



Introduction:
As media attention wanes, the impact of British Petroleum’s Deep Horizon, off-shore drilling disaster continues to unfold. Artists worldwide respond to this new ecological catastrophe in a group show organized by Transnational Temps, an arts collective exploring the interstices of art, ecology and technology. For Andy Deck, one of the founding members of Transnational Temps and the curator of the show, “After a decidedly unsuccessful round of climate negotiations in Copenhagen, the disaster in the Gulf of Mexico frames this exhibition of Earth Art for the 21st Century.”
Now hidden from view by BP’s media campaigns and other de facto censoring actions, the images of oil-covered birds struggling to breathe and fly, oil and dispersant-coated fish, dolphins and whales washing up dead while most sink to the ocean floor, have all but vanished. Partially filling the void are the artists showing here who are recreating topographies: mapping the course of a deadly shadow over our shores and waters; and reinterpreting the sea, its rising levels and largesse, before the vicissitudes of man and nature. Transnational Temps.
———-
Spill >> Forward by Transnational Temps describes itself as an Online Exhibition. It is a website containing images and other media on the theme of oil spills. Some of the images were shown at the MediaNoche gallery from July 30th – November 19th, 2010, with works added or removed so it isn’t just an online catalogue of a meatspace show.
The front page of the site warns that you’ll need a browser that supports HTML5 video and audio, and states that you can view it using patent-free media codecs. From a Free Software and Free Culture point of view this is excellent, your ability to view the art is not restricted by anyone else’s technological or legal machinations. This is also good from an artistic point of view. The software used to view the art can be run and maintained by anyone, making it more accessible, exhibitable and archivable. But this freedom doesn’t extend into the work itself. some of the art uses proprietary software, and none is under a free Creative Commons licence.
The image on the front page, or possibly the image exhibited at the entrance to the exhibition, is not advanced HTML5 video or canvas tag animation but an animated GIF. A Muybridge-ish series of still images of a pelican in flight flickers rapidly up and down as it descends behind an iridescent oil slick that solarizes the bottom half of the image. It’s an effective image in itself, a visually and net.art-historically literate statement that also serves to set the stage for the rest of the show.

This is clearly a politically motivated exhibition, with the theme of the exhibited art centred on a specific historical event (the Deepwater Horizon disaster). Oil spill and petrol station imagery dominates . The resulting art varies from cooly ironic asethetics (Ubermorgen), photo and video journalism (Guillermo Hermosilla Cruzat, S.Slavick & Andrew E.Johnson, Chris Dascher, Adrian Madrid), agitprop (Eric Benson, Geoffrey Michael Krawczyk, Alyce Santoro, Russ Ritell, Terri Garland, Patrick Mathieu), photography(Jessica Eik, Sabina Anton Cardenal), painting(Jessie Mann), collage(Ume Remembers), performance art(Graham Bell), interactive multimedia (Gavin Baily, Tom Corby, Jonathan Mackenzie, Chris Basmajian, Matusa Barros, Mark Cooley), augmented reality (Mark Skwarek and Joseph Hocking) and drawing (Cristine Osuna Migueles, Adrienne Klein, Jesus Andres, Sereal Designers) to video and audio art (Irad Lee, Luke Munn, Gene Gort, Tim Geers, Gratuitous Art Films, Alex George, Collette Broeders, Fred Adam and Veronica Perales, Virginia Gonzalez, Henry Gwiazda, Maria-Gracia Donoso, Jeremy Newman).

This is a lot to take in but the diversity of the work is a strength rather than a weakness, building a broad and visceral response to the Deepwater disaster. Verbal responses to the disaster from politicians seem unconvincingly nationalistic and corporate in comparison. It might seem hypocritical for artists to criticise the source of the energy that feeds us and allows us to make new media art. But we are trapped in that system, and we must be free to criticise it.
Politically inspired artworks have a difficult history, tending to be either bad politics or bad art. The art in Spill >> Forward is excellent, though. Some has a more direct message than others. Again the diversity of the exhibition plays a positive role here. The immediacy of the agitprop images doesn’t need art historical baggage to be effective, but that immediacy provides a social context for the more contemplative or abstract works. The more contemplative or abstract works don’t hammer home a simple political message but they provide an aesthetic context for the more direct images. They work very well together.


Some of the pieces in the show are clearly illustrations or recordings of work, some are electronic media that can be played on a computer, some are clearly designed to be experienced specifically through a computer system. If you removed the political theme of the show it would still be a visually (and audially) and conceptually rich cross-section of contemporary art. I was going to write “digital art” there but the show includes painting, drawing, performance, and other analogue or offline media recorded digitally for presentation online. The celestial jukebox is hungry.
If I had to pick out just a few pieces from the show I’d say that I was struck by the sounds of Luke Munn’s Deepwater Suite, by the visuals of Ubermorgen’s DEEPHORIZON, by the monochrome images and text of Terri Garland’s photography, by the video mash-up of Colette Broeders’ Breathe and by the critical camp of Graham Bell’s Radical Ecology. I think my favourite is Mark Skwarek and Joseph Hocking’s “The Leak in Your Home Town”, an iPhone app that uses the BP logo as an Augmented Reality marker to super-impose a 3D animation of the Deepwater leak over live video of your local BP petrol station. It is art that could only be made now, technologically, aesthetically and socially.
The aesthetic and conceptual competence of the artistic responses to the environmental and human crises of the oil spills in Spill >> Forward make the case for art still being a relevant and capable answer to society’s need to make sense of unfolding events. Art can still provide a much-needed space for reflection, and Spill >> Forward creates just such a space in a very contemporary way.
The text of this review is licenced under the Creative Commons BY-SA 3.0 Licence.
From September 2008 – June 2010, Ellie Harrison undertook a Leverhulme Scholarship on the Master of Fine Art programme at Glasgow School of Art. The thesis published below forms one of the major outcomes of her research during this period. This is part one of four.
The thesis published below forms one of the major outcomes of her research during this period and builds on two earlier essays How Can We Continue Making Art? – which questions whether there is a place for art in a world which is fast approaching environmental catastrophe, and Altermoderism: The Age of Stupid – which uses Nicolas Bourriaud’s Altermodern exhibition at Tate Britain in 2009 as a paradigm for exploring the art world institution’s lack of acknowledgement and action over climate change.
Trajectories: How to Reconcile the Careerist Mentality with Our Impending Doom addresses the ethical implications of continuing to choose the career of artist in the twenty-first century. It is a manifesto of sorts, written from the personal perspective of a young UK-based artist looking to identify worthwhile reasons for continuing down this ‘self-interested’ path, given that the future we are likely to face as a result of climate change, is so different from how we dreamt our careers might pan out whilst growing up under Thatcher and New Labour. It explores how we should aim to evolve our roles as artists, in light of this, and what form a new ‘reconciled practice’ might take.
The graph below shows the projected average global temperature increase over the forthcoming century if we remain on our current trajectory of economic growth and population increase (peaking at 9 billion in 2050), but also incorporate new efficient technologies, a convergent world income and a balanced emphasis on energy sources. This is known as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s ‘scenario A1B’ (IPCC 2001).
The graph is extracted from the official AVOID response to the United Nations Climate Change Summit in Copenhagen in December 2009 published on 26 March 2010. AVOID is a United Kingdom governmental research programme led by the Met Office with the aim of averting dangerous climate change (AVOID 2010).

Looking back, 1979 now emerges as a pivotal year in the recent history of our species. On 6 October this year the US central bank, the Federal Reserve, increased interest rates by 20 points (Fisher 2009, p.33). This act, which on paper appears of little significance, opened the gates to a whole new breed of free-market capitalism which, as a result of reduced regulation, would spread its way all over the globe. It signified the switch between Fordism and post-Fordism as the predominant economic system of production; from the ‘disciplinary societies’ of late modernism characterised by Foucault, to the ‘control societies’ which constitute our present reality (Deleuze 1990). It was the beginning of a carefully choreographed and intricately planned neoliberal project, which would serve the “restoration or reconstitution of naked class power” (Harvey 2007, p.119) to an economic elite; radically transforming the way in which all our lives would operate in its wake. Our attitudes towards work, politics, society; our relationships to one another, even the internal structuring of our own minds, would never be the same again.
It is no coincidence that it was on 4 May 1979 that Margaret Thatcher came to power in the United Kingdom; she was, of course, instrumental in overseeing this ‘revolution’. What is coincidental however is that it was also in 1979, on 11 March to be precise, that my own life began its trajectory. The rapidly changing society into which I was born would not only prove fundamental in shaping the artist I would become, but it would also prove key in determining the ‘mentality’ with which I would come to visualise my future: to plan my career.
‘Thatcher’s children’ as my generation are known, were indoctrinated to believe that the world owed us a living (Blackburn 2009). “Success”, she said, was “a mixture of having a flair for the thing that you are doing; knowing that it is not enough, that you have got to have hard work and a certain sense of purpose”. It was simply a question of making the right career choice. If we aimed for the top, we had just as much chance of getting there as anyone else. All we had to do was look out for number one. The secret, she taught us, was to have a strategy – to “plan your work for today and every day, then work your plan” (M. Thatcher n.d.); to think about what we wanted our lives to be like in the future and then to work flat-out towards that ‘goal’.
In hindsight, it now seems inevitable that my life took the course it did. Entering art school for the first time in 1997 – the year the seminal Sensation exhibition at the Royal Academy of Arts took place – we could see ‘success’ being played out before our very eyes. A group of Young British Artists (YBAs), just one generation older, were now ‘living the dream’. As 18-year-old students, we were now able to visualise the paths we wanted our own lives to take and to see exactly where we aimed to find our fortune. Like most of my art school peers, I was from an “above average social background” – raised in suburbia by a middle class family of teachers. And, as Hans Abbing notes, this added “social capital” gave me the “flair, self-assurance, and… sense of audacity” (Abbing 2002, p.95) which now seemed so essential to commodify and sell myself – to keep going, regardless of failure and rejection, with eyes firmly fixed on the prize.
My career trajectory led me blinkered along a familiar path – a BA (Hons) degree in Fine Art from Nottingham Trent University; a Postgraduate Diploma in Fine Art from Goldsmiths College (where nearly all my YBA role models had been before me). It was as though every incremental step took me ever closer towards my ‘goal’: towards ‘success’. Finally, I won a scholarship to study on the Master of Fine Art (MFA) programme at The Glasgow School of Art; yet another prestigious art school to add to my expanding curriculum vitae. What I hadn’t banked on, however, was that on the very same day I was heading north up the M1 to Glasgow to begin this new stage in my life, the global economic order was fast collapsing around us into its own new distinct epoch, taking with it the belief systems which had been carefully constructed around it over the past 29 years.
On 15 September 2008 the investment bank Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. filed for the biggest bankruptcy in US history with more than $600 billion of debt (Mamudi 2008). Over the course of the next year a slew of bailouts took place all over the world to prevent other banks going under. The neoliberal project had, “in every sense, been discredited” (Fisher 2009, p.78). The ideology on which, knowingly or not, my own life’s trajectory had been modelled was now on the ‘scrapheap’. And, as Mark Fisher suggests, a bleak, empty and relentless state known as ‘capitalist realism’ – in which nobody could believe, but equally nobody could stop – crept in from every corner to fill the void.
Society, it seemed, had reached a hiatus; a ground zero amid a sea of “ideological rubble” (Fisher 2009, p.78). Lots of suggestions emerged about what had gone wrong, lots of questions about where we should go next. From the privilege of my funded MFA place, I was able to enter into my own period of self-reflection about the path I had so blindly been following. Was the vision I upheld of my life in the future essentially a delusion, based on a now defunct model of ‘success’ from the past? Was I suffering from the “self-deceit” (Abbing 2002, p.114) Hans Abbing diagnoses to be prevalent in young artists, coupled with the complete “disavowal” (Fisher 2009, p.13) of the negative side-effects of my complicity in the system of capital? With a sudden and overwhelming urgency it felt essential that I question how I could begin to reconcile my career choice and the entrepreneurial methodology (Abbing 2002, p.96) with which I was pursuing it, with the harsh realities that both science, and now science fiction, are predicting the future actually holds in store…
Films such as The Road (Hillcoat 2009) offer us a very different picture of the forthcoming century. In this barely hospitable, yet eerily recognisable version of our present world there is no Turner Prize, no Frieze magazine to be reviewed in; no canon to become part of. In fact, there is no scope for the non-essential; no room for aesthetics; no space for art at all. Whereas it now appears clear that the trajectory I had planned for my life since art school is constituted by fantasy, the trajectory which befalls the lives of the protagonists of this particular post-apocalyptic vision is in part based on what the current overwhelming scientific evidence points towards.

The United Nations Climate Change Summit which took place in Copenhagen in December 2009 offered what many scientists and campaigners referred to as our ‘last chance’ of averting global catastrophe within the coming century. Prior to the talks the 10:10 Campaign’s ‘call to arms’ statement outlined what sort of trans-governmental worldwide commitment it would be necessary to achieve:
“The best deal currently on the table is that from the EU, which calls for a 30% reduction [in greenhouse gas emissions] by 2020 (compared to 1990 levels). If this deal were to be accepted (which is a very big if, given that Japan argues for 8%, Australia for 5% and America for between 0%-6%) and if the emission cuts were then carried out (which is an even bigger if), this would give us about a 50/50 chance of not hitting the dreaded two degrees. Two degrees is where we trigger runaway climate change [emphasis added]: two leads to three, three to four, four to five, five to six… by which time it’s about over for life on Earth.” (Armstrong 2009b)
Given that Copenhagen was by all accounts a complete failure and that, in fact, not even the least significant of the ‘deals’ presented was agreed upon and signed off, the balance now appears to be swaying decisively towards the latter of these two potential trajectories. We find ourselves “trapped inside a runaway narrative, headed for the worst kind of encounter with reality” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.11). Unless it is fully acknowledged and hastily acted upon in consensus across the globe, climate change “threatens to render all human projects irrelevant” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.6). It appears that it is not just the future of our careers we should be worried about but now, more likely, the fundamental ability of our species to survive on the planet.
The concern of this essay is to uncover exactly how we could have arrived at a situation where these two distinct visions of our future can so wildly diverge – to explore the factors which have allowed our careerism to persist, in light of advice to the contrary. The aim is to illuminate the significance of this ‘now or never’ moment in the history of our species as an opportunity for radical change, and to develop a ‘plan of action’ and a ‘new moral code’ which may help us, as artists, determine what role we can and should play in the reality of the twenty-first century.
To read Part 2 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-24
——-
References:
Armstrong, F., 2009b. What is 10:10? 10:10 Campaign website. Available at: www.1010uk.org/1010/what_is_1010/arms [Accessed April 10, 2010].
Abbing, H., 2002. Why Are Artists Poor?: The Exceptional Economy of the Arts, Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
AVOID, 2010. Will the Copenhagen Accord avoid more than 2°C of global warming? AVOID website. Available at: ensembles-eu.metoffice.com/avoid [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Blackburn, S., 2009. Do we need a new morality for the 21st century? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/nov/02/cambridge-festival-of-ideas.
Deleuze, G., 1990. Society of Control. L’Autre Journal, (1). Available at: www.nadir.org/nadir/archiv/netzkritik/societyofcontrol.html.
Fisher, M., 2009. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative?, Ropley, Hampshire: 0 Books.
Harvey, D., 2007. A Brief History of Neoliberalism, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Hillcoat, J., 2009. The Road, Dimension Films.
IPCC, 2001. Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. GRID-Arendal website. Available at: www.grida.no/publications/other/ipcc%5Fsr/?src=/climate/ipcc/emission [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Kingsnorth, P. & Hine, D., 2009. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. Available at: www.dark-mountain.net/about-2/the-manifesto.
Mamudi, S., 2008. Lehman folds with record $613 billion debt. MarketWatch website. Available at: www.marketwatch.com/story/lehman-folds-with-record-613-billion-debt?siteid=rss [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Thatcher, M., Margaret Thatcher Quotes. About.com website. Available at: womenshistory.about.com/od/quotes/a/m_thatcher.htm [Accessed May 2, 2010].
To read Part 1 of this article visit this link:
http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-24
What is curious about the neoliberal project that kick-started in the year of my birth, is that, from the politics of the preceding decade, it appeared history could have taken a very different course. 1972 marked the publication of The Limits to Growth – a study commissioned by the humanitarian think-tank the Club of Rome to estimate the planet’s reserves of natural resources, “including topsoil, fresh water, minerals, forests and oceans” – questioning for the first time what might be the consequences of “another 100 years of exponential growth” (M. Fowkes & R. Fowkes 2009, p.670). The findings of the study were so significant that they are cited by Maja and Reuben Fowkes as a revelation for the future of humanity on a par with Copernicus’s discovery of Heliocentrism: putting our lives on planet earth sharply into perspective. Essentially the report gave us all the information we needed to know: that the way of life modernity had accustomed us to, was not sustainable. The whole system on which our modern liberal democracies were structured was supported by a myth of continual and infinite progress (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.3) and a universal belief that the future will always be better than the past – that it is always within our capable hands to control our destinies.
Rather than take heed of this advice and look for alternative ways of structuring our societies, what actually began towards the end of the seventies, continuing right up to the present day, was the opposite: a complete and utter acceleration of our production and consumption. Post- The Limits to Growth our lives were allowed to continue in a fashion now no longer based on scientific facts, but on fantasy:
“What this… illustrates is the fantasy structure on which capitalist realism depends: a presupposition that resources are infinite, that the earth itself is merely a husk which capital can at a certain point slough off like a used skin, and that any problem can be solved by the market… The relationship between capitalism an eco-disaster is neither coincidental nor accidental: capital’s ‘need of a constantly expanding market’, its ‘growth fetish’, mean that capitalism is by its very nature opposed to any notion of sustainability.” (Fisher 2009, pp.18-9)
We were allowed to continue because we repressed this truth. Our ‘denial’ was constituted by what Freud described as our inability to hear the things which did not fit easily with the way we envisaged ourselves in the world (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.9). We simply blocked out any hint of a hitch or obstacle to our career trajectories and carried-on regardless. Neoliberalism achieved this ‘state of mind’ purposefully – by pacifying us with the things we thought we wanted, that would make us happy, whilst removing the possibility for resistance. The “drive towards atomistic individualisation” (Fisher 2009, p.37) captured in Margaret Thatcher’s dictum “There is no such thing as Society. There are individual men and women” (M. Thatcher n.d.), plunged us further into our internal solipsistic worlds; from where it became almost impossible to fully empathise with others, to acknowledge the wider consequences of our actions, to see beyond the fantasy – to believe that ‘an alternative’ might be possible. We lost our political ‘agency’ as our liberal democracies became governments-as-administration (Zizek 2009b); appealing to our burgeoning “individual ideals” (Strawson 2008) – to “short-termism” (Brown 2009) – rather than the bigger picture and a realistic long-term plan.
In his recent book First as Tragedy, Then as Farce, Slavoj Zizek describes the strategies the neoliberal policy makers employed to continue to maintain this state of denial well into the twenty-first century, explaining how the negative side effects of the bursting of the dotcom bubble in 2000 had been countered by a push on cheap loans to stimulate the housing market. This had simply allowed the US to “continue dreaming” (Zizek 2009a, p.20) for that little bit longer; essentially just prolonging the global crisis until a later date: until now.
“It’s useless to wait – for a breakthrough, for the revolution, the nuclear apocalypse or a social movement. To go on waiting is madness. The catastrophe is not coming, it is here. We are already situated within the collapse of civilisation.” (The Invisible Committee 2009, p.96)
The significance of this point in history cannot be underestimated. The hiatus caused by this latest epic crisis of capital should have given all of us opportunity for self-reflection. The connections between capitalism and environmental catastrophe have once again been starkly illuminated and so too has our own complicity in, and responsibility for, both. As the many climate scientists and campaigners have been telling us, we now only have one decade left – until 2020 – to stabilise and begin to reduce our rapidly increasing greenhouse gas emissions or we will be unable to avoid hitting the “dreaded two degrees” (Armstrong 2009b) – the tipping point at which we trigger runaway climate change and a rapid irreversible and uncontrollable descent into a new world of which the visions of The Road are not too much of an exaggeration.
Even mainstream politicians hungry for votes are forced to admit that “the age of irresponsibility is giving way to the age of austerity” (Cameron 2009). It does seem “useless to wait” (The Invisible Committee 2009, p.96). Now provides the opportunity to radically rethink the way we live, not just in practical terms, but in the way our minds perceive of ourselves in the future; of what we are working ‘towards’. We need to reverse our very ontological foundations so that we become capable of comprehending the opposite of progress – of approaching life in a world where deflation becomes the norm and where rationing is “inevitable” (Fisher 2009, p.80).
As artists – the producers of the non-essential – this rethink seems all the more vital and all the more urgent. It is now our ‘responsibility’ to redefine our roles within this new world, within the “collapse of civilisation” (The Invisible Committee 2009, p.96). As we approach the inevitable challenges of the forthcoming century we can no longer be immune to ethics – we must begin to question what practical function our work can have. And, if we decide that we can still persist in our roles as artists, then we must begin to generate new ways of finding “intrinsic motivation” when our traditional motivational structures of striving towards ‘goals’ such as “recognition and fame” (Abbing 2002, p.82); of creating a ‘legacy’ for ourselves in the future, no longer seem viable.

It is typical in periods of crisis (and opportunity) such as this to look to the past for guidance. Retrospective critique (as used to ‘set the scene’ for this essay) helps us to understand the causes of our current predicament in terms of a greater historical trajectory, to help us make sense of our own lives biographically. The real challenge, however, is in developing the suggestions, ideas and solutions that are essential to help us move on. The proceeding sections of this essay turn to two manifestos from 2009 which attempt just this: Ecoaesthetics: A Manifesto for the Twenty-First Century by Rasheed Araeen and Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. The intention is to draw together their recurring ideas in order to formulate a ‘plan of action’ which may constitute our ‘new moral code’, and then to examine how some of these ideas are already being put into practice, not just by some artists, but by other more radical elements of society.
In September 2009, the international journal of “critical perspectives on contemporary art and culture” Third Text dedicated an entire issue to contemplating a vision of the future of art, in which Araeen’s manifesto is published. In the preface, Araeen and his co-editor Richard Appignanesi give their own diagnosis of the predicament of artists “now as we face a legacy of failures in modern history that endangers the future prospects of humanity” (Araeen & Appignanesi 2009, p.500). Their suggestion is that we have reached a cynical and solipsistic impasse which it is essential to overcome:
“… the very concept of art will have to liberate itself from the two historical limits of containment and legitimisation. One is containment in the artist’s own narcissist ego; the other is art’s dependence for its legitimisation as art on the institutions that facilitate and promote art only as reified commodities placed in museum and marketplace showcases.” (Araeen & Appignanesi 2009, p.500)

Ego and individualism have always gone hand-in-hand with the relatively autonomous role the artist has historically enjoyed within society, however, it appears that these characteristics have only been exacerbated in recent years. Neoliberal ideology has led to a “convergence of artistic and entrepreneurial values” (J. Thatcher 2009, p.5) – flexible, creative and autonomous modes of operating have been co-opted by the business world, just as ‘the careerist mentality’ has been inherited by artists. Recent mainstream television programmes such as School of Saatchi (Priddle 2009) and Goldsmiths: But is it Art? (Kerr 2010), which pit artists’ egos and entrepreneurial skills against one another, show the extent to which these attitudes have become the norm.
The super-competitive environment of the ‘atomised art world’ engenders a survival instinct in artists which causes us, knowingly or not, to make our sole objective the expansion of our curricula vitae. The emphasis is on the development of a “narrative” – on forming a “brand identity” (Prince 2010, p.10), because this presents itself as the most efficient means to the desired ends of “recognition and fame” (Abbing 2002, p.82). Trapped in a perpetual attempt to impress art world institutions, artists inevitably end up feeding them with the art that they think they want rather than stopping to question exactly what they are producing and why.
In a pre-neoliberal world, choosing the role of artist was seen as an alternative to the mainstream: a point of resistance, a political statement even (Walker 2002) – art offered a potential strategy of “opposition to capitalism” (J. Thatcher 2009, p.6). Now as a small component part in this means / end cycle – art – simply acts an instrument to serve the “career ambitions of self-centred artists” – its “significant critical and social function” (Araeen 2009, p.680) disabled in the process. But, at this particular point in our history, art’s power in “subverting the dominant hegemony” (Mouffe 2007) – in creating an ‘alternative knowledge’ – may be its only redeemable function.
Araeen’s call for art to be liberated from “containment and legitimisation” (Araeen & Appignanesi 2009, p.500) foresees the unprecedented power he believes our ideas could have if completely detached from capitalism:
“It is in fact artistic imagination, not art objects, which, once freed from the self-destructive narcissist ego, can enter this life and not only offer it salvation but put it on the path to a better future.” (Araeen 2009, p.683)
He goes as far as to suggest that artists should “abandon their studios” and “stop making objects” (Araeen 2009, p.684). He urges us to reconfigure our roles to such an extent that our creative skills are put to use in conceptualising real-life practical projects, such as creating solar-powered desalination plants, which simultaneously address the two imminent global challenges of energy and freshwater shortages. Art should renounce its “freedom from function which constitutes its autonomy” (Prince 2009, p.7), leave the world of the ‘non-essential’ and begin to offer us with ‘practical solutions’ to real life problems.
Whereas Araeen’s manifesto (inline with the desperate pleas of environmental campaigns such as 10:10) gives a sense that something can be done to avert ‘our impending doom’. There is, however, another concurrent school of thought which encourages us to embrace our fate. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto was published in 2009 by writers Paul Kingsnorth and Dougald Hine, as a vision of the future of literature in the new form of “uncivilised art” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.13). It takes the pessimism of beliefs such as those of James Lovelock: that humans are too stupid to prevent climate change (Hickman 2010, p.12) and challenges us to invert these to become a positive creative force:
“We live in a time of social, economic and ecological unravelling. All around us are signs that our whole way of living is already passing into history. We will face this reality honestly and learn how to live with it.” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.19)
The key is in developing a sense of objectivity about the systems in which we are enmeshed. We are invited to “stand outside the human bubble”, to “tug our attention away from ourselves and to turn it outwards; to uncentre our minds”: essentially to put “civilisation – and us – into perspective” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.13).
Once we are able to shift our attitude from that of hubris to that of humility, it becomes easier to accept that resources are indeed finite; civilisations do collapse and that species, including our own, become extinct. With this finitude as a certainty, the petty squabbling of the art world and the insignificance of the ‘goals’ we have been striving towards become evident. We can be liberated from our career plans; from the careful crafting of our own personal legacies and can refocus our attentions on the immediacy of the present (Bey 1994), for it is perhaps here where we should learn to find meaning and happiness.
To read Part 3 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-34
————
References:
Abbing, H., 2002. Why Are Artists Poor?: The Exceptional Economy of the Arts, Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
Araeen, R., 2009. Ecoaesthetics: A Manifesto for the Twenty-First Century. Third Text, 23(5), 679-84.
Araeen, R. & Appignanesi, R., 2009. Art: A Vision of the Future. Third Text, 23(5), 499-502.
Armstrong, F., 2009a. Franny Armstrong: If you’re not fighting climate change or improving the world, then you’re wasting your life. The Guardian, 8.
Armstrong, F., 2009b. What is 10:10? 10:10 Campaign website. Available at: www.1010uk.org/1010/what_is_1010/arms [Accessed April 10, 2010].
Bey, H., 1994. Immediatism, Oakland, California: AK Press.
Brown, W., 2009. What will be the legacy of recession? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/oct/26/culture-cambridge-festival-ideas.
Cameron, D., 2009. The Age of Austerity. The Conservative Party website. Available at: www.conservatives.com/News/Speeches/2009/04/The_age_of_austerity_speech_to_the_
2009_Spring_Forum.aspx [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Fisher, M., 2009. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative?, Ropley, Hampshire: 0 Books.
Fowkes, M. & Fowkes, R., 2009. Planetary Forecast: The Roots of Sustainability in the Radical Art of the 1970s. Third Text, 23(5), 669-674.
Kerr, A., 2010. Goldsmiths: But is it Art?, BBC 4.
Kingsnorth, P. & Hine, D., 2009. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. Available at: www.dark-mountain.net/about-2/the-manifesto.
Mouffe, C., 2007. Artistic Activism and Agonistic Spaces. Art & Research, 1(2). Available at: www.artandresearch.org.uk/v1n2/mouffe.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Priddle, A., 2009. School of Saatchi, BBC 2.
Prince, M., 2009. Art & Politics. Art Monthly, (330), 5-8.
Prince, M., 2010. Remakes. Art Monthly, (335), 9-12.
Strawson, P.F., 2008. Social Morality and Individual Ideal. In Freedom and Resentment and Other Essays. London / New York: Routledge, pp. 29-49.
Thatcher, J., 2009. Crunch Time. Art Monthly, (332), 5-8.
Thatcher, M., Margaret Thatcher Quotes. About.com website. Available at: womenshistory.about.com/od/quotes/a/m_thatcher.htm [Accessed May 2, 2010].
The Invisible Committee, 2009. The Coming Insurrection, Los Angeles / Cambridge, Mass.: Semiotext(e).
Walker, J., 2002. Left Shift: Radical Art in 1970s Britain, London / New York: I.B. Tauris.
Zizek, S., 2009a. First As Tragedy, Then As Farce, London: Verso.
Zizek, S., 2009b. In Defense of Lost Causes, London: Verso.
To read Part 1 of this article visit this link:
http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-14
To read Part 2 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-24
Drawing together the diagnoses which recur throughout the literature of the moment, such as Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative? (Fisher 2009), First as Tragedy, Then as Farce (Zizek 2009a) and The Coming Insurrection (The Invisible Committee 2009) alongside the key suggestions, ideas and solutions from these two manifestos, our ‘plan of action’ begins to materialise.
In the spirit of Pascal’s famous ‘wager’ (Hajek 2008) the plan aims to cover all bases: our active and / or passive responses to the situation. Encouraging the belief that we might still be able to use our roles as artists to incite the radical change to our societal structure (in the art world and globally) needed to avert climate catastrophe, whilst simultaneously developing philosophies for coping with our lives – finding meaning and happiness – should our active response fail.
The seven points below offer a set of guidelines for rethinking our lives, which should act as the starting points for redefining our roles as artists and thinking about how it might be possible to reconcile ‘the careerist mentality’ into which we have been inculcated with the possibility of ‘our impending doom’:
1. stand back and view the world objectively
The main focus of Uncivilisation and our greatest existential priority is to enable ourselves to grasp perspective, not only of the relative insignificance of our individual career plans within the wider world, but more pertinently of the fragility of our entire species within the greater timescales of the universe. Once this mind shift is achieved it becomes easier to distil what is actually important in our lives – happiness and our two unending desires for survival and meaning (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.2). Only then will the remaining six points become easier to implement.
2. offer an external critique of the system
In our new ‘state of mind’ it becomes easier to see the systems in which we have been blindly functioning. From beyond the grasp of the dominant hegemony we can offer a vital ‘external critique’. As Chantal Mouffe suggests, our duty as artists then becomes to challenge the “given symbolic order” and the “existing consensus” (Mouffe 2007) – to revivify the belief that ‘an alternative’ is possible.
3. develop ways or working outside institutions
Our criticisms should extend to the hegemony of the art world, severing our dependence on “legitimisation” (Araeen & Appignanesi 2009, p.500). We must have the courage of conviction in our ideas to find ways of operating outside of art world institutions, especially the marketplace. We require what Mark Fisher describes as a “positive disengagement” – a protest of sorts – which should take the form of “collective activity” (Fisher 2006) to help us break out of our entrepreneurial solitude…
4. escape solipsism; work with and not against peers
As individual artists, working alone, we typify the global trend towards what Adam Curtis calls the “empire of the self” (Curtis 2002), in which anxiety and paranoia are rife. For Araeen, it is this “extreme self-centred individualism of art today” which is “a disturbing symptom of its detachment from our collective humanity” (Araeen 2009, p.679). And so, we must prioritise “collective activity” (Fisher 2006), learning to work in co-operation rather than competition with our friends. Peer support will relieve our paranoia and allow our capacities for empathy to be resuscitated.
5. reject ego and embrace anonymity
Collaboration will enable us to surrender our egos to the collective force; liberating our ideas from their “containment” (Araeen & Appignanesi 2009, p.500). We should “flee visibility” and embrace the new powerful, but faceless forms of resistance being pioneered by The Invisible Committee – encouraging us to turn our “anonymity… to our advantage” (The Invisible Committee 2009, pp.112-3).
6. create free ideas, not objects for sale
Our role as artists should be to focus on the creation of ideas, not the production of objects. The rejection of commodity is an important part of our ‘disengagement’ from the marketplace. Our ideas should not remain private property and should be gifted to the ‘creative commons’ for the ‘public good’ (Blackburn 2009). As Hakim Bey suggests in his book Immediatism, “The more imagination is liberated and shared, the more useful the medium” (Bey 1994, p.36).
7. abandon the trajectory; find motivation in immediacy, not legacy
We must cease to think of our art as a means to an end; a way of getting somewhere – into a book, a magazine, an exhibition etc, as it is pointless to base our motivations on a future which will, very likely, not be able to function as the present does. We should abandon the very notion of a career trajectory and learn to focus our attentions on the reality of now. Without an overpowering emphasis on the future our anxieties will begin to dissolve and we will be able to unearth the absolute state of happiness that exists in the “continuous present” (Crisp 1996, p.54). We must remain alert and not complacent, notice and appreciate the things which are actually good and, as Kurt Vonnegut suggests, continually remind ourselves “if this isn’t nice, I don’t know what is” (Vonnegut 2003).

The ‘plan of action’ forms the basis of a new ideology, which acts as a counterpoint to neoliberalism – advocating our extrication from the system of capital that is the “ultimate cause” (Fisher 2009, p.70) of our environmental crisis. Heavy on words such as ‘abandon’, ‘reject’, ‘stand back’ and ‘disengage’ it calls us to make radical changes. It demands that we overcome our “path dependency” (Abbing 2002, p.96) by shifting our goals away from the fantasy status of the ‘successful’ artist. It all makes our new role seem far less glamorous than our dreams may have envisaged – insisting that we renounce our vanity, abandon our egos, move towards collectivism and anonymity; in short, commit “career suicide” (Sharp 2010, p.52).
But would it really be so beneficial to scrap everything and start again – to admit that our lives up until this point had been “lost causes” (Zizek 2009b)? The emphasis of this essay is on the possibility of reconciliation. Therefore, it aims to explore what positive characteristics of ‘the careerist mentality’ that has driven us to take this individualistic path, we might be able to “salvage” (Williams 2009) and, in doing so, reconfigure to become a positive force that can help us put the plan into action all the more effectively: to take the necessary risks and make a stand for the ‘right’ ethical choice.
Counter to Kant’s belief that the fields of ethical decision making (part of ‘practical reason’) and aesthetic decision making (part of ‘judgement’) be kept separate (Guyer 2004), it appears that the gravity of the situation we face means that these two spheres must begin to coincide. Indeed, in his final book Chaosmosis: An Ethico Aesthetic Paradigm, Felix Guattari argues for the culminating phase of art to be one in which it has an integral relationship with ethics (Guattari 2006). And so, the ethical implications of the ‘plan of action’ become difficult to ignore. Its focus on ‘tugging our attention away’ from our obsession with our own lives to reconnect with our “collective humanity” (Araeen 2009, p.679) is clearly a moral proposition, soliciting a shift from prudent self-interest towards more altruistic behaviour.
The conflict that emerges between the self-interest of ‘the careerist mentality’ and the apparently selfless altruism called for by several points of the ‘plan of action’ has long been the concern of moral philosophy. The recurring question being whether they can ever coexist or be reconciled. In her essay Altruism Versus Self-Interest: Sometimes a False Dichotomy, Neera Kapur Badhwar argues that in certain cases, where individuals display particular characteristics, reconciliation of these traditional polarities is possible (Badhwar 1993).
Badhwar’s essay is based on the analysis of extreme instances of altruism (in this case the behaviour of those who rescued / harboured Jews from the Nazis in the Second World War). What is interesting, and indeed relevant, is the way in which she demonstrates how these definitive acts of altruism are able to coexist with self-interested motivations. Her argument is based on an extension of the categories of self-interested motivation from “feeling virtuous, becoming famous, gaining wealth” (Badhwar 1993, p.101) – equate these to the artist’s extrinsic motivations “money, recognition, fame” (Abbing 2002, p.82) – to include “integrity and self-affirmation” (Badhwar 1993, p.101) – read the artist’s intrinsic motivations of “inner gratification or private satisfaction” (Abbing 2002, p.82). Even though she acknowledges that these altruistic acts were carried out with an “awareness of the risk, in the absence of expectations of material, social, or psychological rewards [and with] the spontaneity of their choice to help” (Badhwar 1993, p.96), she demonstrates that it was precisely because these individuals took the risk that they were able to satisfy the:
“fundamental human interest, the interest in shaping the world in light of one’s own values and affirming one’s identity.” (Badhwar 1993, p.107)
Furthermore, she unearths another peculiarity at the heart of the dichotomy of individualism / collectivism (Triandis 1995) which also becomes key to the possibility of reconciliation. The individuals that she studied were compelled to carry out these altruistic acts because they were able to perceive of themselves as part of the “collective humanity” (which Araeen demands we reconnect with) and so had a more developed capacity for empathy. But, moreover, that it was something inherent in their individualism that gave them the “confidence in the value of their mission, and their own capacities for carrying it out” (Badhwar 1993, p.100): to stand away from the crowd and to stand up for what they believed to be right.
Following Badhwar’s argument, it becomes possible to identify the first of the characteristics of ‘the careerist mentality’ we should aim to salvage. For it is our “flair, self-assurance, and… sense of audacity” (Abbing 2002, p.95) which we shall have to depend on in order to take the risk necessary to make a stand against the mainstream.
What might it look like if we took the risk? What might we end up with if we followed the points in the ‘plan of action’ to the word? It is possible that rather than resulting in a radical new type of art practice, what would actually take place is a shift away from art and into the field of activism.
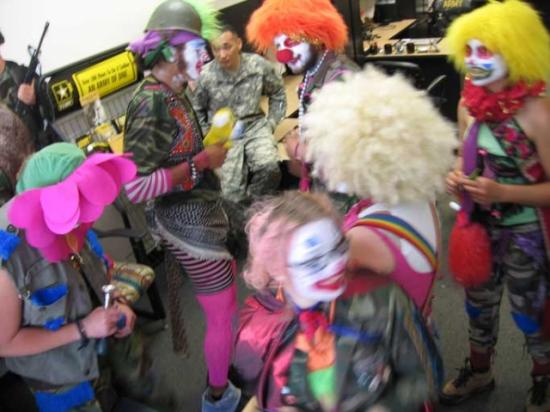

The Clandestine Insurgent Rebel Clown Army (CIRCA) was formed in 2003, to mark the official state visit of George W Bush to London at the onset of the Iraq war. It aimed to bring together “the ancient practice of clowning and the more recent practice of nonviolent direct action” (CIRCA 2003) – staging a series of strategic protests as part of an ongoing offensive against the evils of ‘war’ and ‘capitalism’. Before the protests at the G8 Summit at Gleneagles in 2005, the Rebel Clown Army embarked on a national recruitment tour of the United Kingdom. Anyone and everyone was invited to join, the only stipulation being that Basic Rebel Clown Training (BRCT) was first undertaken.
Much like the ‘plan of action’, the BRCT process focuses on the individual’s emancipation – on “transformation” and “personal liberation” from the dominant hegemony (CIRCA 2003). This internal reprogramming enables clownbatants, as they are known, to shut off their previous assumptions about hierarchical power structures and to step back and see the world with fresh eyes. From this new perspective the absurdity of a situation in which a line of protesters face-up against a line of police, becomes apparent. Beyond the signifiers of each others’ uniforms, Ranciere’s notion of the omnipresence of equality becomes evident (Ranciere 2007) and play and humour then perhaps do seem the natural human responses. Against the forward planning tactics of a traditional army (and indeed the career-minded artist) CIRCA’s emphasis is on spontaneity: “because the key to insurgency is brilliant improvisation, not perfect blueprints” (CIRCA 2003).
In a uniform which combines camo and greasepaint, clownbatants (as Point 5. suggests) ‘reject ego and embrace anonymity’ and so their inhibitions and embarrassment become irrelevant. So much more becomes possible without the worry of how they are perceived, of how others will judge them. Their individual subjectivities come together as a collective force of resistance. Their creativity exists in a space beyond the system of capital and they are utilising it to actively fight back.
The founders of the Rebel Clown Army were so aware of the importance of creativity in the process of resistance and of the potential for an evolution between art and activism, that they later set up the Laboratory of Insurrectionary Imagination (Lab of ii) as “a space to bring artists and activists together” (Harvie et al. 2005, p.249). The idea was to enable situations where they could work together and transfer skills – cultivating confidence in their “creative capacity as [a] fundamental tool for social change” (Lab of ii 2005). Functioning across the public realm, art world institutions and sites of traditional protest, the Lab of ii manages to successfully infiltrate and subvert different aspects of the hegemony. Most recently at Tate Modern in London, where under the banner of Disobedience Makes History – a two-day workshop on “art-activism” – they deliberately disobeyed the curator’s orders, encouraging participants to aim public attacks relating to the climate crises directly at the museum’s sponsors BP (Jordan 2010, p.35).
To read Part 4 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-44
————
References:
Araeen, R., 2009. Ecoaesthetics: A Manifesto for the Twenty-First Century. Third Text, 23(5), 679-84.
Araeen, R. & Appignanesi, R., 2009. Art: A Vision of the Future. Third Text, 23(5), 499-502.
Badhwar, N.K., 1993. Altruism Versus Self-Interest: Sometimes a False Dichotomy. In Altruism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 90-117.
Bey, H., 1994. Immediatism, Oakland, California: AK Press.
Blackburn, S., 2009. Do we need a new morality for the 21st century? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/nov/02/cambridge-festival-of-ideas.
CIRCA, 2003. About the Army. Clandestine Insurgent Rebel Clown Army website. Available at: www.clownarmy.org/about/about.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Curtis, A., 2002. The Century of the Self, BBC 4.
Crisp, Q., 1996. The Naked Civil Servant, London: Flamingo.
Fisher, M., 2006. Reflexive Impotence. k-punk blog. Available at: k-punk.abstractdynamics.org/archives/007656.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Fisher, M., 2009. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative?, Ropley, Hampshire: 0 Books.
Guattari, F., 2006. Chaosmosis: An Ethico Aesthetic Paradigm. In Participation. London / Cambridge, Mass.: Whitechapel / MIT Press.
Guyer, P., 2004. Immanuel Kant. In E. Craig, ed. Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. London: Routledge.
Hajek, A., 2008. Pascal’s Wager. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Available at: plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2008/entries/pascal-wager [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Harvie, D. et al. eds., 2005. Shut Them Down!, Leeds / New York: Dissent! / Autonomedia.
Jordan, J., 2010. On refusing to pretend to do politics in a museum. Art Monthly, (334), 35.
Kingsnorth, P. & Hine, D., 2009. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. Available at: www.dark-mountain.net/about-2/the-manifesto.
Lab of ii, 2005. About Us. The Laboratory of Insurrectionary Imagination website. Available at: www.labofii.net/about [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Mouffe, C., 2007. Artistic Activism and Agonistic Spaces. Art & Research, 1(2). Available at: www.artandresearch.org.uk/v1n2/mouffe.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Ranciere, J., 2007. Hatred of Democracy, London: Verso.
Sharp, C., 2010. Career Suicide. Art Review, (40), 52-4.
The Invisible Committee, 2009. The Coming Insurrection, Los Angeles / Cambridge, Mass.: Semiotext(e).
Triandis, H., 1995. Individualism and Collectivism, Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press.
Vonnegut, K., 2003. Knowing What’s Nice. In These Times. Available at: www.inthesetimes.com/article/knowing_whats_nice [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Williams, E.C., 2009. Putting the punk back in salvage (where it was not to begin with). Socialism and/or Barbarism blog. Available at: socialismandorbarbarism.blogspot.com/2009/08/putting-punk-back-in-salvage-where-it.html [Accessed May 4, 2010].
Zizek, S., 2009a. First As Tragedy, Then As Farce, London: Verso.
Zizek, S., 2009b. In Defense of Lost Causes, London: Verso.
To read Part 1 of this article visit this link:
http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-14
To read Part 2 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-24
To read Part 3 of this article visit this link: http://www.furtherfield.org/articles/trajectories-how-reconcile-careerist-mentality-our-impending-doom-part-34
Returning to Badhwar’s essay, it is important to note the impulsive and/or compulsive nature of the acts of altruism that she studied – “the spontaneity of their choice to help” (Badhwar 1993, p.96). She observes that:
“Those who acted spontaneously, then, acted with a sense that they had no alternative but to help, and that, under the circumstances, helping was nothing special… [Their actions were] a spontaneous manifestation of “deep-seated dispositions which form one’s central identity” or character.” (Badhwar 1993, p.97)
Of course, impulsion and / or compulsion are not the sorts of qualities which can be taught or learnt. As is suggested, you really have to believe in what you are doing in order to act instinctively – in a way which is not premeditated or over-deterministic. In this sense you cannot simply follow a ‘plan’ to be altruistic as this is in its essence self-defeating. It is, however, possible to develop one’s “character” or “identity”, so that we do begin to notice when things are wrong or unjust and we really do feel compelled to act to change them. This is done through periods of self-reflection but also, more importantly, by acquiring knowledge.

Oliver Ressler uses his research-based practice as a way of not only acquiring knowledge for himself, but of disseminating it to others – via video, installation and public realm contexts. His 2008 film What Would It Mean To Win? in collaboration with Zanny Begg focuses on the counter-globalisation protests at the G8 Summit in Heiligendamm in Germany in 2007. The documentary sections of which probe members of resistance movements to consider just what form society might take if they were to ‘win’ what they have been fighting for. His creation of a bank of knowledge about social alternatives is extended in Alternative Economics, Alternative Societies – a documentary, installation and billboard project which presents ideas and proposals for alternative economic and societal models, which all use the rejection of the system of capital as a starting point (Ressler 2007). The research from this project was published as a book in 2007.
Ressler’s book can be seen as a companion to that of art collective Superflex who in 2006 initiated and published Self-organisation / Counter-economic Strategies. As a “toolbox of ideas”, the book puts forward a series of proposals for self-organised models of social and economic systems that also aim to offer an alternative to capitalism (Bradley et al. 2006). Both books aim to spark debate about the negative effects of our current social order and (as Point 2. suggests) ‘to revivify the belief that ‘an alternative’ is possible’.

What is interesting is that the more we learn about the connections between capitalism and environmental catastrophe – the more self-reflection we undertake – the more ‘responsibility’ we inherit. In his famous essay exploring the moral differences between active and passive action Killing and Starving to Death, James Rachels illuminates this notion:
“There is a curious sense, then, in which moral reflection can transform decent people into indecent ones: for if a person thinks things through and realises that he is, morally speaking [in the wrong]… his continued indifference is more blameworthy than before.” (Rachels 2006, p.73)
And so the self-reflexive artist enters into a spiral. The more knowledge that they research and acquire – the more their conscience is likely to compel them to act. The question then becomes whether art is the most efficient way of effecting real change.
According to Artur Zmijewski, his recent work Democracies – a series of documentary clips depicting different protest movements from around the world – is not art. “Art”, according to Zmijewski, “is too weak to present political demand” (Prince 2009, p.6). Artists have in the past reached a similar conclusion – turning to existing political systems as a more direct means of effecting change. In 1980 Joseph Beuys was instrumental in setting up the Green Party in Germany, running as its candidate for the European Parliament, and, in 1988 Maria Thereza Alves co-founded the Green Party in Brazil. In a recent lecture Alves points out that it becomes the role of the artist to “judge in each situation whether art or politics provides a better solution” (Alves 2010).

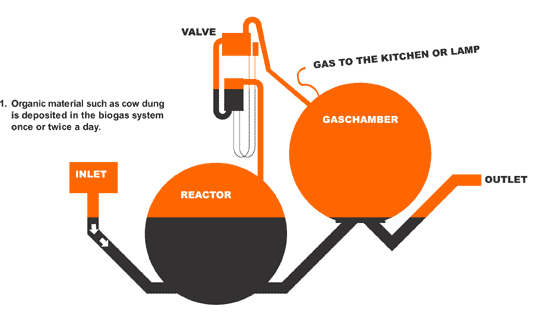
As well as proposing theoretical solutions in book form, Superflex have also attempted to find practical solutions to real life problems in Africa. Although falling under the umbrella of their artistic practice, these projects seem more akin to the sort of thing you might expect to see being pioneered by a charity or a development agency. In 1996-7 they worked with engineers to develop the Supergas system, which is capable of turning compostable waste in the form of human / animal dung into “sufficient gas for the cooking and lighting needs of an African family”, thereby allowing them to “achieve self-sufficiency in energy” (Superflex 1997). The realisation of the Supergas system seems to epitomise the marriage between creative thinking and functionality which Araeen calls for by presenting the example of the desalination plant. What is interesting about this project, and indeed Beuys’ and Alves’ involvement in Green politics, is how it shifts our perception of the role of the artist when viewed as an important component part of a wider practice…
It has been suggested that the most successful campaigning bodies, such as Greenpeace, function “through multi-pronged channels of official, semi-official and illicit activity to negotiate specific ends” (Perry 2010, p.8). They operate under several different ‘hats’ – as a registered charity for raising funds (sometimes even stooping so low as to employ the cynical marketing strategies of the ‘charity-mugger’ on the street) and, at once, as a band of renegade activists aboard the Rainbow Warrior causing real disruption to cruel and exploitative practices and playing tactical media games. They demonstrate a “positive disengagement” (Fisher 2006) from the mainstream, coupled with a savvy co-option of the system, where it clearly presents itself as a more productive solution.
It is possible that the new model for a ‘reconciled artistic practice’ could take a similar form, where the artist (or preferably the collective of artists) balances a variety of activities across different fields. Described as “a group of freelance artist-designer-activists committed to social and economic change” (Myers 2007), Superflex do not ‘abandon’ the art world altogether and, in addition to the projects described above, they continue to work on commissions for its major institutions. For example, in 2009 they made a series of short films The Financial Crisis (Session I-V) for the art market’s number one annual trade fair – Frieze. Like the Lab of ii and following in a long lineage of institutional critique, Superflex appear to understand the benefits of being able to use the system by infiltrating it, criticising and beginning to change it from within.
In now seems evident that our success at adapting to this multi-pronged mode of operation, which straddles real political action, activism and art world insider jobs, depends on our flexibility in approaching different tasks – our ability to wear these different ‘hats’ with conviction and our adeptness at switching between roles. So here it becomes possible to identify the second of the characteristics of neoliberalism which we might aim to salvage. For it is “the very hallmarks of management in a post-Fordist, Control society” – our ‘flexibility’, ‘nomadism’ and ‘spontaneity'” (Fisher 2009, p.28) which we must now begin utilise, as well as our ability to cope with and adapt to change. Both very useful skills to have as the temperatures begin to rise and the food stocks begin to run low.
The final characteristic particular to the career-minded artist, which we must aim to reconfigure as central to our new roles in the twenty-first century, is our work-ethic, which results from our comparatively high levels of intrinsic motivation (Abbing 2002, p.82). The acceleration of work rates is something which has developed across the board under neoliberalism to the extent that we are now “bound” to our work in an “anxious embrace”…
“Managers, scientists, lobbyists, researchers, programmers, developers, consultants and engineers, literally never stop working. Even their sex lives serve to augment productivity.” (The Invisible Committee 2009, p.47)
However, it is the artist’s ability and willingness to work twenty-four-seven often in situations completely removed from wage-labour relations, that makes us ‘exceptional’ (Abbing 2002) and offers the potential, even, to act as a paradigm for a general approach to work in a world beyond capital. For it is this position of “radical autonomy” which presents the opportunity for “real education of our socialised senses and human potentials that releases development in all directions” (Ray 2009, p.546). We continue, over the course of our lives, to relentlessly acquire knowledge, self-reflect and develop, adapt, evolve and act – not for money, but because something inside us – something inherent in our ‘character’ – compels us to. If we could only succeed in “freeing” a small fraction of this exceptional motivation “from the self-destructive narcissist ego” (Araeen 2009, p.683) and releasing it in a more selfless and functional direction, it could still be a hugely positive force for change.
Following Aristotle’s classic assertion that moral excellence is found in a person’s rational capacity to choose the mean between extremes (Mautner 2005, p.43), the introduction to the Cambridge reader on Altruism, in which Badhwar’s essay is published, suggests that:
“The most challenging task of a moral theory is to strike a balance between the weight we give to our own interest and the weight we give to those of others. A theory that directs us to give too much to others is as deficient as one that directs us to give too little.” (Paul et al. 1993, p.ix)
And, so it seems that ‘a reconciled practice’ will also, to a certain extent, be about compromise. It will be about attempting to ‘strike a balance’ between the time we invest in each of the various facets of our activity – direct political action or more conventional art world activity – and about how we best use our judgement as to when to focus on one thing over another. If we can achieve this equilibrium in our ‘multi-pronged approach’ to practice, and indeed in our lives in general, then this is perhaps also where we will find our “private satisfaction” (Abbing 2002, p.82): our happiness.
In a recent interview Ranciere reminds us “that there are certain situations where only reality can be taken into account – there is no room for fiction” (Charlesworth 2010, p.75). What this suggests is that perhaps the balance between the ‘selfish’ and ‘selfless’ activity which artists undertake will only really begin to shift when we are directly confronted with the realities of climate change. As James Lovelock suggests it may well take until the point of real global disaster – such as an event on the scale of the Pine Island glacier breaking off into the ocean causing tsunamis and an immediate and permanent sea rise of two metres (Hickman 2010, p.12) – until we are, through absolute necessity, able to totally reconfigure our motivations. Perhaps only when we do come face-to-face with this “worst kind of encounter with reality” (Kingsnorth & Hine 2009, p.11) will we, as artists, be able to assume our fully functional role in society.
When Franny Armstrong, founder of the 10:10 Campaign, says “if you’re not fighting climate change or improving the world, then you’re wasting your life” (Armstrong 2009a, p.8), she is essentially reinforcing the ‘wager’ set out in our ‘plan of action’. However the future pans out, do you really want to look back on this pivotal moment in the history of our species and say ‘I did nothing’, ‘I did not make a stand’, or do you want to be able to say the opposite and to retain what should be our most commanding of all human motivations – our integrity.
——-
Abbing, H., 2002. Why Are Artists Poor?: The Exceptional Economy of the Arts, Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press.
Alves, M.T., 2010. The Friday Event. The Glasgow School of Art. Available at: www.gsaevents.com/fridayevent/alves [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Araeen, R., 2009. Ecoaesthetics: A Manifesto for the Twenty-First Century. Third Text, 23(5), 679-84.
Araeen, R. & Appignanesi, R., 2009. Art: A Vision of the Future. Third Text, 23(5), 499-502.
Armstrong, F., 2009a. Franny Armstrong: If you’re not fighting climate change or improving the world, then you’re wasting your life. The Guardian, 8.
Armstrong, F., 2009b. What is 10:10? 10:10 Campaign website. Available at: www.1010uk.org/1010/what_is_1010/arms [Accessed April 10, 2010].
AVOID, 2010. Will the Copenhagen Accord avoid more than 2C of global warming? AVOID website. Available at: ensembles-eu.metoffice.com/avoid [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Badhwar, N.K., 1993. Altruism Versus Self-Interest: Sometimes a False Dichotomy. In Altruism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 90-117.
Bey, H., 1994. Immediatism, Oakland, California: AK Press.
Blackburn, S., 2009. Do we need a new morality for the 21st century? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/nov/02/cambridge-festival-of-ideas.
Bradley, W. et al. eds., 2006. Self-organisation / Counter-economic Strategies, New York: Sternberg Press.
Brown, W., 2009. What will be the legacy of recession? The Guardian Culture Podcast. Available at: www.guardian.co.uk/culture/audio/2009/oct/26/culture-cambridge-festival-ideas.
Cameron, D., 2009. The Age of Austerity. The Conservative Party website. Available at: www.conservatives.com/News/Speeches/2009/04/The_age_of_austerity_speech_to_the_
2009_Spring_Forum.aspx [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Charlesworth, J.J., 2010. Jacques Rancière Interview. Art Review, (40), 72-5.
CIRCA, 2003. About the Army. Clandestine Insurgent Rebel Clown Army website. Available at: www.clownarmy.org/about/about.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Crisp, Q., 1996. The Naked Civil Servant, London: Flamingo.
Curtis, A., 2002. The Century of the Self, BBC 4.
Deleuze, G., 1990. Society of Control. L’Autre Journal, (1). Available at: www.nadir.org/nadir/archiv/netzkritik/societyofcontrol.html.
Fisher, M., 2009. Capitalist Realism: Is There No Alternative?, Ropley, Hampshire: 0 Books.
Fisher, M., 2006. Reflexive Impotence. k-punk blog. Available at: k-punk.abstractdynamics.org/archives/007656.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Fowkes, M. & Fowkes, R., 2009. Planetary Forecast: The Roots of Sustainability in the Radical Art of the 1970s. Third Text, 23(5), 669-674.
Guattari, F., 2006. Chaosmosis: An Ethico Aesthetic Paradigm. In Participation. London / Cambridge, Mass.: Whitechapel / MIT Press.
Guyer, P., 2004. Immanuel Kant. In E. Craig, ed. Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. London: Routledge.
Hajek, A., 2008. Pascal’s Wager. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Available at: plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2008/entries/pascal-wager [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Harvey, D., 2007. A Brief History of Neoliberalism, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Harvie, D. et al. eds., 2005. Shut Them Down!, Leeds / New York: Dissent! / Autonomedia.
Hickman, L., 2010. James Lovelock: Fudging data is a sin against science. The Guardian, 10-12.
Hillcoat, J., 2009. The Road, Dimension Films.
IPCC, 2001. Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. GRID-Arendal website. Available at: www.grida.no/publications/other/ipcc%5Fsr/?src=/climate/ipcc/emission [Accessed May 3, 2010].
Jordan, J., 2010. On refusing to pretend to do politics in a museum. Art Monthly, (334), 35.
Kerr, A., 2010. Goldsmiths: But is it Art?, BBC 4.
Kingsnorth, P. & Hine, D., 2009. Uncivilisation: The Dark Mountain Manifesto. Available at: www.dark-mountain.net/about-2/the-manifesto.
Lab of ii, 2005. About Us. The Laboratory of Insurrectionary Imagination website. Available at: www.labofii.net/about [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Mamudi, S., 2008. Lehman folds with record $613 billion debt. MarketWatch website. Available at: www.marketwatch.com/story/lehman-folds-with-record-613-billion-debt?siteid=rss [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Mautner, T., 2005. Aristotle. In The Penguin Dictionary of Philosophy. London / New York: Penguin, pp. 40-4.
Mouffe, C., 2007. Artistic Activism and Agonistic Spaces. Art & Research, 1(2). Available at: www.artandresearch.org.uk/v1n2/mouffe.html [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Myers, J., 2007. Superflex. Frieze Magazine, (106). Available at: www.frieze.com/issue/review/superflex [Accessed May 9, 2010].
Paul, E.F., Miller, F.D. & Paul, J. eds., 1993. Altruism, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Perry, C., 2010. Art v the Law. Art Monthly, (333), 5-8.
Priddle, A., 2009. School of Saatchi, BBC 2.
Prince, M., 2009. Art & Politics. Art Monthly, (330), 5-8.
Prince, M., 2010. Remakes. Art Monthly, (335), 9-12.
Rachels, J., 2006. Killing and Starving to Death. In The Legacy of Socrates: Essays in Moral Philosophy. New York: Columbia University Press, pp. 60-82.
Ranciere, J., 2007. Hatred of Democracy, London: Verso.
Ray, G., 2009. Antinomies of Autonomism: On Art, Instrumentality and Radical Struggle. Third Text, 23(5), 537-46.
Ressler, O., 2007. Alternative Economics, Alternative Societies. Oliver Ressler website. Available at: www.ressler.at/alternative_economics [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Sharp, C., 2010. Career Suicide. Art Review, (40), 52-4.
Strawson, P.F., 2008. Social Morality and Individual Ideal. In Freedom and Resentment and Other Essays. London / New York: Routledge, pp. 29-49.
Superflex, 1997. Supergas. Superflex website. Available at: superflex.net/tools/supergas [Accessed May 5, 2010].
Thatcher, J., 2009. Crunch Time. Art Monthly, (332), 5-8.
Thatcher, M., Margaret Thatcher Quotes. About.com website. Available at: womenshistory.about.com/od/quotes/a/m_thatcher.htm [Accessed May 2, 2010].
The Invisible Committee, 2009. The Coming Insurrection, Los Angeles / Cambridge, Mass.: Semiotext(e).
Triandis, H., 1995. Individualism and Collectivism, Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press.
Vonnegut, K., 2003. Knowing What’s Nice. In These Times. Available at: www.inthesetimes.com/article/knowing_whats_nice [Accessed April 25, 2010].
Walker, J., 2002. Left Shift: Radical Art in 1970s Britain, London / New York: I.B. Tauris.
Williams, E.C., 2009. Putting the punk back in salvage (where it was not to begin with). Socialism and/or Barbarism blog. Available at: socialismandorbarbarism.blogspot.com/2009/08/putting-punk-back-in-salvage-where-it.html [Accessed May 4, 2010].
Zizek, S., 2009a. First As Tragedy, Then As Farce, London: Verso.
Zizek, S., 2009b. In Defense of Lost Causes, London: Verso.
Data Soliloquies
Richard Hamblyn and Martin John Callanan
London: Slade Press, 2009
112 pages
ISBN 978-0903305044
Featured image: Data Soliloquies is a book about the extraordinary cultural fluidity of scientific data
Although much has been said about C.P. Snow’s concept of a “third culture”, we haven’t actually reached an understanding between the spheres of science and humanities. This is caused in part by the high degree of specialisation in each field, which usually prevents researchers from considering different perspectives, as well as the controversies that have arisen between academics, exemplified by publications such as Intellectual Impostures (1998) in which physicists Alan Sokal and Jean Bricmont criticise the “abuse” of scientific terminology by sociologists and philosophers. Yet there is a growing mutual dependency of both fields of knowledge, as the one hand our society is facing new problems and questions for which the sciences have adequate answers and on the other scientific research can no longer remain isolated from society. Some scientists, such as the astronomer Roger Frank Malina, have even argued that a “better science” will result from the interaction between art, science and technology. Malina presents as an example the “success of the artist in residence and art-science collaboration programs currently being established” [1], and considers the possibility of a “scientist in residence” program in art labs.

Our relationship with the environment is certainly one of the main problems we are going to face during this century and it is also a subject that brings up the necessary communication between science and society. The UCL Environment Institute [2] was established in 2003 to promote an interdisciplinary approach to environmental research and make it available to a wider audience. While being representative of almost every discipline in the University College London, it lacked an interaction with the arts and humanities. This gap has been bridged by establishing an artist and writer residency program in collaboration with the Slade School of Fine Arts and the English Department. Among 100 applications, writer Richard Hamblyn and artist Martin John Callanan were chosen for the 2008-2009 academic year: Data Soliloquies is the result of their work.
Despite “belonging” to the field of art and humanities, neither Hamblyn nor Callanan are strangers to science and technology. Richard Hamblyn is an environmental writer and historian who has developed a particular interest in clouds, and Martin John Callanan is an artist whose remarkably conceptual work merges art and different types of media. This may be the cause that Data Soliloquies is by no means a shy penetration into a foreign field of knowledge but a solid discourse which presents a richly documented critique of the apparently ineffective ways in which scientists have made society aware of such a crucial problem as that of climate change. The title of the book has been borrowed for a term that Jon Adams, researcher at the London School of Economics, coined to refer to Michael Crichton’s novels, who uses “scientific” facts to give his imaginative plots an aura of credibility. With this reference, the authors state that the way scientific data is presented actually constitutes a narrative, an uncontested monologue: “…scientific graphs and images have powerful stories to tell, carrying much in the way of overt and implied narrative content (…) these stories are rarely interrupted or interrogated.”[3]
As the amount of data regularly stored in all sorts of digital supports increases exponentially, and new forms of data visualisation are developed, these “data monologues” become ubiquitous, while remaining unquestioned. In his text, Hamblyn exposes the inexactitude in some popular visualisations of scientific data, which have set aside accuracy in favour of providing a more eloquent image of what the gathered evidences are supposed to tell. On the one hand, Charles D. Keeling’s upward trending graph of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration, which according to Hamblyn is “probably the most important data set in environmental science, and has become something of a freestanding scientific icon”[4], or Michael Mann’s controversial “Hockey Stick” graph are illustrative examples of the way in which information displays have developed their own narratives. On the other, the manipulation of data in order to obtain a more visually effective presentation, such as NASA’s exaggeration of scale in their images of the landscape of Venus or the use of false colours in the reproductions of satellite images, call for a questioning of the supposed objectivity in the information provided by scientific institutions.

In the field of climate science, the stories that graphs and other visualisations can tell have become of great importance, as human activity has a direct impact on global warming, but this relation of cause and effect cannot be easily determined. As Hamblyn states: “climate change is the first major environmental crisis in which the experts appear more alarmed than the public” [5]. The catastrophism with which environmental issues are presented to the public generate a feeling of impotence, and thus any action that an individual can undertake seems ineffective. The quick and resolute reaction of both the population and the governments in the case of the “ozone hole” in 1985 points in the direction of finding a clear and compelling image of the effects of climate change. As Hamblyn underscores, this is not only a subject for engineers: “the reality of ongoing climate change has yet to be embraced as a stimulus to creativity –in the arts as well as the sciences– or as a permanent and inescapable part of human societal development” [6].
Martin John Callanan took upon himself to develop a creative response to this issue, and has done so, not simply by creating images or objects but by depicting processes. He states: “I’m more interested in systems –systems that define how we live our lives” [6]. A quick look at his previous work [7] will show how appropriate this statement is: he has visited each and every station of the London underground, collected every command of the Photoshop application in his computer, officially changed his name (to the same he already had), gathered the front page of hundreds of newspapers from around the world and engaged himself in many other activities that are as systematic and mechanical as ironic, poetic or simply nihilistic. During his residency, Callanan created to main projects. The first one, Planetary Order, is a globe in which the patterns of the clouds on a particular date (February 6th, 2009) have been sculpted. The artist composed the readings of NASA’s cloud monitoring satellites in a virtual 3D computer model, which was then laser melted on a compacted nylon powder sphere at the Digital Manufacturing Centre at the UCL Bartlett Faculty of the Built Environment. The resulting object is a sculpture, an artwork more than any sort of model in the sense that it develops a discourse beyond the actual presentation of data. An impeccable white sphere textured by its subtle protuberances, the globe evokes the perfection of an ancient marble sculpture while presenting us with an uncommon view of the Earth, covered with clouds. The clouds, which are usually erased in the depictions of our planet in order to let us see the shapes of the continents (the land which is our dominion), become an icon of climate change and the image of an order which is, in all senses, above us. Callanan freezes the planetary order of clouds in an impossible map, a metaphorical object which appears to us as a faultless, yet fragile and inscrutable machine.
The second of Callanan’s artistic projects is the series Text Trends. Using Google data, the artist has collected the number of searches for selected terms related to climate change in a time range of several years (from 2004 to 2007-2008). With this data, he has generated a series of minimalistic graphs in which two jagged lines, one red and the other blue, cross the page describing the frequency of searches (or popularity) for two competing terms. The result resembles an electrocardiogram in which we can see the “life” of a particular word, as opposed to another, in a simple but eloquent dialogue of abstract forms. Callanan has chosen to confront terms in pairs such as “summer vs. winter”, “climate change vs. war on terror” or “global warming”. Simple as they may seem, the graphs are telling and constitute and visual summary of the book whilst suggesting many other reflections. The final conclusion is presented in the last graph, in which the perception of climate change is expressively described by the image of a vibrant line for the word “now”, much higher in the chart than the flat line for the word “later”.
Pau Waelder
Featured image: Photograph of a creative experiment on more intelligent modes of inhabiting the planet
Open_Sailing‘s biggest achievement is perhaps to have turned our future into an open source project. Led by a group of enthusiasts, gathered around the idea of “we don’t know what will happen, but together we can invent our future and cope”, the project puts forward a very ambitious, action-driven, experiment-led, way of thinking forward. After meeting with the founder of the project, Cesar Harada, Open_Sailing proved to be a much more complex enterprise than I originally thought.
Initially the project started by mapping threats, the idea being that threats can produce something else than fear. Indeed Cesar Harada, was decided to turn threats into design constraints. This constitutes an interesting methodology to deal with the current climate of fear. The exploitation of threat has become the standard procedure to stabilize a permanent state of emergency. Mobilising virtual threats, states acquire exceptional powers that facilitate the implementation of ever more pervasive measures of control. The current case of swine flu is the last of a long list of exercises of mass modulation of fear. War on terror is the paradigmatic one. On the other hand, and following the warnings of the Maya calendar, all sorts of popular tales for an apocalyptic 2012 have started to populate the planet.
The role of Open_Sailing is to function as a catalyst that channels all this energy into the production of a better future. In short, its role is to transform fear into hope. Certainly this functioned as a strong attractor for new collaborators and soon the team started to grow. After putting together large amounts of real-time data about all sorts of dangers such as tsunami, terrorist attacks, nuclear accidents or pandemics, it became clear that the potential safest spots on earth were mostly located at sea. That led to the idea of designing the infrastructure necessary to inhabit those spots based on the concept of ‘Open Architecture’. Fear had been successfully turned into an active force unleashing the creative process. Inspired by this initial concept the Open_Sailing team started a very intense process of scientific, technological, architectural and artistic research that resulted in a first prototype awarded at Ars Electronica: Open_Sailing_01.
“A drifting village of solid and comfortable shelters surrounded by flexible ocean farming units: fluid, pre-broken, reconfigurable, sustainable, pluggable, organic and instinctive.” [1]
This drifting village, which is about 50 metres in diameter and can host four people, is designed to respond to its environment, being able to become compact and endure severe weather conditions, and spreading out to harvest in calm situations. Open_Sailing_01 was supposed to set sail last May 2009 but mis-coordination in the production with Ars Electronica delayed the plan. In the meantime, small intermediary prototypes of different modules are being built and tested constantly, but the Open_Sailing team hopes to put together the main modules of the International_Ocean_Station for general testing by the summer 2010.
One other important thing that came across in the interview with Cesar Harada was how soon after Open_Sailing was set in motion, it became clear that the project was not only about escaping the problematics of our society. It was definitely not an idealistic utopia happening elsewhere and starting a world from scratch. Rather than an exercise of escapism, they realised that the idea of inhabiting those sites where there is no threat had become an experimental laboratory where to grasp the future. Indeed Open_Sailing is very much about finding ways to face and deal with the very problems of our world.

“Be it overpopulation, global warming or energy conflicts, we are living in a time where ‘Apocalypse’ beckons. We need to collectively invent and spread bootstrapping DIY technologies for the forthcoming challenges, not only to survive but to re-invent how we inhabit this planet.” [2]
This became particularly obvious when the team flew to Morocco to try out some live-saving structures. Between the coast of Morocco and the Canary Islands in Spain hundreds of illegal immigrants die every year at sea. A high-seas permanent shelter would provide a low cost life-saving facility for the migrants.
This particular instance is also paradigmatic of the way in which experimentation is carried within the project. Future thinking is developed through material instantiations. This very characteristic process of design and engineering disciplines gives Open_Sailing an exciting palpability, a materiality, a commitment with actualisation that accounts for its potential to bring about real change. Commitment with results drives the project away from the artistic disciplines, but the poetics of the project undeniably brings them back together. A project that in a year of development has acquired such a level of complexity necessarily had to go through a very intense and accelerated process of conceptualisation and experimentation. And there comes the figure of the enthusiast, an experimental survivalist who is willing to take a plane the morning after an idea has come up to participate in a military training testing life-saving technologies.

Even more interesting is perhaps how this enthusiasm becomes contagious and the project starts to work as a truly open source venture. Open_Sailing becomes a powerful autonomous entity that keeps bringing people in a dividing itself into labs. Each new lab engages a whole new group of contributors, with a new set of preoccupations and hopes. The project proves to be definitely not about the implementation of a master plan or utopian blue print, but an example of how open source can literally be applied to the construction of alternative worlds. Within these labs we find different experimental research projects focusing for example on mesh networking; pollution, climate and natural reserve monitoring; sustainable aquaculture in high seas; or energy autonomous systems that generate electricity through wind, sun or wave power.
Now, there is of course the problem of co-option. The research being done is a very useful material with infinite commercial and even military applications. But perhaps this is not something that compromises the success of the project. Rather, its value lies in its capacity to encourage people to co-design their own futures. It is more about joining people that want to create than attracting those that want to buy. Surely, it is the process of creation of alternative that’s been set in motion that is truly significant, even more than the technologies being produced. Furthermore, Open_Sailing manages to reverse the process of co-option, the same way it reverses the effects of threat. Collaborators turn to scientific institutions, corporations, military research, as a useful resource, and then open up the knowledge acquired. This is not a new ‘green design’ product for the consumerist society, it is a spark for a collaborative rethinking of the world.
Stanza, Ximena Alarcón, Peter Cusack, Furtherfield.org, Chris Joseph, Francisco Lopez, Katharine Norman, Aki Pasoulas, Pedro Rebelo, Ambrose Seddon
View Sound Ecologies commission by Chris Joseph.
A day of presentations, participatory workshops and informal performance around themes of urban sound, networked sound, locative media and acoustic ecology the relationship between living beings and their environment, as mediated by sound. Featuring Furtherfield.org (Ruth Catlow and Marc Garrett), and guest speakers Stanza, Peter Cusack, Ximena Alarcón and Pedro Rebelo.
The event is free, and open to anyone interested, including musicians, artists, curators, technologists; ecologically inclined thinkers, makers and doers of all kinds.
BOOKING IS ESSENTIAL
Space is limited. Please reserve your place here.
We hope to offer wireless access. If you wish to have wireless access you MUST email in advance your name, computer model and MAC address to Katharine Norman at Katharine.norman@city.ac.uk by 7 November 2009.
We invite you to contribute sound and AV media on the theme of ‘urban sound’ to VisitorsStudio for incorporation into the mix by participants on the day.
Bring headphones to take part in the VisitorsStudio workshop.
Wear comfortable (and quiet!) clothing and shoes for the soundwalk, and be prepared for rain.
Maps and information about getting to City University London: the Performance Space and Lab are on the lower ground floor of the College Building, entrance on St John Street.
View more details of the day’s events here.
SOUND ECOLOGIES: LISTENING IN THE CITY is a partnership event funded by LCACE convened by Katharine Norman, Department of Music, City University London and Furtherfield.org
Ximena Alarcón – Sounding Underground: Linking urban soundscapes via commuters memories.

Ximena’s practice-led research project studied commuter’s perceptions towards their daily life soundscape in underground public transport systems, taking the case studies of Paris and México City as counterparts of the London Underground. The results are the basis for the creation of a score that becomes an interactive user’s interface in an Internet-based sonic environment: Sounding Underground. Interactivity, understood as “Listening and Remembering”, has taken two main forms: navigation, including written feedback, on the web, and a off-line networked improvisation for groups of four commuters who used their voices to express memories. This approach strives to make commuters contributors in the creation of these environments, and furthermore performers and narrators of their commuting experience. Ximena Alarcón, born in Bogotá, Colombia, in 1972, is a multimedia artist specialising in soundscape, collective memory and interactivity. She completed her PhD in Music, Technology and Innovation at De Montfort University in 2007 with a work entitled An Interactive Sonic Environment derived from commuters’ memories of soundscape: a case study of the London Underground. For the last two years she has been expanding and implementing this work at De Montfort’s Institute of Creative Technologies (IOCT), thanks to an Early Career Fellowship award given by The Leverhulme Trust. One of her objectives is to find a balance between artistic and socially based work within specific soundscapes that involve virtual and real migrations, and with people who are usually outside the artistic scene, doing so by creating narratives in new media.
Peter Cusack

Peter’s presentation will focus on the ‘Your Favourite London Sound’ project that aims to discover what Londoners find positive in their city’s soundscape, an idea that has been repeated in other world cities including Beijing and Chicago. Peter is based in London where he works as a sound artist, musician and environmental recordist with a special interest in environmental sound and acoustic ecology. Projects move from community arts to research into the contribution of sound to our senses of place to recordings that document areas of special sonic interest, e.g. Lake Baikal, Siberia, and Xinjiang, China’s most western province. Recently involved in ‘Sound & the City’ the British Council sound art project in Beijing 2005. His current project ‘Sounds From Dangerous Places’ examines the soundscapes of sites of major environmental damage, e.g. Chernobyl, the Azerbaijan oil fields, controversial dams on the Tigris and Euphratees river systems in south east Turkey. He produced ‘Vermilion Sounds’ a monthly environmental sound program on ResonanceFM radio, London, and is a Senior Lecturer in ‘Sound Arts & Design’ at the London College of Communication. Recently appointed research fellow on the Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council’s multidisciplinary ‘Positive Soundscapes Project’.As a musician he tours regularly at home and abroad. Musical collaborators include Clive Bell, Nic Collins, Alterations, Chris Cutler, Max Eastley, Annette Krebs and Viv Corringham.
Furtherfield.org – Media Art Ecologies
Furtherfield.org have worked with Katharine Norman at City University London to develop SOUND ECOLOGIES: LISTENING IN THE CITY. Furtherfield.org supports experimental practices at the intersection of art, technology and social change. They are currently working to increase opportunities for art making and appreciation, critical debate, exchange and participation in emerging ecological media art practices, and the theoretical, political and social contexts they engage.
Chris Joseph – digital writer and artist
Chris Joseph has been commissioned to provide a visual interpretation of the day’s themes (watch this space!)
Chris Joseph creates electronic literature, multimedia and interactive art, which may include text, images and video, sounds, music and reader/viewer participation. His ongoing projects include Flight Paths, a ‘networked novel’; Inanimate Alice, a series of interactive multimedia stories; and remixworx, a collaborative digital remixing community. Other projects are NRG, a bicycle-powered interactive multimedia installation around the themes of sustainable energy, and The Breathing Wall, a digital novel that responds to the reader’s breathing rate. From September 2006 until September 2008 he was the first Digital Writer in Residence at the Institute of Creative Technologies in De Montfort University, Leicester, UK.
Francisco Lopez – Buildings (New York)

Francisco López is a major international figure in the sound art and experimental music scene. Over the past 30 years he has developed an absolutely personal and iconoclastic sonic universe based on a profound listening of the world. Destroying boundaries between industrial sounds and wilderness sound environments, shifting with passion from the limits of perception to the most dreadful abyss of sonic power, proposing a blind, profound and transcendental listening, freed from the imperatives of knowledge and open to sensory and spiritual expansion. He has realized hundreds of concerts, projects with field recordings, workshops and sound installations in 60 countries of the five continents. His extensive catalog of sound pieces (with live and studio collaborations with over 100 international artists) has been released by more than 200 record labels worldwide, and he has been awarded three times with honorary mentions at the competition of Ars Electronica Festival.
Review of Buildings (New York).
Katharine Norman – Sound Ecologies

Katharine Norman composes computer and electronic music, often using documentary sound and voice, and increasingly writes texts. Her PhD (Princeton, 1993) focused on documentary sound in sound-based art and she has more recently completed a postgraduate diploma in creative writing and new media. She has various bits of sound art and music and writing on the web, and on CDs – including two solo cds: “London” (NMC label) and “Transparent things” (Metier). Increasingly, she writes about music, in particular electroacoustic and electronic music – Sounding Art: Eight Literary Excursions through Electronic Music, a book of experimental writings on recent electronic music (of many kinds and approaches) was published by Ashgate in 2004. She is currently head of the department of Music at City University London, and has previously taught at Goldsmiths (Music), Simon Fraser University (Communications) and Anglia Ruskin University (English).
Aki Pasoulas – City Soundwalk

Aki Pasoulas is a London-based composer of electroacoustic and acoustic music. He lectures at the Universities of City London, Middlesex, and the Arts London, and he is finalising his doctoral research at City University London under the supervision of Denis Smalley. Aki’s research project, funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC), investigates the listener’s experience and interpretation of time passing, and the interrelationships among timescales in electroacoustic composition. Further research interests include psychoacoustics, microsound, spatialisation, sound poetry and the use of voice in non-western musics. Aki originally studied and worked as a graphic designer, before embarking into music studies at the Open University and then at Goldsmiths College, University of London.

Will present a talk on some recent work linking locative media with network performance. Pedro is a composer/digital artist working in electroacoustic music, digital media and installation. His approach to music making is informed by the use of improvisation and interdisciplinary structures. He has been involved in several collaborative projects with visual artists and has created a large body of work exploring the relationships between architecture and music in creating interactive performance and installation environments. Pedro conducts research in the field of digital media, interactive sound and composition. His writings reflect his approach to design and composition by articulating creative practice in a wider understanding of cultural theory. Pedro was Visiting Professor at Stanford University (2007) and the Music Chair for the 2008 International Computer Music Conference. He has been Director of Research at the Sonic Arts Research Centre and is now Director of Education at the School of Music and Sonic Arts, Queen’s University Belfast.
Ambrose Seddon – City Soundwalk
Ambrose Seddon has a background in rock and electronic pop music. After graduating with a degree in music from Goldsmiths College, University of London, he spent a number of years teaching, while writing, producing and performing in various bands, with releases through a number of independent record labels. He completed a Masters degree in electroacoustic composition at City University, London, in 2004, and now continues his studies at City University as a PhD student, supervised by Denis Smalley. His music has been performed in concert internationally, and has been awarded 1’st prize in the Visiones Sonoras Electroacoustic Music Composition Competition, Mexico, 2006, and the European Composition Prize at the International Computer Music Conference, Copenhagen, 2007.

Stanza’s artworks explore artistic and technical opportunities to enable new aesthetic perspectives, experiences and perceptions within context of architecture, data spaces and online environments. His presentation will focus on his online and sonic work in relation to urban and networked spaces. Stanza is a London based British artist who specializes in interactive art, networked spaces, installations and performances. His award winning online projects have been invited for exhibition in digital festivals around the world. Work has been shown at The VeniceBiennale, Tate Britain, The Victoria and Albert Museum. Recipient of Nesta Dreamtime Award, AHRC creative fellowship and numerous prizes. All his artworks can be found at www.stanza.co.uk/
Throughout: LISTENING IN THE CITY. A visual interpretation of the day’s themes by Chris Joseph, digital artist in residence.
Performance Space Foyer
10:00-10:30 WELCOME AND INTRODUCTION
Performance Space, City University London
10:30-13:00 LISTENING IN THE CITY: PANEL PRESENTATIONS AND DISCUSSION
Performance Space
Artistic and research presentations by Stanza, Ximena Alarcón, Peter Cusack and Pedro Rebelo of work with locative media, urban listening, acoustic ecology and networked performance.
13:00-14:00 BUILDINGS (NEW YORK)
Performance Space
A multi-speaker diffusion of Buildings (New York) by Francisco Lopez.
Come in and out, bring your lunch, listen.
14:00-15:30 AFTERNOON WORKSHOP OR SOUNDWALK – All welcome
VISITORSSTUDIO WORKSHOP: URBAN SOUND AND VISION SCAPES
ALG04 (PC lab)
Live AV collaborative mixing led by Marc Garrett, Furtherfield.org (participants please bring headphones).
Places limited.
OR
URBAN SOUNDWALK
Commencing from Performance Space Foyer a City Soundwalk led by Aki Pasoulas and Ambrose Seddon.
15:50-16:00 WORKSHOP PRESENTATIONS
16:00 END
SOUND ECOLOGIES: LISTENING IN THE CITY
Wednesday 18 November 2009, 10am-4pm
City University London, Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB
SOUND ECOLOGIES: LISTENING IN THE CITY is a partnership event funded by LCACE convened by Katharine Norman, Department of Music, City University London and Ruth Catlow, Furtherfield.org