 1996 first on paintings and then moving on to public happenings and web/net art. We’ve been collaborating since, showing our work via our websites at mteww.com and mtaa.net. We’ve earned grants and commissions from Creative Capital, Rhizome.org and SFMOMA and shown at the New Museum, 01SJ Biennial, the Whitney Museum and Postmasters Gallery.
ED: The All Raise This Barn project uses one community to design and another to construct. Barn raising is itself a communal activity, drawing out the best in people and providing a place of sustenance for the Barn owner. How did you come to use a Barn Raising as the central performance subject?
M.River: From the start, Tim and I have been interested in how groups and individuals communicate. How do we speak to each other? What rules do we use? How does communication fail or how can it be disrupted? What is the desire that engines (TW: controls?) all of this – and so on. This interest in exchange is what attracted us to the Internet as a site for art in the beginning.
Along with communication as text, speech or image, we like to use group-building as a method for working with non-verbal communication. We’ve built robot costumes, car models, aliens and snowmen with large and small groups. It’s a type of building that is intuitive and open to creative improvisation. This kind of intuitive building is heightened by placing a time constraint on the performance. In the end it’s not about the end object, which we always seem to like, but more about the group activity.
So, at some point we began to think how large can we do this? A barn-raising seemed like the next level. It’s bigger than human scale and contains a history of group-building. Barns also have a history of being social spaces. Your home is your world but the barn is your dance hall.
ED: Did you envision it as a community event from the beginning?
MR: Yes. An online community, a physical community and a community that overlaps the two.
ED: It’s a hybrid work that draws upon some important conceptual precedents. The instructional aspect takes Lewitt and turns the strict instructions he uses upside down by allowing online decisions to drive the design. Did you find the responses to the online polling surprising?
MR: Yes and no. Like the other vote works we have produced, Tim and I set up how the polls are worded and run. So, even though we try to keep the process as open as possible, the nature of how people interact is somewhat fenced in. Even with a fence, people will find a way to move in strange directions or break the fence. It’s not that we think of the surprising answers as the goal of the work, but it is an important part of the process.
ED: There is also the performance aspect which I find exciting. The performance from both events are well documented. Were there any concerns regarding the transfer of the polls instructions to physical space?
MR: We had the good fortune of doing the work in two sections. When Steve Dietz commissioned ARTBarn (West) for the 01SJ Out of the Garage exhibition, we spoke about the sculpture as a working prototype for how a large pile of lumber could be group-assembled in a day with direction from Internet polling. From this prototype we then had a model for how to go about ARTBarn (East) for EMPAC.
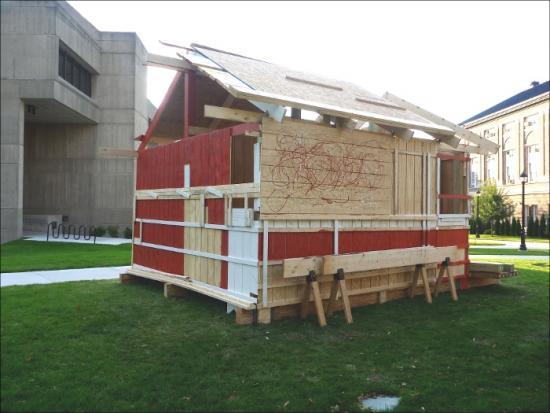


Tim and I had a few loose ground rules on how to approach the translation. One was that we would leave some things open to the interpretation of the crew. Another was that both Tim and I had our favorite poll questions that we tended to focus on. It was impossible to do everything as some polls conflicted with other but some details liked ghosts, dripped paint and open walls seemed to call out to us.
Kathleen Forde, who commissioned ARTBarn (East) for EMPAC, spoke about these details as where the work became more than the sculpture. The small details held the whole process – material, design polls, and performance together.
ED: I think this comment on the details is right. On first glance there is a fun, open appeal to the work. But when you look at the overall project and how the different phases are tied together it becomes really complicated in the mind of the spectator. There are also different definitions of spectator in this work. The spectator who answers the poll, the spectator on the net who is grazing through the documentation, the ones who engage in the physical construction and those who witness the completed barn. It’s not a simple piece when we perform a detailed overview. Did you think about the various types of spectator that would spin off the project? Were the possible roles for the spectator considered after the fact or were they part of the planned concept?
MR: The “ideal spectator” thought first came up for us in a project called Endnode (aka Printer Tree) in 2002. For this work, we built a large plywood Franken-tree with a set of printers in the branches and a computer in the trunk. We then built a list-serve for the tree as well as subscribed it to a few list-serves. When people communicated with the tree, the text was printed out in the exhibition space. At first we talked about the ideal viewer as one who communicated with it online and then saw that communication in the physical space or vice versa.
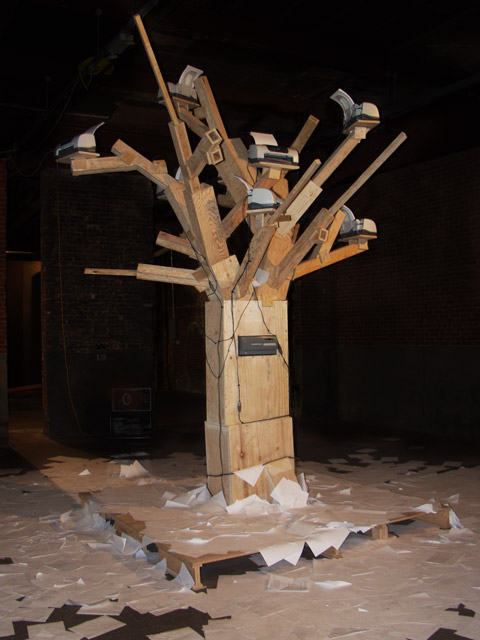


Now I feel that the ideal spectator hierarchy is not as important and possibly limiting. Each experience should be whole as well as point to the larger aspects of the work. People can come in and out of the work on different levels. You voted. You followed the performance documentation. Are you missing an experience if you did not build with us or see the results? Yes, an activity is missed. Can you experience that activity thorough documentation. Somewhat. Are you going to have a better understanding of the work. Probably not. Even for me, some aspect of the work will not be experienced. In Troy, they are programing it as a meeting place now that is it is built.. When they are done with it, they will dismantle it and rebuild it elsewhere as a work space.
I say all this even though it is interesting to me that a work can move in and out of levels of viewer experience. I’m not sure as to the draw of it yet but I do not feel it is about an cumulative effect.
TW: Since Endnode I’ve always liked the idea of an art work that exists in multiple (but overlapping) spaces with multiple (but overlapping) audiences. With our pieces Endnode, ARTBarn and Automatic For The People: () there are 3 distinct (but overlapping) audiences: the online audience, the audience in the physical space and the (select few member) audience that experiences the entire thing.

ED: It’s that opening of possibilities that makes this ultimately a networked piece on many different levels. I find the idea of two barns, a few thousand miles apart yet linked by common purpose really intriguing. I’m talking about the whole set of experiences, not just the physical space of the barn. There’s a collapse of Geographic distance for the community and a richer experience because of that. Was the project conceived as two distinct locations or was that a fortunate turn of events?
MR: Fortune. Kathleen Forde, commissioned ARTBarn (East) for EMPAC then Steve Dietz commissioned the beta version for the 01SJ “Out of the Garage ” exhibition. Everyone liked the idea of the work arching across time and location. We all also liked the idea that the materials would be reclaimed after it stopped being a sculpture. For me, the reclaimation of the materials to use for a functional structure is the final step of the work.
ED: As the final step, the reclamation removes the common space where the community currently shares the sculpture. Does this mean you are going to use the online documentation as the artifact, coming full circle to where the piece began? Is it important to you that the communal memory will share this role?
TW: Yes, the documentation is the artifact. The barn structure or sculpture itself had been conceived as being physically temporary from the beginning.
ED: Thanks to both of you for your time and for this work.
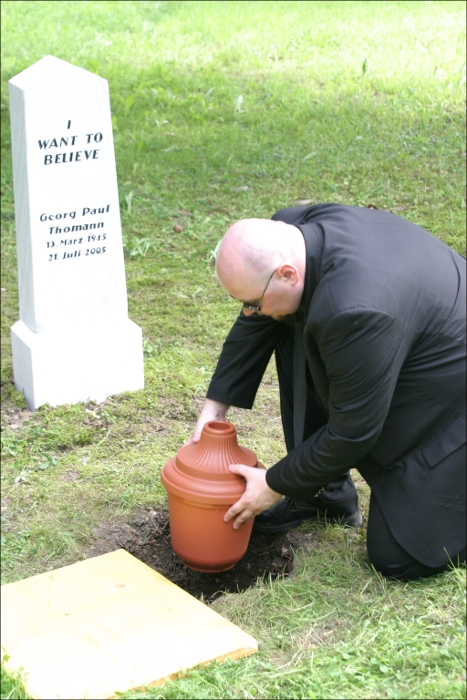
In 2002, when Monochrom was invited to act as the representative of Austria at the Sao Paulo Biennial, instead of going as yourselves, you sent Georg Paul Thomann, one of the country’s most prominent avant guard artists, and also a complete fabrication.
Yes, we were asked to represent the Republic of Austria at the Sao Paulo Art Biennial, Sao Paulo (Brazil) in 2002. However, the political climate in Austria (at that time, the center-right People’s Party had recently formed a coalition with Jorg Haider’s radical-right Austrian Freedom Party) gave us concerns about acting as wholehearted representatives of our bloody nation. We dealt with the conundrum by creating the persona of Georg P. Thomann, an irascible, controversial (and completely fictitious) artist of longstanding fame and renown. Through the implementation of this ironic mechanism – even the catalogue included the biography of the non-existent artist – we tried to solve with pure fiction the philosophical and bureaucratic dilemma attached to the system of representation.
It gave me something of a hearty guffaw to hear about how you and your fellows, manning the Austria country booth as the artist’s technical support staff – the lowliest of low in the art world hierarchy – went about revealing the fictitious nature of the artist.
Yes, we turned the tables. When members of the administration, journalists, or curators asked about the whereabouts of Thomann, our irritated answer was that he hadn’t cared to show up so far, and that he hadn’t helped with anything, because he was supposedly watching porn in his hotel room all day, while we – the members of his technical crew – didn’t care about that bullshit at all. But we informed other technical support teams about the basic idea of the project. They were also given detailed information about Thomann’s non-existence but we did not give them any hierarchic directives about what to do with their knowledge but left it up to them if they wanted to reveal the fake or keep spinning the story. Most people enjoyed doing the latter and they also kept telling different versions of the heard information until finally a bubbling geyser kept erupting in various ways and constantly led to new outbreaks of tittle-tattle.

What happened next, as I heard you describe it, was that “bubbles and bubbles of rumors” began to form around the expansive floor of the biennial. I found this moment in the arc of the project to be particularly interesting and was hoping you could perhaps share some of your thoughts and recollections.
Let’s give you a brief summary of the background. The basic principles of an art-super-structure like a Biennial is simple: lots of little white boxes in which art was set up – and little artists, spreading business cards like prayers. There is a nice German term: “die Warenformigkeit des Kunstlers” (“the commodity value of the artist”). We hardly had any contact with other artists… and that was bad. They came from more than 80 different countries, but they were hiding in their white boxes. Everyone was busy building his or her own little world. Then, during the final setup phase we found out about an incident, which took place in our neighborhood through a copied note.
One year before the Biennial, Chien-Chi Chang had been invited to be the official representative of Taiwan at the Biennial. But then, three days before the opening, his caption – adhesive letters – had been removed from his cube virtually over night. ‘Taiwan’ was replaced with ‘Museum of Fine Arts Taipeh.’ But to Chien-Chi Chang the status as an official representative of Taiwan was very important, because his photography artwork dealt directly with the inhumane psychiatric system in Taiwan.

Chien-Chi was trying to get in contact with the Biennial administration and the chief curator (the German Alfons Hug), but didn’t succeed. Communication was refused. After that he decided to write an open letter, but the creative inhabitants of all the little white art-combs didn’t seem too interested in the artist’s chagrin, who by now wanted to leave the Biennial out of protest.
We were interested in the situation and did some research. We found out that the Chinese delegation had threatened to withdraw their contribution and to cause massive diplomatic problems. To them, Taiwan was clearly not an independent country (c/f ‘One China Policy’) and they put pressure on the Biennial management to get that message out. The management did not make this international scandal public and it was quite obvious why.
monochrom decided to show solidarity with Chien-Chi. We wanted to set an example and show that artists do not necessarily have to internalize the fragmentation and isolation that is being imposed upon them by the structure of the art market, the exhibition business, as well as the economy containing them. For us, though, this is not about taking a stand for either the westernized-economical imperialism represented by Taiwan or for China’s old-school Stalinist imperialism. This is about integrity and solidarity, values that we chose to express through a collaborative act. Together with other artists from various countries we launched a solidarity campaign: we took off some adhesive letters of each collaborating country’s signature and donated them to Chien-Chi Chang. monochrom sponsored the ‘t’ of Austria, while the Canadians donated one of their three as. The other participating artists were from Croatia, Singapore, Puerto Rico and Panama. A lot of artists and curators from other countries refused to support the campaign for fear of – as they would call it – “negative consequences.” WTF? But at least some of the artists were pulled out of their self-referential and insular national representation cubes which, in themselves, so rigorously symbolized the artists’ work and his or her persona as commodities.

After some time we managed to attach a trashy, yet legible ‘Taiwan’ to the outside wall of Chien-Chi Chan’s cube. Numerous journalists took notice of the campaign and Chien-Chi opened his exhibition in front of a cheering audience. Some days later, we found out that Chinese and Taiwanese newspapers massively covered the campaign. One Taiwanese paper used the headline “Austrian artist Georg Paul Thomann saves ‘Taiwan’.” In other words, a non-existing artist saved a country pressed into non-visibility. Who said that postmodernism can’t be radical?
What was it like – even from a kind of phenomenological sense – to be in the midst of this bubbling, to experience the formation of a scandal from its very embryonic moments? Is there something in the interiority of situations like this that you see as essential to the creation of new kinds of solidarity?
First we would have to define what “new kinds of solidarity” mean. What would be the ‘new’ part of it? Does it go beyond old and traditional forms of solidarity? And why should it? I think that classic forms of solidarity were carried out by political groups or other collective entities. They tried to express their (let’s label it as) “old-school solidarity” by pointing their collective fingers at someone who they thought were mistreated: “Look, look this human being is being oppressed!” And they always did it “in the name of something”. Old-school solidarity was one more frickin’ medium that people used to get a message across. Thus it was always part of the realm of representation. Your act of solidarity represents the one you show solidarity with, but your act is also advertisement for yourself, your cause and the (political) identity you wish to construct. Politics is always drama. Best example for this would be the “supporters of Palestine”. There are tons of ethnic groups on this rusty little planet who have to suffer under worse conditions. But nobody seems to be interested in showing solidarity with them. Where are Henning Mankell and Noam Chomsky when you really need them? Involved in some stupid fast-food anti-imperialism. We have to understand that the “object of solidarity” is something you pick for a reason… and most of the time it’s to feel good as a group and to impress your peers. But that has nothing to do with factual, non-reductionist political analysis. Collective entities define themselves through acts of representation and this representation is comparable to the construction of national pride or patriarchal family structures and values. Solidarity can be read as an act of defining identities. And that can be very dangerous, because old school solidarity always wants to be “right”. You are always “the good one” supporting the poor bastards. Smash dichotomies!
What we experienced at the Biennial of Sao Paulo back in the spring of 2002 was a very non-collective act. We were no real group, no leaflets, we had no common agenda, we were a psycho-geographic swarm. There was no basis for acting or speaking as a collective and there was no need to bundle our powers or form an identity. Yes, we tried to recruit other artists to join in our little act of solidarity. But it was no protest, we didn’t protest a certain political agenda because we didn’t want to end up in the old black and white world that, for example, all the apeshit Pro-Tibet supporters live in. Bah! Their ugly flags! Their patriarchal projections! Richard Gere! Yuck! So it was a kind of “free flowing solidarity”, not to be abused to form a political movement or statement. The only form of identity that was formed was the simple idea that even bourgeois artists can decide whether they want to be part of the Biennial and its stupid rules or whether they want to be part of action and fun.
To make it short: we are interested in micro-political solidarity, temporary solidarity that can’t fossilize. Solidarity is important if it can evolve and vanish within a short span of time and all that’s left is rumors and vague commemorations. Let’s call it a process of counteracting – that might be well-known in the field of the urban guerrilla but that so rarely pops up at art shows.

Read Part 1 of the Interview
http://www.furtherfield.org/interviews/interview-johannes-grenzfurthner-monochrom-part-1
Read Part 3 of the Interview
http://www.furtherfield.org/features/interviews/interview-johannes-grenzfurthner-monochrom-part-3
Above image taken by Scott Beale, Laughing Squid.
Marc Da Costa interviews the ever dynamic Johannes Grenzfurthner, founder of monochrom. This is the first of three interviews, where he talks about the project ‘Soviet Unterzoegersdorf’; the fake history of the “last existing appanage republic of the USSR”. Created to discuss topics such as the theoretical problems of historiography, the concept of the “socialist utopia” and the political struggles of postwar Europe. In March 2009 Monochrom presented ‘Soviet Unterzoegersdorf: Sector II’. The game features special guest appearances of Cory Doctorow, Bruce Sterling, Jello Biafra, Jason Scott, Bre Pettis and MC Frontalot.
Since 1993, the Monochrom members have devoted themselves to the grey zones where systems intersect: the art (market), politics, economics, pop, gaiety, vanity, good clean fanaticism, crisis, language, culture, self-content, identity, utopia, mania and despair. The technique underlying Monochrom’s work is that of being and working in the fields of Pop/avant-garde, theory/reflection, interventionism/politics, gaiety/lust/tragedy, (self-)configuration/mystification. The project Monochrom pushes into and beyond these fields is, ‘networking’ events, people, possibilities, material, impetus and identities.” (Zdenka Badovinac, Moderna Galerija Ljubljana)
Grenzfurthner has collaborated with groups such as ubermorgen, Billboard Liberation Front, Esel and Mego (label). Grenzfurthner writes for various online/print magazines and radio stations (e.g. ORF, Telepolis, Boing Boing). Grenzfurthner has served on a number of art juries (e.g. Steirischer Herbst, Graz). He holds a professorship for art theory and art practice at the University of Applied Sciences, Graz, Austria and is a lecturer at University of Arts and Industrial Design in Linz, Austria.
Recurring topics in Johannes Grenzfurthner’s artistic and textual work are: contemporary art, activism, performance, humour, philosophy, sex, communism, postmodernism, media theory, cultural studies, popular culture studies, science fiction, and the debate about copyright.
The ‘Soviet Unterzoegersdorf’, a game created by monochrom, is described as being at once the “last existing appendage republic of the USSR” and located inside the Republic of Austria. Could you speak a bit about the project and its background?
From a conceptual background we have to state that we have been occupied with the construction, analysis and reflection of alternative worlds for quite a long time. A lot of our projects are treating this field partly as a discussion with concepts deriving from popular culture, science and philosophy, and partly as a direct reference to science fiction and fantasy fan culture. We first created the fake history of the “last existing appendage republic of the USSR” in 2001 — ten years after the ‘mighty Soviet Union’ went into this nation-state-splitting-up-process and new countries emerged like Firefox pop-ups that you can’t manage to click away.
We wanted to discuss topics such as the problems of historiography, the concept of “utopia” and “socialist utopia” and the political struggles of postwar Europe in a playful, grotesque way. You have to bear in mind that the real village of Unterzoegersdorf was part of the Post WWII Soviet zone from 1945 until the foundation of the ‘neutral’ Republic of Austria in 1955. Reactionary Austrians talk about 1955 as the ‘real liberation’… and I have to mention that that’s rather typical: cheering when Hitler arrives and being proud members of the Third Reich, afterwards proclaiming that Austria was the first victim of Nazi Germany and complaining about the allied occupation forces — especially the Soviet.

We transformed the theoretical concept into an improvisational theatre/performance/live action role-playing game that lasted two days. That means we really organized bus tours to Unterzoegersdorf — a small village that really exists — and acted the setting; beginning with the harsh EU Schengen border control. Later, in 2004, we started to think about a possible sequel to the performance. We thought that the cultural format of the “adventure game” provided the perfect media platform to communicate and improve the idea.
We started to work in February 2004 and presented ‘Sector 1’ — the first part of the trilogy — in the form of an exhibition in Graz/Austria in August 2005. We released ‘Sector 2’ in 2009, featuring guest stars as Cory Doctorow, Jello Biafra or Bruce Sterling. As the game series uses a 3rd person perspective with photo backgrounds and pictures of real actors as sprites, it took us quite a while to digitize and image process all of the material. This technique was actually first used by Sierra On-Line during the early and mid-1990s — but we are quite proud that we managed to get the feeling of discovering an old computer game that never existed on your old 500 MB hard drive. One aspect of the game is playing with memories and the future of the past. The future is a kind of carrot, the sort tied just in front of the cartoon donkey’s nose so it goes to work, goes off to war, learns Javascript and knows which bits to laugh at in Woody Allen’s Sleeper. You can imagine.


At a HOPE conference a few years back I was interested to hear you talk about the framing of the project as somehow deeply connected with a certain understanding of historiography that you and the other members of monochrom share. Could you elaborate on this a bit?
Debates triggered by postmodern culture have directed our attention towards questions of representation and the relevance of “history” and stories — i.e. The challenging proclamation of a post-histoire, the realization of the impossibility of a meta-narrative of history; the clash between reality and sign systems, the difference between fact and fiction, the impossibility of neutral contemplation or witnessing as well as the positioning of subjective awareness within such representations, etc. All these forms of representation have been playing a central part in the development of national, ethnic and tribal identities since WWII. And (as a by-product of military technology) computer game development is hardly aware of these discourses.
We wanted to combine (retro)gaming and (retro)politics and (crypto)humor to delve into this ongoing discourse. We wanted to harvest the wonderful aesthetic and historic qualities of adventure gaming. It is a commemoration and resurrection, and one more reminder that contemporary gaming (in its radical business-driven state-of-the-artness) should not dare to forget the (un)dead media of the past — or they will haunt them.
If you compare the status of the adventure game in the context of the economic growth of the computer game industry you could state that it is gone. Less than 1% of all computer games written are adventure games. Adventure games are nearly extinct… but only nearly. If media and media applications make it past their Golden Vaporware stage, they usually expand like giant fungi and then shrink back to some protective niche. They just all jostle around seeking a more perfect app.
For many people in the Soviet Unterzoegersdorf team, adventure games are part of their media socialization. For the computer industry it is one of the most successful gaming formats of the past. And for the feminist movement it is proof that a woman — I’m talking about Sierra On-Line’s Roberta Williams — was able to shape the form of a whole industry totally dominated by men.
Computer games are embedded in the cultural framework of technological developments. In the study of technological development and creativity, focusing attention on the failure, the error, the breakdown, the malfunction means opening the black box of technology. Studies have convincingly demonstrated that the widespread inability to understand technological artifacts as fabricated entities, as social and cultural phenomena, derives from the fact that in retrospect only those technologies that prove functional for a culture and can be integrated into everyday life are “left over.” However, the perception of what is functional, successful and useful is itself the product of social and cultural–and last but not least–political and economic processes. Selection processes and abandoned products and product forms are usually not discussed. According to Langdon Winner, there is a sense in which all technical activity contains an inherent tendency toward forgetfulness. Quote: “Is it not the point of all invention, technique, apparatus, and organization to have something and have it over with? (…) Technology, then allows us to ignore our own works. It is license to forget.”
Could you also perhaps talk about the choice of selecting the genre of an adventure game as the incarnation of this downtrodden republic. At the risk of being literal minded, is there any sense in which the existence of ‘Soviet Unterzoegersdorf’ as a kind of place that comes alive through players’ interactions with a program downloaded from the internet has anything to say to how you imagine being able to engage/critique/disrupt the idea of the nation-state?
We are postmodern leftists. A little bit melancholic… but you can count on us. We love to play with layers of consciousness and layers of layers of consciousness. On first view our project could be interpreted as a mock-up of the Soviet Union and the communist state structures that really existed. But, why on Earth do we need so many references to 1980s and 1990s metal music? Or Marvin Minsky? Or Negri? Or Austrian post-WWII history? Or geek adumbrations? Mocking the Soviet State would be much easier. In fact it’s about the wonderful clash between reality and sign systems, the impossibility of neutral contemplation or witnessing as well as the positioning of subjective awareness within such representations. The traditional humanists tend to see the whole philosophic aesthetic postmodern line of thought — from Judith Butler to Lyotard and Derrida — from the wrong angle. Okay, you can’t explain Sun Ra to a Green Day fan now, when he’s laying in the corner, piss-drunk and crooning “Anarchy”. But we think that the (radical) nature of postmodernism is often simply not grasped because people just copy it down into the conservative pattern of thinking which has been indoctrinated into us since the Enlightenment. Of course, on the other hand, it functions as a virus, and there’s nothing wrong with that.
Contemporary art — the field we are usually working in because there’s money — is mostly concerned with systems or systematic concepts. In the context of their work, artists adapt models of individual art-specific or economic or political systems like in a laboratory, to reveal the true nature of these systems by deconstructing them. So would it be fair to say that by their chameleon-like adaptation they are attempting to generate a similar system? Well… the corporate change in the art market has aged somewhat in the meantime and looks almost as old as the ‘New Economy’. Now even the last snotty brat has realized that all the hogwash about the creative industries, sponsoring, fund-raising, the whole load of bullshit about the beautiful new art enterprises, was not much more than the awful veneer on the stupid, crass fanfare of neo-liberal liberation teleology. What is the truth behind the shifting spheres of activity between computer graphics, web design and the rest of all those frequency-orientated nerd pursuits? A lonely business with other lonely people at their terminals. And in the meantime the other part of the corporate identity has incidentally wasted whole countries like Argentina or Iceland. That’s the real truth of the matter.
Read Part 2 of this Interview
http://www.furtherfield.org/features/interviews/interview-johannes-grenzfurthner-monochrom-part-2
Read Part 3 of this Interview
http://www.furtherfield.org/features/interviews/interview-johannes-grenzfurthner-monochrom-part-3
Ambient Information Systems
English, some texts in German. Translator: Nicholas Grindell
400 pages, 6-colour hardbound, 17.5 x 23 cm
edition of 1,500 unique & numbered.
now available at ambient.publishing.
ISBN-13: 978-0-9556245-0-6
Ambient Information Systems by Manu Luksch and Mukul Patel is a hardback book that presents writing, images and art by and about ambient.tv (Luksch and her collaborators) from during the last decade. Its purple and yellow cover tempered by a tracing paper slip-cover, contains almost four hundred pages of sans-serif text cleanly laid out among images and sidebars. As intermedia artists with a strong emphasis on research and dissemination. Recent works have addressed surveillance, corporate data harvesting, and the regulation of public space.
The material presented in the book ranges from written essays and project proposals through preparatory sketches, computer server log files and video screen grabs to modification of the printed book iteslf by unique rubber stamps and scribbling over sections of text. This diverse and detailed presentation of ambient.tv’s work provides an insight into the inspiration, planning and production of some conceptually and aesthetically rich new media art.

There’s a report from Kuwait during Ramadan 2002, a description of using cutting-edge wearable PCs, a discussion of the role of television, information about the harp in mythology, cyborg markets, the UK Data Protection Act, climate change, anti-gentrification, art and systems theory, UAVs, the Pacific plastic dead zone, and much, much more. There are projects that create free networks, dangerous musical instruments, taped-out surveillance camera boundaries, video installations, photographic images, movies of CCTV footage gained through freedom of information requests, manifestos, snowglobes, and cocktails.
(It’s a fascinating pleasure to read but it’s overwhelming to try and review.)
The portrait of Ambient.tv that emerges from all this is of intensive cultural critique pursued through a playful low-fi digital aesthetic. This isn’t a contradiction, the latter is in the service of the former. Ambient.tv’s projects and proposals tackle serious social and political issues. They do so through skilled use of the aesthetics and attitude of low-fi new media art and technological activism.
The wealth of ideas contained in the essays and other writing in the book show how historical, political and philosophical knowledge grounds the resulting art and indicates how it embodies a critique of contemporary culture.

Contemporary culture as seen by Ambient.tv is surveillance culture, the database state with its DNA databases and laws that protect freedom by removing freedom. Ambient.tv is a realistic project, depicting the hidden forms of contemporary society that intrude into our lives. This is heavy stuff, and to air it critically without alienating the audience it requires precisely the playful touch that ambient.tv often bring to their art.
To take the example of FACELESS, 2007, (the first project I personally saw Luksch present), there is an exquisite balance between the disturbing idea of pervasive surveillance, the practical limitations of Freedom Of Information requests, and the visual and science-fictional narrative aesthetic that emerged from this. On their web site it states that it was produced “…under the rules of the Manifesto for CCTV Filmmakers. The manifesto states, amongst other things, that additional cameras are not permitted at filming locations, as the omnipresent existing video surveillance (CCTV) is already in operation.” The result is something more interesting and disturbing to watch than a simple collage of CCTV footage would be. The fact that the work can be made like this, that it can look like this, means something.
This strategy can be seen in “Mapping CCTV around Whitehall”, 2008, as well, which I also reviewed for Furtherfield here, and in many other pieces by Ambient TV.
Reading the proposals and essays shows the depth I suspected to this work, when I first saw it projected in a darkened room is there in its conception and execution.
It’s an intense and inspiring experience to be faced with the textual equivalent of a decade-long open studio. The first essay in the book, a theory-laden piece by Fahim Amir, is almost overwhelming in a different way. It’s pure Theory, which will hopefully sell Ambient.tv to the artworld sectors that thrive on that sort of thing, but it isn’t the best introduction for newcomers to the project’s very accessible art.
But what a rare pleasure to be given such a wealth of insight into art that so acutely depicts our times. “Ambient Information Systems” is an important resource for contemporary artists and critics, an insight into the ideas and development of a very successful new media art practice. The grungey, playful, important realism of Ambient.tv’s work deserves presentation in a context that shows just what has gone into the art and just what people can get out of it. This is it.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
Meat Space and the World Inside the Machine
Danja was an Artist in Residence at Furtherfield’s HTTP Gallery space between the 1st March – 9th April 2010. A Russian born computer artist currently living between Berlin and Rotterdam. Working with diverse methods, technologies and materials Danja ridicules the contemporary affection for digital life and questions the global tendency for cyborgination. Danja co-founded media-lab moddr_ in 2007 which is a joint project at Piet Zwart Institute alumni and WORM Foundation. Based in Rotterdam moddr_ is a place for artists and hackers, engaging with critical forms of media-art practice.
The email interview took place a few weeks after his residency. A recent collaborative project that many readers may already know of, by Danja Vasiliev, Gordan Savicic and Walter Langelaar, all part of moddr.net lab is, Web 2.0 Suicide Machine, which lets you delete your social networking profiles and kill your virtual friends. Danja is certainly prolific, he is also collaborating with New Zealander artist, Julian Oliver who is now based in Berlin. This interview unearths some of the ideas and intentions behind Danja’s personal works, asking what motivates him to use computers, technology and networks, as well as understand more the social contexts and implications of his endeavors.
Marc Garrett: You’ve been on the residency at Furtherfield’s HTTP space http://www.http.uk.net/ for a few weeks now. Before we discuss Netless, the project you have been researching here and some of your other recent works, I think it would be interesting to know about some of your earlier works first. Before the turn of the century you made various net.art pieces. What I find interesting here is that whilst you were creating these works you were also parodying net.art at the same time, was there any particular reason for this kind of approach?
Danja Vasiliev: “HTTP” as an abbreviation was a very significant thing for me throughout the last decade, now having to stay at a place bearing the same title feels like a necessary experience indeed. Fifteen years ago WWW was something very new in Russia and besides the new dial-up aesthetics and world-wide means it brought a complete new layer of existence – “netosphere”, which made my youth. I was trying to understand the technology, though not being of a scientific kind I did it by monkeying around with artworks of others. Later I heard it was called “Open Source” approach. The Website “koala.ru” http://koala.ru.k0a1a.net became a collection of expressionist pages, each page had its own story and often a narrative. Back in the day my arsenal was naturally limited: HTML3, GIF89a (animated) and JavaScript1.2. It felt challenging to work with those tools, file-size was aesthetically just as important as letter-case, and I liked it… I haven’t changed any of the pages since 2002, iirc. The greatest source of my inspiration (image and code -wise) of that time was the baddest of all Superbad – I loved the wackiness yet elegance weaved into the piece. My attraction to /random redirect/ comes from there.
MG: What draws you into using computers in your art practice?
DV: It must be the conflict between the everyday technology and digital life. I’m exploring that edge between the meat space and the world inside the machine. Machine in this case is not just a PC – a single computer is only a part of the network. Acting on those parts adjusts the behavior and perception of the whole – I’m interested in that. Computer hacker attitude and methods are very influential, my works are often merely illustrations of those technological interventions. It makes much more sense to me to try to confront or challenge the technology (and the users) rather then to celebrate the achievements. ‘IT’ today is what politics were yesterday – it and its aesthetics owe to be questioned, broken into pieces, interrogated, sabotaged, reflected upon and ridiculed.
MG: On the NETTIME list on 1st July 2008, Eric Kluitenberg wrote an intriguing essay about your work titled “Turning the machines inside out”.[1] He also discusses something which is close to one of my own interests, about the world as a kind of Interface, metaphorically, virtually and materially “The world according to Rossler is defined by that what transfers between the observer and the “real” world at the interface. It is the interface to the world that defines what can be observed about the “real” world.” Kluitenberg.
Before we talk about Kluitenberg’s concepts regarding his thoughts around your work, I would like to know what your own considerations are in respect of the “World as Interface” and what this means to you?
DV: Well, it always surprises when I come across some theoretical implications confirming, destroying or otherwise connecting to my own work. Perhaps that is why I got to be a maker rather then a thinker – I could never describe the topic I was covering with m/e/m/e 2.0 in a such a profound way as Eric Kluitenberg did. However incapable of posing a verbal question, my intention was indeed to discuss and demonstrate that effect of alienation created by the very medium (or shall I say the interface) of the Web. A System that promotes itself to the users as a fair substitute for reality and provides services for talking, seeing, being and so on, yet fails to escape its own binary jail, i.e. fails to become indeterministic. This determined interface creates determined world – web applications are uploaded straight into our brains. In my perception what we are seeing now is rather reversed or multiplexed inclination of “World as Interface” idea, when devices used for participation in-World and auxiliary systems created around to assist the process, all of this _is_ the World for its users.


MG: Kluitenberg in his essay, viewed your m/e/m/e/2.0 to be part of a tradition “(inadvertently or not) in the best company of a long tradition of “avant-garde” artists who created various sorts of absurd, ironic, impossible, sadistic, insane or ridiculous machines. His likes are the creators of ominous bachelor machines (Duchamp, Lautreamont, Picabia, Roussel, Kafka), self-destructing machines of the Tinguely type, right down to the magically autistic robotic anti-sculptures of Allan Rath.”
For me, what links m/e/m/e/2.0 to our contemporary world and its ever increasing networked existence “and what we know it to be now” is, its playful and direct link and reference to the Internet. It could not be what it is without the Internet, in which millions have been and are still being taught how to adapt and reconfigure relationships with others, and ourselves. We have become part of the networked driven interface via this socially engineered activity. Would it be presumptuous of me to consider m/e/m/e/2.0 to be a kind of portrait, or a physical re-representation of the human mind or perhaps “head”, metaphorically?
DV: m/e/m/e 2.0 is a manifestation of the absence of any human traits in an act of network communication. Of course it is impossible to demonstrate this without the involvement of the main suspect – the object, the sculpture – is only a half of the work, another half is the Internet. Whenever the piece is not online – it is not complete, and as such – kept in a wooden crate. What “m/e/m/e 2.0” ultimately represents is the physicality of the fellow Internet user on the other end of the wire. It is a device that converts digital instances (copies) of netizens into humanoids, adding flesh around immaterial skeletons. By the analogy to what’s known as “modem” (MOdulator-DEModulator, a device used for digital communication over analog, physical mediums), “m/e/m/e 2.0” is a “semi-modem” or just “mo” without “dem” – it materializes (modulates) without caring to convert back into binary format. It lets the users enjoy their own bodily presence while online; much like the famous FuFme device only with some corrections to the current state of things.
The machine of m/e/m/e 2.0 allows its visitor to sense not only the surfaces of the system but also to get into an strange relationship with the concurent users. The $USER begins to understand intimacy over a distance. The mechanical body can not be re-multiplied to a spontaneous number of requests, instead all of the users come to share one analogue broadcast medium. Whenever someone clicks to open a new link, the information is transmitted to all connected users, “meshing” and colliding their sessions. Seemingly a constraint becomes a feature – unbodied cyberspace gets filled with physical presence. The consequence is that it turns web browsing into a broadcast, collective group activity without any predefined rules. Each page is a part of info-system contained with-in m/e/m/e 2.0, all pages are hyper-linked into a mesh that has no beginning or end.

MG: During your residency here in London, you worked on another project called Netless. Could you explain what the project does and why you have chosen to embark on such a venture?
DV: I’m researching a digital communication strategy or technique that would be free from the “panoptical” effect of the Internet. It is too easy to observe and trace users connected to the global network – partly because of the way it is structured, as well as its reliance on the corporate communication channels. It is something about “net neutrality”.
Netless is an attempt to create a new network, alternative to the Internet. More precisely – networks within existing city infrastructures, possibly interconnected into a larger network alike the Internet. Netless is not dependent on specialized data carriers such as cables or regulated radio channels. In fact, there is no permanent connection between all of its hosts (peers) at all – it is net-less. The network is based on the city transportation grid, where traffic of the vehicles are the data carriers. Borrowing the principals from the Sneakernet concept, the information storage devices are physically moved from point A to point B. Numerous nodes of the netless network are attached to city buses or trams. Whenever those vehicles pass by one another a short-range wireless communication session is established between the approaching nodes and the data they contain is synchronized. Spreading like a virus, from one node to another, the data is penetrating from the suburbs into the city and backwards, expanding all over the area in the meanwhile. That broadcast data can be picked-up by anyone.
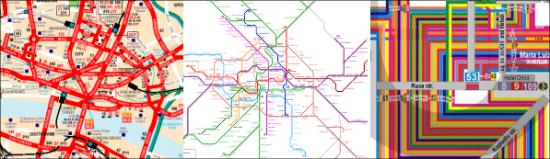
…the similarities between city transportation maps and circuitry of modern networks are not accidental. their purposes are identical – to provide efficient transport flow between all the locations of the area they cover. routes are designed to match the necessary throughput without congesting at peak times. D.Vasiliev.
MG: What kind of information will be shared within a “Netless” system? Also, are these ad hoc mini-networks going to be attached onto vehicles as secret transmitters?
DV: Constrained by the bandwidth limits Netless networks will work most effectively when dealing with short messages. Technically speaking – “ascii” text, or short base64 encoded binaries/images. Textual data is playing well together with human brains – we often do not need to read a complete sentence to understand the meaning – this would be a great way of keeping the data traffic down. If an error occurs during the transmission of a text message, it can be easily “repaired” by the recipient’s brain – less work for hardware, more information can come thorough. The Netless network integrates into the citizens’ living infrastructures, its data-processing and error-correction routines are outsourced to the users. This is a “hybrid” (parasitic) system, it requires the “human” as resource in order to function.

It would be very interesting to collaborate with some city transportation company, like the one that runs all the buses across London, Arriva. It blankets all areas pretty well as I discovered during my residency at HTTP and if every bus would carry a “Netless” node – the performance would be amazing. That said, it wouldn’t be smart to make “Netless” depend on any commercial entity. Instead I’d rather encourage people to follow up on the project development and start putting together their own “Netless” nodes and take those on everyday travels within the cities. The strength (and bandwidth) of any mesh-network grows proportionally to the amount of nodes involved into the network, thus – (random) network maintenance is the sole responsibility of its users..

MG: This idea of independent nodes/activities of communication, asking us to consider the notion of what it would be like to be “off the grid”; is an important issue. It reflects wider concerns around individual freedoms and civil liberties, in an age where corporations are channelling our everyday digital behaviours towards, a more “official” form of mediation. Where top-down, imposed digital infrastructures are dominating the interface of who our digital, data-bodies are, whilst having control and access to our content, not on our terms. It also reminds me of the battle between pirate radio and institutionally implemented radio broadcasts, as in who owns the medium and what is perceived “correct” information when sharing with others?
DV: Definitely, reclaiming the medium (or the net-space for this matter) does not happen on paper or during some international conference on the topic of net-neutrality. Such changes in disposition of the forces – corporate state on one hand and personal interest/freedom on other is a tedious process; approached top-down it might take ages to complete. Revolution starts on the streets! Rather than having endless debates and explaining to the officials about how and why “Inter Net” is different from “Closed Circuit Tele-Vision”, we respond proactively, ahead of the regulations; creating our own communication strategies. I see my role here in exemplifying the conflict and its resolution.
MG: To the more traditional art practitioner out there who may not be so dedicated or as involved as yourself, in using computers and technology as part of the creative process; how do you manage to keep the balance, maintain the essence of what you do, as art?
DV: I’m for sure not “doing art”. I reflect on certain things, certain events, topics. Those often happen to have technological origins – nothing very surprising nowadays. My works are somewhat “improved” versions or “hacks” of our every-day technology and thus – our life. It is an essential thing for me to work with the same means as the means of the subject of my criticism – e.g. /misuse/ a piece of technology to demonstrate its other potentials; it is a more constructive approach.
MG: What other projects can we expect to see in the future other than what we have discussed so far?
DV: More technological interventions… and I was also thinking of building a railway model! People should check http://k0a1a.net more often.
MG: Will do, and thank you very much for the conversation…
DV: Thank you, nice chatting…
—
danja vasiliev
http://k0a1a.net
Danja was also interviewed by Marc on a Furtherfield, radio broadcast 6th April 2010 – Resonance FM. http://www.furtherfield.org/resonancefm.php
Patrick Lichty, renowned conceptually-based artist, writer, curator and activist. He has exhibited internationally since 1990. Featured image: taken by Anne Helmond.
Introduction.
Patrick Lichty is an individual who seems to be like a non-stop engine. A hungry human being, engulfed in a prolific journey of constant exploration, whether it be making artworks, writing, activism, curating, collaborating, researching or teaching; he’s deeply involved and engaged in media arts culture. Since 1990, he has pursued art and writing that explores how we relate to one another through technology and how we relate to it. This includes art, media, and computer technology. “Media are one of the “glues” of civilization, and this glue is as fundamental in representing all aspects of society, culture, and interpersonal relations. I explore this through critical theory, conceptual New Media art, and performance/social intervention.”
Lichty also works in almost all forms of Digital 3D – Animation, VR, Fabrication, Physical Computing. Translating the work for display through video, animation, live installation, electronics, virtual reality, physical computing, robotics, digital fabrication and imaging. As well as realising virtual works into traditional forms such as plates for print, paintings, expanding the focus of his work in a broader context.
Lichty’s work, concepts and practice do not rest in one place, it crosses over into many areas of creative production. By getting his hands dirty with the medium of technology, with its relational aspects. The spirit of the work goes beyond singular catch phrases and one-liners, adding complexity and value which only media art and its ever widening scope can demonstrate.
It’s big art with big ideas, interwoven with micro levels of human emotion, asking questions about life and more. This two part interview aims to clarify some questions I have been wanting to ask Patrick Lichty for a while now, so hang on and lets see what happens…
Start of Interview:
Marc Garrett: You have been deeply engaged in the creation of net art, networked art, media art and related activities at various levels, whether it has involved you making it, writing about or curating it. What inspired you to choose which is, now unquestionably, one of the most contemporary and expansive forms of creativity, in the first place?
Patrick Lichty: This is a question that has come up repeatedly. “Why did you choose (what is now called) New Media, or the intersection between society, technology, and culture?” It is really a matter of examining my native culture, which has been that of technological culture. I was raised by an artist who gave me my first electronics set at the age of 8, and my first computer by the age of 17, while raising me on a steady diet of science fiction. I was a child of McLuhan; growing up in the electric networks on a diet of very hot media. However, I do also paint, and when I think it’s appropriate, I also do use traditional media. In short, I speak this culture because it’s my native language.
MG: To kick off this interview I thought it would serve our readers well to discuss your work from a perspective of themes. Over the years, exploration through your practice has crossed over into many different disciplines and fields. So lets begin with Psychogeography. To those who are unfamiliar with this practice, the most well defined and serious use of it was in 1955 by Guy Debord: “a whole toy box full of playful, inventive strategies for exploring cities … just about anything that takes pedestrians off their predictable paths and jolts them into a new awareness of the urban landscape.”
“Of all the affairs we participate in, with or without interest, the groping quest for a new way of life is the only thing that remains really exciting. Aesthetic and other disciplines have proved glaringly inadequate in this regard and merit the greatest indifference. We should therefore delineate some provisional terrains of observation, including the observation of certain processes of chance and predictability in the streets.” Introduction to a Critique of Urban Geography. Guy Debord
Patrick, one of your projects which springs to mind, is a work called SPRAWL “…an exploration of the suburban American landscape, examining the macrocosmic issues related to suburban expansion by considering the microcosmic issues of the experiences of a bellwether area of the US: Stark County, Ohio. In navigating the landscape you will view over thirty panoramic photographs of sites that are now forever changed by the area’s development as well as interviews on video and historical documents which create a map of the larger social landscape of the surrounding community.”
A complex and involved project. What inspired you to examine the ‘suburban American landscape’ in such a way, and how long did it take to complete?
PL: In talking about Debord’s definition, I’d like to talk about my own interpretation of the idea of Psychogeography. If you consider the word etymologically in contrast with Debord’s meaning, you can say that it should not be limited to the urban landscape, but the relationship of human interaction with any landscape. From this, we move out of the city to any relation between community and space, which is my interest, and I like to term as a practice of ‘land use interpretation’ to borrow Matt Coolidge’s (CLUI) term. All of my work in this range, from SPRAWL to the three projects in varying stages of completion (the Hulett Project, Ghosts of Adak, and SPRAWL 2011) come from a personal observation that expands to a macroscopic discourse through the larger exploration/research of the space.
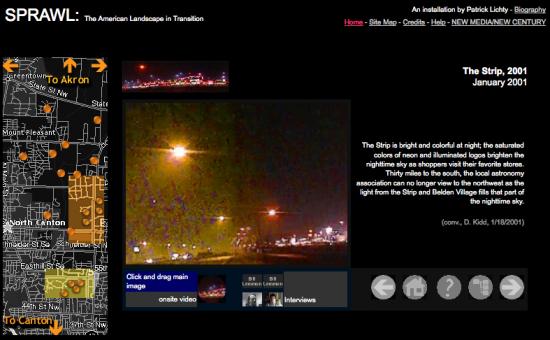
SPRAWL began as a 3-year personal investigation of my own distress about suburban sprawl in the late 1990’s near my home town, and linking this to the larger national conversation regarding sprawl at the time. For reference, I was born in nearby Akron, Ohio – the subject of Chrissie Hynde and The Pretenders song My City Was Gone, which describes the colonization of an industrial city and its countryside by sprawl and shopping malls, so if SPRAWL has a soundtrack, that would be it. I began SPRAWL in 1998, as a series of panoramic photographs of various sites near my home, with just a vague impression that they were a cohesive body of work. Also, the idea of nostalgia for the pastoral farmland of my younger days seemed far too simple to be satisfying, so I knew there was something to it. So, when the Smithsonian American Art Museum put out a call for works dealing with landscape online, I felt this was a fantastic place to really explore this idea in a larger context. Then they offered me the commission, the project went from a set of 32 panoramas to a hyperdocumentary in about three solid months of production, including travelling back to Ohio from Louisiana, interviewing, doing on-site footage, and performing historical research.
What I think is important about SPRAWL is that it’s ‘sensable research’, in that it managed to manifest the ideas I had about this problem, learning a lot more about community ecology, allowing the articulation of a microcosmic issue in macroscopic terms. In more personal terms, it allowed the development of my question of social issues related to my concern with the understanding that my perspective was only one of many, and from examining a multitude of perspectives, I could learn what the larger issues were, and create a discourse with a larger community.
MG: On your website, for the Ghosts of Adak there is a statement of yours, saying “My father and I have something in common. He was born in 1921 and spent 2-1/2 years in the North Pacific campaign on Adak Island in the Western Aleutian Islands in Alaska. I have heard about it since 1962. So I went there for 10 days. And I found him all over again.”
I also visited another site to find out about the community living there, and on this site called Alaska Tracks. Ned Rozell writes “Adak’s having a tough time, and the community of about 200 people in the mid-Aleutians has been struggling since the Navy pulled about 6,000 people out in 1997. It’s got a feel to it now like the Love Canal area of Niagra Falls had in the 1980’s, like everyone took off and left a few ghosts behind.”
How was your 10 days stay there and what did you learn?
Do you have a clear idea of what this project will become? Also, I noticed that it is part of an artist residency program at Eyebeam R&D Atelier NYC. How do you intend to present this work, in a space, on-line or something else?
PL: That’s a book in itself, and probably will be, which is part of your next question. First, why – My father is nearing 90, and for most of my life, he had gone on about this “place” that he had been for a period of time, and recounting endless stories about it. No place else had that sort of impact on him. Does not talk about Seattle, or San Francisco, or even Chicago (all places he had spent time) like that. I also think that as he is nearing 90, and in that he and I have a very strong bond (actually both Lodge brothers, if you can believe that), and I wanted to know about him in the deepest way possible, and probably in so doing, learn about myself and the site. But then, that fits the process.
The issue with Adak is that it is a tremendously complex place even before I overlay my own emotional architectonic. It was the site of the Northern Pacific campaign of the United States versus Japan during the Second World War, mainly as a diversion from Midway. I had made a deal with the CEO of the facility to exchange the photos for a room, a 40-something Niigata-born guy with petrochemical ties, whose father might have been my father’s enemy, and ideologically, probably was mine, but the personal nature of the trip put that on hold. There were a lot of external and internal conflicts that I had to navigate just to get there.

In short, Adak is currently the remains of the Adak Naval Base and surrounding facilities, which is basically a minor port, petrochemical storage facility, a fishery, and home of the westernmost airport linked to the Continental US, further west than Hawaii. If you rent a car, you rent one of the trucks a local offers, the gas comes from the tank farm, and the ‘hotel’ is a number of duplexes that the residents rent out to visitors. There is a General Store, a cafe at lunchtime, and the old VFW becomes the tavern for dinner, offering an entree or some microwaveable snacks along with a full bar. You sign a disclaimer to absolve the Corporation of any liability if you encounter black mold, fall into an old stairwell, sinkhole, run into an old unexploded shell, etc. I’m speaking a little darkly about this place, but it’s pretty rugged with radically changing weather, frequent earthquakes, and they’re still cleaning up the old artillery ranges.
On the other hand, it’s one of the most amazing places to be. It’s right at the edge of civilization, a volcanic arctic island withn no trees and some of the most amazing wildlife you’ve ever seen – eagles, otters, seals, birds. I can see why my father talked about it so much.
One other thing of note is that while doing the project, I’ve run into all sorts of people who have served, lived, or even been born there, as there was a 6,000-person family facility. On the plane from Minneapolis to Anchorage, I ran into an airline pilot who had just been on a caribou hunt there, and he gave me his GPS information and a lot of pictures. On another trip, I ran into a woman who was born there. It was unbelievable.
What did I learn? I learned about a history that few remember, I learned about my own history and how it affects me. I also learned about the local culture, its history, how Alaskan culture meshes with corporate interests to create a lot of the issues seen in mass media. There isn’t a lot of concern for the area from the locals, and actually the Military was doing a decent job with the cleanup. From a more personal level, I also came to understand that everything is transitory. Art, culture, society, all ephemeral in terms of a mountain. Human beings don’t matter very much to a volcano, but definitely the other way around.
When I was walking on the western (uninhabited) side of the island, I had napped on some tundra and realized I didn’t have my GPS or keys – all my keys. I knew where I slept, and I leave my keys in the car a lot. The worst that could happen was that I would have to walk 5 miles into town in a cold drizzle, get Jimbo the Constable to let me into my car and get the truck in the morning. In the end, I learned that if it isn’t a landmine, it’s not that big of a deal.
“Do you have a clear idea of what this project will become? Also, I noticed that it is part of an artist residency program at Eyebeam R&D Atelier NYC. How do you intend to present this work, in a space, on-line or something else?” This is really tough for me – no, I don’t have a clear idea yet because it’s so hard to frame. It probably needs to be a book, but it isn’t going to be done for a couple more years. I’d like it to be a hyperdocumentary like SPRAWL, but not in the same way. Also, I think it would make a great presentation, and the images are really beautiful. As I mention, it’s terribly hard to frame this project, and I think it should be allowed to be large.
MG: Let’s talk about a piece you created with The Yes Men. As many in the know, know – and of course those who have fallen foul to the Yes Men’s activist-pranks; they are legendary cultural saboteurs. They have impersonated World Trade Organization corporate spokespersons, including Dow Chemical Corporation, Bush administration spokesmen on TV, at various business conferences around the world. In order to demonstrate some of the mechanisms that keep bad people and ideas in power. Focusing attention on the dangers of economic policies that place the rights of capital before the needs of people and the environment. They have more recently become more known to a world-wide audience for The Yes Men, a movie.
Could you inform myself, and readers about the mock industrial video ReBurger and how it came about?
PL: Right. The animation work for The Yes Men is a strange beast, because it came from previous work for a group called RTMark, from which some of us came from to do Yes Men, which is well documented in the two movies. Again, the process for these animations, which I later edit into industrial videos is also an odd one. Usually, when there is an intervention (and I have sometimes appeared in person), Mike will give me a call and say something like, “Hey Patrick, we have this idea for this, for that company…” In this case, it was an idea for recycling feces for the Third World, and not much beyond that general concept. At first, I was thinking of translating dietary fiber to textile manufacture, creating a suit that would look like S**t, but shortly thereafter, brainstorming created the McDonald’s parody. I knew it was going to be shown at Plattburgh College, but beyond that, I didn’t have much context. So, that’s where my process in context with the larger presentation sort of diverges. Mike, Andy and Matt were developing the presentation, and I started in on the simple metaphor of eating shit. In short, I get some basic ideas together, and then produce the clips (not the full industrial video).

Beyond that basic joke, it’s really just exaggeration – the idea of an international infrastrucure for the collection of post-consumer waste, the branded toilet, and the special product names, like “McDung”. The scene that seems to get people is the one of the Ronald McDonald Colostomy Machine (the paste dispenser) as it creates the brown coil of reprocessed waste and then presses it into nice patties. For me, this is the use of pure literal metaphor, and maybe that’s why it works. Maybe it’s because it stands for a corporation that offers “choices” for healthy eating that few choose, and McDonalds willingly contributes to the obesity and illness of billions. In my opinion, ReBurger just tells the truth.
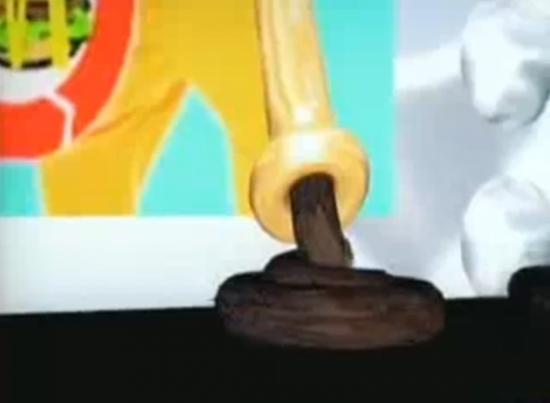

But the reason why people like the video is also a reason why it was a real problem for the sale of the movie at Sundance 2003. Although it was obvious fair use, many in the film industry were also buyers looking at the movie. Mike Bomnano told me that the legal departments of the movie companies were trying to determine the degree of risk of satiring McDonald’s, complete with branding. This was obviously Fair Use under US Copyright, but again, the possibility of an egregious law suit could have happened. In the end, McDonalds decided to ignore the piece, which was great, since I believe it’s one of the stronger Yes Men pieces.
MG: In the UK, June 1997, the infamous McLibel Trial (mcspotlight.org) came to an end. The case was between McDonald’s and a former postman and a gardener from London, Helen Steel and Dave Morris. It ran for two and a half years and became the longest ever English trial. “…Helen and Dave decided that they would stand up to the burger giants in court. They knew each other well from their involvement in community based campaigns in their local North London neighbourhood and felt that although the odds were stacked against them, people would rally round to ensure that McDonald’s wouldn’t succeed in silencing their critics.” The defendants were denied legal aid and their right to a jury, so the whole trial was heard by a single Judge, Mr Justice Bell.
“The verdict was devastating for McDonald’s. The judge ruled that they ‘exploit children’ with their advertising, produce ‘misleading’ advertising, are ‘culpably responsible’ for cruelty to animals, are ‘antipathetic’ to unionisation and pay their workers low wages. But Helen and Dave failed to prove all the points and so the Judge ruled that they HAD libelled McDonald’s and should pay 60,000 pounds damages. They refused and McDonald’s knew better than to pursue it.” Mcspotlight.
I can imagine that McDonald’s were considering their past experience, with cases such as the McLibel Trial. “The legal controversy continued. The McLibel 2 took the British Government to the European Court of Human Rights to defend the public’s right to criticise multinationals, claiming UK libel laws are oppressive and unfair that they were denied a fair trial. The court ruled in favour of Helen and Dave: the case had breached their rights to freedom of expression and a fair trial.”
For your project 8 Bits or Less, in 2002, you wrote a brief statement which I am assuming must be about your own condition, saying “An artist who has become blind (whether physically or ideologically) has resorted to viewing his world through the prosthetic devices that constitute his sense, like cell phones, and wristcams. The result is a distorted landscape that considers Situationist theory, surveillance culture, identity, and alien abduction.” Can I begin by asking why this statement came about and then what part of the project you feel communicates or is expressesed most successfully?
PL: First on the matter of ReBurger, I think that the smarter entities know not to react, but that isn’t always the case. Perhaps the ones who have been burned, now have a smarter PR team.

8 Bits or Less is a series I did that was influenced by several things. For many years, I had felt that as technological artists we are slaves to “innovation”, which is merely an exciting word to stand in for the commercial upgrade path in software and hardware. This set of videos addresses my dissatisfaction with the notion of verisimilitude in regard to techological art, or the “big ticket” piece. Ever since the late 1990’s my response has been to either get by with just enough aesthetic polish to make the work believable/legible, or to willingly embrace a low rez/grayscale time. The lo-fi grayscale is not the same as 8-Bit, which has 256 colors and refers to early personal computing and video games. Perhaps it is closer to my passion for Slow Scan television (a 1970’s video modem technology in which a frame is transmited every 7 seconds) or my position of eschewing resolution and color depth as a form of intransigent aesthetics. In addition, the fact that the frame rate is at most 3 frames per second, and was shot with a Casio Wristcam at one frame every 1.5 seconds was also my homage to Muybridge, mainly in terms of the grayscale and serial qualities of the video. Beyond that, and the fact that each video consists of about 900 frames, all hand edited, perhaps 8 Bits or less is more about my politics about the technological industry and personal differences with New Media and technolust.
On the personal side, 8 Bits or Less is an allusive fable having to do with the fact that I have been blind a couple times in my life, but this blindness can translate to the fact that for a period of time I felt that I had immersed myself in my studio for long enough, that I saw the world primarily from my screen. Therefore, although I had been visually imparied for part of my life, much of which has been fixed by having cataract removal in 1999, I still felt that there was a metaphorical blindness caused by society’s use of mobile devices, the existential distorions of 24-hour cable networks and the Internet. Therefore, the series (if you listen very closely) incorporates a mix of postmodern theory and hyperbolic statements about aliens, obscure jokes about bits and nybbles, surveillance culture and the abjection of low fidelity.
What I think is successful about it is that it holds together at all, or that it engages the viewer without necessarily relying on leading edge technological conceits, but perhaps using the wristcam aethetic is a conceit in itself. Antoher aspect that I have enjoyed about it after five or six years is that it is a really hallucinogenic series of pieces. But then, I think this is the point that Gibson made about cyberspace that has been expanded on by the Baudrillardian mediascape and the Internet – the consensual mass hallucination (facilitated by mass communications).
———
Watch 8 Bits or Less series. Images link to videos online.

A wristful of bits. Found on DVlog.

8 bits or less. Found on DVlog.

http://www.dvblog.org/movies/04_2007/lichty8bit/closevision.mov
Close vision. Found on DVlog.
Big thanks to DVblog for 8 Bits or Less images & video links.
http://dvblog.org/
Decode: Digital Design Sensations
The Victoria and Albert museum, London
8 December 2009 – 11 April 2010
Decode: Digital Design Sensations at the Victoria and Albert Museum (V&A) brings the state of the art in art computing to a venerable cultural institution. Everything from the posters and banners around town to the hoardings on the entrance to the gallery containing the show makes it clear that Decode is a serious cultural event. It’s a spectacle, a dark space alongside the well-lit galleries of the V&A, drawing you in with points of light and distant sounds. The crowds are reassuring for the popularity of art computing yet disconcerting for the experience of the art at times.
Don’t forget to ask for a catalogue as you hand over your ticket on the way in. The sponsor’s foreword should raise a smile to anyone familiar with the software industry, but the introductory essay (which only occasionally becomes the latest casualty of the confusion that the word “open” shows), the details of works in the show and the interviews with Golan Levin and Daniel Rozin are all very informative. The catalogue also draws attention to Karsten Schmidt’s specially commissioned graphic identity for the show, which can be downloaded and modified as Free Software.
The show is divided into three sections. Generative art, data visualisation, and interactive multimedia (or, as the catalogue puts it – Code, Network and Interactivity).

The generative artworks suffer in comparison to the other pieces by being mostly small-scale screen based pieces. However appealing the images are on the screen (and they are) they cannot compete with the projections and three dimensional installations of the other sections. With the exception of an interactive version of the video to Radiohead’s House of Cards by James Frost and Aaron Koblin, the work does not refer to the human figure or to the viewer, another feature of many of the most popular pieces in the other sections. And apart from Matt Pyke’s typographic totem pole, my other favourite piece of the section, the work is calm. Beautiful, but calm. It would reward prolonged contemplation in a quieter environment and might benefit from presentation on a larger scale to better bring out its aesthetic qualities. But this is not that environment, and that presentation is not given to the work here.
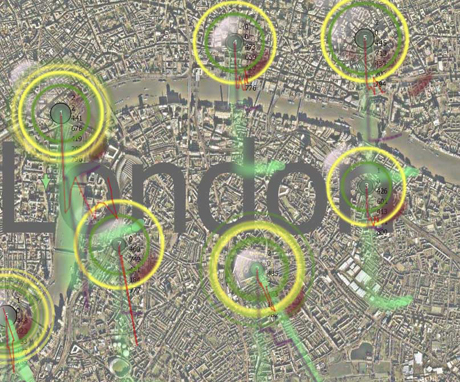
The data visualisation section has more projections and custom hardware, and also has more human interest. The emotion of We Feel Fine by Jonathan Harris and Sep Kamvar, the surveillance state expose of Stanza’s Sensity, CCTV assemblages, Make-Out, the porn-inspired kissing figures of Rafael Lozano-Hemmer and the social data visualizations of Social Collider by Sascha Pohflepp & Karsten Schmidt are sometimes less visually sophisticated than some of the generative pieces, but address current social and technological developments more directly. The world wide web is twenty years old, it has drawn in the mass media and media feeds from the real world, and many of its users produce and encounter gigabytes of data over time. Representing and exploring that technological and cultural environment is something that art can do and that art is particulalry well placed to do given the importance of the aesthetics of interfacing and visualisation to the contemporary web.

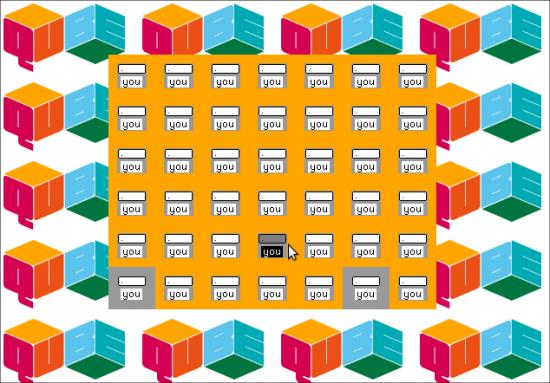
The interactive multimedia section contained the real crowd pleasers of the show, although some of the pieces had “out of order” notices on them when I visited. Yoke’s virtual reality Dandelion Clock controlled by a hairdryer, Ross Phillips’s Videogrid, a physically interactive group portrait and Daniel Rozin’s Weave Mirror, a cybernetic sculpture-cum-display-screen. They all give their audience an aesthetic experience that briefly changes their relationship to the world, and in some cases shows them themselves in that new relationship. Interactive multimedia installation is clearly due a resurgence.
The V&A have presented Decode as a design show. I was struck by this framing of the work when I visited the show, and most of the people I have spoken to about the show since have commented on it as well. Many of the participants are graphic designers or work in design as well as art and education, but much of the work would be poorly served by being regarded as design rather than as art. It is not advertising, or presentation of anything other than itself for the most part. Where the work is information design, the information has been chosen by the designer. That said the art computing MA I attended as a student had to be called a “design” course to get funding, so possibly this is a constant. And the V&A have done a great job of presenting the work and letting it speak for itself to the visiting crowds.
This isn’t quite Cybernetic Serendipity 2.0. It excludes the conceptually and performatively, rougher edges of contemporary art computing. But these exclusions are largely practical; there is no livecoding and there are no email or self-contained web browser-based works. Some of the work is strikingly but subtly political in its representation of current social and political trends such as surveillance, online pornography and the death of privacy.
The V&A have done the conventional artworld and the general public a great service by presenting Decode. The show contains enough big and up-and-coming names in art computing and digital design to provide a convincing if necessarily incomplete survey of the contemporary scene. Decode also serves an important role for artists and students with an interest in or a stake in art computing by focussing attention on what others have achieved that can be built on.
Decode shows the achievements of the personal computing and web eras of art computing becoming established with and recognized by the broader arts establishment. The danger is that the story will finish triumphally here. Processing has become the new Shockwave, and particle systems and shape grammars are not enough in themselves for long without an accompanying progressive and deeper deeper engagement with the aesthetics and history of art, technology, wider society, or all three. Art computing is not immune to technical and aethetic conservatism. To avoid this I think that it needs to intensify, to become more like itself; to become more beautiful, to tackle larger datasets, to become more interactive. In other words, it needs to build on the achievements gathered together and presented here.
http://www.vam.ac.uk/exhibitions/future_exhibs/Decode/
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
Featured image: F.A.T. Lab (Free Art and Technology Lab) were found causing trouble at the Transmediale.10 this year.
An interesting outsider project at Transmediale.10 this year, was F.A.T. Lab (Free Art and Technology Lab). A collective of artists, engineers, scientists, lawyers, musicians and trouble-makers who have been working together for two years, on the intersections of Pop culture and Open source. Their stapline describes them as “An organization who is dedicated to enriching the public domain through the research and development of creative technologies and media”. Beware, they love using the word ‘Fuck’. A lot! Which means they are cool, and some you grown ups may feel slightly unnerved by their over generous outpouring of flippant explitives, but the kids out there just love it!
You can read an explanation of their work in the about section on their website, and view a video presenting some of their ideas and works. With a simple rap base with nasty yellow and pink colors, it could be considered as a joke. Perhaps, to some degree it is, but at another level they are playing around with social contexts of the Internet culture’s, presumptions and acceptance of things. Through an omnipresent ludic approach they reuse what is given to us all with a contemporary pop attitude – showing us the many contradictions from these given systems. Proposing other possibilities in order to loosen and to free things up from the copyright laws and prescribed rules of both big companies and clumsy governments.
One of their projects called Public Domain Donor, consists of D.I.Y stickers saying “In the event of death please donate all intellectual property to the public domain”. They write “Why let all of your ideas die with you? Current Copyright law prevents anyone from building upon your creativity for 70 years after your death. Live on in collaboration with others. Make an intellectual property donation. By donating your IP into the public domain you will “promote the progress of science and useful arts” (U.S. Constitution). Ensure that your creativity will live on after you are gone, make a donation today.”Simple and humurous.

Yet, behind their process of cultural detournment exists a reference to earlier net art critique, by Critical Art Ensemble who way back in 1995 said “Each one of us has files that rest at the state’s fingertips. Education files, medical files, employment files, financial files, communication files, travel files, and for some, criminal files. Each strand in the trajectory of each person’s life is recorded and maintained. The total collection of records on an individual is his or her data body -a state-and-corporate-controlled doppelganger. What is most unfortunate about this development is that the data body not only claims to have ontological privilege, but actually has it. What your data body says about you is more real than what you say about yourself. The data body is the body by which you are judged in society, and the body which dictates your status in the world. What we are witnessing at this point in time is the triumph of representation over being. The electronic file has conquered self-aware consciousness.” The Mythology of Terrorism on the Net. Critical Art Ensemble Summer, 95
Also as stimulating, is the idea Graffiti Markup Language, an XML file type specifically designed for archiving graffiti tags, and easily reproducing them.
For Transmediale.10 they presented a project called Fuck google, one of their more involved works, appropriating the image of Haus der Kultur der Welt, the futuristic bulding hosting Transmediale, formerly known as the Kongresshalle conference hall, a gift from the United States, designed in 1957 by the American architect Hugh Stubbins Jr. as a part of the Interbau exhibition. John F. Kennedy spoke there during his June 1963 visit to West Berlin. Fuckgoogle focuses on reminding us all how this big company has become omnipresent in our digital lives, refering to the risk that too much data is owned and is going to be owned more and more, just by Google alone. It exists as a collection of browser add-ons, open source software, theoretical musings and direct actions.

Not necessarily trying to be a definitive solution against the big G in any sense of the word, but more a reminder, a provocative virus to diffuse. So we have a graffiti firefox skin, fuck google pins, The F.A.T Pad or some plugins to reclaim your public individual space on your browser. Everything is D.I.Y and opensource, so you can easily replicate it. The approach can be find with FuckFlickr a free image gallery script offering everyone who visits a Flicker-like image gallery.

The F.A.T. Lab is an example of technological sabotage. Of course, it’s not a new thing in respect of the hacker community: using the instrument, medium directly, in order to change perceived assumptions of our reality. What is quite new is F.A.T. Lab’s blatant exploitation of everyday Pop culture and its language. The hacker counterculture has always had it’s own way of communication, built in the late 80’s and 90’s. These days, more and more people use the computer, not just hackers. Using Pop culture in order to communicate one’s message could be one possible way to escape the duality culture/counterculture. On the other hand, F.A.T. Lab could be creating a fresh paradigm which allows others who would not normally appreciate hacker culture or even media art culture, filling a space beyond art culture which could be considered as too refined.
Marcello & Gaia: Can you describe who you are and how do you connect each other?
Evan Roth from F.A.T. Lab: We are a group of friends. There’s not any formal application process or open call, many come from typical art organizations. It started out as a group of friends and then slowly, more friends joined. We also made more friends, collaborators on line. Here at Transmediale.10, it’s actually our first chance to meet face to face and some of us have not met before. There are two things that mainly characterize us. On one side, there is the open source culture and advertisement free culture, but also the idea that this all should be fun. Art and political activism doesn’t have to be a boring, the interface of it all, can be accessible to more people. We try to push this candy coding, get the those audiences who are using youtube videos, that is our primary audience. We like it when art organizations pay attention to us but really our main audience is at the borders of things, using different networks, commercial networks out there, happening outside of the gallery.
M&G: If we look at the projects you are showing here there is a kind of aesthetic in common, the colours are really interesting, the pink and the yellow remind us early 90’s spam. Is that aesthetic a primary decision, is the style you choose to define you, or has it just happened in the progress of your work.
E: I answer that in two. There is a thing from open source development culture that is ‘release early and release often’, we try to apply this model to the media production. We try to release ‘early and often’. If you are on the fence where you should release something or not and it is not quite ready, just push out the door, because it is better to have it in the public counter system than not. So the aesthetic of the website is in part probably pushing out the door rather taking care of the nuances or the color it is. We just try to get this thing published quickly. Someone could be sitting on their brilliant idea and waiting for years to release, waiting for some details and then you find that no one really cares about this in the end. But there is also an aesthetic interest in common, that comes from this ‘dirty style’. There is an artist friend, Cory Arcangel who is one of my favorites, and he describes the dirty style as ‘either you take little interest in design so it becomes so un-aesthetic or you over-work it to a point that the work itself becomes something too trivial’. We don’t have meetings about how the website is going or what it looks like.
M&G: Don’t you think that this “dirty style” is somehow hiding the real content or the message? The use of ‘dirty style’ is obviously an answer of the hyper sensibilization, concern of the form but at the same time this makes your work splitting in between the no-attention of form and pushes content in the corner.
E: The way our websites look matter’s less and less now, because people don’t go to websites for content anymore. Most of the traffic in the websites do not even see the pink and the yellow, design. There is some kind of form/function relationship going on. We are interested in rolling up this web 2.0 idea a little bit, and that’s what this installation here is about at Transmediale. The early 90’s aesthetic was with people hand coding html and making tables, not downloading a WordPress thing. In that sense, there is a sort of connection to the DIY, rolling back to the way of 1.0 – where the files are hosted in your own server and not google or yahoo.
M&G: Isn’t it more interesting to try and critique in a more constructive way, creating something else, not just another google appropriation but other kind of net platform for a community? Could that be one of the important challenges for artists now?
E: Open source is a big movement and free culture is even bigger and so we know that there are people out there hacking in this way right now, but we are not programmers, there are programmers taking part but these are not our skills. Our place in this movement is in the media side. We do have programmers in our group but we feel more like media makers. We make these videos and they are kind of funny and taking something from the pop/culture, twisting them, possibly people have a look and pass them around. But there are messages in them. And the messages are trying to reveal the money and the branding business that google is making and saying it is not cool, and being involved in an alternative open source culture looks better. We also have a development tool like fuck flicker and flv player where you can have your own videos up like you tube.
M&G: Why are you are supposed to win this year’s Transmediale? You stood up on the stage during the award claiming the award for yourselves!
E: Oh no, we don’t think we are supposed to win. Do you know Kanye West? This is a USA story, we joked about Kanye a little bit. We’re always trying to pay attention to what is going on in pop culture and surf a little bit. Kanye was notorious for interrupting a ceremony whenever he lost, grabbing the mic. As we were for this fuck google project – last night, the winner was a youtube related project, and google is a sponsor. The message we tried to get across last night, was a reference to this, and we are gonna have an official press release on it soon. But I think that for Transmediale, our project was an anomolie, showing this fuckgoogle in contrast to accepting web 2.0, which is actually a range of projects. We were surprised to be invited, who know’s what for? But we think that it was a very wise decision, and we are really happy to be here.
On their website you can get a clear impression of their feelings towards Google “So, what is so “fuck-worthy†about Mother-google? It is the fact that a corporate entity, even one as beloved and competent as Google, is in control of such a large stake in the digital network and public utility upon which we have all grown so reliant. And, that as a publicly traded company, it doesn’t have to answer to anyone but its largest shareholders, despite the fact that its decisions effect the lives and private information of millions of people. Few even question or raise a voice in opposition to the Google-ification of the Internet.”
There were more than 1,500 submissions for the Transmediale.10 awards, nine art projects were nominated and F.A.T. Lab was a runner up amongst them. Showing contemporary, activist art within a larger more incorporated festival is to be commended, it is not an easy thing to do. And we all know how easy it is to criticize rather than make something ‘real’ and positive happen. F.A.T. Lab are a tangible byproduct of a culture, caught in the trappiings of Hyperreal situations, a confused world losing itself even further into a perpetual state of denial. Pop culture and celebrity related banalities are constantly distracting our gaze. It is an interface which can only handle life via mediated proxy. F.A.T. Lab know’s this, and have adapted themselves to literally scrap with it on their own terms. Their role and place in the world is to get out there on the front line and go places where the common people reside. They want to be on the main stage battling it out, whilst challenging the interface presented to us all – making it their playground.
You can also read Marcello Lussana and Gaia Novati’s article about this year’s Transmediale.10 here…
Mark Napier’s Venus 2.0
Angela Ferraiolo
February 5, 2010
“Now that I’m done’ I find the artwork disturbing. It freaks me out. Maybe I’ll do landscapes for a while to detox.” — Mark Napier
Artist Mark Napier, well-known for the net classics Shredder, Riot, and Digital Landfill, recently exhibited his latest work Venus 2.0 at the DAM Gallery in Berlin. A sort of portrait via data collection Venus 2.0 uses a software program to cross the web and collect various images of the American television star Pamela Anderson. These images are then broken up, sorted by body parts put back together and — as this inventory of fragments cycles onscreen, a leg, a leg another leg — the progressive offset of each rendering of Anderson’s head, arms, and torso makes her reconstructed figure twist, turn and jerk like a puppet. It’s odd looking. Even her creator is a little afraid of her:
“I have to say’ if I ever meet Pamela Anderson in real life I think I’ll completely freak out and run away. I don’t think I could have a conversation with the woman after this project … I started with a sympathetic view of the actual Pamela Anderson. She is part of the spectacle of sexuality in contemporary media. She’s caught in that ‘desiring machine’ as much as any other human’ probably even more so. She has surgically modified her body in order to have greater leverage in the media. Does this put her in control? I think not.”

Napier’s project doesn’t answer or intend to answer the question of who is in control either, but it plays with the possibilities. Although I wasn’t able to see the portrait at its exhibition. I did track down part of the series Pam Standing at a private location here in New York. Napier has also posted video excerpts of the work online. Unfortunately, these still images and clips are a bit too static to really do the piece justice. If you get to see the real thing and if you look for a while, you’ll see what I mean. Venus 2.0 is an amazing jigsaw puzzle, a deceptive surface of shifting layers – part painting and part search result.
The effect is translucent, lyrical, mathematic and creepy. When I implied that it must have taken an awful lot of precision and calculation to get something like this to come together, Napier insisted that focusing on the technology behind Venus 2.0, its algorithm, or even on the unique materiality of networked art in general, is a way of missing the point. The way he relates to Venus 2.0 is through the painter’s hand. What counts is not the data feed, but who were are, what we want and how we behave:
“The artwork is a riff on sexuality as an elaborate hoax played by a precocious molecule that builds insanely complex sculptures out of protein, aka, meat puppets or more simply, ‘us’. These animate shells follow a script that’s written and refined over the past half billion years. And that script is in a nutshell: 1) survive 2) reproduce 3) goto #1. So sexual attraction is the carrot to DNA’s stick. Attraction is part of the machine. In art history this appears as the tradition of Venus. And more recently: Duchamp’s ‘Bride’. Magritte’s ‘Assasin’. Warhol’s ‘Marilyn’. The focus of digital art is still the human being. Don’t be distracted by the gadgets.”
Hi-tech or not, new media artists are by now well-practiced in the technique of unraveling a familiar image to expose an occluded, yet equally valid identity. In Distorted Barbie, Napier relied on a repeated process of digital degradation to blur both the literal and conceptual fiction of the Mattel franchise. Another early project stolen, took the female body apart, presenting attraction as database. Years later these kind of approaches, pixel manipulations and indexing without comment, as well as parsing and remixing have become a sort of standard operating procedure in new media. So much so that as technique becomes more well-known and more accessible, it can be hard to tell one work from another or one artist from the next. With this in mind’ it seems important to note that in the case of Venus 2.0 it is not so much a choice of subject or an organizational scheme that guarantees the final effect, but the manner in which Napier investigates the image and the ways in which Napier illustrates and manipulates both the visual elements of portraiture and his relationship to the figure involved.
Napier builds and destructs, assembles and tears apart, but in doing so tries his best to keep us focused on these activities as processes. At times Pam’s contortions are allowed to expose the wireframe which allegedly guides her construction and at certain key points on the interface, there is also a steady stream of vector coordinates to embody the idea of data. But Napier makes less of technology than another artist might by effacing what some would tend to elaborate on, in order to draw our attention elsewhere – usually towards evolution, gradation and the ways in which images evolve, and by extension the ideas that inspire those images which reflect how unstable elements are, even treacherous:
“I work at probabilities: what is the likelihood that the figure will be totally opaque? How often does it get murky and undefined? How often should I let that happen and for how long? How often does the figure jump? How long till the figure lands and stands up again? How much time is spent in chaotic motion and how much in stillness? How often does something completely messy happen? Like the figure gets tangled up in a ball that has no structure. I don’t know how the piece will play out each minute, but I know what kind of situations will arise in the piece. I can plan those likelihood, and then let the piece play and see what it does.”

So, like the woman who inspired her. Pam Standing is beautiful, but more unsettling. What makes Pamela Anderson the most frequently mentioned woman on the Internet? Why do we mention her? What is it we want when we give our gaze to celebrity? What has celebrity done to attract us? Whatever your answers, what Napier privileges in his response is not a fixed portrait of a star, but a cloud of iteration that produces its own image and reproduces that image, jangled, confused and full of surprises. A portrait whose finest moments are accidental and whose design is an accumulation of fragments that tense and dissolve, floating like clouds one instant and then sinking like lead the next. This is where the imagination takes a step forward and Napier the artist or Napier the geek becomes Napier the puppetmaster, a networked Dr. Coppelious:
“My favorite moment with the PAM series was when I finally got all the math to work so that the body part images displayed correctly and the correct side of the body showed at the right time and the stick figure suddenly started to look like a ‘real’ puppet that was starting to come alive in the golem-esque way that I thought it could when I was sketching out the idea. I had that Dr. Frankenstein moment: ‘She’s aliiiiiiiiiive!!!!!!!!!!!!!’ which was really the point all along, to create this virtual golem that is clearly not alive at all and yet teases us all with this false appearance of life. Venus 2.0.”
Until the layers of arms, legs, breasts and hips collapse in on themselves and Pam is back where she started, a manipulated beauty unable to escape presentation as a collaged monstrosity.
Note: Mark Napier has been creating network art since 1995. One of the earliest artists to deal thematically and formally with the Internet, Napier has been commissioned to create net art by the Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art. His work has appeared at the Centre Pompidou in Paris’ P.S.1 New York’ the Walker Art Center in Minneapolis’ Ars Electronica in Linz’ The Kitchen’ Kunstlerhaus Vienna’ ZKM Karlsruhe’ Transmediale’ iMAL Brussels’ Eyebeam’ the Princeton Art Museum’ la Villette’ Paris’ and at the DAM Gallery in Berlin.
Arriving at the homepage of Ten Thousand Cents, an Internet artwork by Aaron Koblin and Takashi Kawashima, a mottled image of a one hundred dollar bill slowly fades into view. Ben Franklin looks out sedately. Mousing over the large image, the cursor is replaced with a small red rectangle. And here lays the beauty of the project; with the click of each rectangle, a zoomed in portion of the one hundred dollar bill is revealed. On the left side is a high-resolution photograph of that tiny portion of the bill. On the right side, a real-time moving image plays, revealing how the image was drawn by a human hand in a drawing program created by Koblin and Kawashima. There are, in fact, 10,000 such rectangles and each was created by a Turker through Amazon’s Mechanical Turk marketplace.

Over the course of five months (from November 2007 to March 2008) Koblin and Kawashima posted tasks, known as HITs, Human Intelligence Tasks, on Amazon’s Mechanical Turk site. Having broken down an image of a one hundred dollar bill into 10,000 sections, Turkers were tasked with redrawing their assigned section. Each Turker was paid $.01 for the task, making the total payment of drawing a one hundred dollar bill one hundred dollars. (Prints of the project can also be bought for one hundred dollars. All proceeds are donated to the One Laptop per Child (OLPC) project) Each Turker worked anonymously, unaware that what they were drawing was a section of a bill or that their work would eventually be combined with other Turkers’ work to create an art project. The variability is endless. Some Turkers methodically draw in the lines and painstakingly shade in boxes. Some quickly slash the paint tool across the page; one imagines they felt they had better things to do with their time. Some are cheeky, using the space for digital graffiti or messages like “I love U.” Most copy the image exactly. Yet, with the differing movements and tempos, every one suggests a different story and different person behind the tool. I suggest you take a few minutes and watch the unfolding scenes. They are oddly, satisfyingly banal and beautiful.
The project and its presentation on the website are undoubtedly elegant. Yet, the conceptual work behind the piece is a bit murkier. The project description states, “The project explores the circumstances we live in, a new and uncharted combination of digital labor markets, ‘crowdsourcing,’ ‘virtual economies,’ and digital reproduction.” Big and important themes. What are the implications of crowd-sourcing for creative work? For any kind of paid work? Where is the distinction between work and play? Creativity and re-presentation? In this deeply networked age, what are the evolving relations between individual and collective action?
The Mechanical Turk, made by Wolfgang de Kempelen in 1769, caused a sensation in 18th and 19th century Europe, first for its existence as a seemingly intelligent chess playing automaton – one who could beat Ben Franklin and even Napoleon in chess – and subsequently, for being an infamous hoax. Inside of the automaton was in fact a man, a skilled chess player. The Mechanical Turk was no thinking machine. It was an elaborate performance of concealment and human skill.

In 2005, in an ironic (and some might say distasteful) turn of events, Jeff Bezos of Amazon named a new business venture, Amazon Mechanical Turk. The idea was to make a digital marketplace that capitalized on the unique intelligence of human agents. Broken down into microtasks, known as HITs, Mechanical Turk provides a means to accomplish those tasks that humans can do quickly but which would take computers much longer to do, for instance, tagging images, taking surveys or transcribing audio recordings. This Mechanical Turk is also a performance of human skill, one that revels in its basis in human intelligence – Bezos calls it “artificial artificial intelligence” – but one that also operates within a mode of concealment and indeed, alienation.
As Katharine Mieszkowski of Salon wrote about Mechanical Turk in 2006, “There is something a little disturbing about a billionaire like Bezos dreaming up new ways to get ordinary folk to do work for him for pennies.” Critics of Mechanical Turk abound, and their objections point to the insidious labor relations that Mechanical Turk enforces, implying that Mechanical Turk approaches a virtual sweatshop. The system was designed for employers, not employees. The earnings of Turkers fall within a gray area of digital labor, officially being classified as contractor work, subject to high self-employment taxes and no option for benefits. Although a rating system protects employers, in so far as employers can choose to reject a work offer from a Turker or refuse to pay a Turker if the work is completed unsatisfactorily, no such system protects Turkers. As advocates of a Turker Bill of Rights have pointed out, there is no effective outlet within Mechanical Turk for Turkers to voice grievances against employers. What does exist is a vibrant community forum, Turker Nation, where Turkers advise each other on known scammers.

Moreover, although anecdotally Mechanical Turk is understood as more game or past-time than employment, a recent study out of University of California, Irvine’s Informatics Department points out that almost a third of Turkers rely on Mechanical Turk as a source of income. Another study found that nearly half of Turkers report their motivation for working as income related. For this population of Turkers, it is troubling to consider the possibilities of exploitation and unfair labor practices.
In this light, I find the artists’ neat appropriation of the mechanisms of Mechanical Turk unsettling. The implications and the stakes of Mechanical Turk as an economic system are left untouched. And considering that the artists chose to create a representation of money and employ Turkers, these dimensions of economy and labor are present but disappointingly unaddressed.
Yet, the moments in the project that remain in my mind’s eye like lovely specters as I glance at the dollar bill that I traded for coffee this morning, are the movements of the individuals who drew each section. On this level, the project is like a fantastic cabinet in which each drawer opens onto a new wonder. Perhaps what Ten Thousand Cents effectively offers is not a statement about labor politics or late capitalism’s continuing ability to provide structures for domination and exploitation. Perhaps Ten Thousand Cents asks us to take a different step toward understanding “the circumstances we live in,” revealing the endless variability of individual expression. In this networked age, we often act collectively, that is, together, parallel, most often without knowledge of the larger directions toward which our actions will lead. Collaboration, laboring together, is notion whose meaning is expanding and changing in the 21st century. What remains, even among protocols and code, is individuality. Though we are subsumed by larger structures, we do have spaces for self-expression and self-formulation. Leave an exploration of the limits of these spaces to others – and I surely believe we must consider the limitations. Yet we must also explore and value the spaces of possibility and the domains where we are active agents. We are called to remember that every artifact is irreducible to its mere instance in the world – it is a sum of processes and individual actions.
Of course, “the circumstances we live in” also requires us to keep in mind the bottom line. It’s all about the Benjamins, as the phrase goes. In response to a HIT, no less, requesting an answer to the question, “Why do you complete tasks in Mechanical Turk” one Turker wrote, “I do it for the money!”
This article is co-published by Furtherfield and The Hyperliterature Exchange.
Millie Niss, the writer and new media artist, died of swine flu with complications at 5 a.m. on 29th November 2009. Her mother and longtime collaborator, Martha Deed, was with her then. She had been in hospital for four weeks, mostly in intensive care, after picking up the virus, which quickly became serious in her case, probably because she already had respiratory difficulties due to a rare condition known as Behcet’s Disease. She was 36 years old.
The news would have been sad to hear about anyone, but it was especially sad in Millie’s case because she was one of the people in the new media community with whom I felt particularly close. I met her at the trAce “Incubation” conference in Nottingham in 2004. When I first arrived at the conference, I was directed to the part of the room where Michael Szpakowski was because he and I had already struck up an e-mail friendship, and he’d left a message for me at the door. I found him talking to Millie. Michael was only there for that first evening because he had to go and see his father, but Millie was there for the rest of the conference, and I sat next to her at many events. She was dark-haired, overweight and funny: very easy to talk to. Later in the conference, she gave a presentation about how to attach behaviours to objects in Flash, which I attended along with Jim Andrews and others. She kept saying beforehand that she was feeling pretty nervous about it, but she seemed very natural and nerveless when it came to the event. In the beginning, she asked for suggestions from the audience – I think for an initial idea on which to base her Flash piece – and at first, nobody said anything. She suddenly became acerbic – “Oh come on – don’t make me pick on someone like you were a bunch of school kids!” Immediately you could see her as a teacher and imagine how she would have controlled a classroom. I suggested spiders, which set the ball rolling, and from that point onwards, everything went very rapidly. She quickly and expertly demonstrated how to set up a drawing of a spider as a symbol, and attach a behaviour to it so that when the mouse pointed to it, a sound file played. Another thing I remember was that she was very critical of certain aspects of Flash – how you had to import things into your library and then drag them from the library to the stage before you could do anything with them. You could feel her personality’s force, her opinions’ sharpness, and her sense of humour and fun.
From that time onwards, she and I regularly exchanged e-mails. She knew that I worked in the National Health Service, and because she was very much in the mill of health care herself, we had some lengthy correspondence about how the UK system worked, compared with how things worked in the USA. She also sent me two glass unicorns through the post – occasionally, she would run little competitions on her “Sporkworld” website and offer glass unicorns to participants as prizes. The first of these unicorns went to my daughter Rachel, and the second is still sitting on my study window-ledge in a white cardboard box. He used to stand out on his own four feet, but unfortunately, he had an accident with the curtain, and one of his legs got knocked off. I stuck it back on with Superglue, but it fell off again. Millie knew all about this, and I sent her a photograph of the unicorn on my window-ledge – I think I even sent her a second photograph, showing how he looked after his accident and temporary repair. She was always very interested in Rachel and liked to hear my stories about her. Perhaps they reminded her of her childhood, or perhaps she just liked kids.
One thing which came across from Millie’s correspondence, as well as from her work and her occasional online commentaries, was her sense of perspective on new media art. She was grateful to it because it provided an outlet for her creativity which she had never managed to find through traditional print; but all the same, she remained aware that it was a small and specialised field and that a good deal of new media work might seem incomprehensible to “ordinary” people. Her comments about other new media artists reflected this grounded attitude. She preferred work which didn’t reach for the hi-tech solution that a lo-tech one would do – work, in other words, which didn’t employ technology for its own sake, and where the form was dictated by content rather than the other way round. Likewise, she wasn’t particularly bothered whether her output complied with the dictates of new media theory – whether it was interactive, non-linear, coded or networked. The pieces on her website exhibit a cheerful mixture of genres and media: Flash, video, poetry, prose, photography, sound files and plain old HTML rub shoulders in much the same way that political commentary, literary criticism, observations of places and people, food appreciation, nature notes, raucous humour and occasional obscenity rub shoulders in her blog. The groundedness of her art, and her sense of responsibility towards her audience, is demonstrated by the way in which she habitually presented videos on her site in different sizes and resolutions – for example, “Warhol’s Campbell’s Brodo” is available 8.85mb, 6.23 MB and 2.43 MB – so that people with slower connections could sacrifice a bit of quality to save a long wait if they so desired. Similarly, her introduction to “Warhol’s Campbell’s Brodo” explains that “brodo is the Italian word for soup and the restaurant’s name”. Without talking down to her audience or limiting what she wanted to say, she was always at pains to be as clear and user-friendly as she could – and this insistence on clarity and user-friendliness, her desire to reach out to an audience of “ordinary” people whenever possible, was one of the things which made her voice such a distinctive and refreshing one in the new media world.
However, this is not to say that she was any Luddite or uninterested in the theory of any description. One of her best-known pieces of work – a collection of six pieces – is the Oulipoems, reproduced in Volume One of the Electronic Literature Collection in 2006. As Millie explains in her introduction, “Oulipoems is a series of six interactive poetry Flash works… loosely based on the Oulipo movement in French literature, which focused on texts based on constraints… and also on mixtures of literature and mathematics.” One of the Oulipoems is “Morningside Vector Space”, which rewrites a description of a simple incident in various ways, depending on how we move the mouse cursor over a coloured square. The source text reads:
Yesterday, I was walking on Amsterdam Avenue. There were cracks in the sidewalk. I looked up and saw the tall and unfinished Cathedral of St. John the Divine. A man approached me. ‘Excuse me, do you have the time,’ he said. I told him at 5:47. He walked (sic) away. It was windy. The coloured square is marked to indicate the inflexions this text will be given if we hover over different areas – from “Simple-minded” to “Pretentious” on the x-axis and from “Sociological” to “Melodramatic” on the y-axis. If we point to the “Simple-minded” corner, we get this:
I walked. On the sidewalk. By the big church. There was a man. He wanted the time. I gave him my watch. He left. I was cold.
The intersection of “Pretentious” with “Melodramatic” yields this:
A vagrant in tattered clothing invaded my personal space, filling it with his odor. ‘Hey, man, got the time?’ he whined…
The intersection of “Pretentious” with “Sociological” produces:
The sidewalk, unmaintained by the municipality, contained evidence of substance abuse…
– and so forth.
A number of observations come to mind about this piece. First of all, although it isn’t tremendously technically sophisticated, it does reveal a very competent grasp of Flash and object-oriented coding. This grasp is also displayed in many of Millie’s other pieces. Secondly, it demonstrates the “mixture of literature and mathematics” to which Millie refers in her Introduction to the Oulipoems – the idea that different styles of writing can be mapped onto a graph and summoned by pointing at different vectors – and in doing so, it demonstrates a willingness to experiment with text, and an openness to the idea that text in digital literature may sometimes be manipulable by the audience, rather than fixed into a single unquestionable form by the author. Thirdly, “Morningside Vector Space” is funny and accessible. The labels with which Millie marks out her vectored space are humorous, and the texts with which she illustrates these different writing styles are exaggerated for comic effect. At the same time, there is an undercurrent of social observation, with a suggestion of political edge: “I was observing a mixed-income neighborhood on the borders of a low socioeconomic enclave… Lacking funds for a watch, he had to rely on others in the community to be on time for his appointment with the social services…”
Lastly, perhaps least obvious is a powerful sense of place. The piece’s title refers to Morningside Heights, an area of Manhattan in New York. The texts allude to Amsterdam Avenue, a street in Morningside, and the Cathedral of St John the Divine, which stands there. St John the Divine is also known as St John the Unfinished because although it was begun in 1892, it remains incomplete to this day – hence the description of the cathedral as “tall and unfinished”. The coloured vector space in Millie’s piece contains another reference to the cathedral, in the shape of a wobbly but recognisable line drawing of its facade. This sense of place is an important aspect of Millie’s output – not only in videos about places such as “Jewel of the Erie Canal” or “A Hecatomb in Cheektowaga” but also in new media works such as “The Talking Escalator at Penn Station”and “Unscenic Postcards” – and like her interest in politics, it demonstrates her commitment to the “real” world, as well as her talent for observation and comment.
Another of Millie’s Flash pieces, and one of her most personal artworks, is “Biological Time Clock”. In a central pane, the words “womb”, “amoeba”, “bomb”, “bang”, and “boing” appear, accompanied firstly by Millie’s voice intoning the same words, and secondly by drawings of a womb, an amoeba, a womb inflated to the point of bursting, a womb breaking into pieces, and another slightly different drawing of a womb in bits. Underneath this pane appears a randomised sequence of phrases, arguing both for and against getting pregnant and giving birth: “It’s not for me”, “I’d be nurturing”, “I’m more than a womb”, “I’m not together enough”, “maybe I should do it while I can”, and so forth. There are also buttons that allow you to add extra sound effects, such as Millie saying “tick-tock” or chanting “biological”.
There are feminist aspects to the piece – one of the anti-pregnancy phrases is “I don’t want to be a breeding cow”, and another is “I’m more than a womb” – mixed with what seem to be more autobiographical notes, such as “why am I alone?” and “I don’t want to lose my creativity”. However, a question that seems to go to the heart of the piece is what is the word “boing” doing in there? The drawing which accompanies this word is enigmatic. Still, it may be meant to suggest that the womb, which broke apart at “bomb”, is now somehow bouncing back together again – and by implication, that no matter how many times the author talks herself out of childbirth, her consciousness of her womb keeps coming back to bother her afresh. But the word “boing” serves another purpose by introducing into the piece the quirky, unpretentious, comical note essential to Millie’s art. If the word sequence at the heart of the poem were simply “womb, amoeba, bomb, bang,” then both the message and the tone would seem much starker. With “boing” on board, there is a playful and funny element to the piece, a release from serious description into exaggeration, which seems to suggest that Millie herself isn’t taking it completely seriously, and we don’t have to take it completely seriously either.
In some ways, this insistence on the quirky and the wacky might be considered a weakness or a limitation in Millie’s art, flinching away from completely direct and honest engagement with her subject matter, symptomatic of a tendency to let both herself and her audience off the hook, especially if her subject-matter happens to be personal. But it should be borne in mind that Millie had more personal subject matter to deal with than most of us, and her insistence on humour was an essential part of her strategy for dealing with it. One of the anti-pregnancy arguments on “Biological Time Clock” is “I’m not well…” and it is impossible to write about Millie’s art without taking her mental and physical ill health into account, if only because so much of her art deals with it. For many years she was considered – and considered herself – to be mentally ill with Bipolar Disorder. Millie’s experiences of mental illness and the health and social care professionals with whom it brought her in contact are memorialised in “The Adventures of Spork, the Schizophrenic Skua”. As described on Millie’s site:
Millie Niss created Spork… to be a sympathetic and intelligent character who was also an indigent client of the mental health system. The cartoons began to express frustrations about how mentally ill people and welfare recipients are treated, but later on, other issues and pure silliness were added to the Spork series.
Eventually, after years of treatment for mental illness, Millie was diagnosed with Behcet’s disease, a severe disorder of the immune system which can cause depression along with ulcers, skin lesions, stomach problems and inflammation of the lungs. Before this diagnosis, however, she suffered attacks of dangerously acute depression, and one part of her website is devoted to suicide (http://www.sporkworld.org/suicide). The way in which she tackles this subject makes it clear how her sense of humour, far from demonstrating an unwillingness to confront her inner demons, was really evidence of her mental toughness and self-discipline in dealing with them – a refusal to give in to self-pity:
I was often, very often ready to kill myself, but I hate guns and wouldn’t want to use one. And lying on a gun license application was out of the question: I would not sign my name to a paper which said I was not intending to kill myself or was not mentally ill… Hanging was reputed to be painless and so we thought getting sentenced to death was the perfect out: that way you could have the benefit of dying without the guilt of doing it to yourself. It was unfortunate that you had to do something awful to get sentenced to death, though… A big question was the suicide note. Should you leave one or not, and if so what should you say in it? The argument for not leaving a note was a strong one: someone might find the note and stop you from doing it… The desire to write a suicide note that was a literary masterpiece kept me alive at times. I couldn’t kill myself until I thought of something good enough.
In these passages, Millie combines a sharp, satirical, almost gleeful insight into the ironies and self-contradictions of the suicidal mindset with an understated – but nevertheless essential and genuinely tough – conviction of her individuality and status as an artist. As she insists in “Biological Time Clock”: “I have a brain”, “I’m more than a womb”, and “I don’t want to lose my creativity”. In “Suicide”, the idea that she doesn’t want to kill herself until she can devise a sufficiently well-written suicide note is a good joke at her own expense. Still, it also points to something deeper: her writing is her way of dealing with depression and her reason for not succumbing. It gives her a sense of self-worth, and the discipline of art allows her to detach herself from her feelings and sublimate them, thereby gaining some form of control over them.
In an article entitled “Suicide, Art, and Humor”, which she published on Michael Szpakowski’s website “, Some Dancers and Musicians”, Millie wrote that “The artist has a duty, some might say, to produce art. But with that comes the more fundamental duty to stay alive.” This is a typically grounded remark: the artist’s duty to life is “more fundamental” than her duty to art. Referring to her own “Suicide” piece, she goes on: “I was at least trying to be funny… Art is a force that tends towards life… While you are writing a despairing poem, you are, in the act of writing, temporarily suspended from the act of despairing.” The effort to be funny and thereby entertain an audience, art as an affirmation of life, and art/humour as a defence against despair – all of these ideas were essential to Millie’s work.
The same values are apparent on the Sporkworld Microblog, which Millie shared with her mother, Martha Deed. They are present even in the very last days of her final illness. Here is an entry from 16th November: “We like to keep a chipper tone here, and we do not intend this to be a place to list complaints. We also insist that any personal events must be… transformed from raw anecdote into something with literary intent.” Martha actually wrote this, but Millie approved it, and it reflects a shared philosophy that runs right through the site’s contents. “Raw anecdote” is inadmissible, not only because it may lack the “chipper tone” that the Microblog seeks to maintain, but because it also lacks the discipline and detachment of real art. The word “raw” suggests something of the harshness of unfiltered experience. The artist’s job is not to pass on this harshness to the audience direct and unmediated, but to control it through an effort of will, to fit it into a composition, to comment on it, reason about it, make jokes about it and turn it into an element in discourse; and thus to humanise it.
After Millie’s death, Martha published a poem on the Microblog entitled “Travelling with H1N1”, which contains the following lines:
even if it is difficult to be funny
while intubated, you will fight and fight and fight…
you will be sending email on your way to the fluoroscope
with subject lines like
I never thought I would write email while intubated”…
The sense of humour, the refusal to give in, and the determination to fight back against her difficulties by finding something to say about them were all there until the very end. Martha relates that in the intensive care Unit (ICU), although she couldn’t speak because she was on a ventilator, she kept her lines of communication open by writing things down. She struck up a friendship with a nurse supervisor, Tom, who “was astonished at her ability to tolerate the ventilator and keep up a running conversation in her notebooks… He continued to visit her in the ICU and received her candid evaluations of her care there – both good and bad – and he found her to be very funny and brave.”

Mentioning the Sporkworld Microblog, and the fact that it was shared with Martha Deed, brings us to Millie’s frequent and long-term collaborations with her mother. Millie is known as “Spork Major” on the Microblog, while Martha is “Spork Minor”. Apart from the blog, they collaborated on many other works – Martha co-wrote the “Oulipoems” texts, for example, and “Jewel of the Erie Canal” is credited to them both. But one of the largest, most ambitious and most formally developed of their collaborations is News from Erewhon, a series of parallel surreal fictions created by the process of “guided free association”.
News from Erewhon is by no means a perfect work of art. Firstly, the title makes a rather distracting reference to Samuel Butler’s satirical, pseudo-Utopian novel “Erewhon”, which doesn’t really seem to have much to do with the rest of the book. Secondly, each chapter is accompanied by a number of images which zoom up in front of the words and then quickly fade away to allow us to read on. The Introduction argues that these add “another level” to work and that the pictures “appear only briefly to affect the viewer in an almost subliminal manner”. In fact, their main effect is to make you lose your place. Luckily, Millie provides a button which allows us to switch the images off.
Nevertheless, the texts themselves are fascinating. They were written in an almost Oulipo-like manner. Several words were picked randomly from chosen books; then, using these words as “seeds” and incorporating them into their writing as they went along, both Millie and Martha produced a series of eight “miniature fictions, situated halfway between poetry and prose”. As the Introduction says, these fictions suggest “a bizarre alternate universe, whose characters and settings evoke themes such as war and peace, the workplace, and religion. These themes… weave in and out of the texts like strands in a braid. The two authors can also be seen as separate, interacting strands.” The image of strands in a braid suggests both the closeness with which Martha and Millie were able to work together and the fact that they always retained their distinct identities and styles, and News from Erewhon is a good demonstration of this. Millie’s sections are generally longer than Martha’s and more narrative in style, whereas Martha’s tend to be more surreal and poetic. Both, however, display a constant flow of inventive wit. One of the funniest of the lot is Millie’s fourth:
The mice lived in a cream-colored bungalow under Mrs Johnson’s sink. Or so at least it seemed to them. Others less culturally attuned might have seen only some half-eaten Triscuits and the remains of a sesame bagel… “God save all the creatures who crawl under the moon, and all of their offspring,” murmured Chuck in a non-denominational invocation of the Divine. He would feel differently in the morning when he blistered his toe in the empty mousetrap from which the clever mice had stolen the cheese. “God Fuck!” he would swear into the mirror, cursing his fate as he brushed the All Bran from his teeth.
Seed-words for the passage are shown in bold. Here is an extract from Martha’s equivalent passage:
A cream-colored bungalow? How could you? It will curdle in the sun, and this is July, she said… Your invocation of natural disasters has blistered the mirror of my mind, he moaned.
Both writers, it will be noted, start by cheating: instead of introducing the “cream-colored bungalow” into their stories in a literal-minded way, they bring it in obliquely. Martha imagines a bungalow, not the colour of cream, but actually painted with cream on the outside – hence the objection that “it will curdle in the sun” – while in Millie’s story, the bungalow only exists at all in the collective imagination of a family of mice. Martha sticks more closely to an underlying structure suggested by the seed words, producing a more densely written text and poetic texture. This is particularly evident in the alliteration – “colored”, “could”, and “curdle” or “mirror”, “mind”, and “moaned”; but also in the lilting rhythm – “Your invocation of natural disasters has blistered the mirror of my mind, he moaned”. Millie, on the other hand, shows something of the novelist’s delight in incidental detail – “Triscuits”, “sesame bagel”, “under Mrs Johnson’s sink”, and “he brushed the All Bran from his teeth”. Her passage seems to take a serious turn with the phrase “God save all the creatures who crawl under the moon” – simultaneously poetic, literary and religious – yet this moment of gravity is almost immediately reversed by an explosion of comical blasphemy – “God Fuck!”
It would be too simplistic to suggest that Martha was always the more focused and disciplined partner in collaborative work. It should be remembered that Millie was the techno-savvy one, and therefore the design and construction of the Sporkworld site, the Microblog and News from Erewhon were all carried out by her. Her work in this area is always individualistic rather than textbook. Still, at the same time, it exhibits both a powerful emphasis on user-friendly functionality and a considerable visual flair. She may have presented herself as the mercurial, comical, slightly wacky half of the partnership, but there was always a sharpness, toughness, self-discipline and a determination to succeed just under the surface.

On the other hand, Millie’s work undoubtedly has an impulsive element, and in the collaborations, this makes a compelling contrast with Martha’s more studied approach. “God Fuck!” is one example; another is “Voting”, a video made in November 2008 showing Millie’s difficulties, as a disabled individual, in trying to deal with her postal vote form. Her ballot paper combines a list of presidential, senatorial, and Congress options and several constitutional issues specific to North Tonawanda, the town in which Millie and Martha live. As a result, it’s a huge sheet about the size of a tablecloth, with as many creases as an Ordnance Survey map, and just as difficult to flatten or re-fold. Step by step, Martha takes Millie through the different options on offer, with Millie keeping up a gunfire of questions and acerbic commentary, interspersed by short periods of silence during which she gasps for breath. Both Martha and Millie are represented on-screen mainly by their hands – first Martha’s, as she manipulates the ballot paper and fills it out in accordance with Millie’s instructions; then Millie’s, towards the end of the process, as she signs the outside of the envelope to authorise her vote. Apart from this, they are represented by their voices: Martha’s calm and methodical, Millie’s staccato and satirical, but both become increasingly impatient as the difficulties of dealing with the ballot paper become increasingly apparent. Ultimately, Martha can’t get it folded to fit the official envelope. Then Millie has to rehearse her signature because her hands are so afflicted with arthritis that she struggles to hold a pen. Then the envelope is difficult to sign because it’s so fat and unshapely with the ballot paper inside it. Then it turns out that the envelope will have to be taken to the Post Office and weighed because it isn’t pre-franked or freepost; at which point –
MILLIE: Okay, so we’re gonna have to pay postage on top of this… and it has to be weighed because it’s so fucking heavy!
(Slightly shocked pause.)
MARTHA (elaborately self-restrained): Did you mean to put the word “effing” in?
MILLIE (immediately): I did! I absolutely did! I mean, it’s a matter of free speech. The Supreme Court would have upheld my right to say fucking on my own blog. There have been efforts to make it impossible to say that.
MARTHA (holding up the envelope, with a noticeable change of subject): Okay, I think we actually have it done.
It’s a wonderful piece of film-making. Whether or not you agree with what Millie seems to be hinting, that there is a deliberate attempt on the part of the establishment in the USA to discourage people at the margins of society from taking part in the democratic process, or whether you prefer the view that bureaucrats have no conception of the difficulties faced by the people on the receiving end of their bureaucracy; the point that the postal ballot, which is supposed to make it easier for disabled people to vote, actually makes it almost intolerably difficult, has been well and truly established by the end. But the real strength of the video lies partly in the interplay between the two main characters and partly in the underlying theme of Millie’s disability and how they handle it. As with Millie’s work, her illness is central to the meaning of the piece, yet it isn’t about the experience of being ill. It’s about how illness changes your relationship with the rest of society – one of her most powerful themes. But it’s also about coping with that situation through the help of others – in this case, Martha – and through a supreme effort of will.
Much of the poignancy of the piece lies in the soundtrack: Millie gasping for breath on the one hand and Millie rattling off her machine-gun-like commentary on the other. You can’t ignore how ill she is and doesn’t ignore it herself, but she won’t let it shut her up. The video is a gradual crescendo of comedic impatience, culminating in the obscenities at the end. Her outspokenness is a refusal to be silenced by society and the universe, which has trapped her spirit inside such an inappropriate body. She overcomes her difficulties by externalising them. She makes them the subject of her art, and by doing so, she finds her voice.
No doubt Millie would have become an artist of some description, whatever body, circumstances and state of health she was born into. She was sufficiently remarkable for that. But without her ill health, the work she left behind would have been very different: less spiky, poignant, funny and perhaps less urgent. Her output is not defined or limited by her health, but her health gave her her most important themes and powerful moments. The supreme irony of her art is that, like the knotty grain of a piece of burr elm, the things that made her imperfect were the same things that made her unique and beautiful.
©Edward Picot, December 2009
We Feel Fine: An Almanac of Human Emotion
Jonathan Harris and Sep Kamvar
Scribner Book Company, December 2009
ISBN 1439116830
Featured image: We Feel Fine project poster
“We Feel Fine – An Almanac Of Human Emotion” is a hardback book that in just under 300 pages of well designed montages, data visualisations, diagrams, illustrations and text presents and analyses the data gathered by the We Feel Fine project. Started in 2005 and launched in early 2006 by Jonathan Harris and Sep Kamvar, We Feel Fine is based around a database assembled using a webcrawler that searches the blogosphere for statements of the form “I feel” or “I feel like”. Any matches are stored along with as much contextual data as the webcrawler can find (a photograph nearby in the blog post, the poster’s age, gender, and location, local weather). The database contained twelve million such entries by the time the book was published.
Sections of the book categorise statements of feelings by age, gender, the location of the poster, and subject of the statement. Individual statements are presented superimposed over images found in the same blog post. The photographs presented with their accompanying expressions of emotion have a high-contrast, shallow depth of field, and highly focused look that resembles Lomography. But this is a product of the presentation of photographs on the web rather than an hipsterly ironic invocation of the contingent aesthetics of mass photography. The images are for the most part JPEGs, and show the contrast, mach banding and visual noise of that technology.
The montages of “I feel…” statements in a standard format superimposed over an image found in the same blog post serve to provide a (sometimes incongruous) context for the statements that the project is based on. They resemble Gillian Wearing’s “Signs that say what you want them to say and not Signs that say what someone else wants you to say” 1992-3 featured photographs of people holding up placards on which the artist had asked them to write down what was on their mind. Going back further into the history of art, the montages and in a novel way particularly the data visualisations and graphs bear comparison to Vermeer’s seventeenth Century paintings of bourgeois social relations and reverie. Both “Girl reading a Letter at an Open Window” and “We Feel Fine” present social class, social self-presentation, advanced communication technology and consideration of the thoughts of others in a medium and way that epitomises the way people see things in that era.

The book’s volume of data and graphics quantifying social phenomena might resemble a “state of the blogosphere” corporate social media report in some ways, but its presentation directs attention back to the emotions featured rather than trying to tie them to any corporate or governmental agenda. This is a book by, about and for individuals in contemporary mediatised society. I found reading it became quite overwhelming sometimes once I had adjusted to its presentation.
Dictionary definitions, statistical breakdowns of the kinds of words, ages and genders of bloggers and other demographic and affective data are presented in compact graphic form on every page, and larger charts show more general conclusions. Feelings, or the words used to refer to them, are shown to vary between genders and as people age. This is an exemplary application of Edward Tufte’s science of the graphical presentation of information. They even have sparklines. But that science is applied to data that is at its heart qualitative rather than quantitative.
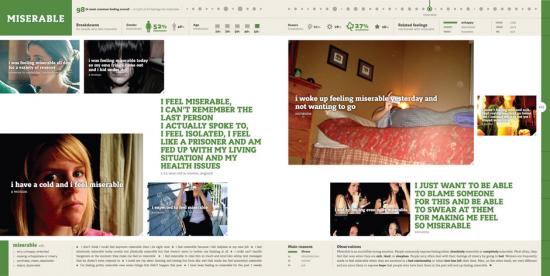
Such “data visualization” was a hot trend in 2009. Visualisations of crime rates, corruption, climate change and other issues can be produced using such data, and have become an important weapon in the arsenal of visual persuasion. On the We Feel Fine web site, feeling data is mapped to coloured blobs in an interactive user interface to the constantly updated (every minute) database. In the book, feelings and demographic information are processed to produce graphics that represent the prevalence of feelings over time, between genders, in different locations and in relation to each other. But as visual persuasion this is directed back to the vividness of human, qualitative experience rather than a more political or economic agenda.
“Sentiment analysis” was also hot trend in social media marketing in 2009 and its limitations quickly became apparent. Current systems simply cannot handle irony, sarcasm, regional differences in the usage of words and in many cases even simple negation. The We Feel Fine system is an exercise in gathering affective or sentiment data to visualise, but it avoids the pitfalls of sentiment analysis by automating only the gathering of the statements of emotion themselves, not analysis of how they relate to what they refer to. This is a classic example of well-chosen limits strengthening a project.
The problem of the relationship between qualitative (how you feel) and quantitative (how many people feel what you feel) data and how to deal with this in a non-voodoo way are avoided in We Feel Fine because of this.
Another 2009 hot trend was “big data”, the assembling of datasets that vary from many megabytes to many gigabytes in size. Datasets from regional and national governments, scientific research and freedom of information requests can be used in “data mining” to search for facts among the numbers. The We Feel Fine system is a good example of a big data dataset (and API, application programming interface, for accessing that data over the web). Unlike global temperature data it neither offers the possibility of objective accuracy nor involves any great risk if it lacks it. But it does reintroduce the human subjectivity that big data threatens to replace with numbers.
The striking thing about this is that although the We Feel Fine book is very much of the zeitgeist for 2009 the web-based system it presents started five years ago in 2005. At that time blogs were regarded by the mass media as disposable, narcissistic and somehow inauthentic. They were an unlikely subject at that time for art concerned with the authentic expression of emotion. We Feel Fine’s history, subject and results therefore both prefigure and go beyond the current state of the art in Internet social and corporate culture.
Harris and Kamvar are admirably candid in laying out the history, methodology, technology and in the case of the book’s production even the finances of their project. The code listings included in the book are tantalising glimpses into how the We Feel Fine server works, allowing a rare chance for students and artists to study such a system, and are licenced under the GPLv3. The book is under the obscure but principled Creative Commons “Founders Copyright” licence which will automatically expire the copyright on the book in twenty years time. This is all invaluable for critique and study of the project by artists, academics and anyone with an interest in art and technology, and more artists should do it.
In the FAQ and other essays contained in the book Harris and Kamvar are open about the methodological strengths and weaknesses of the We Feel Fine system. They acknowledge the limitations and demographics inherent in profiling bloggers (who are younger, wealthier and more technologically savvy than is usual). They also make a convincing case for the very real conceptual strengths of the project, discussing how the system holds up as science and statistics. And the project itself is overwhelming as an aesthetic and, strangely, somehow as a social experience.
Even if we don’t deny or question the existence or status of emotions for ideological reasons, do we know what we really feel? And even if we do know what we really feel can we really express it in a way that will be understood by others? We Feel Fine doesn’t address these questions. They are outside of its scope. Its acceptance of sentiment at face value and its mechanical (re-)production of representations of sentiment might look like the hallmarks of kitsch. But that would deny the subjectivity of the original authors of the expressions of sentiment that We Feel Fine processes. And a progressive art needs to represent the masses, not merely rulers and pop stars. Not everyone will be feeling ironic or critical on any given day. Given this, the transparency, scale and effectiveness of We Feel Fine mean that ideological objections to big data, to emotional taxonomies, or to the very idea of emotion face a problem in the project’s aesthetic and affective success rather than vice versa.
Some of the stories found while researching the posts and presented in the book are heartbreaking or uplifting, but the statistical nature of the project makes these outliers – they are rare events and can be identified as such. What comes through from page after page of casual statements of feeling is an impression of the range of human experience, or at least the range of human expression. If you can adjust to the montage format and the diagrams then the book can inspire sympathy, pity, and joy for your fellow human beings.
The book ends by considering the philosophical and spiritual meaning of feelings, how they affect our lives, and what we can do about this. The data gathered to back up this consideration makes the conclusions both persuasive (this is a paradigmatic representation of humanity) and surprising (that would be telling).
We Feel Fine faces up to the challenge of making Internet art that realistically deals with the scale of the contemporary web. It does this by tackling the millions of daily new entries in the blogosphere but crucially it retains a focus on qualitative, subjective human experience. In its engagement with multiple levels and kinds of representation, from emotional taxonomies and statistical methods to digital photography, weblogs, and data visualisation, it shows just how broad are the range of systems and modes of depiction that artists can and possibly must deal with today. And it’s a project that simply wouldn’t exist if the people who made it couldn’t code.
We Feel Fine is a persuasive and insightful portrait of the individuals that make up the blogosphere. It can be overwhelming in terms of the amount of information and in terms of the volume and strength of emotion presented, but that is part of what makes it vivid. It is a paradigmatic, realistic and persuasive depiction of the qualitative experience of individuals within networked information society.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
“Mapping CCTV around Whitehall”, 2008, is, as its name implies, a performance of mapping Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) security cameras around the UK’s parliament in London and a video record of that performance by Ambient.tv’s Manu Luksch.
Starting with a HAL 9000-like image of a CCTV lens, the video of “Mapping CCTV In Whitehall” has a glitchy techno aesthetic of sound and images with a post-MTV-Style Guide reportage feel. The first half consists of a recording of the police stop-and-search interviewing Luksch under anti-terrorism legislation, with a map of the area superimposed. The second half consists of CCTV views of the range of Camera number 40 being taped out, and of the people caught within those bounds. Words flash on the screen to identify the subjects of CCTV (….Artists! Sexy Arses!). This redeployment of the language of mass media visual persuasion opens up what we see rather than closing it down, making it a very effective encapsulation of the project’s ideas and aesthetics.
(One tiny criticism is that the video ends with a Creative Commons logo but doesn’t specify the licence. Artists, please at least give the licence URL, and do choose the copyleft BY-SA licence if you can…)
Wandering around to locate CCTV cameras may seem like a cosy techno-fetishist performance, a post-cyberpunk flaneur’s stroll around the streets of London with a pencil, an A-Z, and a tri-field meter. But the creeping authoritarianism of still-Thatcherite Britain makes it an act of protest against a specific law and a reversal of the assumptions of our seemingly unstoppable surveillance culture.
The Serious and Organized Crime and Police Act of 2005 criminalized political expression within an exclusion zone for a kilometre around Parliament Square. It is an indicator of the authoritarianism and assumption of privilege that has come to define political culture in the UK. It is too easy to become cynical in the face of such brazenly opportunistic ideology. If art can help to defamiliarise this in a playful and aesthetically rewarding way then it can help to undo that cynicism, and even more to go beyond it.
The assumption that the State needs to know where you are at all times, just in case you are a terrorist or a paedophile, but that you must not know the workings of the State, just in case you are a terrorist or a paedophile, is at odds with the idea of an open society. The area of London that Luksch has mapped is the SOCPA exclusion zone. A map of CCTV cameras is clearly useful to terrorists, and a map of the CCTV cameras near Parliament is clearly an act of dissent against the political consensus that constitutes domestic extremism. The police who interview Luksch touch on these ideas.
A political elite that is fearful both of and for its polity has retreated into managerial, authoritarian, paternalistic risk-management. That polity is conceived of, post-cold-war, not even economically, more nihilistically. This produces the very loss of freedom that it claims to protect against. The paradigm of government has become the watchful parent who is seen to be good by their watchful neighbours because they prevent their child ever straying into danger. But it is impossible to protect the population against all risk and this knowledge leads to impotent fearfulness. “Something must be done” and so security theatre, the spectacle of impossible systems and behaviours designed to reduce the perception of risk to zero, is used to reassure. Although whether the populace or the politicians are meant to be reassured it is hard to tell.
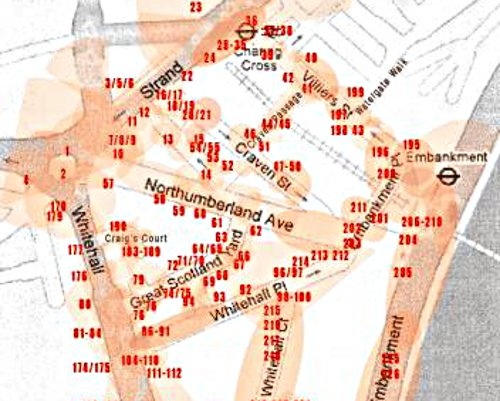
CCTV is part of that reassurance, of the spectacle of security theatre. The UK has the highest density of Closed Circuit Television Cameras (CCTV) in the world. The average Briton is (allegedly) captured on CCTV 300 times a day and there are more cameras in the supposedly open society of the UK than in notionally communist China. Not per head, in total. The area that “Mapping CCTV around Whitehall” focusses on is ground zero for this tendency.
CCTV doesn’t solve crime, it is used to spy on legal protest and it has been placed in school classrooms and pubs.
CCTV recordings are subject to the Data Protection Act, and from 2002-2008 Manu Luksch used personal data requests under the act to obtain the CCTV recordings of her going about her business that she used to make the film “Faceless”. The videos usually had other people’s faces blotted out to protect their privacy, which gave the resulting film its science fiction plot of people starting to lose their faces. But as Luksch was making “Faceless”, the responses to her personal data requests became rarer as the authorities adjusted the balance of power back in favour of themselves.
In 2008, Luksch returned to the subject of CCTV with “Mapping CCTV around Whitehall”, this time mapping out the CCTV cameras themselves within a particular area of London over two days. On the first day she located hundreds of CCTV cameras, on the second she measured the range of the wireless broadcasts of one of them. Part performance, part land art, this has a number of artistic precedents, from the 1960s conceptual artworks that consisted of magnetic fields or patterns of heat, to Situationists strategies for recontextualising the city by navigating it using the wrong map.

Mapping unseen electromagnetic forms was a strategy of some Conceptual Art, whether Art & Language’s landscape art infrared photograph of buried hotwires under a field or gallery-based magnetic and radio-proximity devices. Contemporary artists have used RFID tags Intangible form is irresistible for post-Duchampian attempts to keep the philosophy of art about aesthetics, and for conceptualism it is a way of keeping the artwork open. But the range of a CCTV camera is both definite and, if you have access to the camera, visual. The unseen form of the limits of its observation and the transmission of what it sees tie form to power quite directly.
In “Mapping CCTV around Whitehall” these forms and their composition are part of the landscape of the city. The city is obviously an artificial environment. In contrast, nothing might seem more natural than a painting of the landscape of the countryside. But landscape painting are depictions of valuable property for the landed gentry who commissioned them. They show and by showing make real the products of the ideology of the ruling class using aesthetics. They extend the domain of taste, a novel and socio-economically exclusionary concept, to the presentation of nature as property. They are as artificial, as culturally determined and laden, as cityscapes.

The successor to landscape painting is the “land art” of the 1960s and 1970s with its photographs of walks, mud and stones. Viewed cynically, the ‘land art’ of the 1970s is less about one man’s journey through nature than it is about cheap transport and expensive large-format cameras. It is a predecessor of the logistics art of Relationalism. The Romanticism that it shares with landscape painting is for its audience, not its commissioners. As with much art, those are two separate constituencies.
Art creates visual order and visual form for the unseen ideological order and form of the ruling class. Religious icons, jet-age land art and neoliberal Relationalism all serve this function. Critical art also depicts this ideological order, ideological form, aesthetically but to make it strange and criticise its production or content rather than to promote and naturalise it.
The Situationists treated Natopolitan 1950s Paris as a landscape to be made strange through art in order to critique the ideologies that sought to capture its population. Wandering its streets using the wrong maps was a way of challenging the authority embedded in its layout by the old regime and the new order that sought to impose its own new way of looking at things. Creating rather than using a map again re-arranges an equation, not just the equation of ‘derive’ but of the mass-media mass-politics spectacle that the Situationists were so opposed to. CCTV cameras may not seem like generators of spectacle, but their footage is used to sensationalise media reports of crime and terrorism, and their presence and visibility enforces the message that we are all part of an observed spectacle.

Radical land art sounds oxymoronic. But the aesthetics projected onto a landscape can be used as links to the ideology flattered by those aesthetics. And re-arranging the terms of land art can critique that ideology, or at least expose it to critique. “Mapping CCTV around Whitehall” re-arranges the equation of land art to make art of travelling to cameras in order to map the landscape they observe. This is a kind of critical, urban, reverse land art.
George Orwell’s vision of a mediatised totalitarian society from his novel “1984” is often used as a reference point for Britain’s surveillance culture. But this can obscure as much as it illuminates. Bringing out the true, novel, problems with CCTV surveillance as the default solution to the ruling class’s perception of society’s ills is an urgent and difficult task. As CCTV is a matter of the production and control of images, it is an area that art can usefully comment on. “Mapping CCTV around Whitehall” uses the status of art to represent the dark heart of surveillance ideology. Look upon its works…
http://ambienttv.net/content/?q=mappingcctv
Public screenings include ‘Films by Manu Luksch’ at Cinema2, Centre Pompidou (2009)
Betting on Shorts (2009)
http://ambienttv.net/content/www.bettingonshorts.com
NHK Japan (Japanese National Television, 2008), LIFT (2008)
Watch the video (160 sec, mp4) online at low-res.org
http://lo-res.org/~manu/MAPPINGCCTV.mp4
Or on Vimeo
http://www.vimeo.com/3802118
Featured image: abstract animated visual models working from the audio samples of couples engaging in sexual activities.
Frequency Love is a net art piece, not in the networked sense but conceptually filled to the brim with a net consciousness, a net object. This visual deviation playfully captures the dark side of the Internet and its globally collective and obsessive mannerist activities. It reveals a psychological nuance of the everyday Internet sexual experience.
The source material were originally sound files – mp3’s, consisting of couples copulating. Amateurs submitting and declaring their intimately entwined, feral and visceral exertions for other interested parties to hear and enjoy online. Chris Webb abstracted the audio, the data and transformed them into what now are animated gif images of couples having sex.
There is a contradiction at play built by circumstance, that such esoteric interests of sharing intimate, sexual sound files in virtual private clubs do tend to exude. The inevitable occurs. If the multitude of surfers, search hard enough on the net, they collect hidden information by hook or crook somehow; which is part of the nature of using the Internet medium.
When viewing these works it is as though they are breathing, as if they are real souls, real people, even though you know that they are invented visuals, data into sound. Then you remember that they were real people, but mutated into visual form. The ‘Plexus’, culmination of networked, linked individuals expressing proclivity and what seems an uncontrollable hunger to communicate in a way other than by words, via the motion of sexual intercourse in audio format. There has been a global shift of people exploring new territories regarding their own relational selves. The term virtual is essence of the Internet medium and we used to think that this word stood for the unreal, untouchable but now we know that this is no longer applicable. It is now part of our everyday experience, therefore real.